The global light bulb market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient lighting solutions and the widespread adoption of LED technology. According to Mordor Intelligence, the LED lighting market was valued at USD 85.87 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 146.55 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 9.3% during the forecast period. A critical yet often overlooked component of this growth ecosystem is the lightbulb base — the interface between lamp and fixture that ensures electrical connectivity and mechanical stability. As lighting technology evolves with smart systems and miniaturized designs, the demand for precision-engineered, reliable, and standardized bases has surged. This has spurred intensified innovation and competition among manufacturers of bulb bases, particularly those producing bases compliant with international standards such as Edison screw (E26, E27), bayonet (B22), and bi-pin (GU10, G9) types. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining high-volume production, material durability, and strict quality control to supply base components for the world’s leading lighting brands. Below are the top 10 lightbulb base manufacturers shaping the infrastructure of modern illumination.
Top 10 Lightbulb Bases Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Light Sources
Domain Est. 1997
Website: light-sources.com
Key Highlights: LightSources designs, engineers, manufactures and supplies customized lamps and lighting solutions for large and small OEMS world-wide….
#2 LED Lamps
Domain Est. 1996
Website: satco.com
Key Highlights: SATCO® is a leading supplier of lighting products, offering solutions for commercial, residential, and industrial markets. Read more About us. Our Company….
#3 CEC Industries, LTD.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cecindustries.com
Key Highlights: With over 1500 products manufactured, we are your single-source supplier for light bulb and related electronic, industrial and manufacturing applications….
#4 Norman Lamps, Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: normanlamps.com
Key Highlights: $3.85 delivery 30-day returnsWe carry all the major base types – E26, E39 mogul, GU10, GU24, bi-pin configurations, and dozens more – because we understand that getting the right f…
#5 Keystone Technologies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: keystonetech.com
Key Highlights: Keystone Technologies is a leader in manufacturing quality lighting: LED lamps, indoor and outdoor LED fixtures, sensors & controls, and Ballast & LED ……
#6 Light Bulb Depot®
Domain Est. 1997
Website: lightbulbdepot.com
Key Highlights: Light bulb Depot, 16 locations across the nation and shipping to your door or job site. LED, HID lights and fixtures….
#7 Bulbs.com
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bulbs.com
Key Highlights: Over 100000 businesses rely on us for energy saving fluorescent, halogen and LED replacement lighting! Thousands of items in stock. Click to shop now!…
#8 The Light Bulb Company
Domain Est. 2002 | Founded: 1964
Website: thelightbulbco.com
Key Highlights: Family-owned and locally-focused since 1964. It’s our service that makes the difference! Our goal is to educate our customers about the best lighting options….
#9 Light Bulb Base Types
Domain Est. 2002
Website: superbrightleds.com
Key Highlights: Confused by E26, E12, or E39 light bulb bases? This guide breaks down common screw base types so you can find the right fit for your ……
#10 A Guide to Light Bulb Sizes, Types, Shapes, and Codes.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: gelighting.com
Key Highlights: Light bulb bases also come in a variety of sizes. They are identified by light bulb base codes, with the letter denoting the shape of the base and the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lightbulb Bases
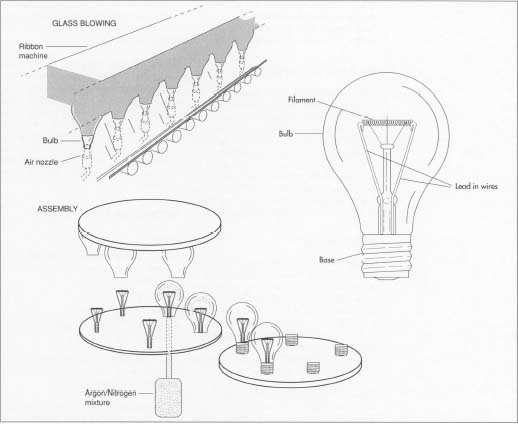
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Lightbulb Bases
The global market for lightbulb bases is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in lighting technology, regulatory shifts, and evolving consumer preferences. Lightbulb bases, once standardized and commoditized, are now adapting to the demands of smart lighting, energy efficiency mandates, and the rise of LED and IoT-integrated systems. Below is an analysis of the key trends shaping the lightbulb base market in 2026.
-
Shift Toward LED-Optimized Bases
By 2026, the dominance of LED lighting will continue to reshape base design and compatibility. Traditional bases like Edison screw (E26/E27) and bayonet (B22) remain prevalent, but they are increasingly engineered for optimal thermal management and electrical contact for LED performance. Specialized bases with improved heat dissipation and secure connectivity are being developed to support long-lasting, high-efficiency LED bulbs. -
Integration with Smart Lighting Systems
Smart home adoption is accelerating, and lightbulb bases are evolving to support intelligent lighting ecosystems. Bases compatible with Zigbee, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi-enabled bulbs—especially in E26/E27 and GU10 form factors—are gaining traction. Some manufacturers are incorporating low-voltage signal contacts within traditional base designs to support dimming, color tuning, and bi-directional communication between bulbs and smart hubs. -
Miniaturization and New Form Factors
As lighting fixtures become more compact and design-focused, especially in architectural and decorative applications, demand for smaller, more versatile bases is growing. Bases like G4, G9, and GU5.3 (MR16) are seeing renewed interest in high-end residential and commercial spaces. Additionally, modular base designs that support plug-and-play LED modules are emerging in commercial retrofit markets. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Global energy efficiency regulations, such as the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and U.S. DOE standards, are pushing manufacturers to design bases that support longer bulb life and recyclability. By 2026, there is increased emphasis on using recyclable metals and reducing material waste in base production. Standardization efforts are also underway to minimize e-waste by ensuring backward compatibility and ease of replacement. -
Regional Diversification and Standardization Challenges
While North America and Europe continue to rely on E26 and E27 bases respectively, regions like Asia-Pacific are seeing hybrid adoption due to local manufacturing and consumer habits. In 2026, companies are focusing on multi-standard bases or adapters to support global distribution. However, fragmentation in voltage requirements and safety certifications still presents challenges for market consolidation. -
Growth in Specialty and Industrial Applications
The industrial, automotive, and healthcare sectors are driving demand for specialized bases with enhanced durability, vibration resistance, and IP-rated sealing. Bases such as G13 (fluorescent), Fa8 (industrial), and proprietary automotive sockets are benefiting from investments in infrastructure and electrification. UV-C and horticultural lighting also require unique base interfaces, further diversifying the market. -
Consolidation and Innovation Among Suppliers
By 2026, the lightbulb base market is seeing consolidation among component suppliers, with major players integrating base manufacturing into broader lighting solutions. Innovations such as corrosion-resistant coatings, gold-plated contacts, and anti-loosening mechanisms are differentiating premium products in competitive segments.
In conclusion, the 2026 lightbulb base market is characterized by technological adaptation, sustainability imperatives, and integration with intelligent systems. While traditional base types remain foundational, their evolution reflects broader trends in energy efficiency, digitalization, and design innovation across the global lighting industry.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Lightbulb Bases (Quality, IP)
Sourcing lightbulb bases—critical components in lighting systems—can present several challenges, particularly regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Durability
One of the most common issues is receiving lightbulb bases made from substandard materials such as low-grade brass, aluminum, or plastic. Inferior materials may lead to poor electrical conductivity, increased risk of overheating, corrosion, or mechanical failure. Bases that lack proper heat resistance or fail under repeated use compromise the safety and longevity of lighting fixtures.
Inconsistent Dimensional Tolerances
Manufacturers, especially low-cost suppliers, may not adhere to international standards (e.g., IEC, ANSI) for base dimensions such as E26, E27, GU10, etc. Even minor deviations can lead to improper fit, arcing, or difficulty in installation. Inconsistent threading or pin alignment increases the risk of product malfunction and customer complaints.
Lack of Safety Certifications
Many sourced bases lack required safety certifications such as UL, CE, RoHS, or VDE. Using uncertified components exposes buyers to regulatory non-compliance, product recalls, and liability in case of fire or electric shock. Always verify that the supplier provides valid, up-to-date certification documentation.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Lightbulb base designs—especially proprietary or patented configurations—may be protected by IP rights. Sourcing from suppliers who produce unauthorized copies (e.g., counterfeit Edison screw bases or patented bi-pin designs) exposes your company to legal action, customs seizures, and brand damage. Always conduct due diligence on supplier legitimacy and avoid vendors offering “compatible” versions of well-known proprietary bases without proper licensing.
Inadequate Testing and Quality Control
Suppliers may skip essential tests such as dielectric strength, temperature rise, and pull-out force. Without proper QC protocols, defect rates can be high, leading to field failures. Request test reports and consider third-party inspections before large-scale orders.
Misrepresentation of Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate performance claims, such as temperature rating (e.g., claiming 250°C when actual is 150°C) or material composition (e.g., labeling a zinc alloy as brass). Independent material verification and sample testing are crucial to avoid misrepresentation.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to trace the origin of components, increasing the risk of inadvertently sourcing from unethical or non-compliant manufacturers. Ensure suppliers provide clear information about their production facilities and raw material sources.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through rigorous supplier vetting, certification verification, IP compliance checks, and quality assurance processes—buyers can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, legal, and safe lightbulb base sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lightbulb Bases
Lightbulb bases—such as Edison screw (E26, E27), bayonet (B22), and pin bases (GU10, G4)—are essential components in lighting products. Proper logistics and compliance management ensure safe transportation, regulatory adherence, and market acceptance. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, shipping, and complying with international standards for lightbulb bases.
Product Classification and HS Code
Correctly classifying lightbulb bases is critical for customs clearance and duty assessment. Lightbulb bases are typically categorized under:
- HS Code 8536.69 – Electrical apparatus for switching or protecting electrical circuits, parts thereof (includes lamp holders and similar fixtures).
Ensure accurate product description and classification based on material (ceramic, plastic, metal), intended use, and design. Consult local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker to verify classification for target markets.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Lightbulb bases, although durable, can be prone to breakage or deformation if not properly protected:
- Cushioning: Use anti-static bubble wrap, corrugated dividers, or molded pulp trays to prevent abrasion and impact.
- Moisture Protection: Include desiccant packs in packaging for ceramic or metal bases to prevent corrosion or condensation.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack,” and “Keep Dry” as appropriate.
- Unit Load Stability: Secure palletized shipments with stretch wrap and corner boards; avoid overloading.
Transportation and Shipping
- Mode of Transport: Lightbulb bases are generally non-hazardous and can be shipped via air, sea, or land freight.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–25°C recommended); avoid exposure to extreme heat or humidity.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin in all international shipments.
- Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities using standard Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP) in sales contracts.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with region-specific electrical and safety standards:
United States
- UL Certification: Required for lamp holders and electrical components under UL 496 (Standard for Plugs and Receptacles).
- FCC Compliance: Not applicable unless bases include electronic components (e.g., smart bases).
- RoHS (State Level): California Proposition 65 may apply if products contain lead or other listed substances.
European Union
- CE Marking: Mandatory under the Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts use of hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in electrical components.
- REACH: Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals; ensure no SVHCs above threshold.
United Kingdom
- UKCA Marking: Required for products placed on the UK market post-Brexit (may accept CE during transition).
- UK RoHS: Mirrors EU RoHS with similar restrictions.
International Markets (e.g., Canada, Australia, Japan)
- CSA (Canada): Certification required under CSA C22.2 No. 18.1.
- RCM (Australia/NZ): Regulatory Compliance Mark for electrical safety and EMC.
- PSE (Japan): Mandatory for certain electrical products under the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Recyclability: Design bases using recyclable materials (e.g., recyclable plastics, metals).
- WEEE Compliance (EU): Ensure take-back and recycling plans are in place if bases are sold as part of complete lighting products.
- Conflict Minerals: If metal components (e.g., brass, tungsten) are used, comply with due diligence requirements (e.g., U.S. Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502).
Quality Assurance and Testing
Conduct routine testing to ensure compliance and durability:
- Electrical Insulation Testing: Verify dielectric strength and creepage distances.
- Temperature Rise Testing: Ensure bases do not overheat under rated loads.
- Mechanical Strength: Test for pull-out force and durability of contacts.
- Corrosion Resistance: Especially important for bases used in humid environments.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for at least five years, including:
– Test reports from accredited labs
– Certifications (UL, CE, RoHS, etc.)
– Material declarations (e.g., IPC-1752)
– Supplier compliance statements
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for lightbulb bases require attention to classification, packaging, regulatory standards, and sustainability. Partnering with certified suppliers, staying updated on regulatory changes, and investing in quality assurance will minimize risks and support global market access. Always consult with legal and compliance experts when entering new markets.
In conclusion, sourcing lightbulb bases requires careful consideration of several key factors including compatibility with bulb types and fixtures, material quality, adherence to industry standards, and supplier reliability. Whether for commercial manufacturing, replacement parts, or specialized applications, selecting the appropriate base type—such as Edison screw, bayonet, or bi-pin—ensures optimal performance and safety. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on cost-effectiveness, production capacity, and compliance with international regulations (like RoHS or UL certification) is essential for long-term success. By prioritizing quality, consistency, and technical specifications during the sourcing process, businesses can ensure reliable integration into lighting systems and meet the demands of both consumers and regulatory bodies.