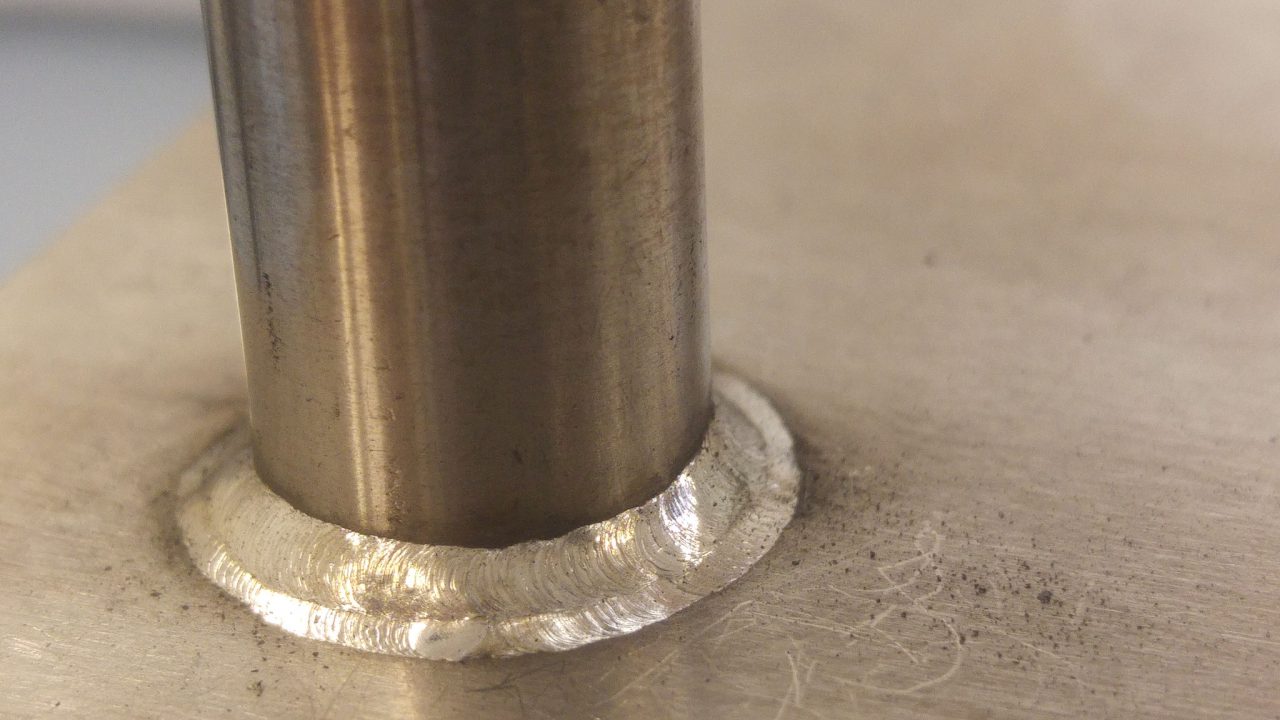
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for high-precision joining technologies in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 1.57 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by the increasing adoption of laser welding for stainless steel—valued for its corrosion resistance, strength, and aesthetic finish—across high-end manufacturing sectors. As automation and Industry 4.0 continue to reshape production floors, manufacturers specializing in laser welding of stainless steel are at the forefront of innovation, delivering solutions that ensure superior weld quality, speed, and repeatability. In this evolving landscape, identifying leading suppliers with proven technological capabilities and global reach is critical for OEMs and contract manufacturers seeking reliable, high-performance welding solutions. Based on market presence, technological expertise, and application impact, here are the top 9 laser welding for stainless steel manufacturers shaping the future of advanced manufacturing.
Top 9 Laserschweißen Edelstahl Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LASER WELDING
Website: edelstahl-mechanik.de
Key Highlights: Edelstahl-Mechanik GmbH ist der Spezialist für Laserschweißen, Laserbearbeitung und Laserschneiden 2D und 3D. Das Unternehmen bietet Dienstleistungen wie ……
#2 Laser Schweißen
Website: ohms-edelstahltechnik.de
Key Highlights: Laser Schweißen für Lügde, Hameln & Bad Pyrmont. Hochpräzise Schweißnähte für Edelstahlbauteile – effizient, verzugsfrei & wirtschaftlich….
#3 LASER & more
Website: laser-more.com
Key Highlights: LASER & more ist seit über 20 Jahren Hersteller hochwertiger Metallkomponenten aus Edelstahl und Aluminium. Wir sind Profis im Laserschweißen, Laserschneiden ……
#4 Laserschweißen • Cloos Group
Website: cloos-group.com
Key Highlights: CLOOS Laserschweißen steht für höchste Präzision und Effizienz – tiefe Nähte, minimale Wärmebelastung und beste Qualität bei Edelstahl, Aluminium und Titan….
#5 Laserschweißen von Edelstahl Baugruppen
Website: lst-brandmayr.at
Key Highlights: Wir schweißen Edelstahl Baugruppen mit einer Blechstärke ab 0,3mm verzugsfrei. Mit unseren modernen halbautomatisierten Anlagen ist es uns möglich, ……
#6 Laserschweissen
Website: montanstahl.com
Key Highlights: Montanstahl ist weltweit Marktführer für das Schweissen von Baustahl- und rostfreien Edelstahlprofilen mittels der Laserschweisstechnik….
#7 MIGAL.CO
Website: migal.co
Key Highlights: Entdecken Sie branchenführende Aluminiumschweißzusätze, Kupferschweißmaterialien, hochwertige Edelstahlschweißprodukte und Nickelschweißlösungen bei MIGAL.CO….
#8 Laser Schweißteile, Laserschweißen, Edelstahl/Kupfer/Metall …
Website: de.hsjfabrication.com
Key Highlights: Hier haben Sie Ihre One-Stop-Lösung zum Laserschweißen von Edelstahl, Kupfer, Aluminium, Eisen, etc. HSJ bietet Ihnen professionellen Laser-Schweißdienst….
#9 Laserschweißen
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: Mit TRUMPF Lasern lassen sich sehr schnell feine Schweißpunkte von einem Millimeter Durchmesser oder auch meterlange, tiefgeschweißte Nähte fertigen….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laserschweißen Edelstahl

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding of Stainless Steel
The global market for laser welding of stainless steel is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing industrial automation, and increasing demand across key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and renewable energy. This analysis outlines the major trends shaping the laser welding of stainless steel landscape in 2026.
-
Increased Adoption of High-Power Fiber Lasers
By 2026, fiber laser technology is expected to dominate the stainless steel laser welding market due to its superior beam quality, energy efficiency, and reliability. High-power fiber lasers (ranging from 6 kW to 20 kW) enable faster welding speeds and deeper penetration, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. Their compatibility with robotic systems further enhances precision and repeatability in welding stainless steel components. -
Rise of Hybrid and Smart Laser Welding Systems
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and real-time monitoring systems into laser welding equipment will become standard by 2026. These smart systems optimize weld parameters dynamically, reducing defects and improving consistency in stainless steel joints. Hybrid welding techniques—combining laser with arc processes—are also gaining traction for thicker stainless steel sections, offering improved gap bridging and reduced porosity. -
Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Battery Manufacturing
The surging demand for electric vehicles is a major driver for stainless steel laser welding. Components such as battery enclosures, cooling plates, and structural parts require high-precision, hermetic welds, which laser technology delivers efficiently. By 2026, the EV sector is expected to account for a substantial share of laser welding applications, particularly in regions like Europe, North America, and China. -
Expansion in Medical and Sanitary Equipment Industries
Stainless steel’s corrosion resistance and hygienic properties make it indispensable in medical devices and food processing equipment. Laser welding ensures clean, spatter-free, and contamination-free joints, meeting stringent regulatory standards. The trend toward miniaturization and complex geometries in medical instruments will further boost demand for precision laser welding solutions. -
Regional Market Shifts and Localization Strategies
Asia-Pacific, especially China and India, will lead market growth due to expanding manufacturing infrastructure and government support for advanced manufacturing. However, reshoring initiatives in North America and Europe—aimed at reducing supply chain dependencies—are also increasing investments in domestic laser welding capabilities for stainless steel. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
By 2026, environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will push manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient laser systems with lower carbon footprints. Advances in laser source efficiency, coupled with closed-loop cooling and recyclable shielding gases, will support greener production processes in stainless steel fabrication. -
Material Innovation and Compatibility Challenges
While austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 304, 316L) remain the primary materials for laser welding, the use of duplex and lean duplex grades is expected to grow, particularly in offshore and chemical processing applications. These materials present challenges in terms of thermal sensitivity and cracking susceptibility, prompting the development of tailored laser parameters and filler wire technologies.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser welding of stainless steel will be defined by technological innovation, sector-specific demand, and a shift toward intelligent, sustainable manufacturing. Companies investing in advanced laser systems, digital integration, and application-specific solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving trends.
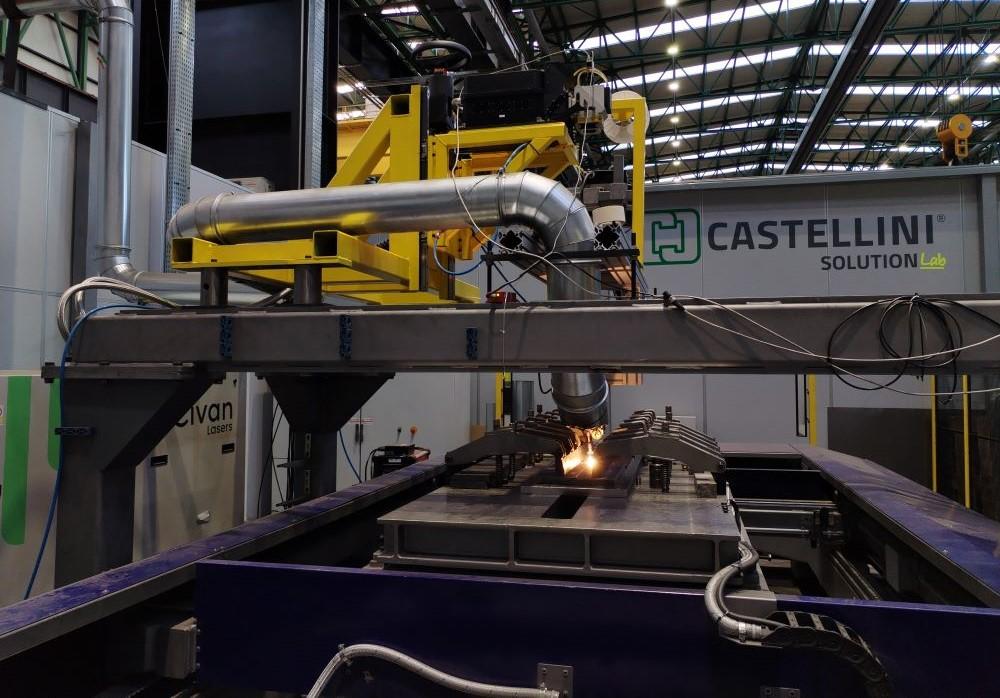

Häufige Fehlerquellen beim Beschaffen von Laserschweißen für Edelstahl (Qualität, IP)
Beim Beschaffen von Laserschweißdienstleistungen für Edelstahl können Unternehmen schnell auf vermeidbare Probleme stoßen, die sich negativ auf die Qualität des Endprodukts und den geistigen Eigentumsschutz (IP) auswirken. Hier sind die häufigsten Fallstrübe:
Unzureichende Qualifikation des Dienstleisters
Ein Hauptfehler liegt in der Auswahl eines Laserschweißdienstleisters ohne ausreichende Fachkompetenz im Umgang mit Edelstahl. Nicht jeder Anbieter verfügt über die nötige Erfahrung, um die besonderen Anforderungen von rostfreiem Stahl – wie thermische Empfindlichkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Nahtqualität – korrekt zu berücksichtigen. Fehlende Zertifizierungen (z. B. nach DIN EN ISO 3834 oder DIN EN 15085) oder Referenzen in der Branche können auf mangelhafte Prozesskontrolle hinweisen.
Fehlende Material- und Prozessdokumentation
Viele Auftraggeber unterschätzen die Bedeutung vollständiger Dokumentation. Ohne klare Spezifikation von Werkstoffgüte (z. B. 1.4301, 1.4404), Schweißparametern, Schutzgasart (häufig Argon oder Mischgase) und Nachbehandlung (z. B. Passivierung) ist eine reproduzierbare Qualität nicht gewährleistet. Zudem fehlt bei fehlender Dokumentation die Grundlage für Audits oder Haftungsfälle.
Mangelnder Schutz geistigen Eigentums (IP)
Ein kritischer Punkt ist der unzureichende Schutz vertraulicher Informationen. Ohne verbindliche Vertraulichkeitsvereinbarungen (NDAs) oder IP-Klauseln im Vertrag riskieren Unternehmen, dass Konstruktionsdaten, Schweißverfahren oder Produktinnovationen an Dritte weitergegeben werden. Dies gilt insbesondere, wenn CAD-Daten oder Fertigungszeichnungen an den Dienstleister übermittelt werden.
Fehlende Prüfung der Schweißnahtqualität
Auftraggeber vertrauen oft blind auf die Aussagen des Dienstleisters, ohne eigene oder neutrale Prüfungen vorzusehen. Visuelle Inspektion, Röntgenprüfung, Dichtigkeitsprüfungen oder metallografische Untersuchungen sollten je nach Anwendung vertraglich festgelegt werden. Fehlende Prüfzertifikate (z. B. nach DIN EN 10204) erschweren die Rückverfolgbarkeit und Haftung.
Unklare Verantwortlichkeiten bei Nacharbeit oder Reklamation
Viele Beschaffungsverträge enthalten keine klaren Regelungen zu Mängelrügefristen, Nachbesserungsansprüchen oder Kostenübernahme bei Ausschuss. Dies führt zu Konflikten, insbesondere wenn Schweißfehler wie Risse, Porosität oder Verzug erst im späteren Fertigungsprozess auffallen.
Fazit
Um Qualitätsmängel und IP-Risiken beim Beschaffen von Laserschweißdienstleistungen für Edelstahl zu vermeiden, ist eine sorgfältige Auswahl des Partners, detaillierte technische Spezifikationen, vertraglicher IP-Schutz und definierte Prüfprozesse unerlässlich. Proaktive Due Diligence spart langfristig Kosten und schützt Innovationen.
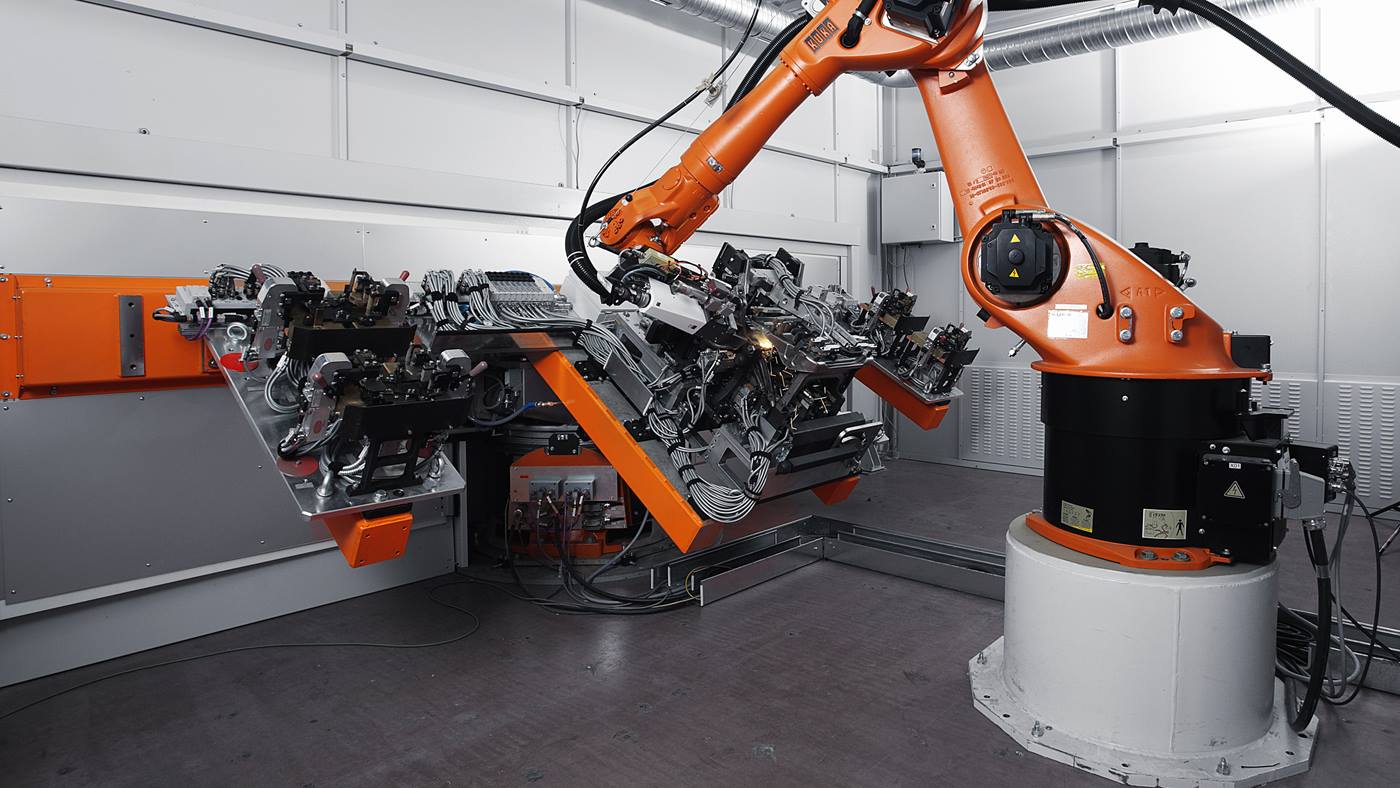
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding of Stainless Steel
Laser welding of stainless steel is a high-precision manufacturing process widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and food processing due to its accuracy, speed, and minimal heat distortion. Ensuring compliance with health, safety, environmental, and quality standards is essential throughout the logistics and welding process. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, compliant, and efficient operations.
1. Material Handling & Storage (Logistics)
- Stainless Steel Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, clean environment to prevent corrosion or surface contamination.
- Use non-sulfur-containing packaging materials to avoid sulfide-induced corrosion.
-
Separate from carbon steel to prevent cross-contamination (e.g., iron particle transfer).
-
Pre-Weld Cleaning
- Remove oils, greases, oxides, and particulates using appropriate solvents or mechanical methods.
-
Ensure surfaces are free of moisture and residues that could cause porosity or defects.
-
Transportation
- Use protective coverings (e.g., plastic film, anti-rust paper) during transit.
- Handle with clean, non-abrasive tools to avoid surface damage.
2. Laser Welding Process Requirements
- Equipment Calibration & Maintenance
- Regularly calibrate laser systems according to manufacturer specifications.
-
Maintain beam alignment, optics cleanliness, and cooling systems.
-
Welding Parameters
- Optimize laser power, travel speed, focus position, and shielding gas flow.
-
Use inert shielding gases (e.g., argon or helium) to prevent oxidation and ensure weld integrity.
-
Joint Preparation
- Ensure precise fit-up and alignment (tolerances typically < 0.1 mm).
- Use clamping fixtures to minimize distortion during welding.
3. Health, Safety & Environmental (HSE) Compliance
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825 & ANSI Z136.1)
- Classify laser systems and implement appropriate controls (e.g., interlocks, warning signs).
- Use protective enclosures and laser safety windows.
-
Provide certified laser safety training for operators.
-
Eye & Skin Protection
- Wear laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength (e.g., 1064 nm for Nd:YAG/fiber lasers).
-
Use full-coverage protective clothing to prevent UV/IR exposure.
-
Fume & Particulate Extraction
- Install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems to capture metal fumes (e.g., chromium, nickel).
- Monitor air quality and conduct periodic exposure assessments (OSHA/REACH guidelines).
-
Use HEPA-filtered fume extractors compliant with EN 15088 or equivalent.
-
Noise & Radiation
- Control noise from assist gases and cooling systems (≤85 dB(A)).
- Shield against reflected laser beams and UV emissions.
4. Quality & Regulatory Compliance
- Welding Standards
- Follow ISO 13919-1 (quality levels for electron and laser beam welding).
-
Comply with ISO 3834 (welding quality requirements) and ISO 15614-11 (laser welding procedure qualification).
-
Inspection & Testing
- Perform visual inspection, dye penetrant testing (PT), radiographic testing (RT), or ultrasonic testing (UT) as required.
-
Use microscopy or cross-section analysis for critical applications.
-
Documentation & Traceability
- Maintain logs of welding parameters, operator certifications, and material certifications (e.g., EN 10204 3.1).
- Implement a traceability system for batch/lot tracking.
5. Environmental & Waste Compliance
- Waste Management
- Collect and dispose of swarf, filters, and contaminated consumables as hazardous waste if applicable.
-
Follow local regulations (e.g., EPA, EU Waste Framework Directive).
-
Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
- Optimize laser usage to reduce energy consumption.
- Consider closed-loop cooling systems and recyclable materials.
6. Personnel Training & Certification
- Ensure welders and operators are certified per applicable standards (e.g., EN 1418 or ISO 14732).
- Provide regular training on laser safety, emergency procedures, and PPE use.
Conclusion
Compliant laser welding of stainless steel requires integrated logistics, strict adherence to safety protocols, and continuous quality control. By following international standards and best practices, manufacturers can ensure safe operations, product integrity, and regulatory conformity across global markets.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich bei der Beschaffung von Laser-Schweißanlagen für Edelstahl feststellen, dass eine sorgfältige Auswahl des Anbieters und der Technologie entscheidend ist. Laser-Schweißen bietet im Vergleich zu konventionellen Schweißverfahren zahlreiche Vorteile wie hohe Präzision, geringe Wärmeeinflusszone, exzellente Nahtqualität und hohe Produktivität – besonders wertvoll beim Schweißen von Edelstahl, wo Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Oberflächenqualität im Vordergrund stehen.
Beim Sourcing sind neben den technischen Spezifikationen (Laserleistung, Wellenlänge, Fokussierung, Integration in bestehende Fertigungslinien) auch Aspekte wie Service, Schulungsangebote, Wartung und Ersatzteilverfügbarkeit zu berücksichtigen. Internationale und nationale Anbieter bieten unterschiedliche Preis- und Leistungsmodelle, wobei eine ganzheitliche Kosten-Nutzen-Analyse (TCO) hilfreich ist.
Ein erfolgreicher Sourcing-Prozess erfordert daher eine klare Definition der Anforderungen, intensive Marktanalyse sowie die Bewertung mehrerer Angebote hinsichtlich Qualität, Zuverlässigkeit und langfristiger Wirtschaftlichkeit. Bei korrekter Auswahl trägt eine Laser-Schweißlösung für Edelstahl wesentlich zur Steigerung der Fertigungsqualität, Effizienz und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit bei.