The global veterinary pharmaceuticals market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing livestock production and rising demand for efficient disease management in swine farming. According to Grand View Research, the global veterinary drugs market was valued at USD 30.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Lincomycin, a lincosamide antibiotic widely used in swine production for controlling bacterial pathogens such as Lawsonia intracellularis and Streptococcus suis, plays a crucial role in maintaining herd health and productivity. With growing emphasis on animal health and optimized farm output, demand for effective antimicrobials like lincomycin continues to rise—particularly in intensive pig farming regions across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. As the market expands, a handful of key manufacturers have emerged as leaders in producing high-quality lincomycin products tailored for swine applications, combining reliability, scalability, and adherence to regulatory standards.
Top 7 Lincomycin For Pigs Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FDA Announces Withdrawal of Combination Drug for Use in Swine
Domain Est. 2000
Website: fda.gov
Key Highlights: FDA Announces Voluntary Withdrawal of Fenbendazole and Lincomycin Combination for use in Swine to Veterinarians, Feed Manufacturers, and Pork ……
#2 Swine Antibiotics and Medications
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pipevet.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $200Pipevet.Com carries the majority of prescription and non-prescription antibiotics for swine use. If you have any questions please feel free to contact us for…
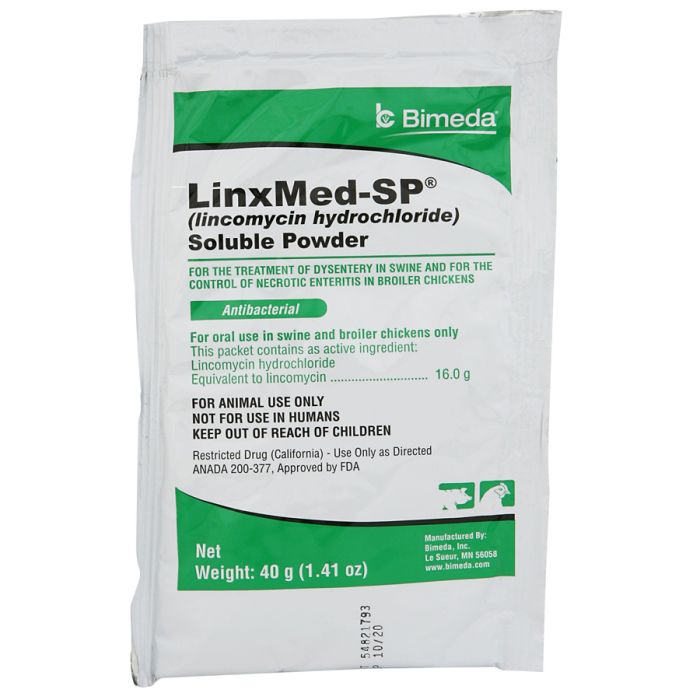
#3 Label: LINXMED
Domain Est. 1997
Website: dailymed.nlm.nih.gov
Key Highlights: SWINE: Directions for Use – INDICATIONS AND USAGE: LinxMed-SP Soluble Powder is indicated for the treatment of swine dysentery (bloody scours). DOSAGE AND ……
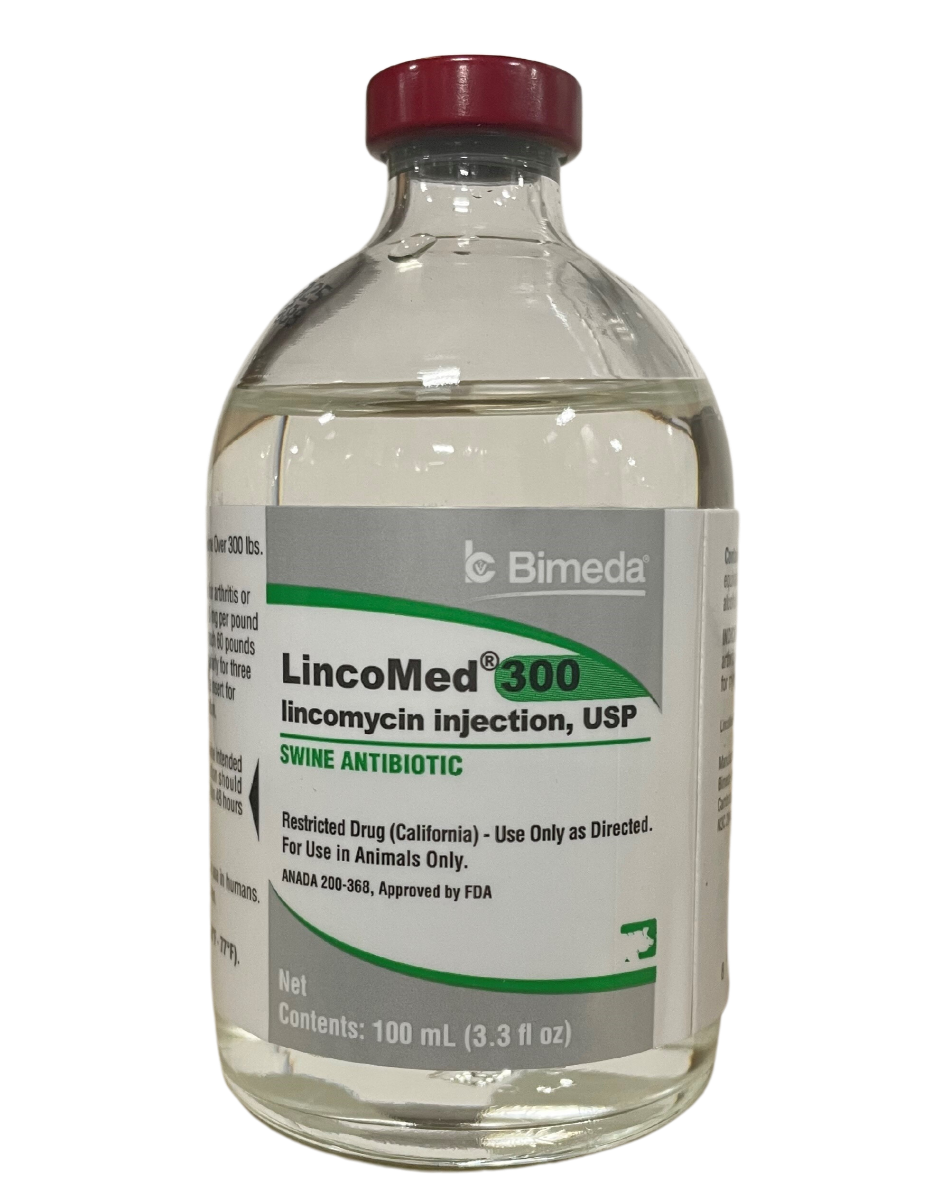
#4 Lincomycin 300 Swine Injectable Rx
Domain Est. 2001
Website: pbsanimalhealth.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $75Indicated for the treatment of infectious arthritis and mycoplasmal pneumonia in swine. Effective against staphylococci, streptococci, erysipelothrix and ……
#5 Lincomycin (LINC) – Medicating Ingredient Brochure
Domain Est. 2002
Website: inspection.canada.ca
Key Highlights: This livestock feed contains a medically important antibiotic. To reduce the development of antimicrobial resistance and maintain effectiveness, use this ……
#6 CCPG Product
Domain Est. 2010
Website: ccpp.com.tw
Key Highlights: Lincomycin-400 W.S. Powder. Ingredients. Each kg contains: Lincomycin HCL………..400 gm (pot.) Dosage Form. W.S. Powder. Indications. Hogs: Treatment of ……
#7 21 CFR 558.325
Domain Est. 2012
Website: ecfr.gov
Key Highlights: (i) “CAUTION: Occasionally, swine fed lincomycin may within the first 2 days after the onset of treatment develop diarrhea and/or swelling of the anus….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lincomycin For Pigs

2026 Market Trends for Lincomycin for Pigs: Key H2-Level Insights
Market Growth and Demand Drivers
The global market for lincomycin in swine production is projected to experience moderate growth by 2026, driven primarily by rising pork consumption in emerging economies and intensified farming practices. Increasing herd sizes in regions such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America are amplifying the need for effective antibiotic therapies to manage bacterial infections like swine dysentery and arthritis. Additionally, regulatory emphasis on animal health and welfare is promoting responsible use of antimicrobials, positioning lincomycin—when used under veterinary supervision—as a key tool in controlled disease management programs.
Regulatory Landscape and Antimicrobial Resistance Concerns
By 2026, stringent global regulations on antibiotic use in livestock, particularly in the European Union and North America, will continue to shape the lincomycin market. Growing concerns over antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are prompting governments and industry bodies to enforce withdrawal periods, limit prophylactic use, and encourage alternatives such as vaccines and probiotics. While these measures may constrain lincomycin demand in developed markets, they also foster innovation in targeted delivery systems and combination therapies aimed at minimizing resistance development.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the lincomycin for pigs market in 2026, fueled by high-density pig farming in countries like China, Vietnam, and India. These regions face recurrent bacterial disease challenges, supporting continued reliance on effective antibiotics like lincomycin. In contrast, North America and Europe are witnessing a shift toward reduced antibiotic dependency, with demand for lincomycin becoming more focused on therapeutic (rather than growth-promoting) applications due to bans on antibiotic growth promoters.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
Leading animal health companies—including Zoetis, Merck Animal Health, and Ceva Santé Animale—are investing in combination products that include lincomycin with other agents (e.g., spectinomycin) to enhance efficacy and combat resistance. By 2026, the market will likely see increased competition based on formulation improvements, such as long-acting injectables and feed premixes with better stability. Digital veterinary tools and precision livestock farming may also integrate with antibiotic use, enabling more data-driven administration of lincomycin.
Supply Chain and Pricing Trends
Global supply chain resilience remains a concern, particularly for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) sourced from Asia. Geopolitical tensions and regulatory scrutiny may impact the availability and cost of lincomycin, potentially leading to price volatility in 2026. However, rising local manufacturing initiatives in key pig-producing countries could mitigate these risks and support market stability.
Sustainability and Future Outlook
As sustainability becomes central to livestock production, the future of lincomycin hinges on its role within responsible antimicrobial stewardship programs. By 2026, market success will depend on balancing effective disease control with compliance, transparency, and integration into holistic herd health strategies. Long-term viability may also be influenced by the development of alternatives, though lincomycin is expected to retain relevance in treating specific Gram-positive infections in swine.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lincomycin for Pigs (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing lincomycin for use in pigs involves several critical considerations, particularly regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) compliance. Failure to address these aspects can lead to ineffective treatment, regulatory violations, animal health risks, and legal consequences. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Compromised Product Quality
– Substandard or counterfeit products: Sourcing lincomycin from unverified suppliers may result in receiving products with incorrect active ingredient concentrations, contaminants, or degraded compounds, reducing therapeutic efficacy.
– Lack of GMP certification: Suppliers not adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) may produce inconsistent or unsafe formulations. Always verify third-party quality certifications.
– Improper storage and handling: Lincomycin is sensitive to temperature and moisture. Poor logistics can compromise stability and potency before the product reaches the farm.
2. Ignoring Regulatory Compliance
– Unapproved veterinary formulations: Using lincomycin formulations not approved for swine in your region may violate local regulations and lead to residue violations in meat.
– Absence of veterinary oversight: Sourcing without a veterinary prescription or guidance can result in improper dosage, resistance development, or illegal use.
3. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
– Sourcing from unauthorized generics: While generic lincomycin is available, some formulations may still be under patent protection. Procuring off-patent versions from non-licensed manufacturers could infringe on IP rights, especially in jurisdictions with strong patent enforcement.
– Unlicensed manufacturing or distribution: Distributors or manufacturers not authorized by the patent holder may sell products that, although chemically identical, violate IP laws, exposing buyers to legal risk.
4. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
– Inadequate batch records or certificates of analysis (CoA): Without proper documentation, it’s difficult to verify the product’s origin, composition, and quality. This also complicates compliance during regulatory audits.
– Opaque supply chains: Sourcing through intermediaries without transparency increases the risk of receiving diverted, expired, or falsified products.
5. Price Over Quality Decisions
– Prioritizing low cost over proven quality often leads to poor clinical outcomes. Extremely low-priced lincomycin may indicate dilution, poor formulation, or illegal production methods.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, always source lincomycin from reputable, regulated suppliers with verifiable quality control processes and full regulatory compliance. Confirm the legal status of the product in your market and ensure alignment with veterinary guidelines and IP laws. Due diligence in sourcing protects animal health, ensures treatment efficacy, and prevents legal exposure.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lincomycin for Pigs
Overview of Lincomycin for Pigs
Lincomycin is an antibiotic used in swine production to treat and control specific bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Lawsonia intracellularis (responsible for proliferative enteropathy) and certain strains of Streptococcus suis. It is typically administered via feed or water medication under veterinary oversight. Proper logistics and strict compliance with regulatory guidelines are essential to ensure animal health, food safety, and legal adherence.
Regulatory Approvals and Labeling
Lincomycin products intended for use in pigs must be approved by relevant national regulatory authorities, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA). Only federally or nationally approved formulations (e.g., Lincomycin hydrochloride) may be used, and administration must follow the approved label instructions precisely. Off-label use is prohibited unless permitted under a valid Veterinary Feed Directive (VFD) or prescription, depending on jurisdiction.
Veterinary Oversight and Prescriptions
In countries like the United States, the use of lincomycin in swine feed is regulated under the Veterinary Feed Directive (VFD). A licensed veterinarian must issue a VFD order before medicated feed containing lincomycin can be used. The VFD must include farm identification, animal description, indication for use, dosage, duration, and withdrawal period. The veterinarian-client-patient relationship (VCPR) must be established and maintained throughout the treatment period.
Procurement and Supply Chain Management
Procure lincomycin from licensed distributors or manufacturers authorized by regulatory agencies. Maintain detailed records of product sourcing, including batch numbers, expiration dates, and Certificates of Analysis (CoA). Ensure storage conditions meet manufacturer specifications (typically cool, dry, and away from direct sunlight). Track inventory to prevent use of expired products and support traceability in case of audit or withdrawal.
Storage and Handling
Store lincomycin powder or premix in its original, sealed container in a secure, dry area with controlled temperature (usually 15–30°C / 59–86°F). Label all storage areas clearly and restrict access to trained personnel. Follow safety data sheet (SDS) guidelines for handling, including use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and masks to prevent inhalation or skin contact.
Administration and Dosage
Administer lincomycin strictly according to labeled directions or VFD instructions. Typical dosage ranges from 22 to 44 mg per kg (10 to 20 mg per lb) of body weight per day, mixed in feed or drinking water, depending on the product and indication. Ensure uniform mixing in feed to avoid under- or over-dosing. Monitor feed and water intake to verify effective delivery and adjust as needed.
Withdrawal Period and Residue Prevention
Observe the established withdrawal period before slaughter to prevent violative drug residues in meat. For lincomycin, the withdrawal period is typically 5 days in the U.S., but this varies by country and formulation. Do not slaughter animals during treatment or before completing the full withdrawal period. Use withdrawal tracking systems (e.g., treatment logs, slaughter scheduling tools) to ensure compliance.
Recordkeeping and Documentation
Maintain comprehensive records for a minimum of two years (or as required locally), including:
– VFD orders or prescriptions
– Product purchase invoices and batch numbers
– Treatment dates, dosages, and duration
– Animal groups treated
– Withdrawal dates and slaughter dates
– Veterinarian contact information and VCPR documentation
Records must be readily available for inspection by regulatory authorities.
Biosecurity and Cross-Contamination Prevention
Prevent cross-contamination of lincomycin with non-medicated feeds by using dedicated mixing equipment or thorough cleaning procedures between batches. Implement biosecurity protocols when handling medicated feed, including equipment sanitation and staff training. Avoid sharing equipment between farms without proper decontamination.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Dispose of unused lincomycin, empty packaging, and leftover medicated feed in accordance with local environmental regulations. Do not dispose of in waterways, soil, or regular trash without proper treatment. Follow manufacturer guidelines and consult local waste management authorities for compliant disposal methods.
Audit and Compliance Readiness
Prepare for routine inspections by regulatory bodies by maintaining up-to-date records, ensuring staff are trained on protocols, and conducting internal audits. Participation in quality assurance programs (e.g., Pork Quality Assurance Plus in the U.S.) can support compliance and demonstrate responsible antibiotic use.
Training and Staff Education
Provide regular training for farm personnel, feed mill operators, and veterinary staff on the proper use, handling, and documentation related to lincomycin. Emphasize the importance of adherence to withdrawal periods, accurate recordkeeping, and antimicrobial stewardship principles to reduce resistance development.
Conclusion
Responsible use of lincomycin in pigs requires a coordinated approach involving veterinary guidance, precise logistics, and rigorous compliance with regulatory standards. By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure effective disease control while safeguarding public health, animal welfare, and market access.
In conclusion, sourcing lincomycin for use in pigs must be conducted responsibly, in strict compliance with veterinary regulations and antibiotic stewardship principles. It is essential to obtain the product through licensed veterinary channels, ensuring it is used only under professional supervision and in accordance with prescribed dosages and withdrawal periods. Proper sourcing helps prevent the development of antimicrobial resistance, safeguards animal welfare, and protects public health. Producers should prioritize preventive health management practices and consider alternatives where appropriate, minimizing reliance on antibiotics like lincomycin. Ultimately, responsible sourcing and use support both sustainable swine production and the broader goal of preserving antibiotic efficacy in veterinary and human medicine.