The global laser cleaning equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-based surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and cultural heritage restoration. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cleaning market size was valued at USD 650.3 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by regulatory pressures to reduce chemical cleaning methods, rising automation in industrial maintenance, and the superior accuracy offered by laser ablation technology. With wood preservation and restoration gaining traction—especially in high-value applications like antique furniture and architectural restoration—laser wood cleaning machines are becoming a preferred choice for non-abrasive, residue-free decontamination. As adoption accelerates, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, system reliability, and application-specific engineering. Here are the top nine laser wood cleaning machine manufacturers shaping this dynamic market landscape.
Top 9 Laser Wood Cleaning Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Machine – Laser Equipment Manufacturer
Website: dplaser.com
Key Highlights: DPLASER is a leading manufacturer & factory of industrial laser welding, laser cutting, laser marking and laser cleaning machines….
#2 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL – a universal professional laser cleaning machine suitable for metal, wood, stone and mixed-material applications….
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#4 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#5 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturer
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide range of laser cleaners, from 100W to 3000W. Our lineup includes handheld, backpack, and trolley-type products to meet diverse cleaning needs….
#6 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: Backpack laser cleaning machine Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine. 01|Backpack cleaner. BK-FLC50SC Max 50W Backpack Pulse Laser ……
#7 Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: wattsan.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning uses powerful laser beams to remove contaminants such as rust, paint, dirt or oxidation from a variety of surfaces….
#8 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning systems from Laser Photonics effectively clean a wide range of materials, including metals, thermoplastics, composites, stone, wood, and concrete ……
#9 ZAC Laser Machine
Founded: 2004
Website: zaclaser.com
Key Highlights: ZAC laser is the professional manufacture since 2004 which sell many laser machines such as laser rust removal-laser cleaning machine, laser engraver-laser ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Wood Cleaning Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Wood Cleaning Machines
The global market for laser wood cleaning machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising environmental awareness, and growing demand across restoration, manufacturing, and heritage conservation sectors. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the industry in 2026:
1. Increased Adoption in Heritage and Restoration Projects
By 2026, laser wood cleaning machines are expected to become a standard tool in cultural heritage preservation. Museums, historical sites, and restoration firms are increasingly favoring laser technology due to its non-abrasive, precise, and chemical-free cleaning capabilities. Governments and cultural institutions are investing in advanced conservation techniques, boosting demand for high-precision laser systems capable of removing soot, grime, and biological contaminants from antique wood surfaces without causing damage.
2. Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency and Accessibility
Innovation in fiber laser technology, automation, and AI-driven control systems is making laser wood cleaning machines more efficient, user-friendly, and affordable. By 2026, next-generation systems are anticipated to feature real-time monitoring, adaptive power output, and improved portability. These advancements lower operational barriers, enabling small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to adopt laser cleaning for fine woodworking, furniture restoration, and architectural detailing.
3. Rising Environmental and Regulatory Pressure
With stricter global regulations on chemical solvents and abrasive blasting methods, industries are turning to eco-friendly alternatives. Laser wood cleaning produces no secondary waste, eliminates the need for toxic chemicals, and reduces water usage—aligning with sustainability goals. By 2026, regulatory incentives and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) commitments are expected to accelerate adoption in construction, shipbuilding, and furniture manufacturing.
4. Expansion in Industrial and Commercial Applications
Beyond restoration, laser wood cleaning is gaining traction in industrial maintenance, particularly for cleaning wooden molds, pallets, and production-line components. The food, packaging, and automotive industries are exploring laser systems for hygienic surface preparation. The flexibility and repeatability of laser cleaning make it ideal for high-precision manufacturing environments, contributing to market growth.
5. Regional Market Growth and Competitive Landscape
Europe and North America remain dominant markets due to strong heritage conservation efforts and early technology adoption. However, the Asia-Pacific region—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—is witnessing rapid growth, fueled by urbanization, infrastructure development, and investments in smart manufacturing. Key players are focusing on R&D, strategic partnerships, and localized distribution to capture emerging opportunities.
6. Cost Reduction and ROI Improvements
Although initial investment remains higher than traditional methods, total cost of ownership for laser wood cleaning systems is improving. By 2026, increased competition, economies of scale, and longer component lifespans are expected to reduce machine prices and enhance ROI, making the technology more accessible to a broader customer base.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser wood cleaning machine market will be characterized by technological maturity, expanding application scopes, and strong alignment with environmental and industrial modernization trends. As the technology becomes more integrated into mainstream wood processing and restoration workflows, it is set to redefine industry standards for precision, sustainability, and efficiency.
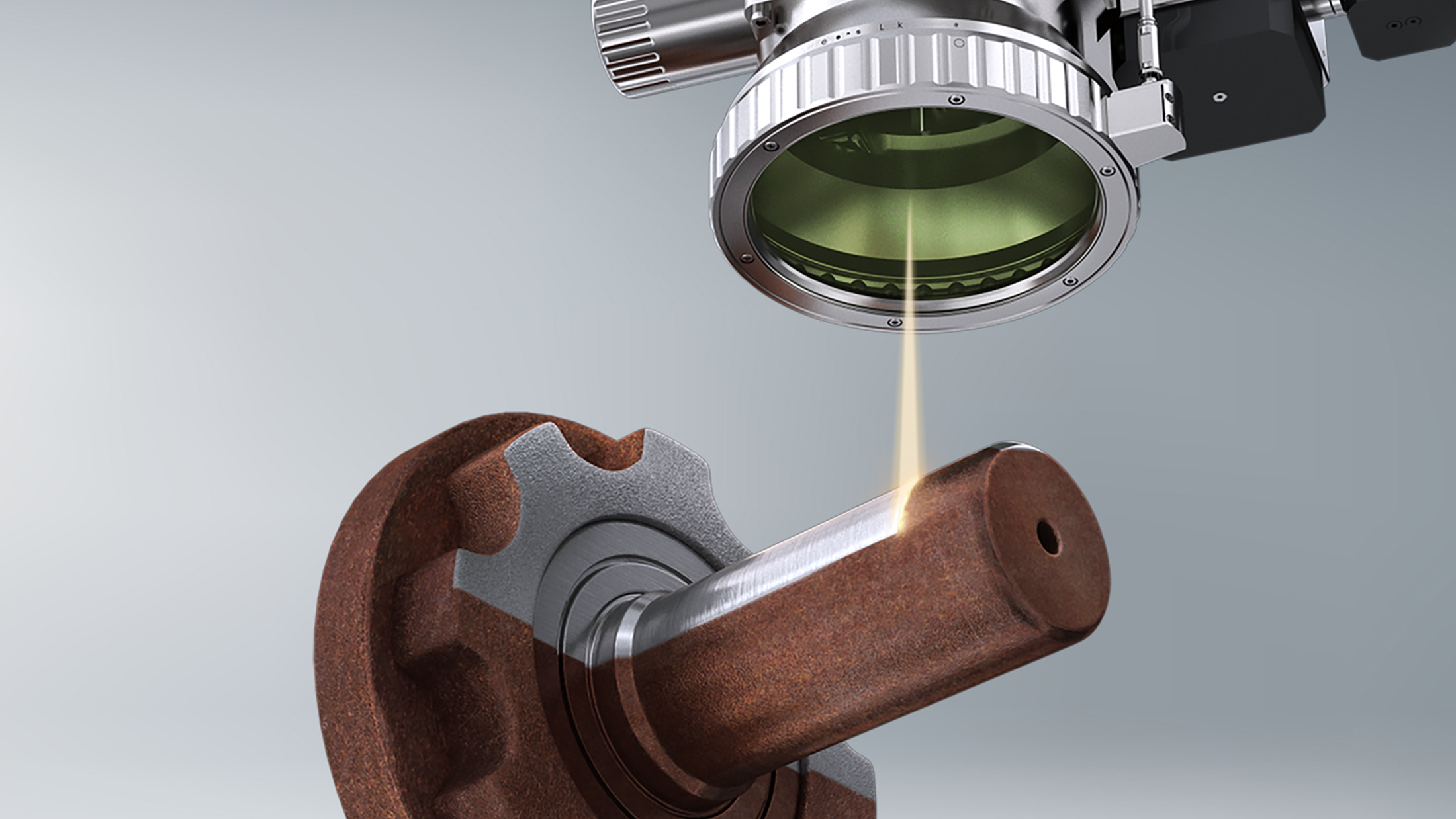

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Wood Cleaning Machines (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a laser wood cleaning machine involves significant investment, and overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to costly problems. Being aware of these common pitfalls helps ensure you select a reliable, effective, and legally sound solution.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many low-cost machines compromise on critical components to meet price points, resulting in unreliable performance and short lifespans. Watch for machines using substandard lasers (e.g., underpowered or unstable diodes), inadequate cooling systems, low-grade motion components, or flimsy enclosures. These flaws lead to inconsistent cleaning results, frequent breakdowns, and safety hazards.
Inadequate or Misleading Performance Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate cleaning speed, depth, or material compatibility. Claims like “cleans all wood types” or “removes paint in seconds” often lack context. Without standardized testing protocols, performance data can be misleading. Always request real-world demonstrations on your specific wood types and contaminants.
Lack of Safety Certifications and Compliance
Laser systems are regulated for safety. Machines without proper certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, IEC 60825) may pose serious risks, including eye or skin exposure, fire hazards, or harmful fumes. Non-compliant equipment may also be blocked at customs or prohibited from use in regulated environments.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Documentation
Poor technical support, unavailability of spare parts, or incomplete operation and maintenance manuals can render even a high-quality machine unusable over time. Ensure the supplier offers timely support, training, and long-term spare parts availability—especially critical for lasers and optical components.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Some manufacturers copy patented designs, software, or control systems from established brands. Purchasing such machines may expose your business to legal risks, including cease-and-desist orders or liability for contributory infringement. Always verify that the supplier owns or has licensed the technology, especially for proprietary algorithms or system architectures.
Hidden Costs from Poor Integration and Maintenance
Low upfront pricing can be deceptive. Machines requiring specialized cooling, power supplies, or exhaust systems add hidden costs. Similarly, high maintenance needs—such as frequent lens replacements or laser recalibration—can dramatically increase total cost of ownership. Ensure full transparency on operational requirements and ongoing expenses.
Inadequate Software and Control Systems
The software interface controls precision, automation, and usability. Poorly designed software may lack essential features like parameter libraries, job memory, or remote monitoring. It can also harbor bugs or compatibility issues. Additionally, proprietary software without clear licensing terms may restrict your usage or prevent future upgrades.
By carefully evaluating suppliers against these pitfalls—prioritizing verified quality, compliance, and legitimate IP ownership—you can make a more informed and secure investment in laser wood cleaning technology.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Wood Cleaning Machine
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate product classification under the Harmonized System (HS) code, typically falling under 8465.99 or 8515.21, depending on primary function and design. Prepare complete export documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, and certificate of origin. Include technical specifications, user manuals, and CE or other relevant conformity certificates to support customs clearance.
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Package the laser wood cleaning machine in a robust, shock-resistant crate with internal cushioning to prevent transit damage. Clearly label packaging with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), product identification, serial number, and compliance marks. Secure all optical and mechanical components to prevent movement. Confirm dimensional weight and freight class with carriers for accurate shipping cost estimation.
Import/Export Regulations and Licenses
Verify if the destination country requires import licenses, special permits, or pre-shipment inspections for industrial laser equipment. Some jurisdictions may regulate laser devices under radiation safety laws (e.g., FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 in the U.S.). Confirm compliance with export control regulations such as EAR (Export Administration Regulations) to determine if an export license is required based on power output and end-use.
Safety and Compliance Certifications
Ensure the machine meets essential safety standards including IEC 60825-1 (laser safety), IEC 61010-1 (safety requirements for electrical equipment), and EMC directives (e.g., EN 55011). Carry valid CE, UKCA, or other regional certifications as required. Include warning labels for laser radiation, high voltage, and moving parts. Provide a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) with each unit.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Submit all required documentation to customs authorities in advance to avoid delays. Be prepared to pay applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on the HS code and declared value. Consider using a licensed customs broker in the destination country to facilitate smooth clearance and ensure tariff classification accuracy.
Transportation and Handling
Use freight carriers experienced in handling precision industrial equipment. Avoid extreme temperatures and humidity during transit. For air freight, comply with IATA regulations regarding battery-powered components (if applicable). Ensure proper securing of the machine during loading/unloading to prevent tipping or impact.
After-Sales Compliance and Support
Provide local service and technical support contact information in the destination country. Maintain records of shipped units for warranty, service, and regulatory traceability. Ensure spare parts and consumables comply with local standards and are available through authorized distribution channels.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Inform customers of end-of-life disposal requirements in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) and RoHS directives (if applicable). Recommend recycling through certified e-waste handlers due to electronic components and potential hazardous materials in laser modules.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Laser Wood Cleaning Machine
Sourcing a laser wood cleaning machine represents a forward-thinking investment in modern, eco-friendly, and highly efficient surface restoration technology. Unlike traditional cleaning methods that rely on chemicals, abrasives, or manual labor, laser cleaning offers precision, minimal substrate damage, and reduced environmental impact—making it ideal for sensitive or historically valuable wooden surfaces.
When sourcing such equipment, it is essential to evaluate key factors including laser power, wavelength suitability for wood (typically fiber lasers around 1064 nm), beam control mechanisms, portability, safety features, and after-sales support. Additionally, choosing a reputable supplier with proven experience in wood and heritage restoration applications ensures optimal performance and longevity of the machine.
While the initial investment may be higher than conventional cleaning tools, the long-term benefits—such as lower operating costs, increased cleaning speed, compliance with environmental regulations, and superior results—justify the expense, especially for professional restorers, conservators, and industrial wood processors.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser wood cleaning machine is a strategic decision that enhances cleaning precision, sustainability, and operational efficiency. As technology advances and becomes more accessible, laser cleaning is poised to become the industry standard in wood conservation and maintenance.