The global laser welding technology market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, high-speed joining solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% through 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that advancements in fiber laser technology and the rising adoption of automation in manufacturing are key catalysts propelling market expansion. As industries prioritize efficiency, weld quality, and minimal heat distortion, laser welding has emerged as a preferred alternative to traditional methods. This surge in demand has intensified competition among technology providers, giving rise to a new generation of innovative manufacturers shaping the future of precision joining. Below, we highlight the top 10 laser welding technology manufacturers leading this transformation through cutting-edge R&D, strategic global reach, and a strong portfolio of industrial solutions.
Top 10 Laser Welding Technology Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#3 Laser Technologies Inc
Website: lasertechnologiesinc.com
Key Highlights: Laser Technologies is a fully integrated turnkey manufacturer specializing in laser cutting and stamping laminations for the motor and generator industry as ……
#4 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#5 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#6 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#7 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a pioneer in the field of mobile laser welding, ALPHA LASER GmbH offers a wide range of high-quality laser welding devices. This includes laser welding ……
#8 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#9 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
#10 Laser Welding & Laser Systems
Website: ewi.org
Key Highlights: EWI can identify and customize laser processes for the unique manufacturing application you have in mind, sticking with you from concept to implementation….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding Technology
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding Technology
By 2026, the laser welding technology market is poised for significant transformation, driven by escalating demands for precision, speed, automation, and sustainability across key industries. Several interconnected trends will shape its trajectory:
1. Dominance of High-Power and Ultrafast Lasers:
* High-Power Fiber Lasers (>10 kW): Will become the standard for heavy-duty applications in automotive (e.g., body-in-white, battery trays) and heavy industry (shipbuilding, construction), enabling faster processing speeds, deeper penetration, and single-pass welding of thick materials, boosting productivity.
* Ultrafast (Pico/Femtosecond) Lasers: Will see accelerated adoption for micro-welding in electronics, medical devices, and semiconductors. Their minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ) prevents damage to sensitive components, enabling previously impossible joins (e.g., transparent materials, dissimilar metals).
2. Intelligence and Automation Integration:
* AI & Machine Learning: Will move beyond basic monitoring to predictive maintenance, real-time process optimization (adjusting parameters based on sensor feedback), and automated defect detection/quality assurance, significantly reducing scrap rates and ensuring consistent weld quality.
* Digital Twins: Adoption will grow, allowing virtual simulation and optimization of welding processes before physical implementation, reducing setup time and improving first-pass yield.
* Seamless Factory Integration: Laser welding cells will be increasingly designed for easy integration with robotic arms, AGVs, and broader Industry 4.0 platforms (MES/ERP), enabling highly flexible and responsive production lines.
3. Material-Specific Advancements and New Applications:
* Dissimilar Materials Joining: Critical for lightweighting (e.g., Al-Steel, Cu-Al in e-motors/batteries). Laser welding, especially with tailored beam shapes (e.g., wobble, scanner) and hybrid techniques, will be essential for solving metallurgical challenges.
* Battery & EV Manufacturing: Will remain the single largest growth driver. Demand for high-speed, high-precision welding of battery tabs (Cu/Al), busbars, cell casings, and power electronics will push laser technology (especially blue lasers for copper) to new limits.
* Additive Manufacturing Integration: Laser welding will see increased use for post-processing (repair, joining AM parts) and hybrid manufacturing processes combining AM and welding.
4. Advancements in Beam Delivery and Process Control:
* Scanning Optics & Wobble Welding: Will become ubiquitous. High-speed scanners enable complex weld patterns, large area processing, and wobble techniques that improve gap bridging, reduce spatter, and enhance weld aesthetics/strength, particularly for fillet and lap joints.
* In-Process Monitoring (IPM): Multi-sensor systems (coaxial cameras, spectrometers, acoustic sensors) providing real-time feedback on melt pool dynamics, keyhole stability, and plasma plume will be standard, enabling closed-loop control and robust quality assurance.
* Blue and Green Wavelength Lasers: Blue lasers (450nm) will gain significant traction for high-reflectivity materials like copper and gold, crucial for EVs and electronics, offering vastly superior absorption compared to traditional IR lasers.
5. Sustainability and Cost Pressures:
* Energy Efficiency: Focus will intensify on reducing the energy consumption of laser systems and associated cooling. More efficient laser sources (e.g., diodes, advanced fiber lasers) and optimized processes will be key selling points.
* Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers will prioritize lower maintenance, longer component life (e.g., optics), higher uptime, and reduced consumables (shielding gas via optimized techniques like laser-arc hybrid) over just initial machine cost.
* Circular Economy: Laser welding’s potential for repair and remanufacturing of high-value components (e.g., aerospace, industrial machinery) will be increasingly leveraged, supporting sustainability goals.
6. Market Consolidation and Regional Shifts:
* Consolidation: Expect continued M&A activity as larger players acquire specialized technology providers (e.g., in ultrafast lasers, IPM, automation) to offer comprehensive solutions.
* Asia-Pacific Growth: China will remain the largest market, driven by EV and electronics manufacturing. Growth will also be strong in India, Southeast Asia, and South Korea.
* Supply Chain Resilience: Geopolitical factors will push manufacturers towards regionalized supply chains, impacting laser source and component sourcing, potentially benefiting local/near-shore suppliers.
Conclusion for 2026:
The laser welding market in 2026 will be defined by intelligence, versatility, and application-specific solutions. It will move beyond being just a joining tool to becoming an integral, data-driven element of smart manufacturing ecosystems. Success will belong to providers offering not just lasers, but complete, optimized, and sustainable welding solutions tailored to the demanding requirements of EVs, advanced electronics, and next-generation industrial production. The convergence of high-power, ultrafast, and intelligent technologies will unlock new possibilities in material joining and manufacturing efficiency.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Welding Technology: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser welding technology—whether equipment, subsystems, or services—presents unique challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, compromised product integrity, legal disputes, and significant financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Verification of Performance Specifications
Suppliers may overstate laser power, beam quality (M² factor), welding speed, or repeatability. Without independent validation or third-party testing, organizations risk acquiring systems that fail to meet production requirements, resulting in inconsistent welds, increased scrap rates, and unplanned downtime.
Lack of Process Validation and Traceability
A critical pitfall is accepting equipment without documented process validation (e.g., welding parameter optimization, metallurgical analysis). Without traceable test results and quality control protocols, it becomes difficult to ensure consistent weld integrity across batches or to comply with industry standards (e.g., ISO 15614, AWS D17.1).
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Training
Low-cost suppliers may offer limited technical support, training, or spare parts availability. This lack of service infrastructure can lead to prolonged machine downtime, improper maintenance, and suboptimal utilization, undermining the long-term reliability and performance of the laser system.
Use of Substandard Components
Some suppliers may reduce costs by using lower-grade optics, cooling systems, or control electronics. These components degrade faster, compromise beam stability, and increase maintenance costs, ultimately affecting weld quality and system lifespan.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unclear Ownership of Customized Solutions
When laser systems are customized for specific applications, the ownership of design modifications, process parameters, or software algorithms may not be clearly defined in contracts. This ambiguity can result in disputes over IP rights, especially if the supplier reuses proprietary configurations with other clients.
Risk of IP Leakage During Technology Transfer
Sharing sensitive production data, material specifications, or process know-how with suppliers increases the risk of IP exposure. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and data protection measures, critical competitive information may be inadvertently disclosed or misappropriated.
Dependence on Proprietary Software and Closed Systems
Many laser welding platforms rely on proprietary software that limits user access to core algorithms or diagnostic tools. This creates vendor lock-in, restricts process optimization, and hinders in-house troubleshooting, potentially exposing the buyer to long-term IP and operational dependencies.
Infringement of Third-Party Patents
Suppliers may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., beam delivery methods, pulse shaping techniques) without proper licensing. Purchasers could face legal liability for patent infringement even if unintentional, particularly in regulated industries such as aerospace or medical devices.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should conduct thorough due diligence, including technical audits, IP risk assessments, and legal reviews of contracts. Clear agreements on IP ownership, warranties, and service level agreements (SLAs) are essential. Additionally, engaging independent experts for system validation and ensuring compliance with international standards can significantly reduce risks associated with quality and intellectual property in laser welding technology sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding Technology
Introduction to Laser Welding Technology
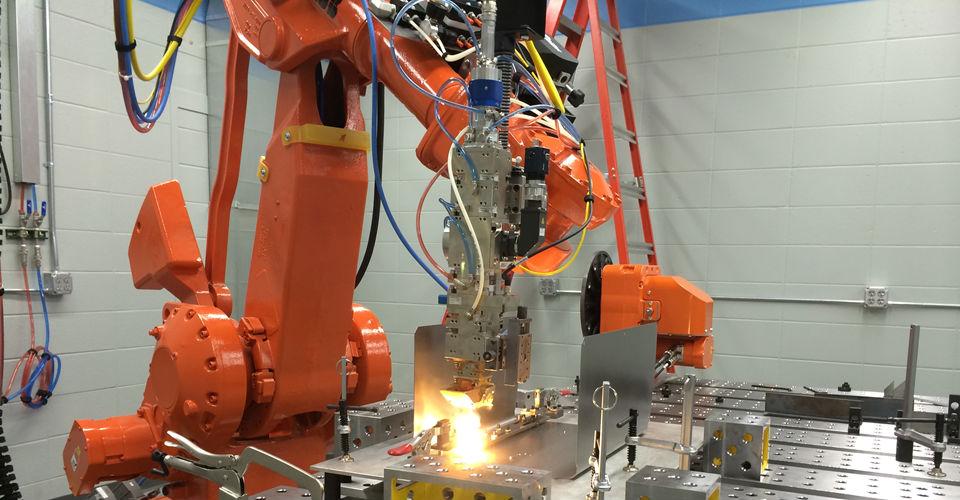
Laser welding technology utilizes high-intensity laser beams to join materials with precision and minimal heat input. Commonly employed in automotive, aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and electronics industries, this advanced process offers high-speed, repeatable, and clean welds. However, its implementation requires strict adherence to logistics planning and regulatory compliance to ensure safety, quality, and operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser welding systems are subject to multiple international and local regulations. Key compliance standards include:
– ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers) – Specifies safety guidelines for laser operations in the U.S.
– IEC 60825-1 – International standard for laser product safety, covering classification and labeling.
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910.133/134 – Governs personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety eyewear.
– FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 & 1040.11 – Regulates laser products in the United States, including performance standards.
– CE Marking (EU) – Requires compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
Facilities must maintain documentation of compliance, including laser classification reports, safety interlock validations, and operator training records.
Safety and Hazard Mitigation
Laser welding poses several risks, including exposure to optical radiation, fumes, electrical hazards, and fire. Proper mitigation strategies include:
– Laser Enclosures and Interlocks: Full enclosure of the laser beam path with safety interlocks to halt operation if opened.
– Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Use of local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems to capture hazardous airborne particles and metal fumes.
– Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandatory use of laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) ratings, flame-resistant clothing, and face shields.
– Beam Path Control: Ensuring beam alignment is performed only by trained personnel using alignment tools and low-power settings.
– Emergency Shut-Off: Clearly marked emergency stop buttons accessible at all workstations.
Facility and Workspace Planning
Effective logistics begin with proper facility design:
– Controlled Access Zones: Designate Class 1 or Class 4 laser areas with clear signage and access restrictions.
– Environmental Controls: Maintain stable temperature and humidity levels to ensure laser system performance and longevity.
– Space Requirements: Allow sufficient clearance around equipment for maintenance, ventilation ducting, and operator movement.
– Floor Load Capacity: Verify structural support for heavy laser systems, power supplies, and robotic arms.
Electrical and cooling infrastructure (e.g., chillers) must be sized appropriately and installed per manufacturer specifications.
Equipment Import and Export Considerations
Cross-border logistics for laser welding systems may involve:
– Export Controls: Lasers above certain power thresholds may be subject to ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations) in the U.S.
– Customs Documentation: Accurate HS codes (e.g., 8515.21 for laser soldering/welding machines) and commercial invoices detailing specifications.
– Certification Requirements: Equipment must carry required certifications (CE, UKCA, CCC, etc.) for destination markets.
– Battery and Power Supplies: Lithium-ion components in automated systems may require special shipping documentation under IATA/IMDG regulations.
Transportation and Handling Procedures
Due to the sensitivity of laser components:
– Shock and Vibration Protection: Use anti-vibration mounts and crated packaging during transit.
– Climate-Controlled Transport: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures and humidity.
– Handling Protocols: Use appropriate lifting equipment; never tilt or drop laser sources or optical components.
– Inventory Tracking: Implement serialized tracking for high-value components and compliance-critical parts.
Operator Training and Certification
Compliance and operational safety depend on trained personnel:
– Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a designated LSO responsible for safety audits, hazard assessments, and training oversight.
– Initial and Refresher Training: Mandatory for all operators and maintenance staff, covering emergency procedures, PPE use, and system operation.
– Certification Records: Maintain logs of training completion and refresher schedules in accordance with ANSI and OSHA standards.
Maintenance and Calibration Logistics
Scheduled maintenance ensures compliance and performance:
– Preventive Maintenance Plans: Follow manufacturer-recommended intervals for optics cleaning, coolant replacement, and alignment checks.
– Calibration Records: Document laser power output, beam alignment, and safety system tests. Calibration must be traceable to national standards (e.g., NIST).
– Spare Parts Management: Maintain critical spares (lenses, nozzles, protective windows) and ensure authenticity and compatibility.
– Service Provider Qualifications: Use only certified technicians for repairs involving laser or safety systems.
Waste and Environmental Compliance
Laser welding generates byproducts requiring proper disposal:
– Metal Fumes and Particulates: Collected filter media must be treated as hazardous waste if contaminated with regulated metals (e.g., chromium, nickel).
– Coolant and Lubricants: Spent fluids must be disposed of per RCRA (U.S.) or equivalent local regulations.
– End-of-Life Equipment: Decommissioned lasers must be recycled in accordance with WEEE (EU) or local e-waste directives.
Documentation and Audit Readiness
Maintain a comprehensive compliance portfolio:
– Equipment manuals, laser classification labels, and conformity declarations
– Risk assessments and safety procedures
– Training records and LSO documentation
– Maintenance logs and calibration certificates
– Air quality monitoring reports (if applicable)
Regular internal audits help identify gaps and prepare for regulatory inspections.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of laser welding technology hinges on integrating robust logistics with strict compliance protocols. By aligning facility planning, transport, safety, and documentation practices with global standards, organizations can ensure operational excellence, regulatory adherence, and a safe working environment.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Welding Technology
Sourcing laser welding technology represents a strategic investment in advancing manufacturing capabilities, improving product quality, and enhancing operational efficiency. The precision, speed, and repeatability offered by laser welding systems make them ideal for high-demand applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. When evaluating potential sources, it is essential to consider factors such as system performance, integration capabilities, total cost of ownership, supplier support, and scalability.
Choosing the right supplier involves not only assessing technical specifications but also ensuring reliability, after-sales service, and long-term partnership potential. Advances in fiber and hybrid laser technologies continue to expand the applicability and cost-effectiveness of these systems, making them increasingly accessible for mid-sized and growing manufacturers.
In conclusion, procuring laser welding technology should align with both current production needs and future growth objectives. A well-informed sourcing decision will enable organizations to achieve higher weld quality, reduce waste, and maintain a competitive edge in an evolving industrial landscape.