The global laser welding services market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision joining solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 6.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% through 2028. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of automation, the need for high-speed and high-accuracy welding processes, and advancements in fiber and disk laser technologies. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights that the escalating use of laser welding in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing—particularly in battery and powertrain systems—is a key market catalyst. As industries prioritize efficiency, durability, and miniaturization, the demand for specialized laser welding services continues to rise, positioning leading manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and service delivery. Below are the top 10 laser welding services manufacturers shaping the future of precision manufacturing.
Top 10 Laser Welding Services Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 High Quality Laser Welding Services by Laser Weld Inc
Domain Est. 2006
Website: laserweldinc.com
Key Highlights: Experience precision laser welding with Laser Weld Inc offering advanced technology and exceptional craftsmanship for all your industrial needs….
#2 Laser Technologies Inc
Domain Est. 1998
Website: lasertechnologiesinc.com
Key Highlights: Laser Technologies is a fully integrated turnkey manufacturer specializing in laser cutting and stamping laminations for the motor and generator industry as ……
#3 LaserStar Technologies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#4 Laserax
Domain Est. 2012
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#5 Equipment & Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#6 Civan Lasers
Domain Est. 2021
Website: civanlasers.com
Key Highlights: Dynamic Beam Lasers are a cutting-edge technology that makes welding faster, deeper, and of higher quality, changing the way welding is done today….
#7 Denaliweld
Domain Est. 2023
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#8 Laser Welding
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#9 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Domain Est. 2000
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
#10 Laser Welding Solutions
Domain Est. 2005
Website: laserweldingsolutions.com
Key Highlights: Laser Welding Solutions provides state-of-the-art surface technologies and 3D printing to assist in the product improvement efforts of our goal-driven ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding Services
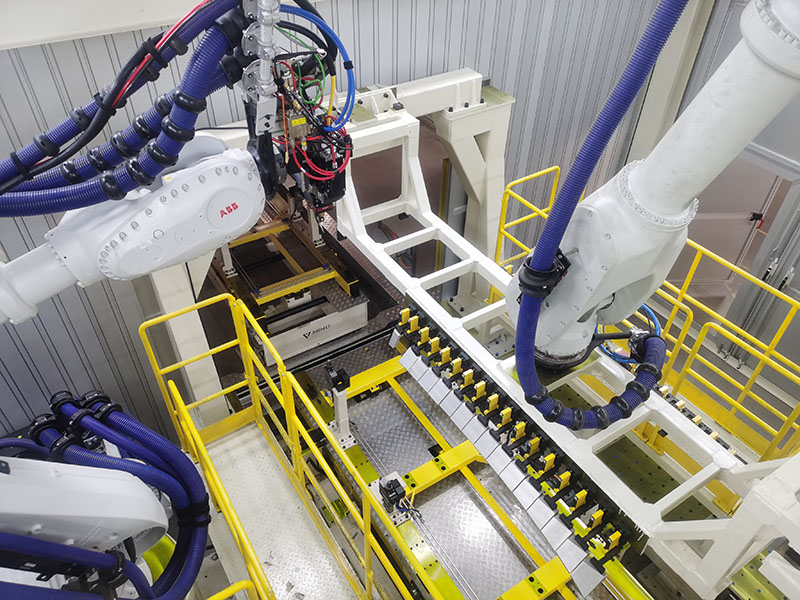

2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding Services
As industries continue to prioritize precision, efficiency, and automation, laser welding services are poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by technological advancements, rising demand in key sectors, and a global push toward sustainable manufacturing, the laser welding market is expected to experience robust growth and innovation. Below are the key trends shaping the future of laser welding services in 2026.
Advancements in High-Power and Ultrafast Lasers
By 2026, high-power fiber lasers exceeding 10 kW will become standard in industrial settings, enabling deeper penetration and faster processing speeds for thick materials used in heavy industries such as shipbuilding and construction. Concurrently, ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) laser welding is gaining traction in micro-manufacturing sectors, including medical devices and electronics, due to its ability to create clean, cold-weld joints with minimal heat-affected zones. These technological leaps will expand the application scope of laser welding into previously inaccessible domains.
Integration with Automation and Industry 4.0
Laser welding services are increasingly integrated into smart manufacturing ecosystems. By 2026, the convergence of laser systems with robotics, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven process optimization will be commonplace. Predictive maintenance, adaptive welding parameters via machine learning, and digital twin simulations will enhance precision and reduce downtime. This integration supports mass customization and just-in-time production models, particularly in automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Battery Manufacturing
The global shift toward electric mobility will be a major growth driver for laser welding services. In 2026, laser welding will be critical in battery pack assembly, where precision and reliability are paramount. Processes such as tab welding, busbar joining, and sealing of battery enclosures rely heavily on laser technology for consistent quality and throughput. As EV production scales, demand for high-speed, high-accuracy laser welding solutions will surge, especially in regions with strong EV adoption like North America, Europe, and China.
Expansion in Medical and Aerospace Applications
The medical device industry will increasingly adopt laser welding for implantable devices and surgical tools due to its biocompatible, hermetic sealing capabilities. Similarly, aerospace manufacturers will rely on laser welding for lightweight, high-strength joints in turbine components and airframes. Demand for reduced weight and improved fuel efficiency will push adoption of advanced laser techniques such as remote scanning and hybrid laser-arc welding.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will influence the adoption of laser welding over traditional methods. By 2026, laser systems will offer improved energy efficiency, reduced material waste, and lower emissions—making them a preferred choice in green manufacturing initiatives. Closed-loop recycling of laser gases and modular system designs will further enhance the environmental profile of laser welding services.
Regional Market Developments
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the largest market for laser welding services due to strong industrial automation and electronics manufacturing. However, North America and Europe are expected to see accelerated growth due to reshoring efforts, government incentives for advanced manufacturing, and investments in clean energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
By 2026, laser welding services will be at the forefront of advanced manufacturing, driven by technological innovation, sector-specific demands, and sustainability imperatives. Companies investing in skilled workforce training, R&D, and digital integration will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this dynamic market.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welding Services (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser welding services can deliver high precision and efficiency, but overlooking key risks—particularly in quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection—can lead to costly setbacks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Many suppliers lack robust quality assurance systems, leading to inconsistent weld integrity. Without standardized procedures such as weld parameter validation, real-time monitoring, or post-weld non-destructive testing (NDT), defects like porosity, cracking, or incomplete fusion may go undetected. Always verify that the service provider adheres to recognized standards (e.g., ISO 3834, AWS D1.1) and can provide documented process validation and traceability.
Insufficient Process Documentation and Traceability
Laser welding is highly sensitive to parameters like power, speed, focus, and shielding gas. If the supplier fails to document these parameters or maintain batch-specific records, reproducing consistent results becomes difficult. Lack of traceability also complicates root cause analysis during failure investigations, especially in regulated industries like medical or aerospace.
Inexperienced or Underqualified Personnel
Even with advanced equipment, operator skill is critical. Providers may use undertrained staff who cannot optimize laser settings or troubleshoot process deviations. Confirm that technicians are certified (e.g., through the American Welding Society or equivalent) and have experience with your material type and joint configuration.
Poor Material and Fit-Up Control
Laser welding demands tight tolerances in part fit-up and material consistency. Suppliers who do not enforce strict incoming inspection or fixturing protocols risk misalignment and weld defects. Ensure the provider has processes to verify part geometry and cleanliness before welding.
Inadequate Intellectual Property Protection
Sharing technical designs, CAD files, or proprietary welding procedures with a third party poses IP risks. Without strong legal safeguards—such as comprehensive non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clauses restricting the use or replication of your designs—your innovations may be exposed. Always audit the supplier’s IP policies and data security measures before engagement.
Lack of IP Ownership Clarity in Contracts
Ambiguity in contracts about who owns process developments, tooling, or custom fixturing can lead to disputes. If the supplier develops a unique welding procedure for your part, does that become their IP? Define ownership rights explicitly in service agreements to prevent future legal conflicts.
Insecure Data Handling Practices
Digital files required for laser welding (e.g., CAM programs, 3D models) can be vulnerable to cyber threats or unauthorized access. Choose providers with secure data management systems, access controls, and compliance with data protection standards (e.g., ISO 27001), especially when dealing with sensitive or military-grade applications.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, companies can ensure reliable, secure, and compliant laser welding partnerships.
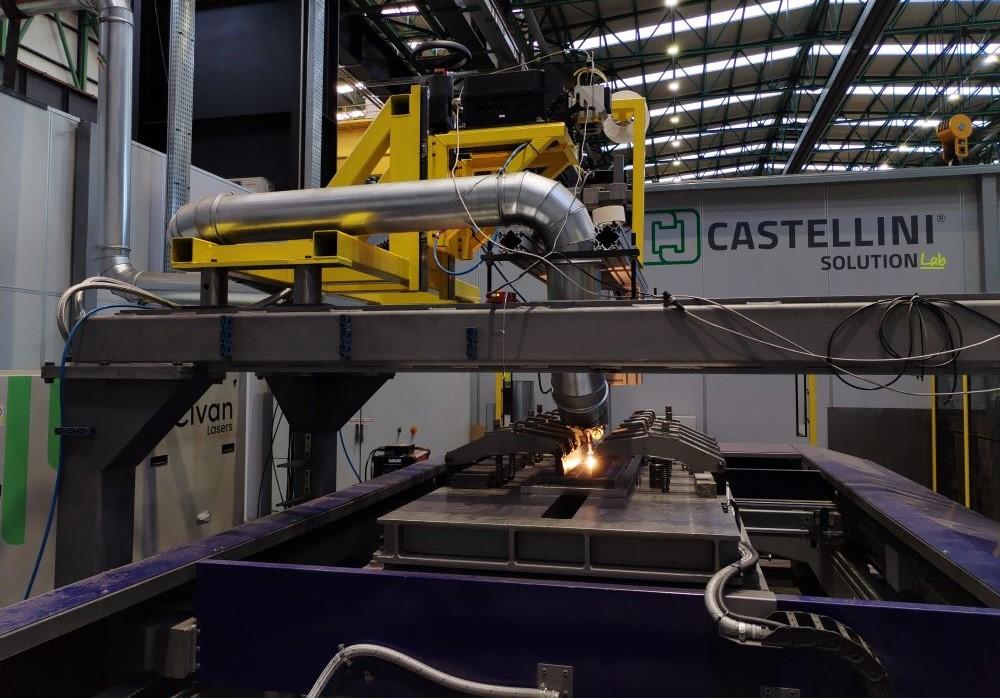

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding Services
Service Overview and Scope
Laser welding services involve the use of high-intensity laser beams to join materials with precision, minimal distortion, and high repeatability. These services are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, medical device, and electronics manufacturing. This guide outlines the logistics and compliance requirements necessary for the safe, legal, and efficient delivery of laser welding services.
Facility and Equipment Requirements
Laser welding operations must be conducted in controlled environments that meet industry standards. Facilities should include designated welding zones with proper enclosures, ventilation, and fume extraction systems. All laser equipment must be regularly maintained and calibrated in accordance with manufacturer specifications and ISO 9022 standards for optics and laser systems. Equipment should be registered and labeled with appropriate Class 4 laser warning signs.
Regulatory Compliance
Providers of laser welding services must comply with local, national, and international regulations. Key compliance standards include:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Ensures workplace safety, including hazard communication and protective controls.
– ANSI Z136.1: Provides safety guidelines for the use of lasers in industrial environments.
– IEC 60825-1: International standard for laser product safety.
– ISO 3834 & ISO 15614-11: Quality requirements and qualification testing for fusion welding of metallic materials, including laser-specific procedures.
– REACH and RoHS: Compliance may be required depending on the materials being welded, especially in electronics or medical applications.
Personnel Qualifications and Training
All operators and technicians must be certified in laser safety (e.g., Certified Laser Safety Officer – CLSO) and possess documented training in laser welding techniques. Training records must be maintained and updated annually. Personnel should be trained in emergency shutdown procedures, fire response, and handling of hazardous materials generated during welding (e.g., metal fumes).
Material Handling and Traceability
Customers must provide detailed material specifications, including alloy type, certifications (e.g., Mill Test Reports), and any surface treatments. All incoming materials must be logged and stored under appropriate conditions. Traceability must be maintained throughout the welding process using barcoding or digital tracking systems to ensure quality control and compliance with industry requirements such as AS9100 (aerospace) or ISO 13485 (medical devices).
Shipping and Receiving Protocols
Parts entering and leaving the facility must be handled using documented procedures to prevent contamination or damage. Packaging must protect sensitive components, especially optics and precision-welded assemblies. Shipping documents must include material certifications, process parameters, and non-destructive testing (NDT) results when applicable. Carriers must be vetted for experience with high-value or sensitive industrial components.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Each laser welding job must be supported by a documented Work Instruction and Welding Procedure Specification (WPS). Post-weld inspections (e.g., visual, dye penetrant, X-ray, or CT scanning) must be performed as required. All quality records, including inspection reports, calibration logs, and non-conformance reports, must be archived for a minimum of 10 years or per customer-specific requirements.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Measures
Laser welding generates hazardous fumes, intense light, and potential fire risks. Facilities must have:
– Fume extraction systems certified to capture metal particulates.
– Interlocked laser enclosures and emergency stop mechanisms.
– Personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser-safe eyewear, flame-resistant apparel, and respiratory protection.
– Spill kits and fire suppression systems suitable for metal fires (e.g., Class D extinguishers).
Customer Compliance Requirements
Customers may impose additional compliance obligations, such as:
– ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) for defense-related components.
– DFARS (Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement) for materials sourcing.
– Nadcap accreditation for special processes in aerospace.
Service providers must verify and document adherence to all customer-specific quality and regulatory requirements prior to order fulfillment.
Record Retention and Audit Preparedness
All operational, compliance, and quality records must be securely stored and readily accessible for audits. Internal audits should be conducted quarterly, with external audits (e.g., ISO, Nadcap) scheduled annually. Documentation must support full traceability from raw material to final inspection.
Emergency Response and Incident Reporting
A documented emergency response plan must be in place for laser-related incidents, including eye exposure, fire, or equipment failure. All incidents must be reported internally and, when required, to regulatory bodies such as OSHA. Root cause analysis and corrective actions must be recorded and implemented to prevent recurrence.
In conclusion, sourcing laser welding services offers a strategic advantage for industries requiring high-precision, consistent, and efficient joining solutions. With superior accuracy, minimal heat distortion, and strong, clean welds, laser welding is ideal for complex components in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. When selecting a service provider, it is essential to evaluate their technical capabilities, equipment quality, industry experience, and certifications to ensure alignment with project requirements. Additionally, considering factors such as cost-effectiveness, lead times, and post-weld support contributes to a successful outsourcing partnership. By choosing the right laser welding supplier, businesses can enhance product quality, streamline manufacturing processes, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.