The global laser welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, automated manufacturing solutions across industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. According to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.09 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.9% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady expansion, citing advancements in fiber laser technology and rising adoption in electric vehicle (EV) production as key growth catalysts. With industrial automation accelerating and manufacturers prioritizing energy efficiency and weld quality, leading laserschweißmaschine (laser welding machine) manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation. In this evolving landscape, seven companies stand out for their technological expertise, global reach, and strong market presence—setting the standard for performance and reliability in laser-based joining solutions.
Top 7 Laserschweißmaschine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ODM & OEM Service
Website: laserdh.com
Key Highlights: DH Technology is a laser equipment enterprise integrating R&D, production and sales, and an authoritative manufacturer of global laser processing solutions….
#2 Laserschweißmaschine Archives
Website: hispeedlaser.com
Key Highlights: Hispeed Laser Technology Ltd. is a laser marking machine manufacturer established to produce and supply laser marking machines and provide laser marking ……
#3 Fiber Laser Welding Machine JQ
Website: jqlaser.com
Key Highlights: It features a powerful 1000 watt laser that can weld metals up to 5mm thick. The machine is also equipped with an automatic fume extractor and a water cooling ……
#4 High Power Laser Cutting Machine
Website: hglaserglobal.com
Key Highlights: HGLASER is a leading provider of laser cutting machine, laser marking mahcine and laser cleaning machine.Email:[email protected]….
#5 Automatische Laserschweißmaschine
Website: vistmac.com
Key Highlights: Automatic laser welding machine with is robot laser welding machine, it is automatic welding any steel products….
#6 Laser welding machines
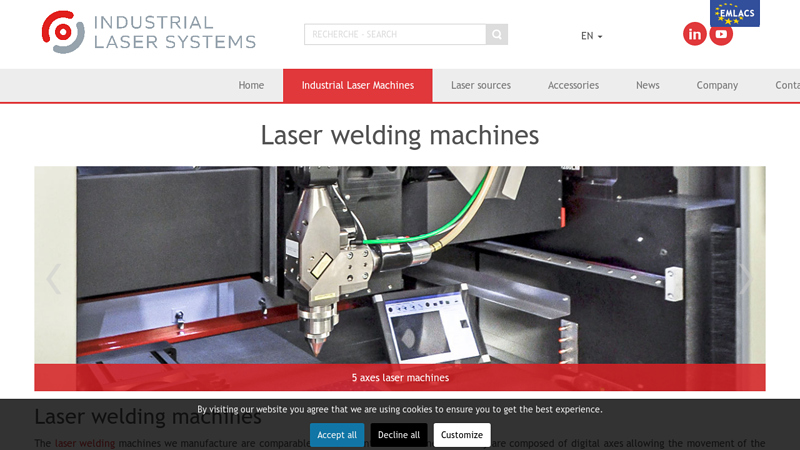
Website: industrial-laser-systems.com
Key Highlights: The laser welding machines we manufacture are comparable to a conventional machine tool. They are composed of digital axes allowing the movement of the part….
#7 Laser Welding Machine
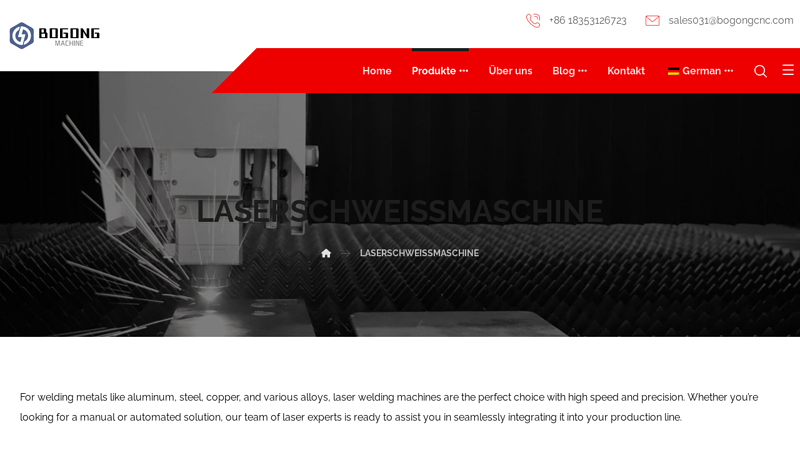
Website: bogonglazer.com
Key Highlights: The BOGONG Handheld laser welding machines with feature of lexible and user-friendly. it can weld stainless steel, mild steel, carbon steel, aluminum alloy, and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laserschweißmaschine

H2: Market Trends for Laser Welding Machines (Laserschweißmaschine) in 2026
By 2026, the global market for laser welding machines (Laserschweißmaschinen) is projected to experience robust growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising automation, and increasing demand across key industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. Several key trends are expected to shape the landscape of this sector:
-
Increased Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The rapid expansion of the electric vehicle industry is a primary driver for laser welding machine demand. Laser welding offers high precision, speed, and reliability—critical for battery pack assembly, power electronics, and lightweight structural components. By 2026, EV production facilities worldwide are expected to integrate more advanced fiber and disk laser systems, enhancing manufacturing efficiency and weld quality. -
Growth of High-Power and Ultrafast Lasers
Technological innovation is pushing the development of higher-power laser systems (exceeding 10 kW) and ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers. These enable deeper penetration, faster processing speeds, and minimal heat-affected zones, making them ideal for complex and high-tolerance applications in aerospace and medical device manufacturing. -
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Laser welding systems are increasingly being equipped with IoT connectivity, AI-driven process monitoring, and real-time quality control features. In 2026, smart laser welding cells will be commonplace in automated production lines, enabling predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and adaptive welding parameters—improving yield and reducing downtime. -
Expansion in Asia-Pacific Markets
China, India, South Korea, and Japan are expected to dominate market growth due to strong government support for advanced manufacturing and rising investments in automation. China, in particular, will remain the largest market, supported by its domestic production of laser components and government initiatives like “Made in China 2025.” -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient laser systems with lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact. Fiber lasers, known for their high wall-plug efficiency, will continue to displace older CO₂ and lamp-pumped systems. Additionally, recyclability of components and reduced consumables are becoming key selling points. -
Rise in Hybrid and Multi-Function Systems
Hybrid laser-arc welding and combination systems that integrate cutting, welding, and cladding functionalities will gain traction. These systems offer versatility and cost savings, appealing to job shops and large-scale manufacturers seeking flexible production solutions. -
Supply Chain Localization and Resilience
Post-pandemic and geopolitical factors are prompting companies to localize laser machine production and component sourcing. In Europe and North America, there will be increased investment in onshore manufacturing capabilities to reduce dependency on global supply chains, particularly for critical high-tech components.
In summary, the Laserschweißmaschine market in 2026 will be characterized by technological sophistication, broader industrial adoption, and a shift toward intelligent, sustainable, and integrated manufacturing solutions. Companies that innovate in automation, software integration, and energy efficiency will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.

Häufige Fallstricke beim Bezug von Laserschweißmaschinen (Qualität, IP)
Beim Beschaffen einer Laserschweißmaschine sind neben technischen und finanziellen Aspekten besonders Qualitätsmerkmale und der Schutz von geistigem Eigentum (IP) kritisch. Hier finden Sie die häufigsten Fallstricke:
Unzureichende Qualitätsprüfung und -dokumentation
Viele Käufer unterschätzen die Bedeutung einer lückenlosen Qualitätsdokumentation. Besonders bei Anbietern aus Niedriglohnländern fehlen oft Zertifizierungen wie ISO 9001, CE-Kennzeichnung oder prüffähige Prüfprotokolle für die Laseroptik und Kühlung. Fehlende Kalibrierdaten oder unklare Herkunft der Komponenten (z. B. Laserquelle von unbekanntem Hersteller) können zu erheblichen Störungen in der Serienproduktion führen.
Mangelnde IP-Sicherheit beim Technologietransfer
Beim Kauf einer maßgeschneiderten Laserschweißlösung besteht die Gefahr, dass sensible Produktionsdaten, CAD-Modelle oder spezifische Schweißparameter an den Maschinenhersteller weitergegeben werden – ohne ausreichende vertragliche Absicherung. Ohne klare IP-Klauseln im Vertrag kann der Hersteller diese Informationen für Wettbewerber nutzen oder die Technologie nachbauen.
Fehlende Absicherung von Software und Steuerungslogik
Die Steuerungssoftware einer Laserschweißmaschine enthält oft firmenspezifische Algorithmen oder Prozessoptimierungen. Wird die Software nicht als urheberrechtlich geschütztes Werk definiert und lizenziert, kann der Hersteller das Recht behalten, diese weiterzuverwenden oder zu modifizieren – mit erheblichen Risiken für die Prozesssicherheit und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit.
Unklare Garantie- und Supportleistungen
Viele Anbieter werben mit langen Garantiezeiten, schließen aber kritische Bauteile wie Laserdioden oder Scanner aus. Zudem fehlt oft ein vertraglich zugesicherter Support im Störungsfall, insbesondere bei internationalen Lieferanten. Sprachbarrieren, lange Reaktionszeiten oder fehlende Ersatzteilverfügbarkeit können Produktionsausfälle verursachen.
Falsche IP-Strategie bei kundenspezifischen Entwicklungen
Wird eine Maschine gemeinsam mit dem Lieferanten entwickelt, ist entscheidend, wer die Rechte an den neuen Entwicklungen hält. Ohne klare vertragliche Regelung bleibt das IP oft beim Hersteller – was spätere Anpassungen, Reparaturen oder den Betrieb an anderen Standorten erschwert oder teuer macht.
Fazit
Um diese Fallstricke zu vermeiden, sollte bereits in der Ausschreibungsphase auf lückenlose Qualitätsdokumente, umfassende IP-Vereinbarungen und klare Supportbedingungen geachtet werden. Eine rechtliche Prüfung der Verträge durch Spezialisten für Technologie- und Urheberrecht ist dringend empfohlen.
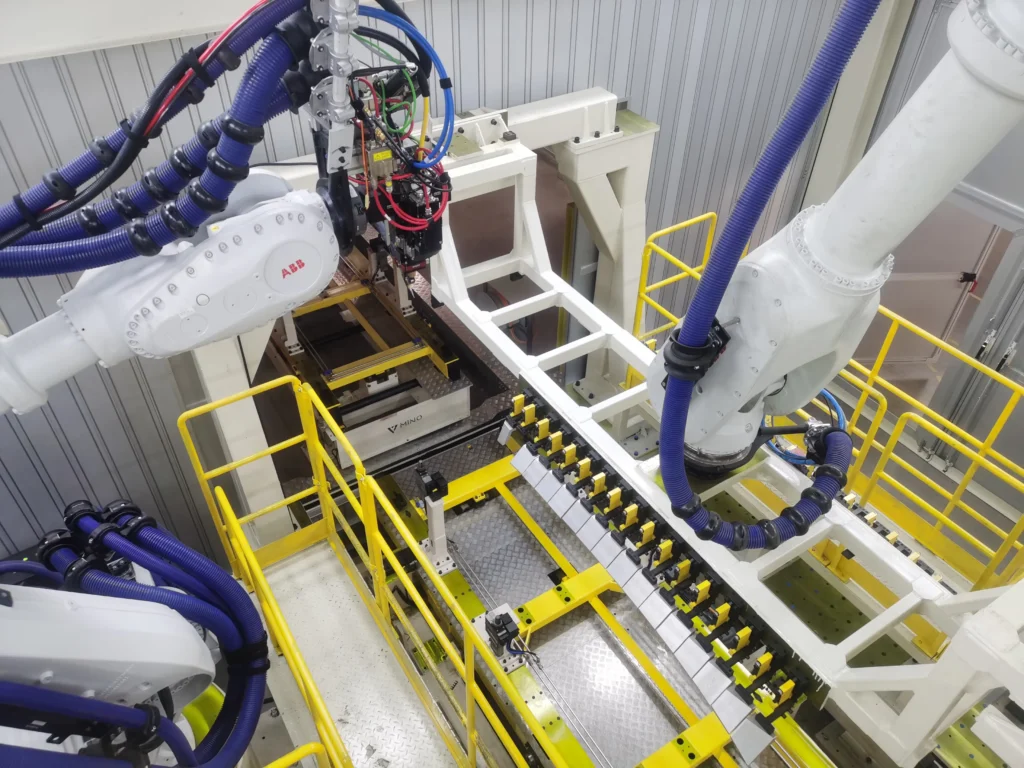
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laserschweißmaschine (Laser Welding Machine)
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the international shipment, import, and operation of a Laserschweißmaschine (laser welding machine). Adherence to these guidelines ensures legal compliance, safety, and smooth transportation.
Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the laser welding machine for customs and regulatory purposes. Utilize the correct Harmonized System (HS) code, typically falling under 8462.21 or 8515.21, depending on automation and specific functionality. Prepare a detailed commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin. Include technical specifications such as laser class, power output (kW), wavelength, and control system type.
Laser Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser welding machines are classified according to IEC 60825-1. Most industrial models are Class 4 lasers, posing significant hazards including skin burns, eye damage, and fire risks. The machine must bear appropriate warning labels and comply with local and international safety standards (e.g., CE marking in the EU, FDA/CDRH regulations in the US). Provide a Declaration of Conformity and ensure the machine includes safety interlocks, emergency stops, and protective enclosures.
Packaging and Handling
Use robust, shock-resistant packaging with adequate internal bracing to secure the machine during transit. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Equipment” warnings. Include desiccants if shipping to humid climates to prevent condensation. Secure optical components and remove or protect the laser head if recommended by the manufacturer.
Transportation Requirements
Ship via freight (sea or air) depending on urgency and cost. For air transport, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations—while most laser systems are not classified as dangerous goods, batteries (if present) or coolant may require special handling. For sea freight, ensure compliance with IMDG Code if applicable. Maintain stable temperature and humidity during transit to protect electronic components.
Import Regulations and Duties
Verify import requirements in the destination country, including potential need for an import license, conformity assessment, or registration with local authorities (e.g., BfS in Germany for radiation-emitting devices). Calculate and prepare for applicable customs duties, VAT, and import taxes based on the HS code and declared value. Engage a licensed customs broker if necessary.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Upon arrival, installation must be performed by qualified personnel in accordance with local regulations. Ensure proper grounding, ventilation (for fumes and cooling), and integration with facility safety systems. Conduct a site safety assessment, including beam path containment and interlock verification. Provide operator training on safe use, emergency procedures, and maintenance.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Dispose of replaced components (e.g., laser diodes, filters, coolant) according to local environmental regulations. Many parts may be classified as electronic waste (WEEE) or hazardous waste. Maintain records of disposal for compliance audits.
Record Keeping and Audit Preparedness
Retain all compliance documentation—including test reports, conformity certificates, shipping records, and training logs—for a minimum of five years. These may be required during regulatory inspections or customs audits.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Welding Machine (Laser-Schweißmaschine):
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, production needs, supplier capabilities, and cost considerations, sourcing a laser welding machine represents a strategic investment in precision, efficiency, and long-term manufacturing competitiveness. The selection process has highlighted key factors such as laser type (e.g., fiber, CO₂, or disk), power output, automation compatibility, beam quality, and service support, all of which must align with specific application demands—ranging from automotive component fabrication to high-precision medical device manufacturing.
Sourcing from reputable suppliers with proven expertise in laser technology ensures reliability, regulatory compliance, and access to technical support and maintenance. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—beyond initial procurement to include energy consumption, consumables, training, and downtime—is crucial for maximizing ROI.
In conclusion, acquiring the right laser-Schweißmaschine enhances manufacturing capabilities, improves weld quality and consistency, reduces material waste, and supports the shift toward advanced, automated production systems. A well-informed sourcing decision positions the organization for greater agility, innovation, and quality leadership in a competitive industrial landscape.