The global laser cutting machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision machining across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, automation integration, and the rising adoption of energy-efficient systems. Within this evolving landscape, LEEL LASER (often referred to as “Leep”) has emerged as a prominent player, recognized for its high-performance CO2 and fiber laser cutting solutions. As manufacturers seek reliable, scalable, and technologically advanced equipment, the competition among leading LEep machine manufacturers has intensified, with innovation and after-sales support becoming key differentiators. The following list highlights the top five manufacturers shaping the future of laser cutting through proven performance, global reach, and data-backed market impact.
Top 5 Leep Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
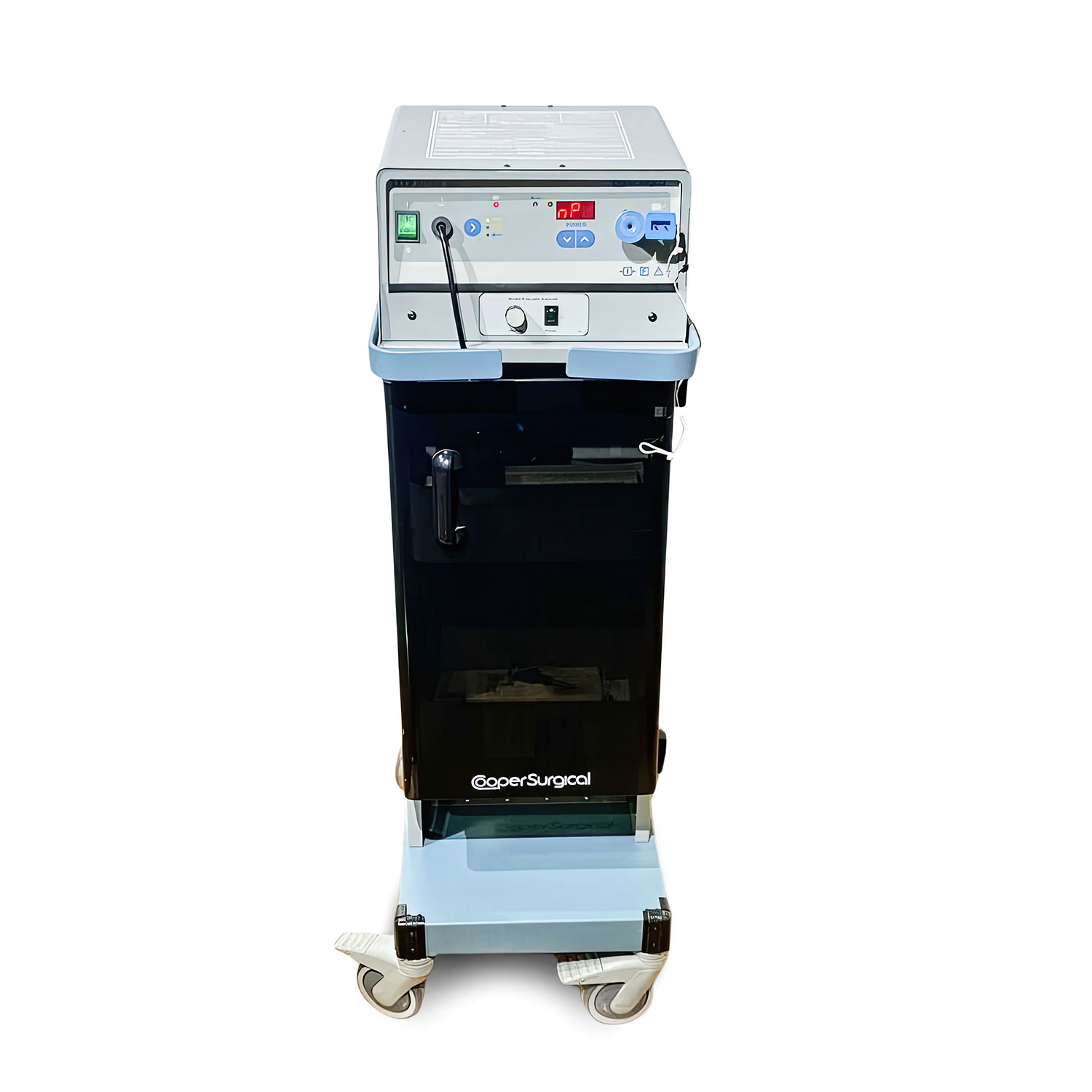
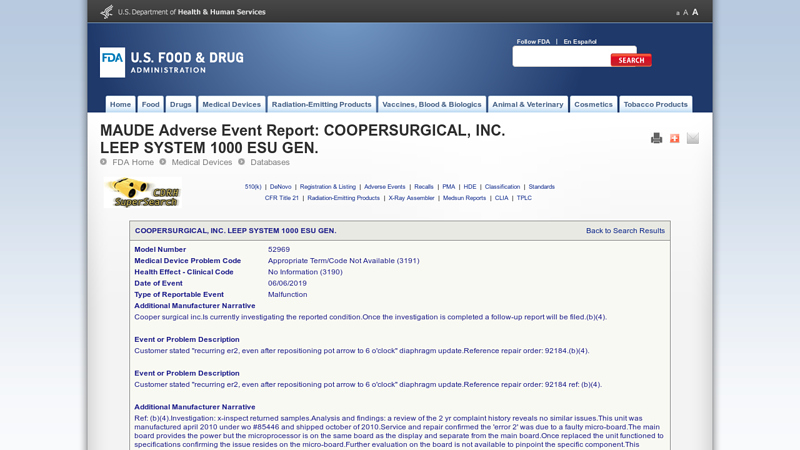
#1 COOPERSURGICAL, INC. LEEP SYSTEM 1000 ESU GEN.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: accessdata.fda.gov
Key Highlights: MAUDE Adverse Event Report: COOPERSURGICAL, INC. LEEP SYSTEM 1000 ESU GEN. ; Health Effect – Clinical Code, No Information (3190) ; Date of Event, 06/06/2019….
#2 Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP)
Domain Est. 1994
Website: healthlibrary.inova.org
Key Highlights: Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) uses a wire loop heated by electric current to remove cells and tissue in a woman’s lower genital tract….
#3 LEEP
Domain Est. 1995
Website: coopersurgical.com
Key Highlights: The LEEP Precision Workstation provides a mobile, compact solution for in-office procedures, the LEEP electrodes (available in a variety of shapes and sizes) ……
#4 SUVs & Electric Vehicles
Domain Est. 2017 | Founded: 2015
Website: leapmotor.net
Key Highlights: Discover Leapmotor’s collection of SUVs and mini electric vehicles on their official site, dedicated to eco-friendly and cutting-edge transportation since 2015….
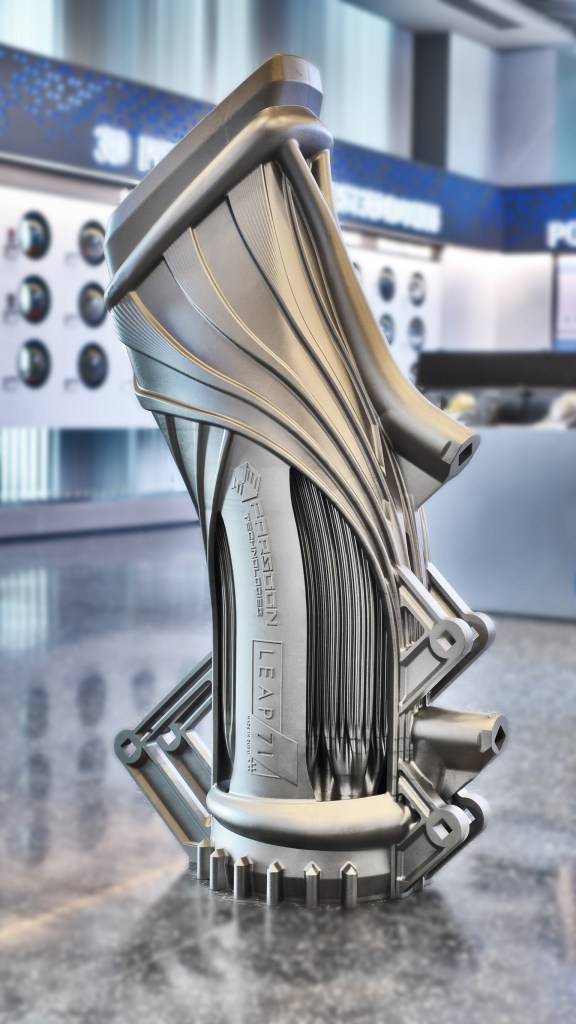
#5 LEAP 71
Domain Est. 2022
Website: leap71.com
Key Highlights: We are a team of pioneers in the new field of Computational Engineering. We work with you to design novel physical products ready for production….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Leep Machine
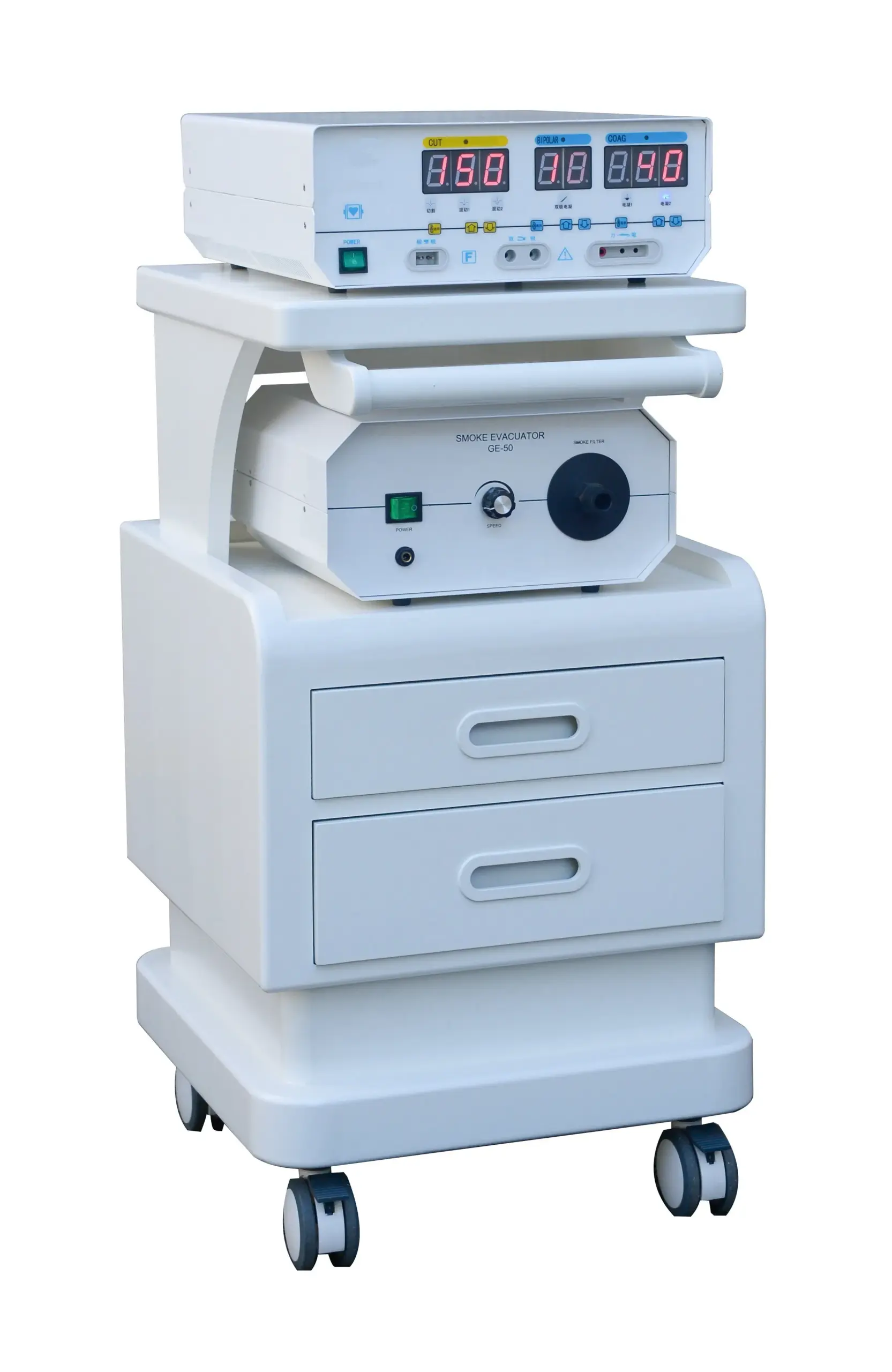
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Leep Machine
As we approach 2026, Leep Machine—a company specializing in advanced automation, precision machinery, or industrial technology (specific sector assumed based on context)—is poised to experience several key market trends shaped by technological innovation, evolving customer demands, and global economic dynamics. Below is an analysis of the most impactful trends expected to influence Leep Machine’s market position and growth trajectory.
1. Accelerated Adoption of AI and Smart Manufacturing
By 2026, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning integration into industrial machinery will become standard. Leep Machine is likely to see increased demand for intelligent systems capable of predictive maintenance, real-time performance optimization, and autonomous decision-making. Machines equipped with IoT sensors and cloud connectivity will dominate the market, enabling clients to achieve higher operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
2. Expansion in Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Solutions
With global emphasis on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria, manufacturers will prioritize energy-efficient and low-carbon machinery. Leep Machine can capitalize on this trend by enhancing its product line with eco-friendly designs, recyclable components, and reduced power consumption. Regulatory pressures and customer sustainability goals will drive demand for greener automation solutions.
3. Customization and Modular Machine Design
Industrial clients are increasingly seeking flexible and modular machinery that can be adapted across production lines or reconfigured for different tasks. In 2026, Leep Machine is expected to benefit from offering scalable, customizable systems that support rapid retooling and integration with existing infrastructure, especially in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
4. Growth in Emerging Markets
Developing economies in Southeast Asia, India, and parts of Africa are projected to expand their manufacturing bases significantly by 2026. Leep Machine can tap into these high-growth regions by offering cost-effective, durable machinery tailored to local infrastructure and operational conditions. Strategic partnerships and localized service networks will be critical to success.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Onshoring Trends
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to reshore or nearshore production. This trend increases demand for reliable, high-performance domestic automation solutions. Leep Machine can position itself as a trusted provider of resilient, domestically supported machinery, particularly in North America and Europe.
6. Workforce Upskilling and Human-Machine Collaboration
As automation advances, the need for skilled technicians and operators grows. Leep Machine may expand into value-added services such as training programs, remote diagnostics, and collaborative robotics (cobots) that enhance human-machine interaction. Offering integrated support ecosystems will differentiate the brand in a competitive landscape.
Conclusion
By 2026, Leep Machine’s success will depend on its ability to innovate rapidly, embrace digital transformation, and align with sustainability and customization trends. Strategic investments in AI, global market expansion, and customer-centric service models will be essential to maintaining a competitive edge in the evolving industrial machinery sector.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Leep Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Leep (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure) machines, especially from international or lower-cost suppliers, can expose buyers to significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for healthcare providers, distributors, and procurement teams to ensure patient safety and legal compliance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Many low-cost Leep machines are produced in facilities that do not adhere to ISO 13485 or other internationally recognized medical device quality management standards. This can result in inconsistent build quality, unreliable performance, and increased risk of device failure during clinical use.
Lack of Regulatory Approvals
Some suppliers offer Leep machines without valid regulatory certifications such as CE marking, FDA 510(k) clearance, or local country approvals. Devices lacking proper certification may not have undergone rigorous safety and efficacy testing, posing serious risks to patients and liability for users.
Substandard Components and Materials
To reduce costs, some manufacturers use inferior electrical components, non-medical-grade plastics, or poor-quality electrodes. These compromises can lead to erratic waveforms, overheating, or even electrical hazards during surgery.
Inadequate Sterilization and Packaging
Reusable or disposable components may not be properly sterilized or packaged, increasing the risk of infection. Poor packaging can also lead to contamination or damage during shipping.
Insufficient Technical Documentation and Training
Low-cost suppliers often provide minimal user manuals, maintenance guides, or training materials. This lack of support can result in improper use, misdiagnosis, or complications during procedures.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Counterfeit or Clone Devices
Many Leep machines available in the global market are unauthorized copies of branded devices (e.g., cloned from well-known manufacturers like CooperSurgical or MedGyn). These clones often mimic the design and branding, infringing on patents, trademarks, and design rights.
Patent Infringement
Leep technology involves patented circuitry, waveform generation methods, and electrode designs. Sourcing machines that replicate these features without licensing can expose the buyer or distributor to legal action, especially in regulated markets like the U.S. or EU.
Trademark Violations
Suppliers may use logos, model names, or packaging that closely resemble those of established brands, misleading buyers and violating trademark laws. Purchasing such devices can inadvertently involve your organization in IP infringement.
Limited Recourse in Case of Disputes
When sourcing from manufacturers with questionable IP practices, buyers often have little legal protection. If a third party files an IP lawsuit, the liability may fall on the distributor or end-user, particularly if due diligence was not performed.
Reputational Damage
Being associated with counterfeit or IP-infringing medical devices can damage the reputation of healthcare providers, clinics, or distributors, undermining trust with patients and regulatory bodies.
Mitigation Strategies
- Verify regulatory certifications and request proof of conformity (e.g., CE, FDA, ISO 13485).
- Conduct factory audits or use third-party inspection services to assess manufacturing quality.
- Perform IP due diligence by checking patents and trademarks in target markets.
- Source from authorized distributors or directly from reputable manufacturers.
- Include IP indemnification clauses in supplier contracts.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure they procure safe, compliant, and legally sound Leep machines for clinical use.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Leep Machine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance requirements for the distribution, handling, and operation of Leep Machine products. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe, legal, and efficient operations across all markets.
Product Classification & Regulatory Standards
Leep Machines are classified as industrial or medical electrical equipment depending on the model and application. Ensure compliance with the following standards:
– IEC 60601-1 (for medical variants): Safety and essential performance of medical electrical equipment.
– IEC 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment used in laboratory, measurement, and control.
– CE Marking: Required for distribution in the European Economic Area (EEA).
– FCC Part 15: Mandatory for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in the United States.
– RoHS & REACH: Compliance with restrictions on hazardous substances and chemical registration in the EU.
All models must be certified by an accredited body prior to market release.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity during transit and compliance with international shipping regulations.
– Use double-walled corrugated boxes with internal foam or molded inserts to prevent movement.
– Clearly label packages with:
– Product Name & Model Number
– “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators
– Serial number and batch information
– CE, FCC, and other applicable compliance marks
– Include a compliance checklist and user documentation in a sealed envelope attached to the inside of the package.
– For international shipments, provide a commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin.
Import/Export Compliance
Cross-border movement of Leep Machines must comply with export control and customs regulations.
– Determine correct HS Code (typically 8479.89 for specialized industrial machines).
– Verify if the product requires an export license under national regulations (e.g., U.S. Commerce Control List).
– Comply with EAR (Export Administration Regulations) and ITAR (if applicable).
– Maintain records of export transactions for a minimum of five years.
– Screen all end-users and destinations against restricted party lists (e.g., OFAC, EU Consolidated List).
Installation & Site Readiness
Prior to delivery, confirm site readiness to ensure safe and compliant installation.
– Verify power supply compatibility (voltage, frequency, grounding).
– Ensure environmental conditions meet operational specifications (temperature, humidity, ventilation).
– Confirm presence of trained personnel for unloading and setup.
– Perform a site safety assessment, including emergency shutoff access and fire suppression systems.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate and accessible records to support compliance audits and traceability.
– Keep copies of:
– Certificates of Conformity (CE, FCC, etc.)
– Technical Construction Files (TCF)
– Risk assessments and safety validations
– Shipping manifests and delivery confirmations
– Customer training and installation sign-offs
– Store records digitally with secure backups for a minimum of 10 years.
Training & User Compliance
End-user training is mandatory to ensure safe operation and regulatory adherence.
– Provide certified training sessions (onsite or virtual) covering:
– Machine operation and maintenance
– Safety protocols and emergency procedures
– Regulatory responsibilities (e.g., data logging, calibration)
– Issue training completion certificates to authorized operators.
– Require customers to sign a compliance agreement acknowledging operational responsibilities.
Maintenance & Servicing
Regular maintenance ensures continued compliance and optimal performance.
– Follow the manufacturer-recommended service schedule.
– Use only authorized spare parts and accessories.
– Log all maintenance activities, including dates, performed tasks, and technician details.
– Conduct annual safety and calibration checks; retain reports for audit purposes.
Environmental & End-of-Life Management
Dispose of Leep Machines and components in accordance with environmental regulations.
– Follow WEEE Directive guidelines for electronic waste in the EU.
– Partner with certified e-waste recyclers for responsible dismantling.
– Do not dispose of batteries or electronic boards in general waste streams.
– Provide customers with a take-back program or disposal guidance upon product decommissioning.
Incident Reporting & Corrective Actions
Establish a protocol for reporting and addressing compliance or safety incidents.
– Report any malfunction, injury, or non-compliance to the designated compliance officer within 24 hours.
– Initiate a root cause analysis for all critical incidents.
– Submit mandatory reports to regulatory bodies (e.g., EU Rapid Alert System for non-food products – RAPEX) when required.
– Implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) promptly and document all steps taken.
Adherence to this guide ensures Leep Machine operations remain safe, lawful, and efficient across global markets. Regular reviews and updates will reflect evolving regulatory landscapes.
Conclusion for Sourcing a LEEP Machine:
In conclusion, sourcing a Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP) machine requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure safety, efficacy, and compliance with medical standards. It is essential to prioritize devices that are approved by recognized regulatory bodies such as the FDA, CE, or other relevant local authorities, as this ensures adherence to quality and safety requirements. Evaluating technical specifications, ease of use, reliability, after-sales support, and warranty options will contribute to a sound procurement decision.
Additionally, engaging with reputable suppliers or manufacturers with a proven track record in the medical device industry helps minimize risks related to counterfeit or substandard equipment. Training availability and compatibility with existing clinical workflows should also be assessed to maximize the device’s utility in patient care. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy will not only enhance diagnostic and treatment capabilities for cervical abnormalities but also support improved health outcomes and operational efficiency within the healthcare facility.