The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precise, and non-abrasive surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and heritage conservation. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 452.3 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.2% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by stringent environmental regulations favoring solvent-free cleaning methods and the rising adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies. As industrial players prioritize efficiency and sustainability, laser cleaning has emerged as a superior alternative to traditional techniques like sandblasting and chemical cleaning. With innovation accelerating and system costs gradually declining, a competitive landscape of manufacturers has formed, led by companies investing heavily in R&D and automation integration. The following list highlights the top eight laser cleaning manufacturers at the forefront of this transformation, leveraging technological prowess and global reach to capture growing market opportunities.
Top 8 Laserreinigen Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: P-Laser specializes in the production of industrial laser cleaning systems. With over 35 years of expertise in surface treatment and more than 450 systems ……
#2 Laser Cleaning vs. Dustless Blasting
Website: dustlessblasting.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is a non-contact technology that uses laser beams to remove contaminants, rust, paint, and other surface coatings….
#3 Laser cleaning
Website: ak-industry.de
Key Highlights: During laser cleaning, a high-power laser beam removes stubborn dirt, old coatings or unsightly deposits from the surface in a controlled manner….
#4 Laser Cleaning
Website: eraserlaser.de
Key Highlights: Discover the power of laser cleaning for metal, wood, stone and more. Efficient, residue-free and eco-friendly – precision cleaning made in Germany….
#5 Die 4JET Gruppe – Innovative Lasersysteme und
Website: 4jet.de
Key Highlights: 4JET entwickelt innovative Lasersysteme zum Reinigen, Strukturieren, Markieren, Schneiden und Modifizieren von Materialien, um hochwertige Bauteiloberflächen zu ……
#6 laser reinigungsgerät
Website: pulsar-laser.at
Key Highlights: Die erste luftgekühlte CW-Laserreinigungsmaschine – FOX P CL 1500A! Geringer Energieverbrauch bei 1500 W Reinigungsleistung! Die Laser-Rost- und ……
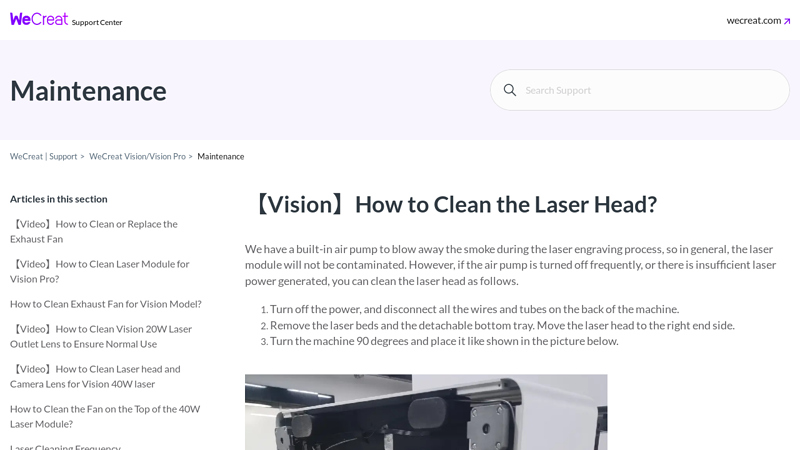
#7 【Vision】How to Clean the Laser Head? – WeCreat
Website: support.wecreat.com
Key Highlights: 【Vision】How to Clean the Laser Head? · Turn off the power, and disconnect all the wires and tubes on the back of the machine. · Remove the two screws that ……
#8 CrealityFalcon Laser Engraver General Maintenance Guide
Website: crealityfalcon.com
Key Highlights: This guide will walk you through the essential steps and best practices for maintaining your laser machine, helping you to keep it in top condition….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laserreinigen

H2: Market Trends for Laser Cleaning in 2026
The global laser cleaning market is poised for substantial growth by 2026, driven by increasing industrial automation, stringent environmental regulations, and the rising demand for non-abrasive, eco-friendly surface treatment solutions. The H2 2026 outlook highlights several key trends shaping the adoption and evolution of laser cleaning (Laserreinigen) technologies across industries.
1. Accelerated Industrial Adoption
By H2 2026, laser cleaning is expected to gain deeper penetration in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation sectors. Industries are increasingly replacing traditional cleaning methods—such as sandblasting, chemical solvents, and dry-ice blasting—with laser systems due to their precision, reduced waste, and lower long-term operational costs. The automotive sector, particularly in Europe and Asia, is investing heavily in laser cleaning for rust removal, paint stripping, and weld preparation, boosting market expansion.
2. Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Stringent environmental regulations in the EU, North America, and parts of Asia are pushing industries to adopt sustainable practices. Laser cleaning produces no secondary waste, requires no chemical consumables, and is fully compliant with environmental standards such as REACH and RoHS. This regulatory tailwind is expected to accelerate adoption, especially in regions with strong green manufacturing initiatives.
3. Technological Advancements and Cost Reductions
By H2 2026, ongoing advancements in fiber laser technology—such as higher pulse frequencies, improved beam quality, and modular designs—are making systems more efficient and accessible. Equipment costs have declined significantly since 2020 due to economies of scale and increased competition among manufacturers in China, Germany, and the U.S. This cost reduction is enabling small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to adopt laser cleaning, broadening the market base.
4. Integration with Automation and Industry 4.0
Laser cleaning systems are increasingly being integrated into automated production lines and robotic cells. By H2 2026, smart laser cleaning stations equipped with AI-driven vision systems and real-time monitoring are becoming common, especially in high-precision applications like aerospace component maintenance and nuclear decontamination. Connectivity with IoT platforms allows predictive maintenance and process optimization, enhancing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
5. Regional Growth Dynamics
Europe remains a leader in laser cleaning technology adoption, particularly in Germany, France, and Italy, where strong industrial bases and environmental policies support innovation. In Asia-Pacific, China and Japan are driving demand due to rapid industrial modernization and government-backed green manufacturing programs. North America is witnessing increased adoption in the defense and energy sectors, with notable growth in laser-based maintenance for oil & gas infrastructure.
6. Expansion into New Applications
Beyond traditional industrial uses, laser cleaning is finding new applications in cultural heritage restoration, medical device manufacturing, and electronics. By H2 2026, the restoration of historical monuments using ultra-precise lasers is gaining traction, supported by public funding and conservation initiatives. Additionally, the semiconductor and battery manufacturing industries are exploring laser cleaning for surface preparation at micro scales.
Conclusion
The H2 2026 landscape for Laserreinigen reflects a maturing market characterized by technological maturity, regulatory support, and expanding use cases. With continued innovation and decreasing costs, laser cleaning is transitioning from a niche solution to a mainstream industrial process, positioning the market for sustained growth beyond 2026.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laserreinigen (Laser Cleaning) Equipment – Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
When sourcing laser cleaning systems, businesses often encounter critical challenges related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal risks, and financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent or Substandard Performance
Many low-cost laser cleaning machines, especially from less reputable suppliers, suffer from poor beam quality, unstable output power, and inadequate duty cycles. This results in inconsistent cleaning performance, incomplete surface treatment, or damage to the substrate. Buyers may receive units that fail to meet promised specifications under real-world conditions.
2. Use of Non-Industrial Components
Some suppliers use consumer-grade or repurposed laser components not designed for industrial environments. These components degrade quickly under continuous operation, leading to frequent downtime and high maintenance costs. Look for systems with industrial-grade diodes, robust cooling systems, and durable optical components.
3. Lack of Proper Certification and Compliance
Reputable laser cleaning systems must comply with international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety, CE, FDA). Sourcing from suppliers without proper certifications increases safety risks and may prevent deployment in regulated industries such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
4. Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Poor service networks and limited availability of spare parts can cripple operations. Some suppliers, particularly those based in distant regions, may offer little technical support, leading to prolonged downtime when maintenance is required.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Risk of Infringing on Patented Technologies
Laser cleaning involves proprietary technologies in beam delivery, pulse control, and software algorithms. Sourcing from manufacturers that copy or reverse-engineer patented systems exposes the buyer to legal liability. Conduct due diligence to ensure the supplier owns or legally licenses all core technologies.
2. Unclear or Missing IP Ownership Documentation
Ambiguity in contracts regarding IP rights—especially for custom-developed systems—can lead to disputes. Ensure that purchase agreements explicitly state whether the buyer obtains any rights to embedded software, firmware, or process know-how.
3. Exposure to Counterfeit or Knockoff Equipment
The growing demand for laser cleaning has led to an increase in counterfeit systems. These often mimic branding and technical specifications of established brands but lack genuine IP and performance. Always verify the supplier’s credentials and seek direct engagement with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
4. Data and Process Security Risks
Modern laser systems often include IoT connectivity and process monitoring software. Sourcing from untrusted vendors may introduce cybersecurity vulnerabilities or unintended data sharing, potentially compromising sensitive manufacturing processes or client information.
Mitigation Strategy
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier vetting, request third-party performance testing, verify certifications, and consult legal experts to review IP clauses in procurement contracts. Prioritize transparency, traceability, and long-term support over initial cost savings.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laserreinigen
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for laser cleaning operations (Laserreinigen), ensuring safe, efficient, and legally compliant processes in industrial and commercial environments.
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Laser cleaning systems are precision instruments requiring careful handling during transportation and setup. Always use manufacturer-approved packaging and secure transport methods. Ensure that:
- Equipment is securely fastened during transit to prevent vibration damage.
- Environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) are monitored and maintained within operational ranges.
- Only trained personnel handle unpacking and initial setup to avoid mechanical or optical misalignment.
Site Preparation and Installation
Before deployment, conduct a site assessment to verify compatibility with laser cleaning equipment requirements:
- Confirm stable power supply with correct voltage and grounding.
- Ensure adequate ventilation, especially when removing coatings or contaminants that may release particulates.
- Designate a controlled access area to prevent unauthorized entry during operation.
- Install appropriate safety signage and barriers in accordance with laser safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825).
Regulatory Compliance
Laserreinigen operations must comply with national and international regulations regarding laser safety, environmental protection, and worker health:
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825 / EN 60825): Classify the laser system and implement required protective measures, including interlocks, emergency stops, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Workplace Safety (OSHA / EU-OSHA): Conduct risk assessments and ensure operators are trained in safe handling procedures.
- Environmental Regulations (EPA / REACH / RoHS): Manage waste materials (e.g., ablated particles) according to hazardous substance guidelines. Use filtration systems to capture airborne contaminants.
- Noise Emission Standards: Monitor and mitigate noise levels if auxiliary equipment (e.g., extractors) exceeds permissible limits.
Operational Procedures
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) must be established and documented:
- Perform pre-operation checks (cooling systems, beam alignment, exhaust filters).
- Calibrate laser parameters based on material type and contamination level.
- Maintain logbooks for maintenance, incidents, and personnel training.
- Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance.
Waste Management and Environmental Protection
Laser cleaning generates particulate matter that may contain hazardous materials (e.g., heavy metals, paint residues):
- Use HEPA-filtered extraction units to capture airborne particles.
- Classify waste according to local regulations and dispose of through certified hazardous waste handlers.
- Conduct regular filter inspections and replacements to ensure system efficiency.
Personnel Training and Certification
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate laser cleaning systems:
- Provide comprehensive training on laser hazards, emergency response, and equipment operation.
- Maintain records of training and certifications.
- Conduct periodic refresher courses and safety drills.
Documentation and Auditing
Maintain accurate records to demonstrate compliance during audits:
- Equipment manuals, maintenance logs, and calibration records.
- Risk assessments and safety data sheets (SDS) for materials being treated.
- Incident reports and corrective action plans.
- Proof of personnel training and regulatory permits.
International Shipping Considerations
When transporting laser cleaning equipment across borders:
- Verify export control regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR) if applicable.
- Ensure compliance with customs requirements, including proper classification (HS codes) and documentation.
- Confirm that laser safety labels and manuals meet destination country standards.
Emergency Preparedness
Establish emergency protocols for:
- Laser exposure incidents (eye or skin).
- Fire caused by laser-material interaction.
- System malfunction or uncontrolled beam emission.
- Evacuation and first aid procedures.
Store emergency contact numbers and ensure on-site access to first aid kits and fire extinguishers.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure that Laserreinigen operations are conducted safely, efficiently, and in full compliance with applicable laws and industry standards.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Cleaning Equipment
Sourcing laser cleaning equipment requires a careful evaluation of several key factors to ensure optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and long-term reliability. Laser cleaning offers significant advantages over traditional methods, including precision, environmental friendliness, reduced substrate damage, and minimal maintenance. However, the initial investment and complexity of the technology necessitate a strategic sourcing approach.
When selecting a supplier, it is essential to consider the supplier’s technical expertise, product quality, safety certifications, after-sales support, and service network. Prioritizing suppliers that offer customizable solutions—tailored to specific industrial applications such as rust removal, mold cleaning, or surface preparation—ensures better integration into existing workflows. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership (including energy consumption, maintenance, and training) provides a more accurate picture than initial purchase price alone.
Furthermore, sourcing from reputable manufacturers with proven track records in industrial laser solutions helps mitigate risks related to equipment performance and safety compliance. As laser cleaning technology continues to evolve, establishing relationships with innovative and forward-thinking suppliers can provide access to the latest advancements and future-proof operations.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of laser cleaning equipment hinges on a balance between technical suitability, supplier reliability, and long-term value. With the right partner and equipment, laser cleaning can significantly enhance operational efficiency and sustainability across a wide range of industries.