The global market for versatile machine tools continues to expand, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing across automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global milling machines market size was valued at USD 15.78 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by increasing automation, advancements in CNC technology, and the need for multifunctional machinery that optimizes floor space and operational efficiency. Among these innovations, lathe milling machine combos—hybrid systems that integrate turning and milling capabilities—have gained significant traction. These machines enable manufacturers to perform multiple operations in a single setup, reducing cycle times and improving accuracy. As industries pursue leaner, more agile production processes, the demand for high-performance combo machines is on the rise. In response, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining technical expertise, robust R&D, and global reach to shape the future of advanced machining. The following list highlights the top nine lathe milling machine combo manufacturers driving this evolution.
Top 9 Lathe Milling Machine Combo Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 TRAUB
Domain Est. 2001
Website: index-group.com
Key Highlights: With its INDEX and TRAUB brands, the INDEX Group is today on of the leading manufacturers of CNC turning machines, automatic lathes & turn-mill centers….
#2 MLD
Domain Est. 2001
Website: baileigh.com
Key Highlights: Features · Runs on 110 volts. · 2 independent 1 hp motors (for the lathe and the mill) reduce wear and tear and give this combination machine a longer life….
#3 EMCO lathes & milling machines manufacturer, CNC training …
Domain Est. 2007
Website: emco-world.com
Key Highlights: EMCO has been a leading manufacturer of lathes and milling machines for over 75 years and offers a wide range of development opportunities….
#4 WMT CNC Industrial Co.
Domain Est. 2018
Website: cncwmt.com
Key Highlights: WMTCNC China offers a wide range of CNC and Conventional machines, main products are CNC milling machines, CNC Lathe, Vertical Machining Center, CNC turning ……
#5 kc
Domain Est. 1997
Website: kingcanada.com
Key Highlights: 16″ X 20″ COMBO LATHE/MILL · Two powerful 3/4 HP 110V motors · Lathe chuck and drill chuck safety guards with limit switch protection and standard tool post ……
#6 EMAG Machine Tools
Domain Est. 1997
Website: emag.com
Key Highlights: EMAG offers cnc metalworking machines from turning to grinding with a machine tool solution for every application….
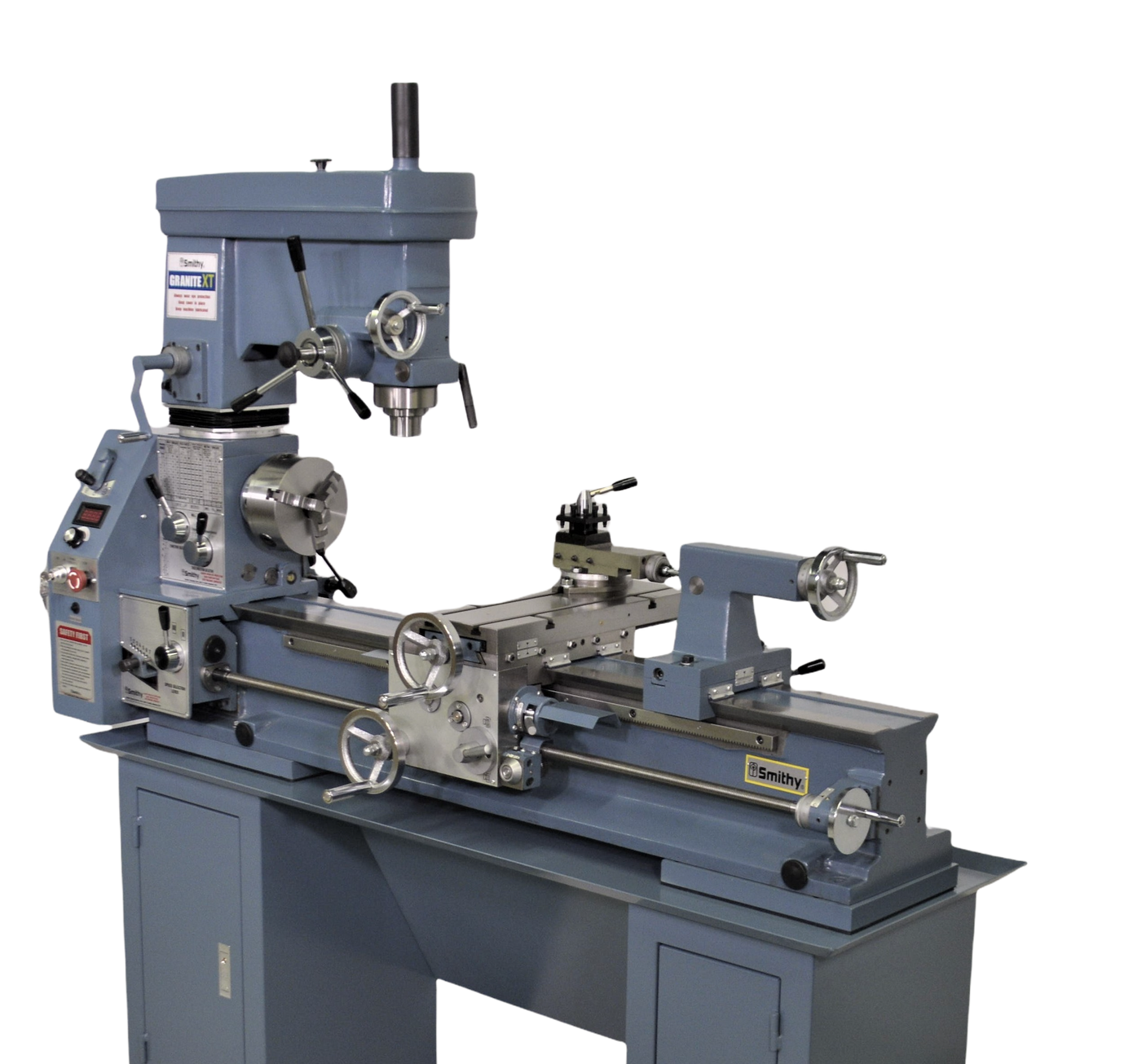
#7 Granite XT 1340 110V Lathe Mill Combo
Domain Est. 1998
Website: smithy.com
Key Highlights: In stock 8-day deliveryHigher precision than other combo tools: Granite components are machined to tighter specs – bearings are higher grade – basic design is higher precision….
#8 UNITED MACHINING
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gfms.com
Key Highlights: The portfolio includes milling, EDM, laser texturing, laser micromachining, and additive manufacturing machines. Our advanced spindles, automation, tooling, and ……
#9 Weiss Machinery Combined Milling Lathe
Domain Est. 2023
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lathe Milling Machine Combo

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Lathe Milling Machine Combo
The global market for lathe milling machine combo systems is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automation, growing demand for multi-functional machine tools, and the expansion of high-precision manufacturing across industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and energy. These hybrid machines—combining the turning capabilities of lathes with the contouring and drilling precision of milling machines—are increasingly favored for their space efficiency, reduced setup times, and enhanced productivity.
One of the key trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the integration of smart manufacturing technologies. Lathe milling combos are expected to feature enhanced IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. This shift toward Industry 4.0 standards allows manufacturers to optimize machine performance, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Additionally, demand for compact and versatile machines is rising, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking cost-effective solutions without sacrificing precision. Machine tool manufacturers are responding by introducing scalable, modular combo systems that can be customized for specific production needs, further boosting adoption across diverse sectors.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is projected to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, particularly in China, India, and South Korea. Government initiatives supporting advanced manufacturing and domestic production are accelerating investments in high-efficiency machine tools. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on upgrading legacy systems with advanced CNC-based lathe milling combos to maintain competitiveness in high-mix, low-volume production environments.
In summary, by 2026, the lathe milling machine combo market will be characterized by increased technological integration, a focus on versatility and precision, and strong regional growth—positioning these hybrid machines as critical assets in modern manufacturing ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lathe Milling Machine Combo (Quality, IP)
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing a lathe milling machine combo is encountering units built with substandard materials and poor craftsmanship. Low-cost machines may use cast iron substitutes or thin steel frames that compromise rigidity, leading to vibration, reduced precision, and shorter machine lifespan. Buyers often overlook structural integrity in favor of upfront cost savings, only to face frequent breakdowns and inaccurate machining results.
Inadequate Spindle Performance
The spindle is critical for both lathe and milling operations. Many combo machines feature underpowered or poorly balanced spindles that cannot maintain consistent RPM under load. This results in poor surface finishes, tool wear, and limitations in material compatibility. Sourcing a machine without verifying spindle specifications (e.g., taper type, RPM range, power) can lead to performance bottlenecks in production environments.
Lack of Precision and Repeatability
Combo machines often sacrifice precision to integrate two functions into one footprint. Poor-quality linear guides, backlash in lead screws, and inadequate calibration can severely impact dimensional accuracy. Users may find that parts produced are inconsistent, especially in repeat production runs, undermining quality control and increasing scrap rates.
Overstated Technical Specifications
Manufacturers—particularly in competitive low-cost markets—may exaggerate key specs such as horsepower, maximum cutting depth, or positional accuracy. Without independent verification or third-party testing, buyers risk investing in machines that fail to deliver on promised performance, leading to production delays and added costs.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many suppliers, especially those operating internationally, offer limited technical support, training, or spare parts access. When a critical component fails, long lead times for replacements can halt operations entirely. This lack of service infrastructure is a major pitfall, particularly for businesses relying on continuous machining.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Design Infringement Risks
Some lathe milling combo machines on the market, especially from lesser-known manufacturers, may infringe on patented designs or replicate branded models without authorization. Sourcing such equipment exposes companies to legal risks, including customs seizures or liability claims. Buyers should ensure suppliers can provide documentation proving legitimate design rights and compliance with IP laws.
Inadequate Safety Features and Regulatory Compliance
Low-cost combo machines may lack essential safety mechanisms such as emergency stops, proper guarding, or CE/UL certification. Using non-compliant equipment not only endangers operators but may also violate workplace safety regulations, resulting in fines or shutdowns during inspections.
Poor Integration of Lathe and Milling Functions
A core challenge with combo machines is the effective integration of both functionalities. Poor design can result in compromised workspace, limited tool access, or manual mode-switching that reduces efficiency. Buyers may discover that the machine excels at neither turning nor milling, making it a jack-of-all-trades but master of none.
Conclusion
Sourcing a lathe milling machine combo requires careful due diligence to avoid pitfalls related to quality, performance, and intellectual property. Prioritizing reputable suppliers, verifying technical claims, and assessing long-term support options are essential steps to ensure a reliable and legally sound investment.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lathe Milling Machine Combo
Overview
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the import, export, transportation, installation, and operation of a Lathe Milling Machine Combo. Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, safety, and efficient operations across international and domestic supply chains.
Classification & HS Code
Lathe Milling Machine Combos are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 8458.11.00 (for turning centers) or 8459.11.00 (for milling centers), depending on the primary function. Confirm the correct classification with your customs broker, as misclassification may result in delays, fines, or incorrect duty assessments.
Import/Export Regulations
- Export Controls: Verify if the machine contains controlled components (e.g., precision controls, CNC systems) subject to export regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or the EU Dual-Use Regulation.
- Import Duties & Taxes: Research applicable import duties, VAT, and customs fees in the destination country. Use a commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading for clearance.
- Certificates of Origin: Provide a Certificate of Origin if required by trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN, RCEP) to qualify for duty reductions.
Packaging & Transportation
- Crating: Machine must be securely crated with shock-absorbing materials and moisture barriers to prevent damage during transit.
- Weight & Dimensions: Confirm transport feasibility—check machine dimensions, gross weight, and center of gravity. Use forklift pockets or lifting points as indicated.
- Carrier Requirements: Coordinate with freight forwarders for appropriate transport mode (air, sea, or land). Ensure compliance with IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations if applicable.
- Insurance: Obtain all-risk cargo insurance covering transit, loading, and unloading.
Installation & Site Preparation
- Foundation Requirements: Install on a level, vibration-free concrete foundation per manufacturer specifications. Allow for expansion/contraction in temperature-variable environments.
- Power Supply: Match local voltage (e.g., 208V, 220V, 380V), phase (single/three-phase), and frequency (50/60 Hz). Use dedicated circuits to avoid voltage drops.
- Ventilation & Clearance: Provide adequate space for operation, maintenance, and chip/coolant management. Maintain minimum clearance as specified in the manual.
Safety & Operational Compliance
- Machinery Directive (EU): Comply with the EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC. Ensure CE marking, risk assessment, and a Declaration of Conformity are provided.
- OSHA (U.S.): Follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subpart O for machine guarding, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and operator training.
- ISO Standards: Adhere to relevant standards such as ISO 12100 (safety of machinery) and ISO 23125 (safety of lathes).
- Emergency Stops & Guards: Verify all safety interlocks, emergency stops, and protective guards are functional before operation.
Environmental & Waste Management
- Coolant & Lubricants: Handle cutting fluids in compliance with EPA (U.S.) or REACH/CLP (EU) regulations. Recycle or dispose of waste fluids through licensed providers.
- Metal Chips & Swarf: Classify chips for proper disposal or recycling. Some metal types (e.g., aluminum, stainless steel) may require segregation.
- Noise Emissions: Monitor noise levels; provide hearing protection if operating above 85 dB(A). Use enclosures or sound-dampening materials if necessary.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain the following records:
– Technical file (risk assessment, design drawings, test reports)
– User manuals and safety instructions (in local language)
– Maintenance logs and calibration records
– Import/export licenses and customs declarations
– Safety training certifications for operators
Maintenance & Regulatory Audits
- Schedule routine maintenance as per manufacturer guidelines to ensure compliance and machine longevity.
- Prepare for regulatory audits by keeping documentation organized and accessible.
- Update compliance status if machine modifications are made.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and strict adherence to compliance standards ensure the safe, legal, and efficient deployment of Lathe Milling Machine Combos. Always consult local authorities, customs experts, and the equipment manufacturer to confirm all requirements are met.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Lathe Milling Machine Combo
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, budget constraints, supplier reliability, and long-term operational needs, sourcing a lathe milling machine combo presents a strategic advantage for enhancing workshop efficiency and versatility. These multifunctional machines offer significant space savings, reduced setup times, and improved workflow integration by combining turning and milling capabilities in a single setup.
The analysis confirms that while initial investment costs may be higher compared to purchasing individual machines, the long-term benefits—such as increased productivity, reduced labor requirements, and minimized material handling—justify the expenditure, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises or job shops with diverse machining needs.
Key considerations such as machine rigidity, precision, control system compatibility, tooling options, and after-sales support must be prioritized during vendor selection. Engaging with reputable suppliers offering comprehensive warranties, training, and service networks ensures sustained machine performance and uptime.
In conclusion, sourcing a lathe milling machine combo is a cost-effective and operationally sound decision that supports manufacturing flexibility, scalability, and competitiveness. With careful planning and due diligence, this integrated solution can significantly elevate production capabilities and contribute to long-term business growth.