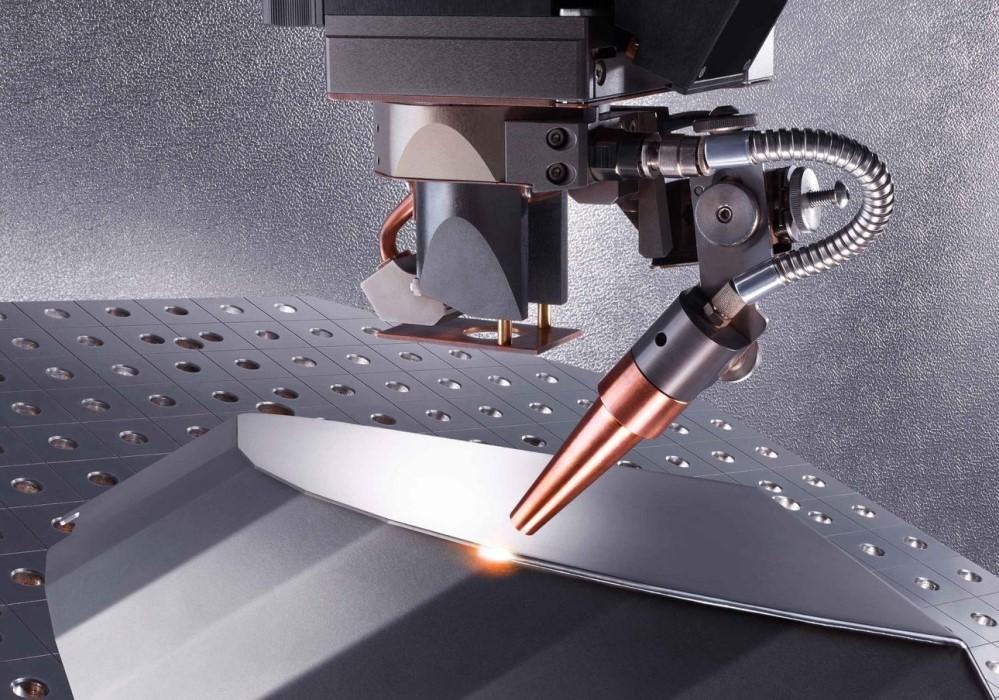
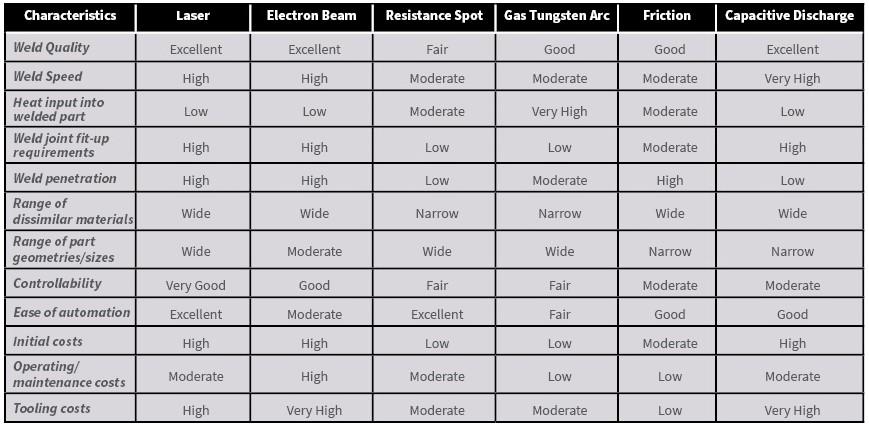
The global laser welding equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, efficient joining technologies across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.3% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing, and the need for stronger, cleaner welds with minimal distortion. As competition intensifies, manufacturers are prioritizing welding strength, consistency, and throughput. Based on performance data, market presence, and technological innovation, the following ten companies have emerged as leaders in delivering laser welding solutions with superior joint strength and reliability.
Top 10 Laser Welding Strength Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#2 Ultra
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a non-contact, highly precise process that enables manufacturers of miniature components to create strong, high-quality ……
#3 Laser welding
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: TRUMPF lasers can create fine weld points of just a millimeter in diameter in an instant, as well as deep-welded seams stretching over several meters….
#4 Branson
Website: emerson.com
Key Highlights: The GLX Laser welders provide you with greater design freedom and increased production throughput as well as superior weld strength, quality, speed and ……
#5 Laser Welding
Website: weiss-aug.com
Key Highlights: Weiss-Aug offers precision laser welding services for aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. Contact us to learn more about our laser welding ……
#6 Precision in laser processing & metrology
Website: precitec.com
Key Highlights: Precitec offers solutions for laser cutting, welding, metrology and additive manufacturing – leading in precision, quality and process reliability….
#7 Leading Laser Welding Companies
Website: lasercuttingcompanies.com
Key Highlights: Save time and easily find the USA’s top laser welding companies with years of experience in producing high precision, heavy duty products at competitive ……
#8 Welding Services
Website: dugganmfg.com
Key Highlights: The team at Duggan provides exceptional Robotic Welding, Resistance Welding, Laser Welding, along with other assembly services for aerospace, ……
#9 Laser Gear Welding
Website: precollc.com
Key Highlights: Gear welding is a straightforward laser welding application that is fast and efficient. Preco manufactures laser systems and provides contract manufacturing ……
#10 Laser Welding
Website: gemmfg.com
Key Highlights: We provide advanced laser welding services for mission-critical metal components used in industries such as aerospace, defense, telecommunications, medical, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding Strength
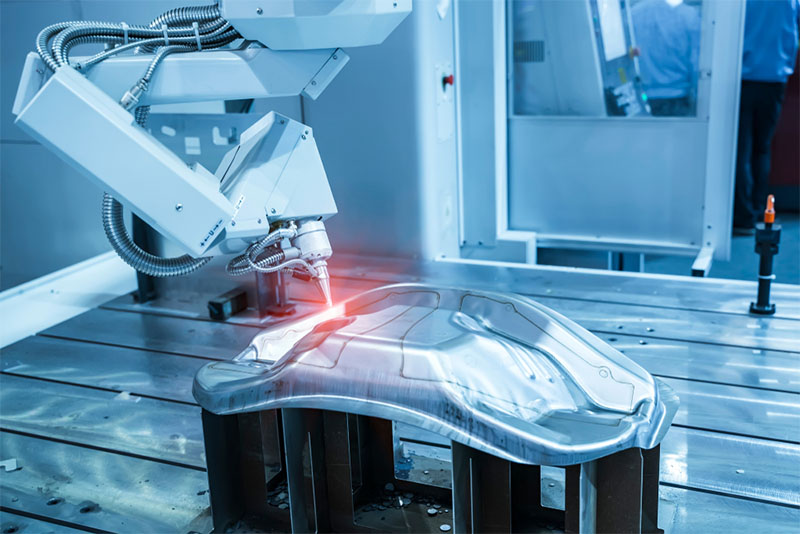

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding Strength
By 2026, the market for laser welding strength is poised for significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology, evolving industry demands, and a heightened focus on manufacturing efficiency and quality. The concept of “strength” in this context extends beyond mere mechanical properties to encompass process reliability, consistency, and the ability to meet stringent application requirements across key sectors. Here’s an analysis of the dominant trends shaping this landscape:
-
Demand for Higher Strength-to-Weight Ratios & Lightweighting:
- Automotive & Aerospace: The relentless push for fuel efficiency and electrification (EVs) will drive demand for laser welding of ultra-high-strength steels (UHSS), advanced aluminum alloys, and dissimilar material combinations (e.g., steel-aluminum). Laser welding’s precision and low heat input are crucial for maintaining the integrity of these heat-sensitive, high-strength materials without excessive softening in the heat-affected zone (HAZ).
- Trend Impact: Increased adoption of fiber lasers with higher beam quality (BPP) and tailored beam profiles (e.g., wobble, oscillation, spatial/polarization control) to achieve deeper penetration, narrower HAZ, and superior fusion zone microstructure, directly translating to higher joint strength and fatigue resistance.
-
Rise of High-Power & Multi-Kilowatt Lasers:
- Productivity & Deep Penetration: The availability and affordability of single-mode and multi-mode fiber lasers exceeding 10 kW will enable significantly faster welding speeds and deeper penetration capabilities. This is critical for thick-section welding in heavy industries (shipbuilding, construction, energy) and large components in aerospace and automotive (battery trays, structural parts).
- Trend Impact: Enhanced strength through deeper, more consistent penetration and reduced porosity (achieved with optimized keyhole dynamics at high power). However, managing spatter and maintaining weld quality at these speeds requires sophisticated process monitoring and control systems, linking strength directly to process stability.
-
Advancements in Process Monitoring & Control for Consistency:
- Quality Assurance: Achieving and verifying consistent high strength requires real-time monitoring. By 2026, integrated solutions combining Coaxial Welding Monitoring (CWM – monitoring plasma/plume), spectroscopy, photodiodes, and high-speed cameras will become standard, especially in safety-critical applications (automotive, medical, aerospace).
- Trend Impact: Closed-loop control systems using AI/ML algorithms will analyze monitoring data in real-time to automatically adjust laser parameters (power, focus, speed) to compensate for variations (joint fit-up, material properties, contamination), ensuring weld strength remains within tight tolerances. This directly addresses the need for reliability and traceability.
-
Growth in Remote & 3D Scanning Welding:
- Flexibility & Complex Geometries: Galvanometer-based scanning systems (remote welding) allow rapid beam positioning without moving the heavy laser source or optics. This enables welding complex 3D paths on large structures (e.g., car bodies, battery packs) with high speed and precision.
- Trend Impact: Optimized scanning strategies (wobble, spiral, figure-8) improve melt pool stability, reduce porosity, and enhance fusion, leading to more uniform microstructures and higher, more predictable joint strength. The ability to access difficult areas also improves overall structural integrity.
-
Focus on Dissimilar & Advanced Material Joining:
- Material Innovation: The need to combine materials with different properties (e.g., steel for strength, aluminum for weight) is growing. Laser welding, particularly with tailored heat input control, is a key enabler.
- Trend Impact: Development of specialized techniques like laser-assisted metal deposition (LAMD) for functionally graded joints or precise control of intermetallic compound (IMC) formation in dissimilar welds will be critical. Achieving strong, reliable bonds between dissimilar materials without brittle phases or excessive distortion is a major driver of R&D, directly impacting market demand for solutions that guarantee strength.
-
Increased Automation & Integration with Smart Factories (Industry 4.0):
- Robotics & Cobots: Laser welding cells will be increasingly integrated into fully automated production lines, utilizing advanced robotics and collaborative robots (cobots) for flexibility and safety.
- Trend Impact: Seamless data flow between CAD/CAM, welding equipment, and MES/SCADA systems will enable predictive maintenance, optimized scheduling, and full traceability of weld parameters and quality data. This digital thread ensures consistent process execution, a fundamental prerequisite for achieving and proving required weld strength.
-
Sustainability & Energy Efficiency:
- Green Manufacturing: While not directly “strength,” the high electrical-to-optical efficiency of modern fiber lasers (>40%) compared to older technologies reduces operational costs and environmental impact.
- Trend Impact: This efficiency makes high-strength laser welding a more sustainable choice, aligning with corporate ESG goals. Reduced heat input also minimizes distortion, potentially reducing post-weld machining and material waste, contributing indirectly to the overall structural efficiency and strength of the final product.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the “strength” of laser welding will be defined not just by the mechanical properties of the weld itself, but by the robustness, consistency, and intelligence of the entire welding process. The market will be dominated by solutions offering:
* Ultra-high power and precision for demanding materials and thick sections.
* Integrated, AI-driven process monitoring and control ensuring zero-defect, high-strength welds.
* Flexibility through remote scanning and advanced robotics for complex applications.
* Proven capability in joining challenging dissimilar and advanced materials.
* Seamless integration into digital, sustainable manufacturing ecosystems.
Suppliers who can deliver systems that demonstrably guarantee high, reliable strength through advanced technology and data-driven process control will be the leaders in the 2026 laser welding market.
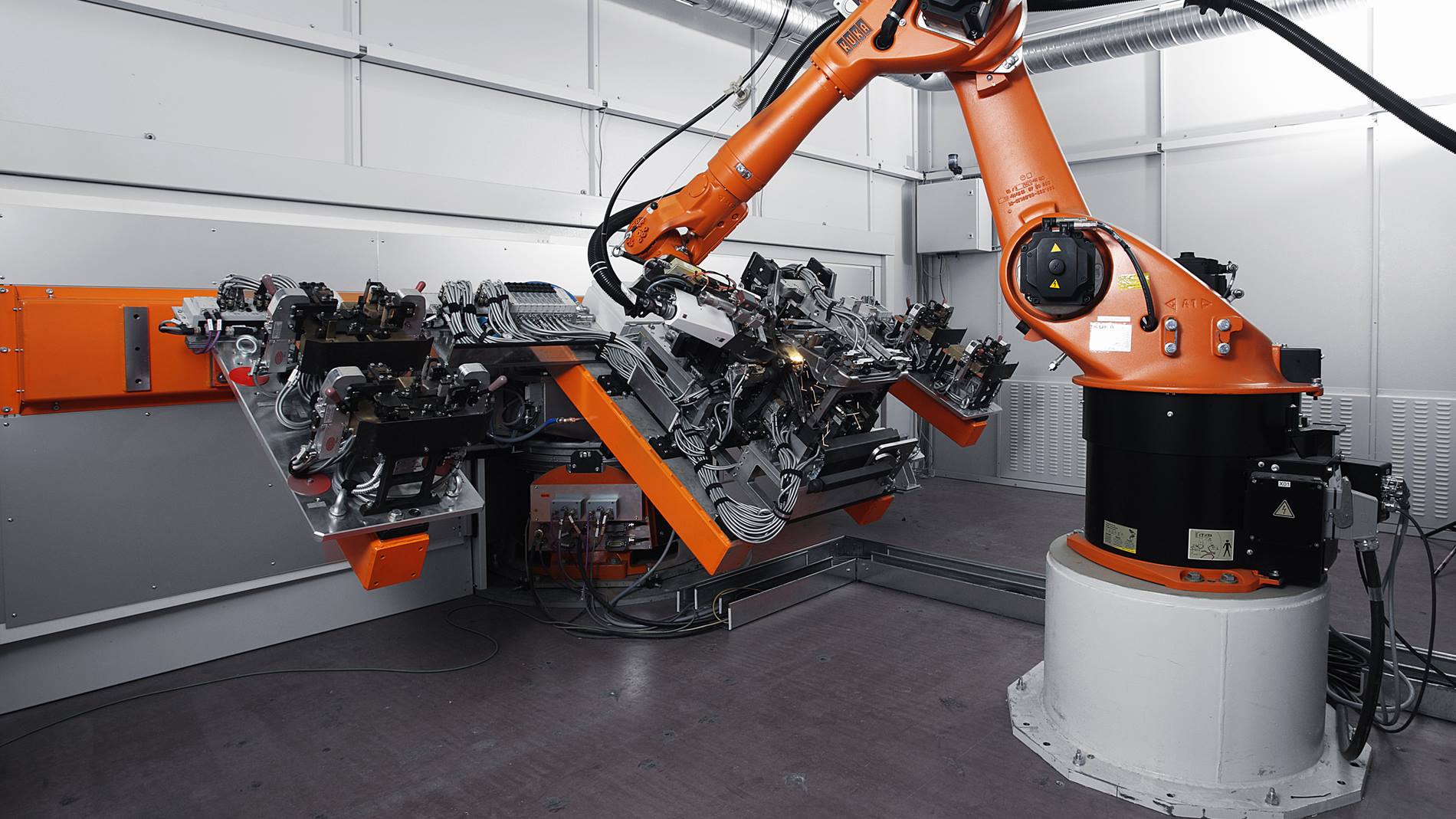
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Welding Strength (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser welding services or equipment, overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to significant project setbacks, safety risks, and legal exposure. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Validation of Weld Quality and Strength
Many buyers assume laser welding inherently guarantees high strength, but without proper validation, this can lead to structural failures. Common issues include inconsistent penetration, porosity, cracking, or incomplete fusion—especially when process parameters aren’t optimized for the specific material and joint design.
- Pitfall: Relying solely on supplier claims without independent testing or documented process validation (e.g., weld procedure specifications, WPS).
- Mitigation: Require third-party testing (e.g., tensile, shear, bend, microsection analysis) and validation of process control methods such as real-time monitoring (e.g., weld seam tracking, plasma monitoring).
Lack of Process Documentation and Traceability
Transparent documentation is essential for quality assurance and regulatory compliance, particularly in industries like automotive, aerospace, or medical devices.
- Pitfall: Failing to secure detailed records of laser parameters (power, speed, focus, shielding gas), material certifications, and post-weld inspections.
- Mitigation: Contractually mandate full traceability and access to process documentation, including SPC (Statistical Process Control) data and non-conformance reports.
Overlooking Intellectual Property Risks
Laser welding often involves proprietary techniques, automation systems, or unique joint designs. Without clear agreements, IP ownership and usage rights can become contested.
- Pitfall: Assuming that the buyer owns improvements or custom tooling developed during the project, or allowing suppliers to use your designs in work for competitors.
- Mitigation: Define IP ownership upfront in contracts. Specify who owns process innovations, tooling, and data. Include confidentiality (NDA) and non-compete clauses where appropriate.
Selecting Suppliers Without Relevant Industry Certification
Not all laser welding providers meet stringent industry standards, leading to compliance gaps and rejected parts.
- Pitfall: Choosing vendors based solely on cost without verifying certifications (e.g., ISO 3834, AWS D1.1, AS9100).
- Mitigation: Require proof of relevant quality management and welding certifications, and audit suppliers’ facilities when feasible.
Underestimating the Importance of Material and Joint Compatibility
Laser welding performance is highly sensitive to material composition, surface condition, and joint fit-up.
- Pitfall: Assuming a supplier can weld any material without reviewing metallurgical compatibility or conducting feasibility studies.
- Mitigation: Collaborate early with the supplier on material selection and joint design. Conduct prototype weld trials before full-scale production.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—especially around quality validation and IP protection—companies can ensure reliable, legally secure, and high-performance laser welding outcomes.
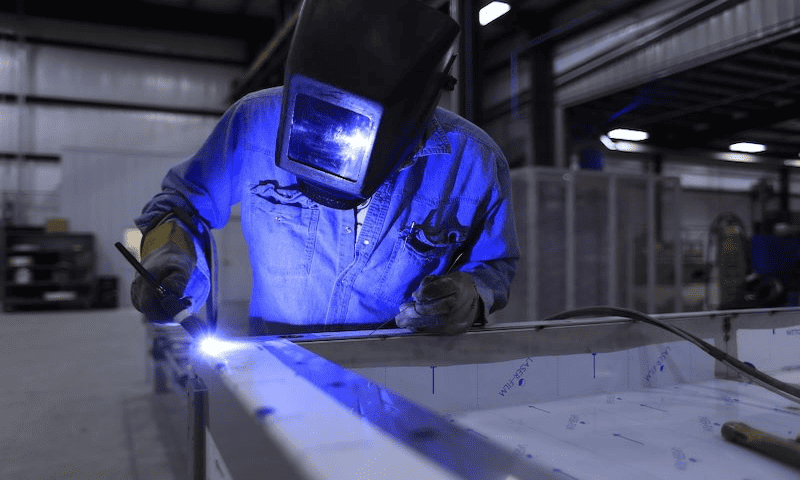

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding Strength
Overview
Laser welding is a high-precision joining process widely used across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and manufacturing due to its ability to produce high-strength, consistent welds. Ensuring the strength and integrity of laser welds requires not only advanced technical execution but also adherence to logistical and regulatory compliance standards. This guide outlines key considerations in logistics and compliance related to laser welding strength.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Adherence to international and industry-specific standards is critical to ensure laser weld strength meets required safety and performance benchmarks. Key standards include:
- ISO 15614-11: Qualification testing of welding procedures for laser and hybrid laser-arc welding.
- AWS D17.1/D17.1M: Specification for Fusion Welding for Aerospace Applications.
- ASME BPVC Section IX: Rules for the qualification of welding procedures, welders, and welding operators.
- EN 14179-1: Non-destructive testing of welds – Visual testing of fusion-welded joints.
- IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
Organizations must maintain certification documentation and ensure all welding personnel are qualified per these standards.
Material Traceability and Documentation
To ensure weld strength consistency, full material traceability is essential:
- Maintain Material Test Reports (MTRs) for base and filler materials.
- Track lot and heat numbers from raw material to final product.
- Use digital systems (e.g., ERP or MES) to log welding parameters, operator IDs, and inspection results.
- Archive welding procedure specifications (WPS), procedure qualification records (PQR), and non-destructive testing (NDT) reports for compliance audits.
Welding Process Control and Validation
Laser welding strength depends on precise control of process parameters:
- Monitor and record laser power, welding speed, focal position, shielding gas flow, and pulse characteristics.
- Conduct periodic validation of equipment using standardized test coupons.
- Implement Statistical Process Control (SPC) to detect deviations and ensure repeatability.
- Perform regular calibration of laser systems and sensors per manufacturer and ISO 9001 requirements.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) and Quality Assurance
Verification of weld strength requires comprehensive inspection protocols:
- Use NDT methods such as ultrasonic testing (UT), radiographic testing (RT), and dye penetrant inspection (PT) as applicable.
- Implement in-line monitoring systems (e.g., weld vision systems, acoustic emission sensors) for real-time defect detection.
- Establish acceptance criteria based on industry standards and customer specifications.
- Retest or reject non-conforming welds; document all corrective actions.
Handling, Storage, and Transportation
Post-weld logistics impact final product integrity:
- Protect welded components from mechanical damage, moisture, and contamination during handling and storage.
- Use protective coatings or packaging where necessary to prevent corrosion.
- Follow documented handling procedures to avoid stress on weld zones during transport.
- Label components with weld date, batch number, and inspection status.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance
Laser welding operations must comply with safety regulations to protect personnel and facilities:
- Implement laser safety enclosures and interlocks per ANSI Z136.1 and IEC 60825.
- Provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety eyewear.
- Ensure proper ventilation and fume extraction to manage metal particulates and ozone.
- Conduct regular safety training and risk assessments.
Audit Preparedness and Continuous Improvement
Maintain readiness for internal and external audits:
- Schedule routine internal audits of welding processes and documentation.
- Address non-conformances promptly using a corrective and preventive action (CAPA) system.
- Stay updated on regulatory changes and emerging industry best practices.
- Invest in operator training and technology upgrades to enhance weld strength and compliance.
Conclusion
Achieving and maintaining high laser welding strength requires a robust integration of precise technical processes with disciplined logistics and compliance management. By adhering to recognized standards, ensuring traceability, validating processes, and prioritizing safety, organizations can deliver reliable, high-integrity welds that meet both customer and regulatory expectations.
In conclusion, sourcing laser welding for strength-critical applications offers significant advantages in terms of precision, consistency, and joint integrity. The high energy density of laser welding enables deep penetration and narrow weld seams, resulting in minimal heat-affected zones and reduced distortion—key factors in maintaining the structural strength of the materials. When properly implemented with appropriate parameters and quality controls, laser welding produces strong, repeatable joints suitable for demanding industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
However, the success of laser welding largely depends on material compatibility, joint design, surface preparation, and the expertise of the welding provider. Therefore, careful supplier qualification, thorough process validation, and ongoing quality assurance are essential to ensure that the sourced laser welding meets required strength and performance standards. Ultimately, when sourced effectively, laser welding is a reliable and efficient method for achieving high-strength, durable welds in advanced manufacturing applications.