The global laser cutting market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cutting machine market was valued at USD 5.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts continued expansion, citing advancements in fiber laser technology and increasing adoption of automation in production processes as key drivers. As industries prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and reduced operational costs, the need for high-performance lasersvetsning—laser welding—solutions has intensified. This growing demand has positioned leading manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, pushing the boundaries of speed, precision, and integration capabilities. The following overview highlights the top nine lasersvetsning manufacturers shaping the future of advanced manufacturing.
Top 9 Lasersvetsning Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
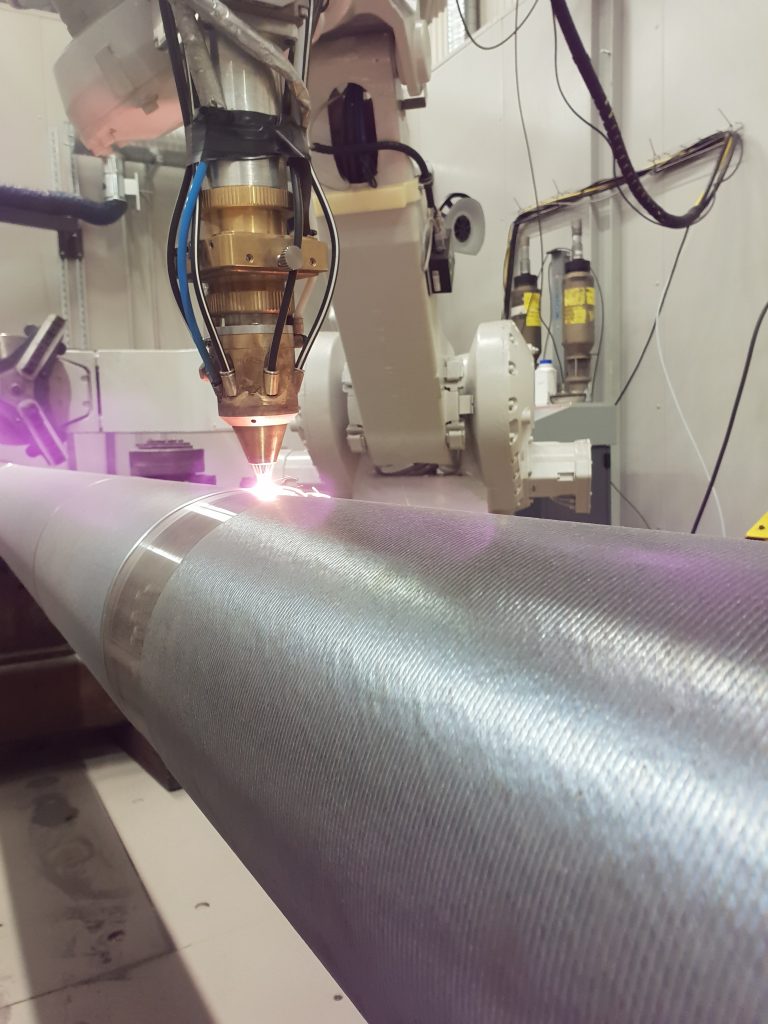
#1 China Laser Welding Manufacturer Leverantör Factory
Website: se.guoshenglaser.com
Key Highlights: Guosheng Laser är en av de mest professionella lasersvetsningstillverkarna och leverantörerna i Kina, specialiserad på att tillhandahålla anpassad service ……
#2 Research for a sustainable future
Website: swerim.se
Key Highlights: The metals research institute Swerim conducts needs-based industrial research and development concerning metals and their route from raw material to finished ……
#3 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
#4 Lasertech
Website: lasertech.se
Key Highlights: Lasertech startade sin verksamhet år 2000 på Bofors Industriområde i Karlskoga med målsättningen att bli ett ledande företag inom avancerad Lasersvetsning….
#5 Lasersvetsning
Website: lpp.se
Key Highlights: Vår lasersvetsning med en effekt på 5 KW möjliggör imponerande svetsning i tjocklekar upp till 6 mm i rostfritt material. Den här teknologin erbjuder ……
#6 HT Laser lasersvetsning sverige skärning bockning
Website: htlaser.fi
Key Highlights: Lasersvetslösningar ger snabbt och kostnadseffektivt svetssömmar av enhetlig kvalitet. Lasersvetsning är lämplig för många material….
#7 Lasersvetsning
Website: l-tech.se
Key Highlights: Vi är experter inom precisionssvetsning med laser, vilket möjliggör arbeten med extrema precision och minimal värmepåverkan. Denna teknik är särskilt ……
#8 Lasersvetsmaskiner och ljusbågssvetscell
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: Lasersvetsanläggningar är idealiska för exakt svetsning av metaller. Med ljusbågssvetscellen får du en enkel start inom automatiserad svetsning….
#9 Lasersvetsning
Website: manufacturingguide.com
Key Highlights: … Lasersvetsning. Lasersvetsning. Manufacturing Guide Sweden AB / Qimtek AB Kungsholmsgatan 28, 112 27 Stockholm [email protected] · +46 (0) 651 30 08 ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lasersvetsning

H2: Market Trends for Laser Welding (Lasersvetsning) in 2026
As we approach 2026, the laser welding (commonly referred to as lasersvetsning in Scandinavian markets) industry is poised for significant transformation driven by technological innovation, increased automation, and growing demand across key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and renewable energy. Below is an analysis of the major market trends shaping the laser welding landscape in 2026, with a focus on technological, economic, and regional developments.
1. Advancements in Laser Technology and Process Efficiency
By 2026, fiber lasers continue to dominate the market due to their superior energy efficiency, reliability, and beam quality. Developments in high-power fiber lasers (10–30 kW range) are enabling deeper penetration welding and faster processing speeds, particularly in heavy industries such as shipbuilding and pipeline manufacturing.
- Ultrafast and Pulsed Lasers: Increased adoption of pulsed and ultra-short pulse lasers is enhancing precision in micro-welding applications, especially in electronics and medical device manufacturing.
- Wavelength Innovation: Emerging visible-light and green-wavelength lasers are improving weld quality on highly reflective materials like copper and aluminum—critical for electric vehicle (EV) battery production.
2. Growth in Electric Vehicle and Battery Manufacturing
The EV boom is a primary driver for laser welding demand. Battery pack assembly, busbar welding, and cell interconnection processes rely heavily on high-precision laser welding.
- In 2026, the global EV market is expected to surpass 40 million units annually, increasing demand for automated laser welding systems in battery gigafactories.
- Laser welding ensures minimal heat distortion and high conductivity in battery connections, making it the preferred joining method for lithium-ion and solid-state battery production.
3. Integration with Smart Manufacturing and Industry 5.0
Laser welding systems are increasingly integrated into smart factories, utilizing real-time monitoring, AI-based quality control, and digital twins.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors and IoT-enabled welding systems allow for real-time diagnostics, reducing downtime and optimizing performance.
- Human-Robot Collaboration: Industry 5.0 principles emphasize flexible production where laser welding robots work alongside human operators, especially in low-volume, high-mix manufacturing environments.
4. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt cleaner, more efficient production methods.
- Laser welding consumes less energy than traditional arc welding and produces fewer emissions.
- By 2026, companies are prioritizing laser systems with lower carbon footprints and recyclable components, aligning with EU Green Deal objectives and similar global initiatives.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
- Europe (Including Scandinavia): Sweden, Germany, and France lead in laser welding adoption, particularly in automotive and industrial equipment sectors. Nordic countries are investing heavily in green manufacturing, favoring laser-based processes.
- Asia-Pacific: China and South Korea remain dominant in volume, driven by electronics and EV production. Japan continues to innovate in precision laser applications.
- North America: U.S. reshoring efforts and government incentives (e.g., Inflation Reduction Act) are boosting domestic EV and clean energy manufacturing, increasing laser welding deployment.
6. Challenges and Barriers
Despite growth, the market faces challenges:
– High Initial Investment: Advanced laser systems require significant capital, limiting access for SMEs.
– Skill Gaps: Shortage of skilled technicians for operating and maintaining laser systems.
– Material Limitations: Welding dissimilar metals and certain composites remains technically challenging.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser welding market is expected to exceed $15 billion globally, with a CAGR of approximately 8–10% since 2023. The convergence of automation, sustainability, and advanced materials is reshaping lasersvetsning into a core enabler of next-generation manufacturing. Companies that invest in adaptive, intelligent laser systems and workforce training will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.
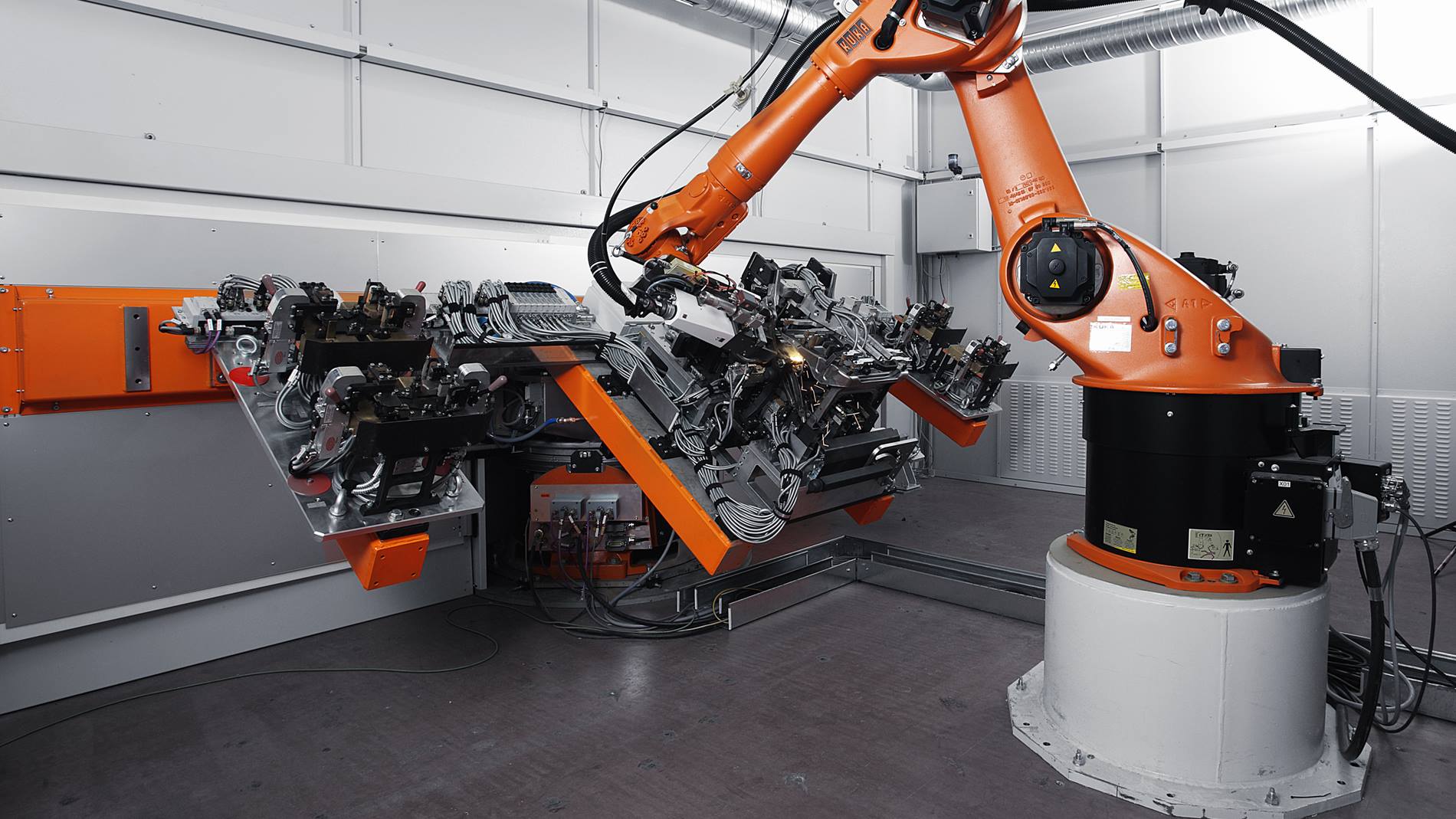
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welding (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser welding services or equipment involves several critical risks, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps in selecting reliable partners and safeguarding business interests.
Quality Inconsistencies and Process Reliability
One of the primary challenges in sourcing laser welding is ensuring consistent quality across production batches. Variations in laser parameters, material preparation, or operator skill can lead to defects such as porosity, cracking, or incomplete fusion. Suppliers may lack proper process validation or quality control systems (e.g., ISO 3834 or IATF 16949), resulting in unreliable weld integrity. Without standardized procedures and proper documentation, reproducibility becomes a major concern, especially in high-precision industries like automotive or medical devices.
Inadequate Intellectual Property Protection
Laser welding often involves proprietary designs, specialized tooling, or unique process parameters that constitute valuable IP. When outsourcing, there’s a risk that suppliers may not have robust confidentiality agreements or IP clauses in place. Unauthorized use, replication, or reverse engineering of components or processes by the supplier—or their subcontractors—can lead to IP theft. Additionally, unclear ownership of process improvements developed during collaboration may result in legal disputes and loss of competitive advantage.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Many suppliers fail to provide comprehensive documentation of welding procedures (e.g., WPS—Welding Procedure Specifications), material certifications, or traceability records. This absence complicates quality audits, regulatory compliance, and root cause analysis in case of failures. Without clear documentation, ensuring compliance with industry standards (such as ASME or EN) becomes difficult, increasing liability risks.
Insufficient Technical Expertise and Support
Not all laser welding providers possess the necessary technical expertise, especially for advanced applications like remote welding, hybrid processes, or automated systems. Choosing a supplier based solely on cost may result in inadequate process development, poor troubleshooting, and limited post-delivery support. This can delay production and increase long-term costs due to rework or downtime.
Hidden Costs and Scalability Issues
Initial quotes may not reflect the full scope of required services, such as fixturing, programming, or process validation. As production scales, suppliers might lack the capacity or equipment to maintain quality and delivery timelines. Failure to assess scalability and total cost of ownership upfront can lead to disruptions and unforeseen expenses.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers—evaluate their certifications, request sample welds, and audit their quality management systems. Implement strong contractual protections, including clear IP ownership clauses and NDAs. Require detailed documentation and ensure alignment on technical requirements and scalability plans before finalizing agreements.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lasersvetsning
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for laser welding (Lasersvetsning) operations, ensuring safe, efficient, and legally compliant processes across manufacturing and industrial environments.
Regulatory Compliance
All laser welding activities must adhere to national and international safety standards. Key regulations include:
– ISO 11553 (Safety of machinery – Laser processing machines)
– IEC 60825 (Safety of laser products)
– EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC
– OSHA standards (29 CFR 1910) for workplace safety (applicable in the U.S.)
Ensure equipment is CE-marked where required and undergoes regular safety audits.
Laser Safety Classification
Lasers used in welding are typically Class 3B or Class 4. These require:
– Controlled access to laser operation areas
– Installation of interlocks and emergency stop mechanisms
– Proper labeling of laser hazards
– Use of protective housing and beam enclosures
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Operators must wear appropriate PPE, including:
– Laser safety goggles with correct optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength
– Flame-resistant clothing
– Face shields and protective gloves
– Hearing protection (if auxiliary equipment generates high noise)
Facility Requirements
The workspace must support safe laser welding operations:
– Ventilation and fume extraction systems to capture hazardous airborne particles
– Non-reflective surfaces to minimize beam reflection risks
– Laser safety curtains or barriers around the work area
– Clearly marked laser operation zones with restricted access
Training & Certification
Only trained and authorized personnel may operate laser welding equipment. Training must include:
– Laser safety principles
– Machine operation and emergency procedures
– Hazard recognition and PPE use
– First response to laser-related incidents
Maintain training records and conduct refresher courses annually.
Equipment Maintenance & Documentation
Regular maintenance is critical for compliance and performance:
– Schedule preventive maintenance per manufacturer guidelines
– Keep logs of inspections, repairs, and safety checks
– Ensure beam alignment and cooling systems are functioning correctly
– Document compliance with safety standards and audit readiness
Transport & Handling of Laser Equipment
When transporting laser welding systems:
– Secure all optical components to prevent misalignment
– Use manufacturer-approved packaging for sensitive parts
– Follow hazardous material guidelines if batteries or coolants are involved
– Comply with ADR regulations for road transport (if applicable in Europe)
Waste & Environmental Compliance
Laser welding produces hazardous byproducts, including:
– Metal fumes and particulates (e.g., chromium, nickel, manganese)
– Ozone and nitrogen oxides from high-intensity beams
Ensure proper filtration, disposal of filters, and air quality monitoring per local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, EEA).
Incident Reporting & Emergency Procedures
Establish protocols for:
– Immediate shutdown in case of beam exposure or fire
– Reporting of near-misses and injuries
– Medical follow-up for laser exposure incidents
– Evacuation and containment procedures for fume leaks or equipment failure
Record Keeping & Audits
Maintain comprehensive records, including:
– Equipment logs and calibration certificates
– Operator training certifications
– Risk assessments and safety inspections
– Incident reports and corrective actions
Regular internal and third-party audits ensure continued compliance.
Conclusion
Adherence to logistics and compliance standards in laser welding operations is essential for worker safety, environmental protection, and legal conformity. Implementing this guide supports operational excellence and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Cutting Services
In conclusion, sourcing laser cutting services requires careful evaluation of several key factors to ensure quality, cost-efficiency, and timely delivery. It is essential to assess potential suppliers based on their technological capabilities, material expertise, precision, and capacity to meet project specifications. Certifications, industry experience, and customer references can provide valuable insight into a supplier’s reliability and performance.
Additionally, considering geographical location, lead times, and communication efficiency helps in building a responsive and resilient supply chain. While cost is an important factor, it should be balanced against value—prioritizing quality, consistency, and technical support over low pricing alone.
Ultimately, establishing long-term partnerships with trusted laser cutting providers enables improved collaboration, faster turnaround, and scalability for future needs. By implementing a structured sourcing strategy, businesses can leverage advanced laser cutting technology to enhance product quality and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.