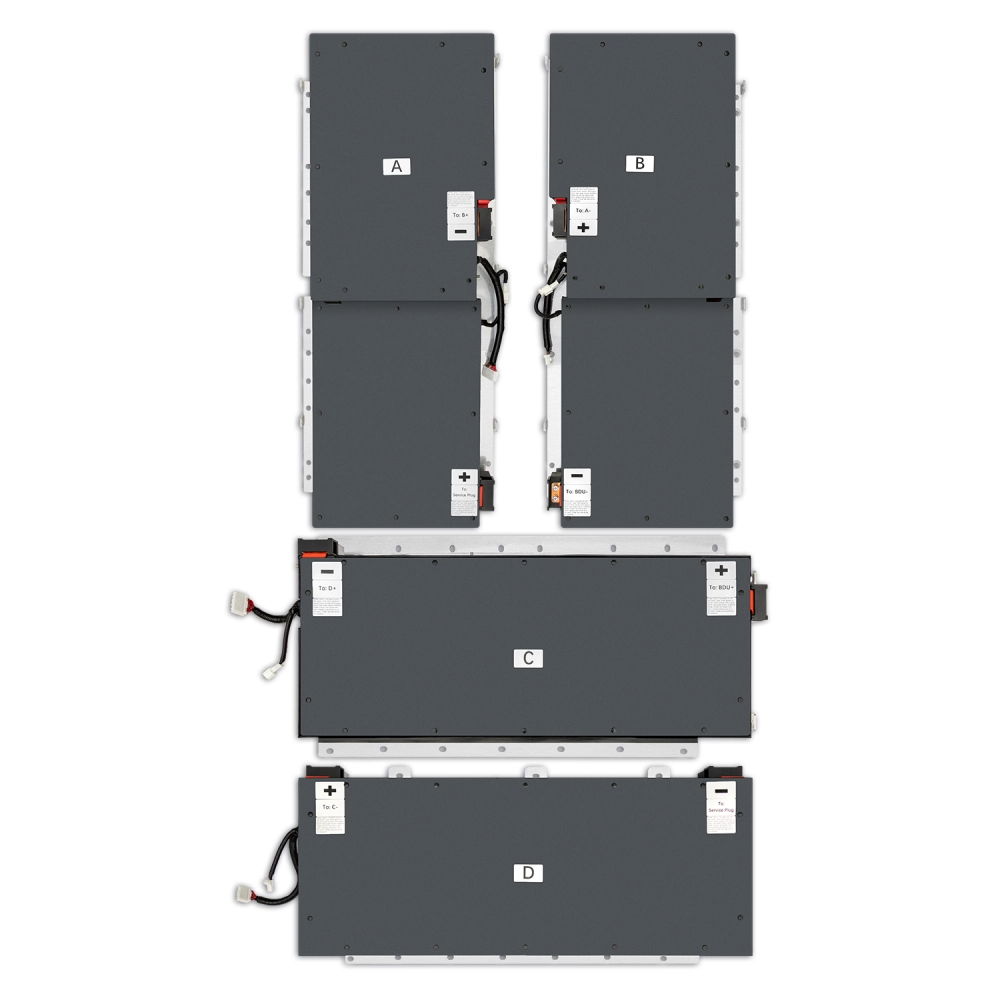
The global lithium-ion battery market, driven by escalating demand in electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, and energy storage systems, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16.4% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. With EV adoption accelerating worldwide, niche segments such as leaf battery replacements—modular or drop-in solutions for aging EV battery cells—are gaining traction among automotive aftermarket and fleet maintenance providers. As aging electric vehicle fleets require cost-effective refurbishment, demand for reliable, high-performance leaf battery replacements has spurred innovation among specialized manufacturers. Backed by market expansion forecasts from Mordor Intelligence, which estimates the EV battery market to exceed USD 150 billion by 2028, this segment is poised for significant growth. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront, combining technical precision, scalable production, and compliance with industry standards to meet rising aftermarket and OEM retrofit needs.
Top 8 Leaf Battery Replacement Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 VIVNE Leaf battery replacement and upgrade
Domain Est. 2023
Website: vivnevs.com
Key Highlights: We are a factory specializing in electric vehicle battery upgrade services, covering models Nissan Leaf (ZE0, AZE0, ZE1), Nissan e-NV200 and BMW i3….
#2 Bms for nissan leaf batterys?
Domain Est. 2006
Website: diyelectriccar.com
Key Highlights: Nissan Leaf. Leaf Battery replacement costs are now official. $5,400 plus your pack as a core valued at $1k is what you pay. Warranted pack ……
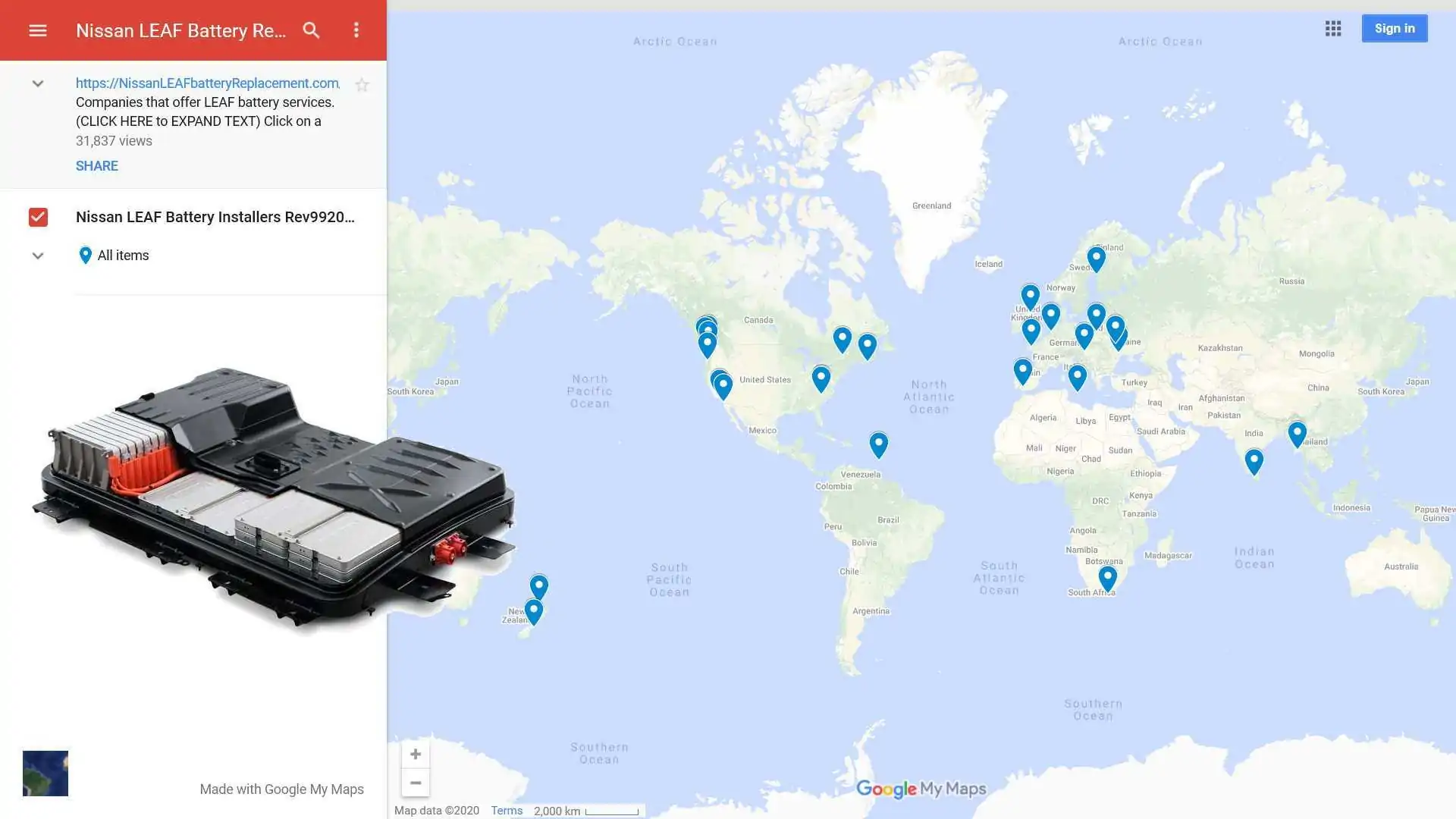
#3 Nissan Leaf Owner Creates World Map For Battery
Domain Est. 2012
Website: insideevs.com
Key Highlights: A 2013 Nissan Leaf owner, Sal Cameli wants to help people like him find battery packs replacement companies with the ……
#4 Nissan LEAF Battery Replacement Cost Explained
Domain Est. 2019
Website: findmyelectric.com
Key Highlights: In this article, we’ll walk you through signs of poor battery performance, the Nissan LEAF battery warranty, how much it costs to replace the battery on a ……
#5 Nissan LEAF Battery Replacement
Domain Est. 2020
Website: nissanleafbatteryreplacement.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to the. Nissan LEAF Battery Replacement Website! (click here). Below you will find a Google Map that shows pin-points of companies…
#6 Some Geniuses Are Swapping Brand
Domain Est. 2021
Website: theautopian.com
Key Highlights: You can either buy a set of battery modules to swap in to your original Nissan Leaf battery housing, or you can buy a complete plug-and-play ……
#7 Nissan LEAF Battery Replacement Guide
Domain Est. 2020
Website: recurrentauto.com
Key Highlights: The Nissan LEAF has model years that range from 2011 to 2022 and battery sizes that range from 22 to 62 kilowatt hours (kWh)….
#8 Leaf Nissan Electric Car
Domain Est. 2023
Website: ihybridbattery.com
Key Highlights: A battery swap is a like-for-like replacement — swapping your Leaf’s battery with another one of the same capacity and model generation. A battery upgrade ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Leaf Battery Replacement

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Leaf Battery Replacement
As the global shift toward sustainable transportation accelerates, the market for Nissan Leaf battery replacements is expected to experience significant transformation by 2026. Driven by aging first- and second-generation Leaf models entering their second decade of service, evolving battery technologies, and increasing consumer demand for cost-effective electrified mobility, several key trends are shaping the Leaf battery replacement landscape.
1. Rising Demand Due to Vehicle Longevity
By 2026, a substantial number of Nissan Leaf vehicles—especially early models from 2011 to 2017 with 24–30 kWh battery packs—will require battery replacements due to capacity degradation. With improved vehicle reliability and growing consumer confidence in EV longevity, owners are increasingly opting to replace aging batteries rather than trade in their vehicles. This trend is driving strong aftermarket and OEM replacement demand.
2. Growth of Third-Party and Refurbished Battery Solutions
The high cost of OEM battery packs has spurred a robust market for third-party and remanufactured battery solutions. By 2026, companies specializing in battery refurbishment, reconditioning, and compatible aftermarket packs are expected to capture a growing share of the Leaf replacement market. These options offer 30–50% cost savings compared to OEM replacements, appealing to budget-conscious consumers.
3. Advancements in Battery Technology and Capacity Upgrades
By 2026, battery replacement services are increasingly offering capacity upgrades—such as installing 40 kWh or even 62 kWh modules into older Leafs—effectively modernizing the vehicle’s range and performance. This “battery swapping for upgrade” trend is made possible by improved standardization and the availability of used or surplus battery packs from newer EVs.
4. Expansion of Battery Recycling and Sustainability Initiatives
With environmental concerns mounting, the 2026 market emphasizes responsible battery disposal and recycling. Companies involved in Leaf battery replacements are partnering with recycling firms to ensure old lithium-ion packs are properly processed. Furthermore, some replacement programs now include trade-in incentives for old batteries, promoting a circular economy.
5. OEM and Dealership Involvement with Extended Warranty Programs
Nissan and authorized dealerships are expected to enhance their battery replacement offerings by 2026, including extended warranty options, certified reconditioned packs, and bundled service plans. These programs aim to retain customer loyalty and compete with the growing independent aftermarket.
6. Integration with Second-Life Battery Applications
As Leaf batteries are replaced, many are being repurposed for stationary energy storage (e.g., home solar storage). This secondary market adds value to retired batteries and is influencing replacement economics—some service providers now offer discounts in exchange for old packs to be used in second-life applications.
7. Regional Market Variations
Demand for Leaf battery replacements will vary significantly by region. Markets with high early EV adoption—such as the U.S. West Coast, Western Europe, and Japan—will see the highest activity. Government incentives for EV maintenance and green technology may further stimulate replacement rates in these areas.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Leaf battery replacement market will be characterized by innovation, affordability, and sustainability. With aging EV fleets and technological advancements converging, consumers will have more options than ever to extend the life of their Nissan Leafs—making battery replacement a key component of the broader EV ecosystem.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Leaf Battery Replacement (Quality, IP)
Sourcing replacement batteries for electric vehicles like the Nissan Leaf involves navigating several critical challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to safety hazards, legal complications, and poor performance. Below are key issues to watch for:
Poor Quality and Safety Risks
One of the most significant pitfalls when sourcing Leaf battery replacements is encountering substandard battery packs. Many third-party or aftermarket suppliers offer lower-cost alternatives that may use recycled or refurbished cells, inconsistent cell grading, or inadequate battery management systems (BMS). These compromises can lead to reduced range, premature failure, overheating, or even fire hazards. Without rigorous testing and quality control—such as capacity verification, cell balancing, and thermal management validation—buyers risk installing unreliable or dangerous components.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
Many replacement batteries, especially from non-OEM or overseas suppliers, lack essential safety certifications such as UN38.3, IEC 62133, or UL standards. Without these, the battery may not comply with transportation, installation, or operational regulations. Using uncertified batteries can void vehicle warranties, complicate insurance claims, and expose users to regulatory penalties.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Sourcing aftermarket batteries can inadvertently involve IP violations. OEMs like Nissan hold patents and design rights on battery pack architecture, BMS software, communication protocols, and physical configurations. Unauthorized replication of these components—especially software and control systems—can constitute copyright or patent infringement. Buyers and suppliers may face legal action if replacement batteries copy proprietary technology without licensing, even if the cells themselves are generic.
Incompatible BMS and Software Integration
Even if a battery appears physically compatible, differences in the Battery Management System (BMS) can prevent proper communication with the Nissan Leaf’s onboard systems. Proprietary communication protocols and software encryption mean that non-OEM batteries may not integrate correctly, leading to error codes, charging issues, or failure to operate. Reverse-engineering these systems to achieve compatibility may breach software licensing agreements or anti-circumvention laws (e.g., DMCA in the U.S.).
Misrepresentation of Capacity and Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate battery capacity (e.g., advertising a “40kWh” pack that delivers only 30kWh under real conditions) or use ambiguous labeling (e.g., total cell capacity vs. usable pack capacity). This misrepresentation undermines buyer expectations and vehicle performance. Transparent, third-party-verified specifications are essential but often missing in low-cost supply chains.
Short Warranty and Lack of Support
Many third-party battery suppliers offer limited or no warranty, or provide support only in their home country. Given the high cost and critical function of EV batteries, inadequate after-sales service can leave buyers stranded when issues arise. Reliable technical support, warranty coverage, and clear return policies are often overlooked but crucial.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven quality control, valid certifications, transparent specifications, and legal compliance. Engaging with reputable vendors, verifying IP licensing where applicable, and insisting on compatibility testing can mitigate risks and ensure a safe, reliable Leaf battery replacement.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Leaf Battery Replacement
This guide outlines the key logistical and compliance considerations for the safe and efficient replacement of the lithium-ion battery in the Nissan Leaf. Adherence to these procedures ensures regulatory compliance, worker safety, and environmental protection.
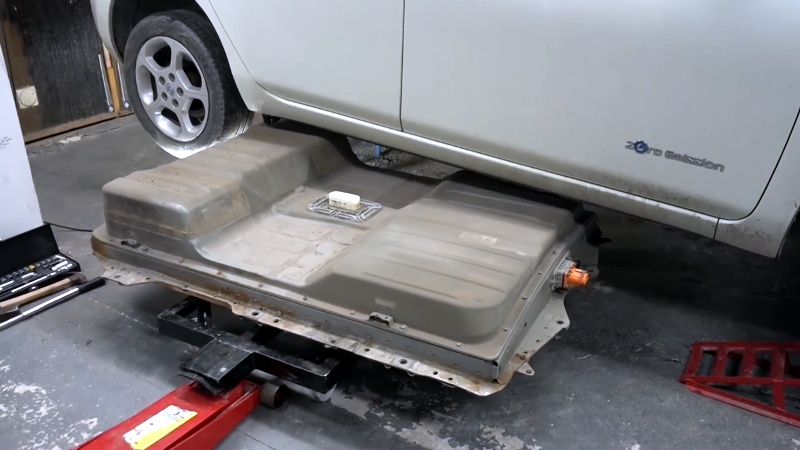
Battery Removal and Handling Procedures
Prior to removal, ensure the vehicle is powered down and the high-voltage system is fully isolated in accordance with Nissan’s service manual. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including insulated gloves, safety glasses, and non-conductive footwear. The battery pack is heavy (approximately 300 kg / 660 lbs); utilize a certified lift table or hoist with a battery removal fixture to prevent injury and damage. Avoid puncturing, dropping, or exposing the pack to water, fire, or extreme temperatures. Label the removed battery as “Used Lithium-Ion Battery – Handle with Care.”
Transportation Requirements
Used Leaf battery packs are classified as hazardous materials under international and national regulations, including UN 3480 (Lithium-ion batteries, not packed with equipment). When transporting, secure the battery in a rigid, non-conductive container that prevents movement and short circuits. The container must be labeled with the proper shipping name, UN number, hazard class (Class 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods), and orientation arrows. All transport documentation (e.g., Dangerous Goods Declaration) must be completed by a certified hazardous materials handler. Use only carriers authorized to transport Class 9 hazardous materials.
Storage and Environmental Compliance
Store removed batteries in a dedicated, dry, well-ventilated area away from combustible materials and direct sunlight. The storage area must be equipped with fire suppression (e.g., Class D fire extinguisher or sand) and spill containment measures. Do not store batteries for extended periods—coordinate timely shipment to a certified recycling or refurbishment facility. Comply with local environmental regulations, including the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the U.S., WEEE Directive in the EU, or equivalent legislation, which mandate proper tracking and disposal of electronic waste.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain detailed records for each battery replacement, including vehicle identification number (VIN), date of replacement, battery serial number, condition at removal, and destination of the battery (e.g., recycling facility name and tracking number). Retain records for a minimum of three years to support compliance audits and warranty claims. Ensure all personnel involved are trained in hazardous material handling, electrical safety, and environmental regulations.
Disposal and Recycling
All end-of-life Leaf batteries must be sent to a facility certified under the Responsible Recycling (R2), e-Stewards, or equivalent standards. These facilities recover valuable materials (e.g., lithium, cobalt, nickel) and ensure environmentally sound processing. Never dispose of lithium-ion batteries in regular landfill or incineration. Confirm that the recycling partner provides a certificate of recycling or destruction for compliance verification.
Conclusion for Sourcing Leaf Battery Replacement:
Sourcing a replacement battery for the Nissan Leaf requires careful consideration of cost, quality, warranty, and installation. While original equipment manufacturer (OEM) batteries offer reliability and compatibility, their high cost has led many owners to explore alternative options such as refurbished, remanufactured, or third-party aftermarket batteries. Advances in battery technology and an increasing number of specialized suppliers have improved accessibility and affordability, making replacements more viable than ever.
Proper research is essential—evaluating supplier reputation, battery health (measured in State of Health %), warranty terms, and professional installation services can significantly impact long-term performance and value. Additionally, environmental considerations and proper recycling of old battery modules should not be overlooked.
Ultimately, with the growing ecosystem of EV support and falling battery prices, sourcing a Leaf battery replacement is increasingly feasible. A well-informed decision can extend the vehicle’s lifespan, maintain driving range, and continue supporting sustainable transportation goals.