The global laserschneiden (laser cutting) market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for high-precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cutting market size was valued at USD 8.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is underpinned by technological advancements that enhance cutting accuracy, speed, and repeatability—particularly improvements in tolerances, which are critical for complex engineering applications. As manufacturers increasingly prioritize micron-level precision, leading players in the laserschneiden space are advancing their systems to achieve tighter tolerances, often within ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm ranges. Based on performance data, technological innovation, and market presence, the following three manufacturers stand out for delivering superior laser cutting tolerances in the industry.
Top 3 Laserschneiden Toleranzen Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tolerances and accuracy in laser cutting
Website: teprosa.de
Key Highlights: All cutting parts are manufactured according to the standard DIN ISO 2768-1 m (general tolerances) for the geometric dimension, unless otherwise agreed with ……
#2 Laser cutting tolerances & accuracy
Website: retero.ch
Key Highlights: Laser cutting tolerances and accuracy at a glance: with practical examples, comparison and tips for feasibility analysis….
#3 Tolerances and Manufacturing Capabilities
Website: laserboost.com
Key Highlights: Bei LaserBoost verwenden wir das Schneiden mit Stickstoff, das es uns ermöglicht, sehr präzise und saubere Schnitte durchzuführen. Unten zeigen wir die ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laserschneiden Toleranzen
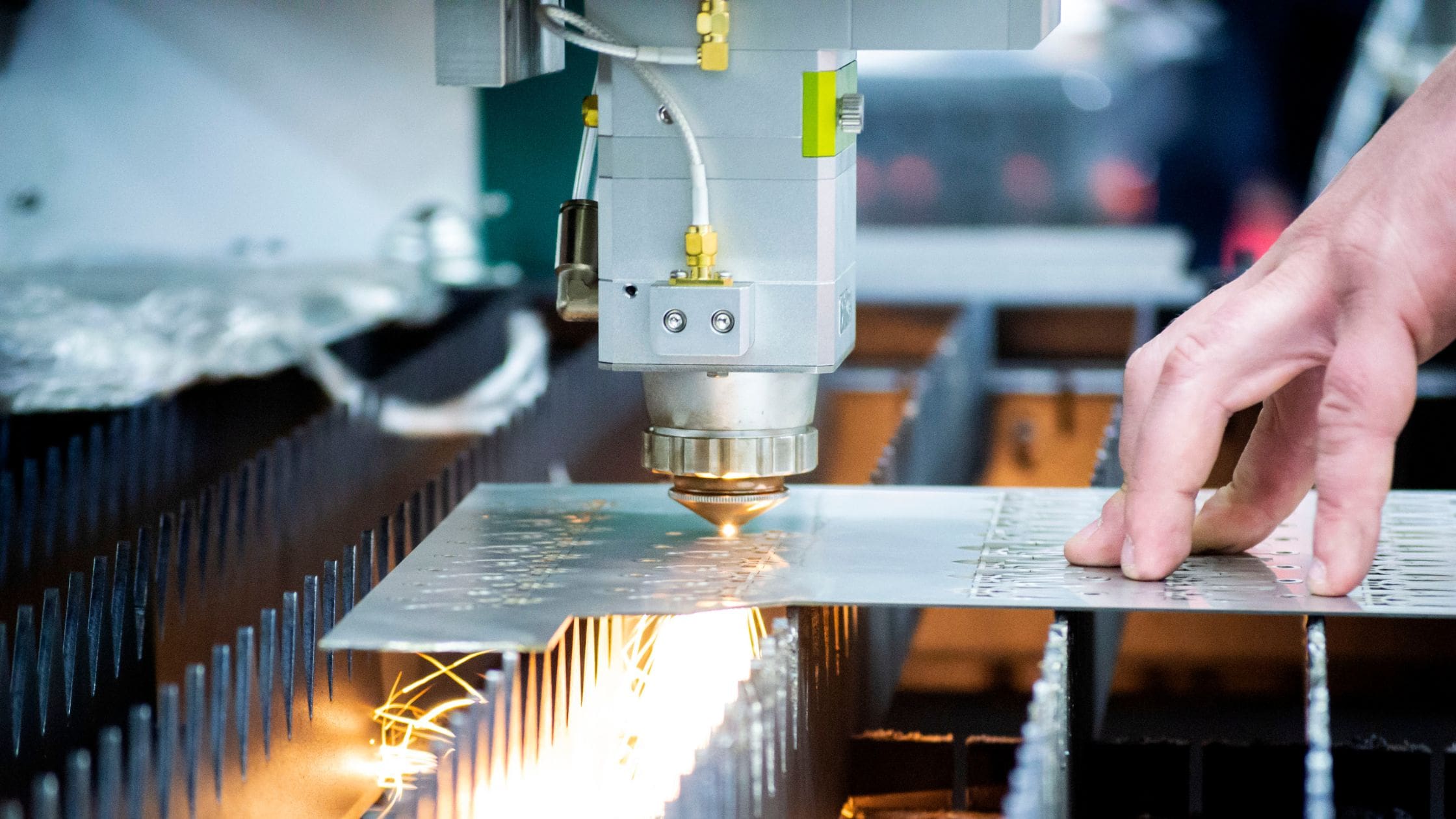

H2: Market Trends in Laser Cutting Tolerances (2026 Outlook)
As the manufacturing sector evolves with increasing demands for precision, efficiency, and customization, laser cutting technologies continue to play a pivotal role—particularly in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. By 2026, the market for laser cutting tolerances is expected to reflect significant advancements driven by technological innovation, material diversification, and the integration of Industry 4.0 principles.
-
Tighter Tolerances Through Enhanced Beam Control
A key trend in 2026 is the widespread adoption of ultra-high-precision laser systems capable of achieving tolerances within ±0.025 mm or better. Advancements in fiber and ultrafast (pico- and femtosecond) lasers enable superior beam focus and reduced heat-affected zones, allowing for micron-level accuracy. These improvements are especially critical in high-tech sectors where part consistency and edge quality are paramount. -
Rise of Adaptive Feedback Systems
Real-time monitoring and closed-loop control systems are becoming standard in laser cutting machines. Integrated sensors and AI-driven analytics adjust cutting parameters dynamically to maintain tight tolerances despite material inconsistencies or environmental fluctuations. By 2026, over 60% of industrial laser systems in developed markets are expected to incorporate such adaptive technologies, minimizing scrap rates and improving yield. -
Material-Specific Tolerance Optimization
With growing use of advanced materials—including high-strength alloys, composites, and thin-film substrates—manufacturers are tailoring laser parameters to maintain tolerance integrity across diverse substrates. In 2026, software platforms will offer intelligent material databases that automatically suggest optimal cutting strategies based on desired tolerances and material properties. -
Standardization and Certification Pressures
Global supply chains are demanding uniformity in laser cutting tolerances, prompting the development of more rigorous standards (e.g., ISO 9013:2023 updates). By 2026, compliance with tolerance certification will become a competitive differentiator, especially in regulated industries like aerospace and medical manufacturing. -
Growth in Micro-Laser Cutting Applications
The miniaturization of components in electronics and medical devices is driving demand for micro-laser cutting with sub-10-micron tolerances. This niche segment is projected to grow at over 12% CAGR through 2026, supported by innovations in beam delivery and motion control systems. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Europe and North America lead in adopting high-tolerance laser systems due to stringent quality requirements and strong R&D investments. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—is rapidly expanding its precision manufacturing capacity, with local suppliers increasingly offering high-accuracy laser solutions tailored to regional needs.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser cutting tolerances will be defined by a convergence of precision engineering, digitalization, and material innovation. As industries demand ever-tighter tolerances, laser cutting technology will continue to evolve, positioning itself as an indispensable tool in advanced manufacturing.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laserschneiden Toleranzen (Quality, IP)
When outsourcing laser cutting (Laserschneiden) services, especially with tight tolerance requirements, several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can undermine project success. Being aware of these risks helps ensure reliable results and protects your business interests.
Inadequate Understanding of Tolerance Capabilities
Suppliers may overpromise or lack the machinery and expertise to consistently achieve specified tolerances. Variations in material thickness, laser calibration, and operator skill can lead to dimensional inaccuracies. Always verify the supplier’s technical specifications, request sample parts, and review their quality control processes before committing.
Poor Quality Control and Documentation
Many laser cutting providers lack rigorous quality assurance systems. Missing or inconsistent documentation—such as inspection reports, material certifications, or process validation—can compromise traceability and compliance, particularly in regulated industries like automotive or medical devices. Ensure the supplier adheres to recognized standards (e.g., ISO 9001) and provides full documentation.
Inconsistent Material and Surface Quality
Tolerance precision is affected not only by cutting accuracy but also by material inconsistencies and post-processing. Poor edge quality, burrs, or heat-affected zones can require additional finishing, increasing costs and lead times. Clarify surface finish expectations upfront and confirm the supplier performs edge quality checks.
Lack of IP Protection Agreements
Sharing technical drawings and CAD files with external vendors poses significant intellectual property risks. Without a clear non-disclosure agreement (NDA) or IP clause in the contract, your designs could be replicated or shared with competitors. Always establish legal safeguards before disclosing sensitive information.
Unsecured Data Transfer and Digital Security
Transmitting design files over unsecured channels increases the risk of data leakage. Ensure the supplier uses encrypted file transfers and secure data handling practices. Also, confirm they do not retain copies of your designs after project completion unless explicitly authorized.
Overlooking Post-Processing Requirements
Tight tolerances often require secondary operations like deburring, grinding, or coating. If these steps are not coordinated with the laser cutting phase, cumulative errors can occur. Discuss the full production workflow with the supplier to ensure alignment on dimensional targets across all stages.
Failure to Audit Supplier Processes
Relying solely on supplier claims without on-site audits or third-party certifications can lead to quality surprises. Conduct regular audits or require certifications (e.g., machine calibration logs, staff training records) to verify ongoing compliance with your tolerance and IP requirements.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, companies can secure high-precision laser cutting results while protecting their proprietary designs and maintaining product integrity.

Laserschneiden Toleranzen: Logistik- und Compliance-Leitfaden
Beim Laserschneiden von Metallen und anderen Materialien sind präzise Maßhaltigkeiten entscheidend für die Funktion und Montage von Bauteilen. Um sicherzustellen, dass Produkte den Qualitätsanforderungen entsprechen und rechtliche sowie logistische Vorgaben eingehalten werden, ist ein strukturierter Ansatz in Logistik und Compliance unerlässlich.
Toleranzspezifikationen und Normen
Die Einhaltung von Toleranzen beim Laserschneiden basiert auf internationalen und branchenspezifischen Normen. Wichtige Referenzdokumente sind:
- ISO 2768: Allgemeintoleranzen für Längen- und Winkelmaße ohne individuelle Toleranzangabe.
- DIN 2310-4: Richtlinie für das Schneiden von Metallen – Toleranzen beim Laserschneiden.
- ISO 9013: Thermisches Schneiden – Klassifizierung von Schnittqualität und Maßhaltigkeit.
Diese Normen definieren Toleranzklassen (z. B. fein, mittel, grob) in Abhängigkeit von Materialdicke, Werkstoffart und Schneidverfahren. Beispiel: Bei einer Materialstärke von 3 mm kann die Längentoleranz zwischen ±0,1 mm (fein) und ±0,3 mm (grober Schnitt) liegen.
Dokumentation und Qualitätsmanagement
Compliance erfordert lückenlose Dokumentation:
- Technische Zeichnungen müssen alle relevanten Toleranzen gemäß geltenden Normen klar definieren.
- Prüfberichte (z. B. mit Koordinatenmessgerät CMM) sind für serienmäßige Teile obligatorisch.
- Das Qualitätsmanagementsystem (gemäß ISO 9001) muss Prozesse zur Überwachung und Nachverfolgung von Toleranzeinhaltung beinhalten.
Logistische Prozesse sollten sicherstellen, dass ausschließlich geprüfte und dokumentierte Teile weiterverarbeitet oder versandt werden.
Material- und Prozesskompatibilität
Nicht alle Materialien und Dicken erlauben die gleiche Toleranzgenauigkeit. Logistische Planung muss berücksichtigen:
- Materialtyp (Stahl, Edelstahl, Aluminium, Kunststoff)
- Materialdicke (dünnblech vs. dickwandig)
- Schneidgas und Laserleistung
Ein Wechsel des Materials oder der Dicke erfordert ggf. eine Neuanpassung der Maschinenparameter und eine erneute Prozessfreigabe gemäß Produktionskontrollplan (PPAP).
Transport und Handhabung
Tolerante Bauteile können durch unsachgemäße Handhabung oder Transport beschädigt werden:
- Mechanische Verformung durch unzureichende Lagerung oder Stapelung
- Oberflächenbeschädigungen durch Reibung oder Schlag
Daher sind folgende logistische Maßnahmen erforderlich:
- Einsatz kundenspezifischer Verpackungen (z. B. Schutzfolien, Trennelemente, stabile Umverpackungen)
- Klar gekennzeichnete Lagerzonen für präzise Teile
- Schulung des Personals in sachgemäßer Handhabung
Lieferantenaudit und Zuliefererkette
Bei Fremdbezug von Laserschnittteilen ist die Compliance der Zulieferer zu prüfen:
- Auditierung auf Basis von VDA 6.3 oder IATF 16949 (für Automotive)
- Verlangen von Prozess- und Prüfdokumentation
- Regelmäßige Stichprobenprüfung eingehender Ware
Dokumentierte Lieferantenqualifizierung ist zentraler Bestandteil der Compliance.
Änderungsmanagement
Änderungen an Zeichnungen, Materialien oder Prozessen müssen systematisch verwaltet werden:
- Einsatz eines Engineering Change Management (ECM)-Systems
- Freigabe durch befugte Stellen (Konstruktion, Qualität, Fertigung)
- Rückverfolgbarkeit aller Änderungen (Lot-/Chargennummerierung)
Dies verhindert die Auslieferung nicht konformer Teile und sichert die Rückverfolgbarkeit im Sinne der Produktsicherheitsverordnung (GPSG) oder REACH.
Fazit
Die Einhaltung von Laserschneid-Toleranzen erfordert nicht nur technische Präzision, sondern ein integriertes System aus Normkonformität, Dokumentation, Qualitätsmanagement und sorgfältiger Logistik. Nur so lassen sich rechtliche Risiken minimieren, Kundenanforderungen erfüllen und langfristig wettbewerbsfähige Prozesse sicherstellen.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich für die Beschaffung von Laserschneidtoleranzen folgendes festhalten:
Die Qualität und Genauigkeit des Laserschneidprozesses hängt von einer Vielzahl von Faktoren ab, darunter Materialart, Materialdicke, Laserleistung, Schnittgeschwindigkeit sowie der Maschinengenauigkeit. Bei der Beschaffung von lasergeschnittenen Bauteilen ist es entscheidend, klare und realistische Toleranzen vorzugeben, die sowohl den Anforderungen des Endprodukts als auch den technologischen Möglichkeiten des Fertigungsprozesses gerecht werden.
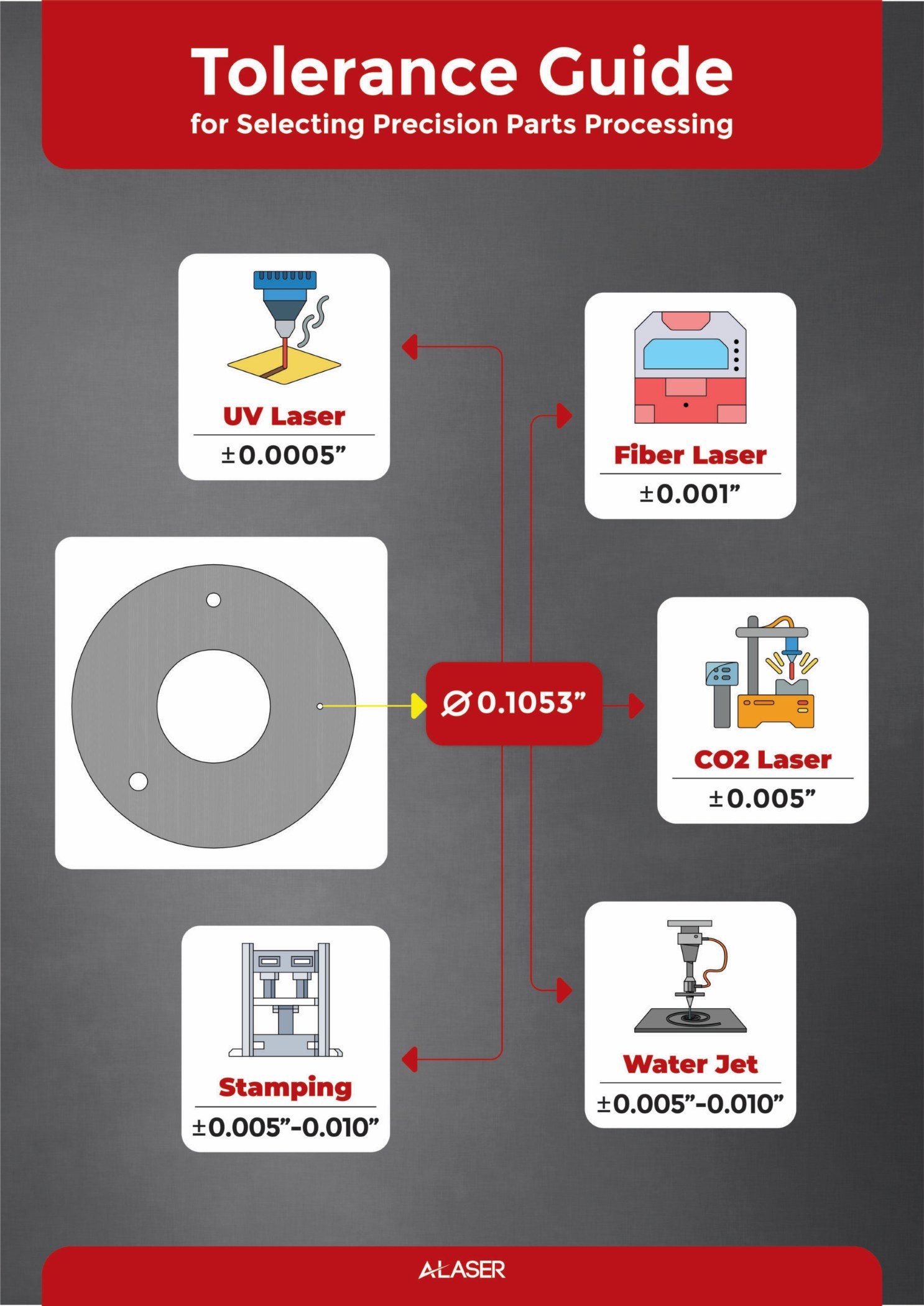
Typische Laserschneidtoleranzen liegen im Bereich von ±0,1 mm bis ±0,2 mm bei dünnen Blechen aus Stahl, Edelstahl oder Aluminium, können aber je nach Dicke und Material abweichen. Für anspruchsvolle Anwendungen mit engen Toleranzen ist eine enge Zusammenarbeit mit dem Zulieferer sowie gegebenenfalls eine Postbearbeitung notwendig.
Um Kosten und Fertigungszeiten zu optimieren, sollten Toleranzen nur dort verschärft werden, wo es funktionell erforderlich ist. Eine gut durchdachte Konstruktions- und Beschaffungsstrategie, unter Berücksichtigung der üblichen Prozessschwankungen und der Fähigkeiten des Laserschneidanbieters, gewährleistet eine wirtschaftliche und zuverlässige Produktion.
Fazit: Realistische, material- und prozessgerechte Toleranzen im Lastenheft zu definieren und frühzeitig mit dem Laserschneidzulieferer abzustimmen, ist entscheidend für Qualität, Wirtschaftlichkeit und Termintreue bei der Beschaffung lasergeschnittener Bauteile.