The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision surface treatment technologies across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 862.7 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1,942.5 million by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 14.2% during the forecast period. This surge is largely attributed to the rising adoption of laser rust removal as a non-abrasive, chemical-free alternative to traditional cleaning methods. As industries prioritize sustainability and operational efficiency, manufacturers of industrial lasers are innovating rapidly to meet the need for high-power, reliable rust removal systems. In this competitive landscape, a select group of companies are leading the charge with advanced laser technology tailored for corrosion control and surface restoration.
Top 10 Lasers That Remove Rust Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Explore PULSAR Laser P CL laser cleaning machines for industrial rust removal and paint stripping. Compare SHARK P CL, PANDA P CL and FOX P CL….
#2 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#3 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#4 Laser Cleaning Systems
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Fiber laser cleaning systems can remove rust and general corrosion. These contaminants can be completely removed with no damage to the substrate. Learn More….
#5 Top Laser Rust Cleaning Machines for Efficient Rust Removal
Website: woodrowscientific.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning removes rust precisely without abrasion or toxic waste, unlike sandblasting or chemical methods. Ever wondered how lasers can be ……
#6 Laser Rust Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: KEYENCE offers two laser machines that can remove rust—the hybrid laser marker and the fiber laser marker. Both machines offer a non-abrasive way to remove rust ……
#7 Laser Rust Removal
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: Watch this super fast rust removal from carbon steel panel with the new ultra-lightweight Vulcan handheld from Powerlase. The nature of laser cleaning ……
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#9 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: sltl.com
Key Highlights: This futuristic laser cleaning solution can capably remove rust, oil, paint, grease, colour and other particles from the surface of the metals….
#10 Laser Cleaning Rust Removal
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Our equipment uses pulsating lasers to blast away any contaminants from metal surfaces. This process is eco-friendly, as you won’t need any ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lasers That Remove Rust

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Lasers That Remove Rust
1. Rising Adoption Across Industrial Sectors
By 2026, laser-based rust removal technologies are expected to experience significant growth in industries such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and heavy manufacturing. The demand is being driven by the need for environmentally safe, precise, and non-abrasive surface cleaning methods. Unlike traditional techniques like sandblasting or chemical treatments, laser rust removal produces no secondary waste and preserves the underlying material integrity, making it ideal for high-precision applications.
2. Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
Advances in fiber laser technology—particularly in power efficiency, portability, and automation—are making laser rust removal systems more accessible. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to offer compact, handheld laser devices with improved user interfaces and integrated safety features, lowering the barrier to entry for small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, economies of scale and increased competition are projected to reduce equipment costs, accelerating adoption.
3. Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
With global regulations tightening around industrial emissions and waste disposal, companies are shifting toward greener alternatives. Laser rust removal emits no chemicals, produces no wastewater, and generates minimal particulate matter (when paired with filtration systems), aligning with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. The EU’s Green Deal and similar initiatives in North America and Asia-Pacific are expected to incentivize the use of sustainable de-rusting technologies.
4. Integration with Robotics and AI
A major trend in 2026 is the integration of laser rust removal systems with robotics and artificial intelligence. Automated robotic arms equipped with laser cleaning heads are being deployed in production lines for consistent, high-speed surface preparation. Machine learning algorithms enable real-time detection of rust levels and adjustment of laser parameters, improving efficiency and reducing operator dependency.
5. Expansion in Maintenance and Restoration Markets
Beyond industrial manufacturing, the restoration of historical artifacts, bridges, rail infrastructure, and vintage vehicles is fueling demand. Laser technology allows for selective rust removal without damaging delicate substrates, making it the preferred method in preservation projects. Museums, government agencies, and private restoration firms are increasingly investing in laser cleaning solutions.
6. Regional Market Growth
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Japan, is anticipated to lead the market due to rapid industrialization and investments in advanced manufacturing. North America and Europe will follow, driven by regulatory support and technological innovation. Governments and private sectors in these regions are funding R&D in laser applications, further boosting market expansion.
7. Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite growth, challenges remain—high initial investment, safety training requirements, and limited awareness among traditional maintenance teams. However, as education and demonstration projects increase, these barriers are expected to diminish. By 2026, the global laser rust removal market is projected to expand at a CAGR of over 12%, with increasing standardization and broader industry acceptance paving the way for mainstream adoption.
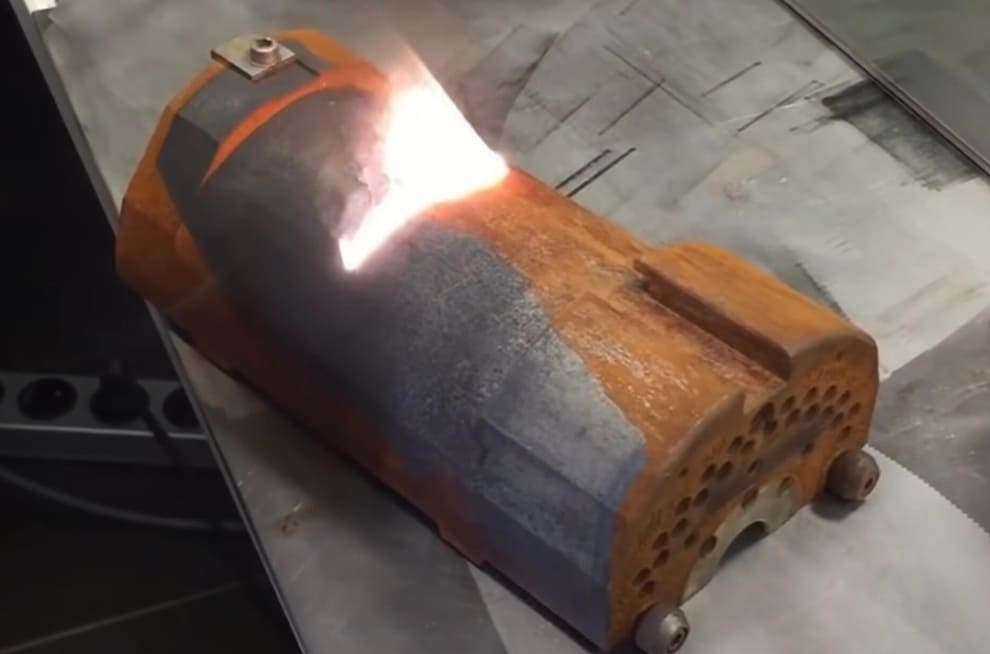

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lasers That Remove Rust: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser systems designed for rust removal, businesses must navigate several critical pitfalls related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these factors can lead to ineffective equipment, costly downtime, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
Poor Build Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Many low-cost or unverified suppliers offer laser rust removal systems that appear cost-effective but often compromise on core components. Substandard lasers, cooling systems, or motion controls can result in inconsistent rust removal, reduced operational lifespan, and frequent maintenance needs. Without proper documentation or third-party certifications (such as CE, FDA, or ISO), buyers risk acquiring systems that fail to meet safety or performance standards.
Lack of Technical Support and After-Sales Service
High-performance laser systems require expert installation, calibration, and ongoing technical support. Sourcing from manufacturers without established service networks—especially in international markets—can leave users stranded when issues arise. The absence of accessible training, spare parts, or troubleshooting assistance significantly increases total cost of ownership and reduces operational efficiency.
Misrepresentation of Specifications and Capabilities
Some suppliers exaggerate laser power, scanning speed, or removal efficiency to appear competitive. For example, advertising peak pulse power instead of average power can mislead buyers about actual performance. Without independent testing or verifiable case studies, customers may end up with underperforming systems unsuitable for their industrial applications.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing lasers from manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement raises serious legal concerns. Many inexpensive systems may incorporate cloned or reverse-engineered technology, infringing on patents held by legitimate innovators. Buyers risk being drawn into litigation, having equipment seized at customs, or facing liability for using unauthorized technology—especially in regulated industries or export-sensitive markets.
Inadequate IP Protection in Contracts
Even when dealing with reputable suppliers, failing to secure proper IP clauses in procurement contracts can be detrimental. Ambiguities around ownership of custom integrations, software, or process optimizations may prevent companies from protecting their own innovations or scaling the technology across operations. Clear agreements on IP rights, licensing, and confidentiality are essential.
Supply Chain and Component Traceability Issues
The origin of key components—such as laser sources, scanners, or control software—may be obscured, especially with OEM-supplied systems. Without full component traceability, it becomes difficult to assess IP legitimacy, ensure compliance with trade regulations (e.g., U.S. Entity List restrictions), or manage supply chain disruptions.
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, prioritize suppliers with proven track records and transparent operations, and consult legal experts to safeguard intellectual property throughout the sourcing process.
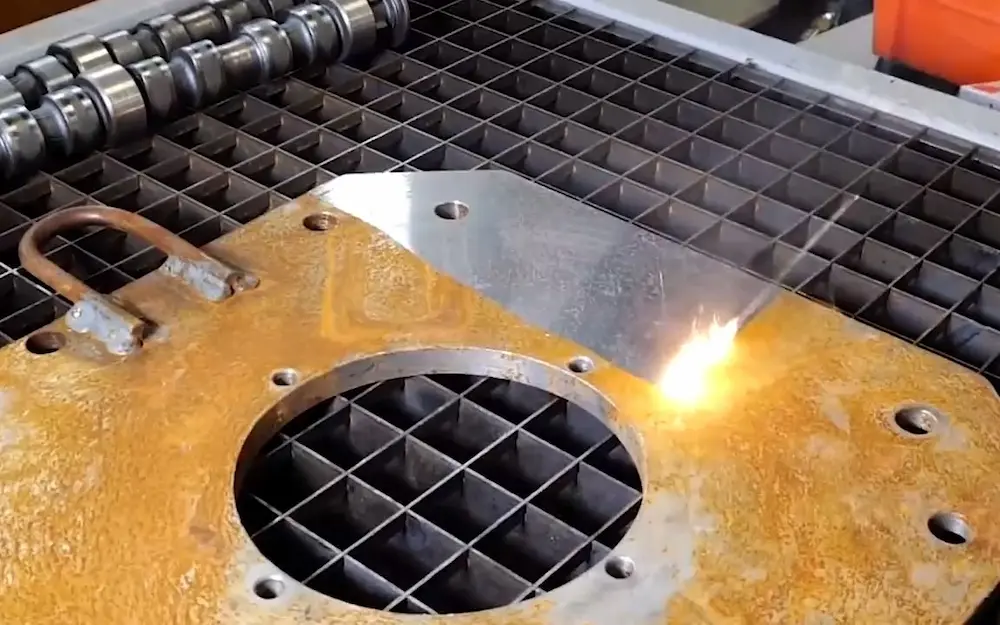

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lasers That Remove Rust
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Lasers designed for rust removal fall under industrial laser systems and are subject to various international, national, and regional regulations. These systems typically use high-powered pulsed fiber lasers to ablate surface contaminants such as rust, paint, or oxides from metal substrates. Due to their power levels and intended industrial use, they are classified as Class 4 lasers under the IEC 60825-1 standard, which governs laser safety.
Understanding the correct classification is essential for compliance with transportation, import/export, and workplace safety laws. These systems may also be subject to machinery directives (e.g., EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
International Shipping and Export Controls
When shipping laser rust removal systems internationally, exporters must comply with export control regulations such as:
- U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) – Administered by the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS), certain high-powered lasers may be listed under the Commerce Control List (CCL), specifically ECCN 6A003. This may require a license for export to certain countries.
- International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) – While most industrial lasers are not ITAR-controlled, verification is essential to confirm that the system does not fall under USML Category XII.
- Wassenaar Arrangement – International agreement monitoring dual-use goods, including high-energy laser systems. Participating countries may impose additional scrutiny on shipments.
Ensure proper documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, clearly describe the product as “Industrial Laser Equipment for Surface Cleaning” to avoid customs delays.
Import Regulations by Region
European Union
- Comply with CE marking requirements under:
- LVD (Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU)
- EMC Directive 2014/30/EU
- Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC
- Laser Product Standard EN 60825-1
- Provide a Declaration of Conformity and technical file.
- Register with local authorities if required under national implementations (e.g., German ProdSG).
United States
- FDA/CDRH (Center for Devices and Radiological Health) regulates laser products under 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11.
- Manufacturers must file a Laser Product Report and provide proper labeling (e.g., warning labels, aperture classification).
- Importers must ensure compliance before customs clearance.
China
- Requires CCC (China Compulsory Certification) for certain electrical equipment.
- High-power lasers may need additional approvals from MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology).
- Labeling must be in Chinese, including safety warnings and technical specifications.
Other Regions
- Canada: Compliance with Health Canada’s Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA).
- Australia: Must meet standards under the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA).
- Japan: Requires compliance with the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law (DENAN) and radiofrequency regulations.
Transportation and Packaging Requirements
- Lasers are sensitive to shock, vibration, and temperature changes. Use:
- Shock-absorbent packaging with internal bracing.
- Desiccants to prevent moisture damage.
- Climate-controlled shipping for extreme environments.
- Clearly label packages with:
- “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators.
- Laser warning symbols (IEC 60825).
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Drop”).
- For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations—though Class 4 lasers are generally not classified as dangerous goods, some battery-powered units may contain lithium batteries requiring special handling.
Workplace Safety and Compliance
End users must comply with occupational safety standards:
- OSHA (U.S.): Requires control measures such as interlocks, beam enclosures, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- ANSI Z136.1: Provides guidelines for safe use of lasers in industrial settings.
- ISO 11553: Safety of laser processing machines—applies directly to laser cleaning systems.
- Mandatory training for operators, including laser safety officer (LSO) designation in larger facilities.
Documentation and Labeling
Ensure all units are permanently labeled with:
– Manufacturer name and address
– Laser class (e.g., “CLASS 4 LASER PRODUCT”)
– Wavelength and maximum output power
– Warning labels in local language(s)
– Serial number and compliance marks (CE, UKCA, FCC, etc.)
Include user manuals with:
– Safety instructions
– Installation guidelines
– Maintenance procedures
– Emergency shutdown steps
Conclusion
Complying with logistics and regulatory requirements for laser rust removal systems ensures safe, efficient global distribution and protects manufacturers and end users from legal and operational risks. Always consult local regulatory bodies and consider using certified third-party compliance services to streamline market entry.
Conclusion: Sourcing Lasers for Rust Removal
Laser rust removal has emerged as a highly effective, environmentally friendly, and precise alternative to traditional methods such as sandblasting, chemical treatment, or mechanical scraping. When sourcing lasers for rust removal, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance, safety, and return on investment.
First, prioritize lasers with appropriate power output—typically in the range of 500W to 2000W—depending on the scale and severity of rust removal tasks. Higher wattage systems offer faster processing speeds and are better suited for industrial applications, while lower-wattage systems may suffice for smaller or maintenance operations.
Second, evaluate pulse duration and beam quality. Short-pulse, high-peak-power fiber lasers are particularly effective at ablating rust without damaging the underlying substrate. Advanced models with intelligent control systems and adjustable parameters allow greater precision and adaptability across different materials and rust levels.
Third, consider the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase price, maintenance requirements, training, and energy consumption. While the upfront cost of laser rust removal systems is higher than traditional methods, the long-term savings from reduced media costs, waste disposal, labor, and surface rework can be significant.
Additionally, ensure that suppliers offer adequate technical support, safety training, and compliance with international safety standards (such as CE, FDA, or IEC). Integrating safety features like enclosures, fume extraction, and interlock systems is essential for operational safety.
Finally, choose reputable manufacturers or suppliers with proven experience in industrial laser cleaning applications. Reading customer reviews, requesting live demonstrations, and reviewing case studies can help assess real-world performance.
In conclusion, sourcing the right laser for rust removal involves balancing technical capabilities, operational needs, and long-term costs. With the correct system, businesses can achieve cleaner, more sustainable, and efficient surface preparation while enhancing workplace safety and reducing environmental impact.