The global bolt manufacturing industry is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and industrial machinery sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global fasteners market was valued at USD 108.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. Left hand bolts, a specialized product category used in applications requiring reverse threading to prevent loosening under rotational forces—such as in turbines, conveyors, and certain automotive components—are seeing increased adoption in precision engineering and heavy machinery. As industries prioritize reliability and performance, manufacturers specializing in left hand bolts are scaling innovation and production capabilities. This report highlights the top nine manufacturers excelling in quality, technical expertise, and market reach within this niche but critical segment of the fastener industry.
Top 9 Left Hand Bolt Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Empire Bolt & Screw Inc.
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1972
Website: empirebolt.com
Key Highlights: Established in 1972, Empire Bolt & Screw is a trusted, family-owned distributor for custom threaded products, quality fasteners, & industrial goods for a ……
#2 Lamons
Domain Est. 2002
Website: lamons.com
Key Highlights: Lamons is one of the largest custom gasket, bolt, & seal manufacturers globally, committed to providing industry leading sealing solutions. Call us today!…
#3 American Bolt
Domain Est. 2003
Website: americanboltcorp.com
Key Highlights: American Bolt Corp is a high quality industrial fastener supplier for a variety of different industries. We provide top fastener solutions to meet any need!…
#4 Custom Manufactured Bolts
Domain Est. 2003
Website: g-fast.com
Key Highlights: Need custom bolts? We manufacture hex bolts, shoulder bolts, stud bolts, drilled bolts & unusual special bolts. A custom bolt manufacturer you can trust….
#5 NutsandBolts.com
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nutsandbolts.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 30-day returnsYour One-Stop Shop For Fasteners. Seamless shopping with expert support for your projects. Shop Now. Essential Fastener Kits….
#6
Domain Est. 1997
Website: arp-bolts.com
Key Highlights: ARP was the first company to design and engineer fasteners specifically for racing. We developed many patented process for manufacturing high strength ……
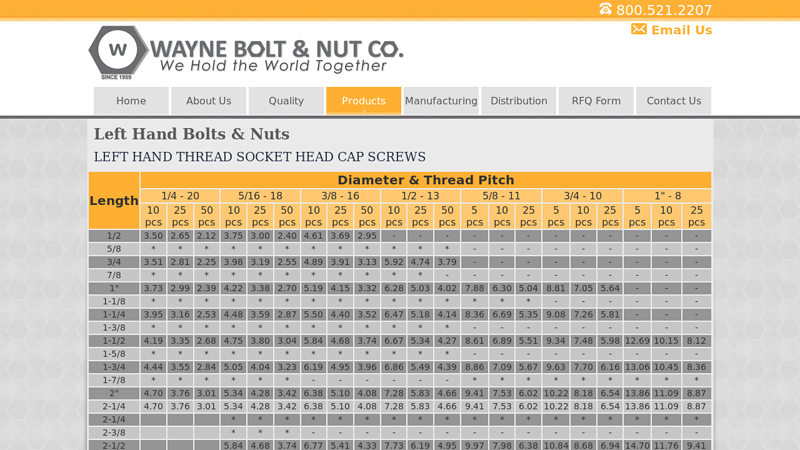
#7 Left Hand Bolts & Nuts
Domain Est. 2002
Website: waynebolt.com
Key Highlights: Left Hand Bolts & Nuts · LEFT HAND THREAD SOCKET HEAD CAP SCREWS · LEFT HAND THREAD HEX HEAD TAP BOLT · Navigation · Products · Contact Us….
#8 Left
Domain Est. 2003
Website: fastenright.com
Key Highlights: Left-hand threaded fasteners are predominantly made to order and any product with a thread can be made with a left hand thread if required….
#9 Hex Bolt
Domain Est. 2007
Website: us.misumi-ec.com
Key Highlights: 1–4 day delivery 30-day returnsHex Bolt – 304 Stainless Steel, M4 – M16, Coarse, Left-Hand Threaded【1-100 Pieces Per Package】. Part Number: Please Configure to get your Part Number…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Left Hand Bolt

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Left-Hand Bolt
The global market for specialized fasteners, including left-hand bolts, is poised for notable shifts by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing, evolving industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. Left-hand bolts—engineered with reverse threading to resist loosening in high-vibration or counterclockwise rotational environments—are gaining strategic importance across key sectors. Below are the anticipated market trends for left-hand bolts in 2026:
1. Rising Demand in High-Performance Industries
Industries such as aerospace, automotive racing, heavy machinery, and wind energy are expected to increase adoption of left-hand bolts to enhance mechanical reliability. In wind turbines, for example, left-hand bolts are crucial in rotor assemblies where rotational forces can loosen standard fasteners. As global investment in renewable energy accelerates, especially in offshore wind farms, demand for vibration-resistant components like left-hand bolts will grow steadily.
2. Expansion in Electric Vehicle (EV) and E-Mobility Applications
The EV sector is exploring left-hand threading solutions for motor assemblies and drivetrain components where reverse torque is present. With the global EV fleet projected to surpass 100 million by 2026, niche fastener applications are gaining prominence. OEMs are increasingly specifying left-hand bolts in motor housings and gearbox systems to prevent self-loosening, driving innovation and volume production.
3. Automation and Precision Manufacturing Integration
Advances in automated manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies are enabling more precise and cost-effective production of left-hand bolts. CNC machining and robotic assembly lines are reducing production lead times and minimizing errors in thread orientation. This scalability supports wider adoption beyond niche or custom applications into standardized industrial use.
4. Material Innovation and Lightweighting
The push for lightweight materials in transportation and aerospace is influencing left-hand bolt development. By 2026, high-strength alloys, titanium, and composite-based fasteners with left-hand threading are expected to enter mainstream use. These materials offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios while maintaining the anti-loosening benefits of reverse threading.
5. Standardization and Global Supply Chain Development
Historically seen as specialty items, left-hand bolts are moving toward broader standardization (e.g., ISO and DIN specifications). This trend improves interoperability and reduces procurement complexity. Global supply chains are adapting, with manufacturers in Asia, Europe, and North America expanding production capacity to meet anticipated demand, particularly from emerging markets in Southeast Asia and India.
6. Emphasis on Predictive Maintenance and Smart Fastening
Integration with smart manufacturing systems is leading to the development of “smart” left-hand bolts embedded with sensors to monitor tension, temperature, and wear. These innovations support predictive maintenance, reducing downtime in critical infrastructure. By 2026, such intelligent fastening solutions could represent a growing segment of the high-end left-hand bolt market.
7. Sustainability and Circular Economy Considerations
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are prompting manufacturers to adopt recyclable materials and energy-efficient production methods. Left-hand bolts made from recycled alloys or designed for easy disassembly and reuse will gain favor, especially in automotive and consumer electronics sectors.
Conclusion
By 2026, the left-hand bolt market is expected to transition from a niche component to a strategically critical element in advanced mechanical systems. Driven by technological innovation, sector-specific demands, and sustainability goals, the market will likely see increased standardization, broader industrial adoption, and integration with digital manufacturing ecosystems. Companies that invest in R&D, automation, and sustainable practices will be well-positioned to capitalize on this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Left-Hand Thread Bolts (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing left-hand thread bolts presents unique challenges compared to standard fasteners, particularly in the areas of quality control and intellectual property (IP) compliance. Being aware of these common pitfalls can help avoid costly delays, performance failures, and legal risks.
Inconsistent or Substandard Quality
Left-hand thread bolts are less commonly manufactured than right-hand versions, which can lead to quality inconsistencies. Many suppliers may produce them as special or custom orders, increasing the risk of deviations in material composition, heat treatment, thread accuracy, and dimensional tolerances. Without rigorous quality assurance protocols—such as certified material test reports (MTRs), proper tensile testing, and thread inspection—there’s a heightened risk of receiving bolts that fail under load or do not meet required specifications.
Additionally, some overseas manufacturers may replicate designs without adhering to international standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM, DIN), resulting in non-conforming products that compromise safety and reliability. Always verify supplier certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and request sample testing before large-scale procurement.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Left-hand thread bolts may be part of patented fastening systems or engineered solutions protected under IP law. Sourcing generic or unlicensed copies—especially from suppliers in regions with lax IP enforcement—can expose your company to legal liability. For example, certain aerospace, automotive, or industrial applications use proprietary fastener designs where the thread direction (left-hand) is integral to the patented mechanism.
Procurement teams may inadvertently violate patents by sourcing “compatible” or “equivalent” parts without confirming freedom-to-operate. This is particularly risky when suppliers advertise “same as” or “fits OEM” without authorization. Always conduct due diligence on the design origin and consult legal or technical experts when sourcing specialized fasteners to ensure compliance with patent and trademark regulations.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Due to their niche use, left-hand bolts often lack full traceability in the supply chain. Missing or falsified documentation—such as mill certs, test reports, or manufacturing origin—can hinder compliance with industry regulations (e.g., AS9100 for aerospace). Without proper traceability, it becomes difficult to investigate failures or demonstrate due diligence during audits.
Supplier Reliability and Long-Term Availability
Few suppliers specialize in left-hand threaded fasteners, leading to potential supply chain vulnerabilities. Relying on a single or unproven vendor increases the risk of delivery delays, discontinuation, or quality drift over time. It’s essential to qualify multiple reliable suppliers and confirm their capability to consistently reproduce the correct thread form and hand.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, establish clear technical specifications, work with reputable and certified suppliers, conduct third-party quality audits when necessary, and perform IP reviews for critical applications. Proactive management of both quality and legal aspects ensures reliable performance and protects your organization from avoidable risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Left Hand Bolt
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for handling, shipping, storing, and using Left Hand Bolt components in manufacturing, distribution, and assembly environments. Proper adherence ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Product Identification and Specifications
Left Hand Bolt refers to threaded fasteners with a left-hand thread orientation, meaning they tighten when turned counterclockwise and loosen when turned clockwise—opposite to standard (right-hand) threads. These bolts are used in specialized applications where rotational forces could loosen standard bolts (e.g., bicycle pedals, certain machinery components).
Key specifications include:
– Thread direction: Left-hand (LH)
– Material: Typically steel, stainless steel, or alloy variants
– Grade/Strength: Varies by application (e.g., Grade 5, Grade 8, or metric classes)
– Finish: Zinc-plated, galvanized, or plain
– Compliance markings: Must meet ISO, ASTM, or DIN standards as applicable
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling prevent mix-ups with standard right-hand bolts and ensure traceability.
- Clear Labeling: Each package must be labeled “LEFT HAND THREAD” or “LH” in bold, legible text.
- Color Coding: Use distinct color labels (e.g., red or orange) to differentiate from standard fasteners.
- Barcoding/QR Codes: Include unique identifiers for inventory tracking and compliance audits.
- Inner Packaging: Use compartmentalized trays or blister packs to prevent damage and maintain orientation.
- Outer Packaging: Use durable, moisture-resistant containers suitable for domestic and international transit.
Storage and Handling
To maintain quality and prevent accidental misapplication:
- Segregated Storage: Store Left Hand Bolts separately from right-hand bolts using designated bins or shelves with clear signage.
- Environmental Controls: Store in dry, temperature-controlled areas to prevent corrosion.
- Handling Procedures: Train personnel to inspect thread direction before use; implement a double-check protocol in assembly lines.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO): Apply FIFO inventory rotation to avoid obsolete stock.
Transportation and Shipping
Ensure safe and compliant transport across supply chains.
- Domestic Shipments: Comply with DOT regulations for hazardous materials if applicable (e.g., plating chemicals). Most bolts are non-hazardous but must be properly packaged to prevent shifting.
- International Shipments:
- Declare accurate HS Code (e.g., 7318.15 for threaded fasteners).
- Include proper export documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin).
- Comply with destination country’s import standards (e.g., CE marking in EU, ASME/ASTM in USA).
- Freight Classification: Classify under NMFC code for fasteners; use appropriate packaging to reduce freight damage claims.
Regulatory Compliance
Meet all relevant industry and regional standards.
- ISO Standards: ISO 898-1 (mechanical properties), ISO 965 (thread tolerances).
- ASTM Standards: ASTM A307, A449, or A574 depending on grade and application.
- REACH & RoHS: Confirm compliance if selling in the EU; ensure no restricted substances in plating or materials.
- Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT): For US-bound shipments, ensure supply chain security compliance if applicable.
- Traceability: Maintain batch/lot records for at least 5 years to support recalls or audits.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
- Incoming Inspection: Verify thread direction, dimensions, strength grade, and surface finish upon receipt.
- Certificates of Conformance (CoC): Require CoC from suppliers for every batch.
- Testing: Conduct periodic torque and tensile strength tests per ISO or ASTM protocols.
- Non-Conformance Handling: Establish a quarantine and corrective action process for defective bolts.
Training and Internal Controls
- Employee Training: Educate procurement, warehouse, and assembly staff on identifying and handling left-hand bolts.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Document processes for storage, inspection, and usage.
- Audit Readiness: Conduct internal audits annually to verify compliance with this guide.
Emergency and Recall Preparedness
- Recall Plan: Establish a fastener recall protocol including customer notification, batch tracking, and root cause analysis.
- Incident Reporting: Log any misapplication or failure related to incorrect bolt usage.
Adherence to this Logistics & Compliance Guide ensures the safe and effective use of Left Hand Bolts while minimizing risks of error, non-compliance, and liability. Regularly review and update procedures to reflect regulatory changes and operational improvements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Left-Hand Thread Bolts
After evaluating various sourcing options, it is concluded that left-hand thread bolts, while less common than standard right-hand thread fasteners, are readily available from specialized suppliers, industrial distributors, and manufacturers with the capability to produce custom or non-standard threaded components. Key considerations when sourcing include material specifications, thread standards (such as ISO or UNC/UNF), required certifications, and volume needs.
Primary sourcing strategies include procuring from established industrial supply companies (e.g., McMaster-Carr, Misumi, Grainger), engaging fastener manufacturers directly for custom orders, or utilizing global B2B platforms like Alibaba for cost-effective bulk procurement—while ensuring quality control measures are in place.
Although lead times may be longer and costs slightly higher due to lower production volumes, ensuring correct specifications and traceability is critical to avoid assembly issues, safety risks, or equipment failure. Therefore, it is recommended to establish relationships with reliable suppliers, maintain accurate inventory records, and verify product samples before full-scale ordering.
In conclusion, with proper supplier vetting and clear technical requirements, sourcing left-hand thread bolts can be efficiently managed to support specialized mechanical applications such as rotating parts, where reverse threading prevents loosening under operational forces.