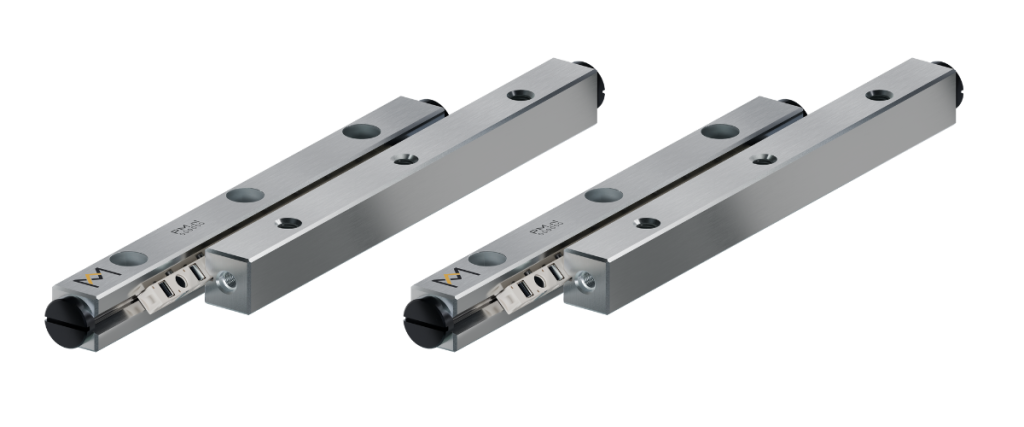
The global linear slide rail bearings market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision motion control systems across industries such as automation, automotive, electronics, and industrial machinery. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the linear motion components market—including linear guides, rails, and bearings—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global linear guide market size was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by advancements in factory automation and increasing adoption of robotics. As industrial efficiency becomes a competitive differentiator, manufacturers of high-performance linear slide rail bearings are playing a pivotal role in enabling smoother, more accurate, and durable motion systems. In this landscape, ten key players have emerged as market leaders, combining technological innovation, global reach, and comprehensive product portfolios to meet the escalating demands of modern manufacturing.
Top 10 Linear Slide Rail Bearings Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SCHNEEBERGER linear technology
Domain Est. 1996
Website: schneeberger.com
Key Highlights: SCHNEEBERGER U.S.A. is a leading manufacturer for linear technology and linear motion systems technology….
#2 Linear Slide Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: linearslides.net
Key Highlights: Del-Tron is a linear slide manufacturer/distributor of ball bearing slides, crossed roller tables, roller slides, multi-axis positioning stages, xy tables….
#3 Linear
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: The Slide Rail is a low-priced limited-type linear guide made of steel plate precision-formed by rolling….
#4 Del
Domain Est. 1996
Website: deltron.com
Key Highlights: Del-Tron Precision manufactures high-performance linear motion slides and precision slides for automation, medical, and aerospace applications….
#5 Nippon Bearing: Linear Bearings
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nbcorporation.com
Key Highlights: Nippon Bearing | NB Corporation specializes in manufacturing high-quality linear bearings and linear motion systems….
#6 Ball Rail Systems
Domain Est. 2000
Website: boschrexroth.com
Key Highlights: Ball Rail linear guide systems from Rexroth provide the optimal combination of accuracy, speed, load-bearing capabilities, and price to performance….
#7 Linear Guides
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: NSK Linear slides – designed for superior linear motion: the different series of linear guides meet the needs of the various industries we serve….
#8 PM
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pm.nl
Key Highlights: Discover Precision PM designs and manufactures linear bearings, linear slides and tailored positioning systems designed to customer specifications. As an ……
#9 Linear Bearings, Shafts, Guides
Domain Est. 2008
Website: pbclinear.com
Key Highlights: PBC Linear manufactures and supplies linear bearings, shafts, guides, actuators and slew ring bearings….
#10 Profile Rail Linear Guides
Domain Est. 2008
Website: thomsonlinear.com
Key Highlights: Our profile rail guides consist of a complete assortment of rails and carriages in a broad range of styles, sizes and unique features produced to industry ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Linear Slide Rail Bearings
2026 Market Trends for Linear Slide Rail Bearings
The linear slide rail bearings market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industrial automation demands, and global economic shifts. Key trends shaping the industry include accelerated automation, heightened demand for precision and efficiency, material and design innovations, sustainability imperatives, and regional market dynamics.
Increasing Automation and Industry 4.0 Integration
The continued expansion of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing is a primary driver for linear slide rail bearings. By 2026, factories will increasingly deploy robotics, collaborative robots (cobots), and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), all of which rely heavily on high-performance linear motion systems. Integration with IoT sensors and predictive maintenance systems will become standard, with smart bearings capable of real-time monitoring of load, temperature, and wear. This shift not only enhances system reliability but also reduces unplanned downtime, making intelligent linear bearings a critical component in future-ready production environments.
Demand for Higher Precision, Speed, and Load Capacity
As industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, medical devices, and aerospace push the boundaries of precision engineering, linear slide rail bearings must deliver tighter tolerances, smoother motion, and greater rigidity. By 2026, there will be growing demand for ultra-high-precision rails used in lithography machines, robotic surgery systems, and high-speed CNC applications. Manufacturers will focus on innovations in preloading techniques, surface finishing, and recirculation systems to minimize friction and vibration, enabling faster cycle times and improved product quality.
Advancements in Materials and Coatings
Material science will play a pivotal role in the evolution of linear slide rail bearings. Lightweight materials such as high-strength aluminum alloys and composite materials will gain traction, particularly in applications where energy efficiency and reduced inertia are critical. Additionally, advanced coatings—such as diamond-like carbon (DLC), ceramic, and corrosion-resistant polymers—will enhance durability in harsh environments, including food processing, cleanrooms, and outdoor automation. These improvements extend service life and reduce maintenance frequency, offering long-term cost savings.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will influence product design and manufacturing processes. By 2026, linear bearing manufacturers will prioritize energy-efficient designs that minimize friction and power consumption. Recyclable materials, reduced lubrication requirements (including grease-free or maintenance-free options), and eco-conscious production methods will become competitive differentiators. The market will also see increased adoption of linear systems in renewable energy applications, such as solar panel manufacturing and wind turbine assembly lines.
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the dominant market due to robust electronics and automotive manufacturing. However, nearshoring and supply chain diversification trends—especially in North America and Europe—will create opportunities for localized production. Geopolitical factors and trade policies may accelerate investments in regional manufacturing hubs, prompting linear bearing suppliers to strengthen local partnerships and distribution networks to ensure supply chain resilience by 2026.
Growth in Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional industrial sectors, linear slide rail bearings will see rising adoption in emerging fields such as electric vehicles (EVs), 3D printing, and automated logistics. In EV production, precision linear systems are essential for battery assembly and motor manufacturing. In e-commerce, high-speed sorting systems and automated warehouses will depend on reliable linear motion technology. These expanding applications will diversify market opportunities and drive innovation in compact, modular, and scalable bearing solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 linear slide rail bearings market will be characterized by smarter, more efficient, and sustainable products tailored to the needs of advanced automation. Companies that invest in R&D, digital integration, and flexible manufacturing will be best positioned to capitalize on these dynamic trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Linear Slide Rail Bearings (Quality & IP)
Inadequate Quality Verification
Many suppliers, especially those from low-cost regions, may provide bearings that fail to meet stated precision, load, or durability standards. Buyers often assume specifications are accurate without independent verification, leading to premature wear, misalignment, or system failure in precision applications.
Misrepresentation of Brand or Origin
Counterfeit or rebranded linear rail bearings are widespread. Suppliers may falsely claim products are from reputable manufacturers (e.g., THK, HIWIN, Bosch Rexroth) when they are inferior copies. This compromises performance and voids warranties, with limited recourse due to ambiguous supply chains.
Overlooking IP (Intellectual Property) Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate patented designs infringes intellectual property rights. Even unintentional use of counterfeit or cloned components can expose end-users to legal liability, import bans, or reputational damage, especially in markets with strong IP enforcement.
Inconsistent Tolerances and Interchangeability
Low-quality rails and carriages often exhibit poor dimensional consistency, making them non-interchangeable—even within the same batch. This complicates maintenance and replacement, particularly when integrating with existing OEM systems that depend on standardized tolerances.
Poor Material and Surface Treatment Quality
Substandard materials or inadequate surface hardening (e.g., insufficient case depth or improper nitriding) reduce load capacity and corrosion resistance. This leads to rapid degradation under heavy or continuous use, especially in harsh environments.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide certification (e.g., RoHS, ISO), material test reports, and batch traceability. Many budget suppliers omit these, making it difficult to verify compliance, diagnose failures, or meet regulatory requirements in industries like medical or aerospace.
Underestimating Environmental Protection (IP Ratings)
While linear bearings aren’t typically assigned full IP ratings like enclosures, contamination resistance is critical. Poorly sealed or unsealed carriages allow dust, chips, and moisture ingress, accelerating wear. Assuming all “industrial-grade” bearings offer sufficient protection is a common oversight.
Ignoring Long-Term Support and Spare Parts Availability
Choosing obscure brands may result in discontinued models or unavailable spare carriages and rails. This increases machine downtime and lifecycle costs, especially for global operations requiring consistent part availability over years.
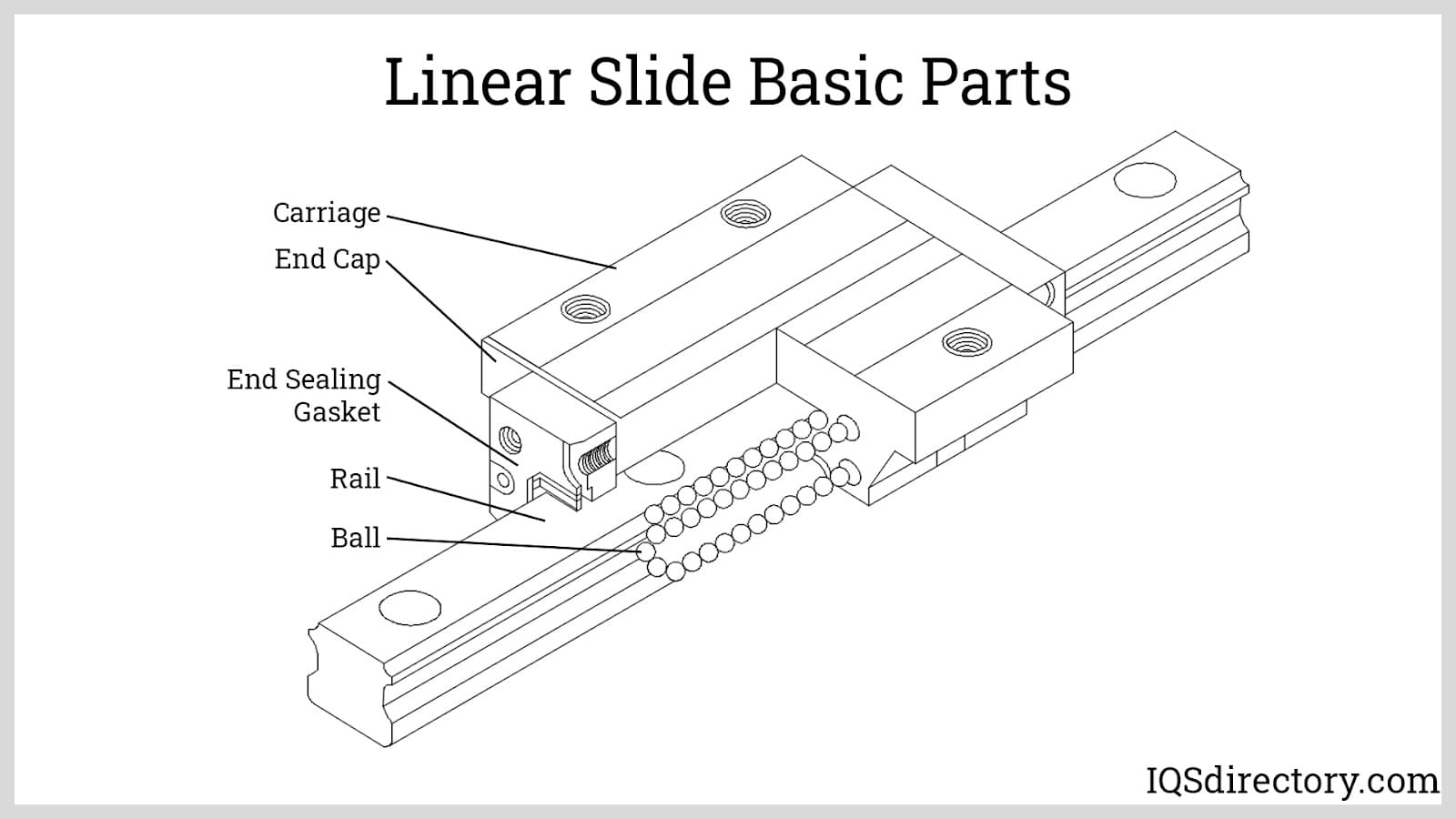
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Linear Slide Rail Bearings
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the import, export, storage, and handling of linear slide rail bearings. Adhering to these guidelines ensures smooth operations, regulatory compliance, and product integrity.
Import and Export Regulations
Linear slide rail bearings may be subject to international trade regulations depending on destination, origin, and material composition. Key compliance aspects include:
– Harmonized System (HS) Code Classification: Typically classified under HS Code 8482.80 (Other anti-friction bearings). Confirm the precise code with local customs authorities to ensure correct tariffs and documentation.
– Export Controls: Bearings may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.) if intended for military or dual-use applications. Verify end-use and end-user requirements.
– Country-Specific Restrictions: Some countries impose import restrictions or require certifications (e.g., CE marking for the EU, KC for South Korea, INMETRO for Brazil). Ensure compliance with destination market standards.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging and handling are crucial to prevent damage during transit and storage:
– Protective Packaging: Use anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper, sealed plastic wrap) and sturdy outer cartons to protect against moisture, dust, and mechanical shock.
– Labeling: Clearly label packages with product details, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”), and any required regulatory markings.
– Handling Procedures: Use appropriate lifting equipment; avoid dropping or dragging packages. Maintain cleanliness to prevent contamination of bearing surfaces.
Storage Conditions
Optimal storage extends product life and maintains performance specifications:
– Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled area (recommended: 10–30°C, humidity <60%). Avoid condensation and direct sunlight.
– Positioning: Keep bearings in original packaging and store horizontally to prevent deformation. Do not stack heavy items on top.
– Shelf Life: Bearings with lubrication have a recommended shelf life (typically 2–5 years). Follow manufacturer guidelines for rotation and usage.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Ensure bearings meet relevant international and regional standards:
– ISO Standards: Confirm bearings comply with ISO 14728 (Rolling bearings — Linear motion bearings).
– RoHS and REACH Compliance: Verify materials are free from restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) as required in the EU and other regions.
– Material Declarations: Provide compliance documentation (e.g., Certificate of Conformance, Material Safety Data Sheet) upon request.
Transportation and Shipping
Select appropriate shipping methods based on urgency, cost, and destination:
– Mode of Transport: Choose air, sea, or ground transport based on lead time and fragility considerations.
– Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Include HS codes and declared values.
– Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities using standard Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) to avoid misunderstandings.
Quality and Traceability
Maintain product traceability and quality assurance:
– Batch Tracking: Retain batch/lot numbers and manufacturing dates for traceability.
– Inspection: Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify quantity, quality, and packaging compliance.
– Supplier Audits: Work with certified suppliers who adhere to quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
Adhering to this logistics and compliance framework ensures reliable supply chain performance and legal conformity for linear slide rail bearings across global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Linear Slide Rail Bearings
Sourcing linear slide rail bearings requires a careful balance between performance requirements, cost efficiency, and long-term reliability. After evaluating various suppliers, bearing types, materials, and industry standards, it is clear that selecting the right linear slide rail bearings involves understanding the specific application demands such as load capacity, precision, speed, environmental conditions, and expected service life.
High-quality bearings from reputable manufacturers offer superior durability, smoother motion, and reduced maintenance, ultimately contributing to improved machine performance and uptime. While initial costs may be higher, the long-term benefits—such as reduced downtime, lower replacement frequency, and enhanced operational efficiency—often justify the investment.
Additionally, considering factors like availability, lead times, technical support, and compatibility with existing systems is crucial for seamless integration and supply chain stability. Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers ensures consistent quality and facilitates future scalability.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach focused on total cost of ownership, rather than upfront price alone, will lead to optimal performance and reliability of linear motion systems. By prioritizing quality, technical specifications, and supplier partnerships, organizations can ensure efficient, precise, and durable linear guidance solutions for their applications.