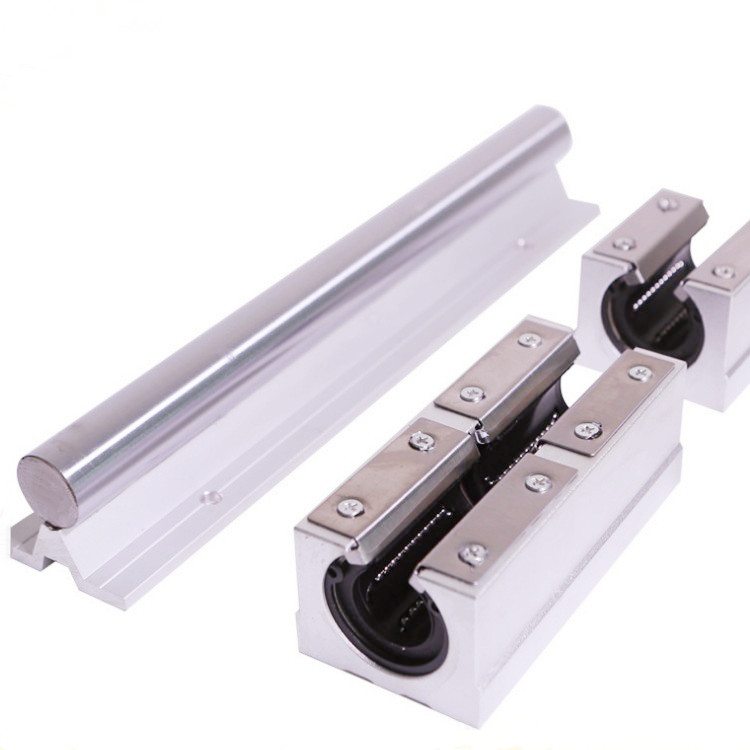
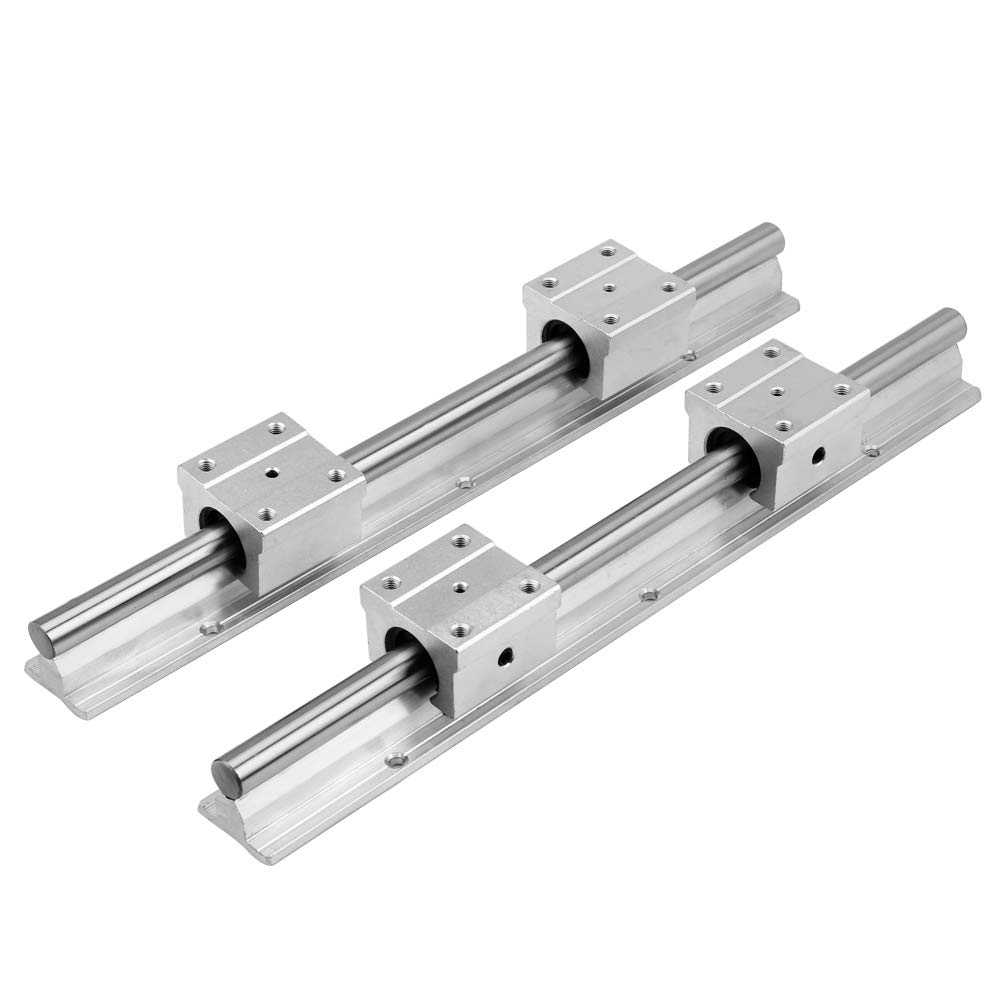
The global linear motion components market, including slide rails and linear bearing systems, continues to expand rapidly, driven by increasing automation across industries such as manufacturing, automotive, semiconductor, and healthcare. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the linear motion market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by rising demand for precision machinery, energy-efficient systems, and advancements in industrial automation. With factories adopting more sophisticated linear guidance systems to enhance positioning accuracy and reduce maintenance costs, the need for high-performance linear bearing slide rails has become critical.
In this competitive landscape, certain manufacturers have emerged as leaders due to innovation, reliability, and global supply capabilities. Drawing on market data and industry benchmarks, we’ve identified the top nine linear bearing slide rail manufacturers shaping the future of motion control. These companies not only dominate in market share but also lead in R&D investment, product miniaturization, and integration with smart manufacturing platforms.
Top 9 Linear Bearing Slide Rail Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SCHNEEBERGER linear technology
Domain Est. 1996
Website: schneeberger.com
Key Highlights: SCHNEEBERGER U.S.A. is a leading manufacturer for linear technology and linear motion systems technology….
#2 Chambrelan
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1956
Website: chambrelan.com
Key Highlights: Chambrelan, Manufacturer of heavy duty drawer slides and linear ball bearing guide rails for industrial professionals since 1956….
#3 Linear Slide Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: linearslides.net
Key Highlights: Del-Tron is a linear slide manufacturer/distributor of ball bearing slides, crossed roller tables, roller slides, multi-axis positioning stages, xy tables….
#4 Linear
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: Slide Rail. The Slide Rail is a low-priced limited-type linear guide made of steel plate precision-formed by rolling….
#5 Rollon
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rollon.com
Key Highlights: Our selection of telescopic slide rails is guaranteed to support your linear load. Telescopic slides are linear guides with precision ball or rollers. These ……
#6 Del
Domain Est. 1996
Website: deltron.com
Key Highlights: Del-Tron Precision manufactures high-performance linear motion slides and precision slides for automation, medical, and aerospace applications….
#7 Ball Rail Systems
Domain Est. 2000
Website: boschrexroth.com
Key Highlights: Ball Rail linear guide systems from Rexroth provide the optimal combination of accuracy, speed, load-bearing capabilities, and price to performance….
#8 Linear Slide, Guide Rail and Motion Systems Product Catalog
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nbcorporation.com
Key Highlights: Browse our line of products for all your linear motion needs. We manufacture products that provide the best linear motion solutions for our customers….
#9 Linear Bearings, Shafts, Guides
Domain Est. 2008
Website: pbclinear.com
Key Highlights: PBC Linear manufactures and supplies linear bearings, shafts, guides, actuators and slew ring bearings….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Linear Bearing Slide Rail

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Linear Bearing Slide Rail
The global linear bearing slide rail market is anticipated to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automation, precision engineering, and industrial digitization. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Increased Demand from Automation and Robotics
The expansion of industrial automation and robotics across manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare sectors is a primary driver. Linear bearing slide rails are critical components in robotic arms, CNC machines, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). As industries prioritize efficiency and precision, demand for high-performance, low-friction linear motion systems is expected to rise steadily through 2026. -
Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Semiconductor Manufacturing
The booming EV industry requires high-precision assembly lines, where linear slide rails ensure accuracy in battery module placement and motor assembly. Similarly, semiconductor fabrication facilities rely on contamination-resistant, ultra-precise linear guides for cleanroom environments. These high-tech sectors are projected to contribute significantly to market growth. -
Adoption of Smart and IoT-Enabled Linear Systems
Integration with Industry 4.0 is leading to the development of smart linear bearing systems equipped with sensors for real-time monitoring of load, temperature, and wear. By 2026, predictive maintenance capabilities and data-driven performance optimization will become standard features, particularly in advanced manufacturing ecosystems. -
Material and Design Innovation
Manufacturers are investing in lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys and engineered polymers to reduce inertia and energy consumption. Additionally, advancements in sealing technologies and corrosion resistance are expanding applications in harsh environments, including food processing and outdoor equipment. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the dominant market due to strong manufacturing bases and government support for automation. However, North America and Europe are expected to see accelerated growth due to reshoring initiatives and investments in smart factories. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
With increasing regulatory and corporate focus on sustainability, linear bearing systems designed for energy efficiency and longer service life are gaining preference. Recyclable components and reduced lubrication requirements are emerging as competitive differentiators.
In conclusion, the linear bearing slide rail market in 2026 will be characterized by technological innovation, integration with digital systems, and expanding applications across high-growth industries. Companies that prioritize R&D, sustainability, and customization are likely to lead the evolving market landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Linear Bearing Slide Rails (Quality & IP)
Sourcing linear bearing slide rails involves more than just matching dimensions and load ratings. Overlooking critical factors related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to performance issues, reliability problems, and legal risks. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Choosing Based on Price Alone
Selecting the lowest-cost option often means compromising on material quality, precision machining, and manufacturing consistency. Cheap rails may use inferior steel, have poor surface finishes, or inconsistent tolerances, leading to premature wear, increased friction, and reduced accuracy. This results in higher total cost of ownership due to maintenance, downtime, and early replacements.
Ignoring Tolerance and Precision Grades
Not all slide rails are created equal in terms of precision. Assuming all rails meet high standards can lead to integration issues. Using a rail with inadequate tolerance (e.g., incorrect flatness, parallelism, or straightness) can cause binding, misalignment, and reduced repeatability in precision applications like CNC machines or medical equipment.
Overlooking Manufacturer Certification and Traceability
Reputable manufacturers provide material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH) and production traceability. Sourcing from suppliers without documented quality control processes increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or subpar components. Lack of traceability also complicates recalls or failure analysis.
Assuming Interchangeability Without Verification
Many low-cost suppliers claim interchangeability with well-known brands (e.g., THK, Hiwin). However, slight dimensional differences or deviations in mounting hole patterns, rail profiles, or preload settings can prevent true interchangeability. This leads to fitment issues, reduced performance, and potential damage to mating components.
Disregarding Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Using or sourcing rails that infringe on patented designs exposes your company to legal liability. Some suppliers produce “copycat” rails that mimic protected technologies (e.g., recirculating ball systems, preload mechanisms). Purchasing such products may result in cease-and-desist orders, product recalls, or litigation, especially in regulated or export-sensitive industries.
Failing to Audit the Supply Chain
Relying solely on distributor claims without verifying the actual manufacturer or production facility increases exposure to counterfeit goods. Unannounced audits or factory inspections help ensure the supplier adheres to quality standards and owns the IP or has proper licensing for the products they sell.
Neglecting Long-Term Support and Warranty
Low-cost suppliers may lack technical support, spare parts availability, or warranty coverage. If a rail fails in the field and replacement or troubleshooting is delayed, it can halt production. Ensure the supplier offers reliable after-sales service and documented warranty terms.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, you can ensure reliable performance, maintain compliance, and protect your company from both operational and legal risks when sourcing linear bearing slide rails.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Linear Bearing Slide Rail
Overview
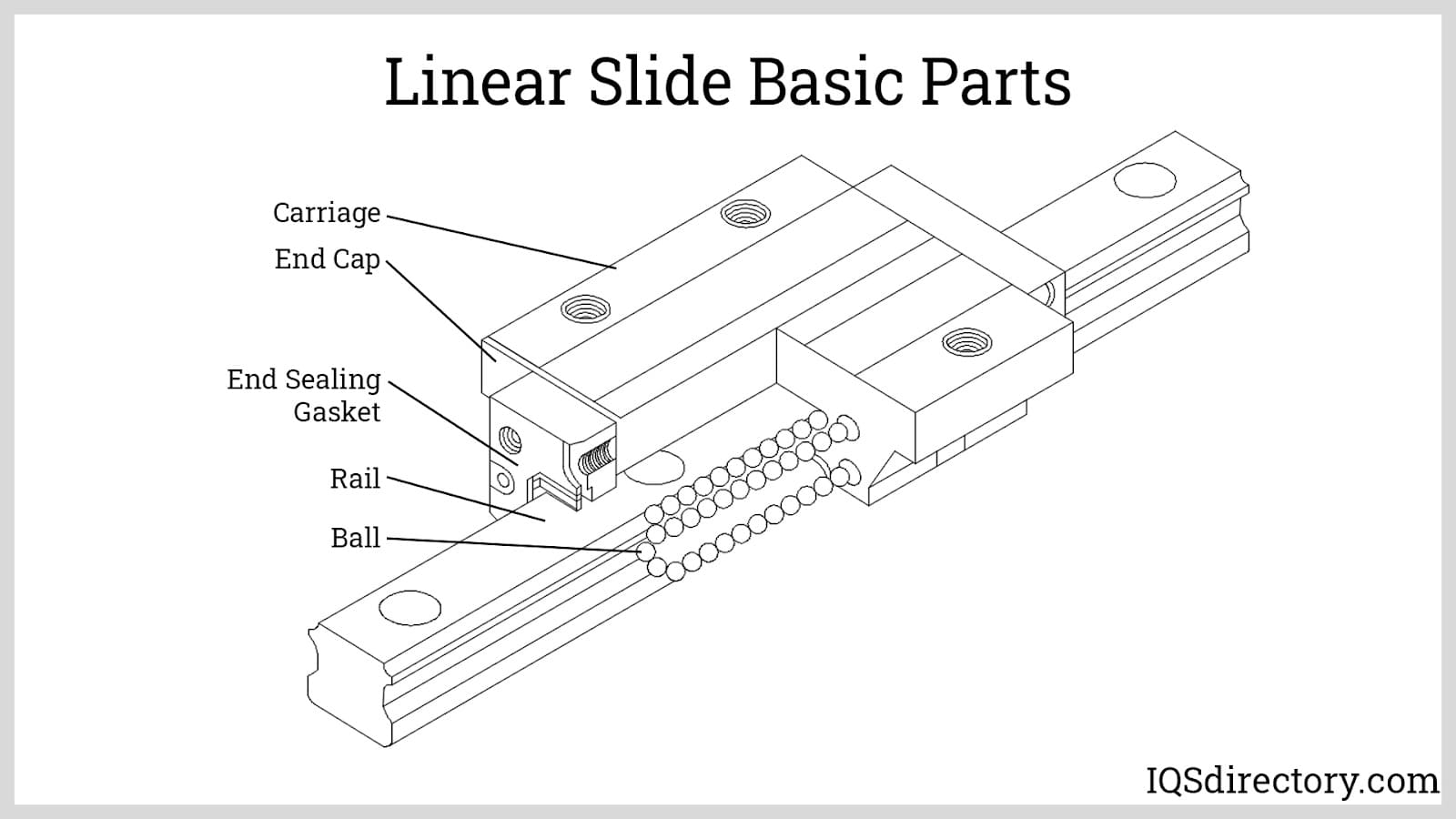
Linear bearing slide rails are precision components used in automation, machinery, and industrial equipment. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure product integrity, regulatory adherence, and efficient supply chain operations.
Packaging Requirements
- Use anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper or sealed plastic wrap) to protect components from moisture and oxidation.
- Secure rails and bearings in rigid, labeled containers to prevent bending, impact, or misalignment during transit.
- Include protective end caps or spacers where applicable to maintain rail straightness.
- Clearly label packages with part numbers, quantities, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”).
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment (temperature: 15–25°C, humidity: <60% RH).
- Keep rails horizontally supported at multiple points to prevent sagging or deformation.
- Avoid exposure to dust, chemicals, and direct sunlight.
- Rotate stock using FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory practices to prevent long-term storage degradation.
Transportation Guidelines
- Use palletized shipments with adequate strapping and corner protection.
- Avoid extreme temperatures during transit—do not leave containers in direct sun or freezing conditions.
- For international shipments, ensure compliance with IATA (air) or IMDG (sea) regulations if lubricants are present.
- Choose carriers experienced in handling precision mechanical components.
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS Compliance: Confirm that materials (e.g., steel, coatings, lubricants) comply with EU Directive 2011/65/EU on hazardous substances.
- REACH: Ensure no restricted SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) are present above threshold levels.
- Conflict Minerals: Comply with U.S. Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502; provide CMRT (Conflict Minerals Reporting Template) if applicable.
- Export Controls: Verify ECCN (Export Control Classification Number); most slide rails are classified under EAR99, but confirm based on design and end-use.
Documentation Requirements
- Include Certificate of Conformance (CoC) with each shipment.
- Provide material declarations (e.g., RoHS, REACH compliance statements).
- Maintain traceability records (batch/lot numbers, manufacturing dates).
- For customs clearance: commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill.
Import/Export Considerations
- Classify under correct HS Code (e.g., 8483.50 for linear motion units).
- Check destination country requirements (e.g., CE marking in Europe, CRN in Canada).
- Be aware of tariffs, trade agreements, and import restrictions in target markets.
- Use Incoterms® clearly (e.g., FOB, DDP) to define responsibilities and liabilities.
Quality & Handling Procedures
- Train warehouse and logistics staff on proper handling techniques.
- Inspect incoming and outgoing goods for damage or contamination.
- Avoid direct hand contact with bearing surfaces to prevent oil transfer and corrosion.
- Lubrication: Ensure factory-applied grease is intact; re-lubricate only as per manufacturer specs.
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Dispose of packaging materials in accordance with local recycling regulations.
- Handle lubricants as per SDS (Safety Data Sheet) guidelines.
- Ensure compliance with OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent workplace safety standards during handling.
Supplier & Customer Communication
- Align logistics specifications with suppliers and end users.
- Clearly define compliance expectations in procurement contracts.
- Provide technical support documentation (installation guides, load ratings) with shipments when needed.
Continuous Improvement
- Audit logistics and compliance processes annually.
- Monitor regulatory updates (e.g., EU Green Deal, SCIP database).
- Implement feedback loops from customers and logistics partners to optimize packaging and shipping methods.
Conclusion for Sourcing Linear Bearing Slide Rails:
After thorough evaluation of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and quality standards, the sourcing of linear bearing slide rails should focus on a balanced approach that prioritizes reliability, precision, and long-term performance. Key factors such as load capacity, stroke length, accuracy, environmental resistance, and compatibility with existing systems must align with application demands. Selecting reputable suppliers with proven track records in delivering consistent quality, certified materials, and technical support is essential to ensure operational efficiency and minimize downtime.
While cost is a consideration, opting for the lowest-priced option may compromise system longevity and performance. Instead, a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis—including maintenance, replacement frequency, and potential system failures—should guide the decision-making process. Establishing strong partnerships with suppliers who offer customization, timely delivery, and responsive service can further enhance supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, the successful sourcing of linear bearing slide rails involves a strategic blend of technical suitability, supplier reliability, and lifecycle cost efficiency. By implementing a structured procurement process grounded in these principles, organizations can achieve optimal performance, durability, and value in their motion control applications.