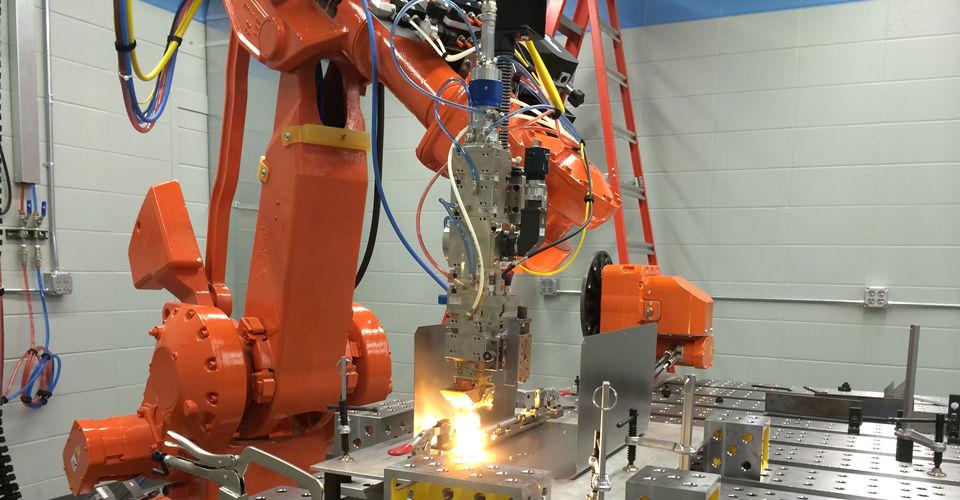
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, high-speed joining technologies across key industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 2.27 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing, and the push for energy-efficient production processes. Mordor Intelligence further projects that the market will register a CAGR of over 6.8% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, highlighting the growing adoption of laser welding in electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing and lightweight material assembly. As industrial players seek greater accuracy, repeatability, and lower operational costs, leading manufacturers have responded with innovative laser welding solutions. In this evolving landscape, the top 10 laser welding process manufacturers are distinguished by their technological leadership, global footprint, and capacity to deliver scalable, high-performance systems tailored to modern production demands.
Top 10 Laser Welding Process Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#3 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#4 Laser Company for Industrial Laser Solutions
Website: laserline.com
Key Highlights: The leading laser company for integrated & customized diode laser manufacturing solutions for various industries & applications….
#5 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a pioneer in the field of mobile laser welding, ALPHA LASER GmbH offers a wide range of high-quality laser welding devices. This includes laser welding ……
#6 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#7 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#8 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
#9 Laser Plastic Welding
Website: emerson.com
Key Highlights: Laser plastic welding uses no friction, vibration or harsh movement and is the ideal choice for any sized part requiring a precise join….
#10 Fives laser systems for welding and cutting
Website: fivesgroup.com
Key Highlights: Fives’ laser systems are proven for success. We have expertise in all aspects of laser processing, including welding, 3D cutting, cleaning and marking….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding Process
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding Process
The laser welding market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and the broader push towards automation and sustainability. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
H2: Dominance of High-Power and Ultrafast Lasers
By 2026, high-power fiber lasers (exceeding 10 kW) will dominate heavy industrial applications such as automotive body-in-white and shipbuilding, enabling faster processing speeds and deeper penetration. Concurrently, ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers will gain traction in precision sectors like medical device manufacturing and electronics, where minimal heat-affected zones and high accuracy are critical. This dual-track advancement allows laser welding to serve both high-throughput and micron-level joining needs.
H2: Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Laser welding systems in 2026 will increasingly feature embedded sensors, real-time monitoring (e.g., coaxial vision, plasma monitoring), and AI-driven process control. Integration with digital twins and cloud-based platforms will enable predictive maintenance, adaptive welding strategies, and seamless traceability—key components of smart factories. This shift enhances weld quality consistency and reduces scrap rates, appealing to industries with strict regulatory standards.
H2: Expansion in Electric Vehicle (EV) Production
The surge in EV manufacturing will remain a primary growth driver. Laser welding is essential for battery pack assembly (e.g., busbar and cell-to-pack welding), electric motor components, and lightweight aluminum structures. By 2026, specialized laser systems optimized for copper and aluminum welding—materials notoriously difficult to join with conventional methods—will see accelerated adoption, especially as EV production scales globally.
H2: Growth in Hybrid and Remote Welding Technologies
Hybrid laser-arc welding (HLAW) will expand in applications requiring deep penetration and high deposition rates, such as in heavy machinery and pipeline construction. Simultaneously, remote laser scanning systems—using galvanometric mirrors for high-speed beam positioning—will grow in automotive and consumer electronics for their flexibility and reduced cycle times. These technologies improve efficiency and lower operational costs.
H2: Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
As industries prioritize decarbonization, laser welding’s inherent energy efficiency compared to traditional methods will be a key selling point. By 2026, manufacturers will emphasize eco-design, recyclable components, and reduced consumable use. Additionally, closed-loop recycling of laser gases and energy recovery systems will become standard, aligning with corporate ESG goals.
H2: Regional Market Diversification and Automation Adoption
While Asia-Pacific (led by China, Japan, and South Korea) will remain the largest market due to robust manufacturing ecosystems, North America and Europe will see accelerated growth driven by reshoring initiatives and increased automation in aerospace and defense. Collaborative robots (cobots) equipped with compact laser heads will enable flexible, small-batch production, particularly in SMEs.
In summary, by 2026, the laser welding process will be defined by smarter, faster, and more adaptable systems serving high-growth industries—especially EVs and advanced manufacturing—while aligning with global trends in digitalization and sustainability.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing the Laser Welding Process (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser welding as a manufacturing process—whether through contract manufacturers, equipment suppliers, or technology partners—organizations often encounter critical challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to compromised product performance, supply chain vulnerabilities, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Process Validation and Qualification
A common oversight is assuming that laser welding capabilities are standardized across vendors. Without rigorous process validation—including procedure qualification records (PQR), weld parameter optimization, and non-destructive testing (NDT) protocols—sourced components may exhibit defects such as porosity, incomplete fusion, or cracking. Always require documented evidence of process control (e.g., adherence to ISO 15614 or AWS D1.1 standards) and insist on sample production runs with full inspection.
Poor Control of Input Variables
Laser welding is highly sensitive to material composition, surface condition, joint fit-up, and environmental factors. When outsourcing, suppliers may not consistently control these variables unless explicitly contractually bound. Failure to specify tolerances for material grade, cleanliness, and part geometry can result in inconsistent weld quality. Include detailed technical specifications and require incoming material certifications.
Lack of Real-Time Process Monitoring
High-quality laser welding increasingly relies on in-process monitoring (e.g., seam tracking, plasma monitoring, or photodiode feedback). Sourcing from vendors without these capabilities increases the risk of undetected defects. Ensure the supplier employs real-time monitoring systems and provides data logs for traceability and root cause analysis.
Insufficient Post-Weld Inspection and Traceability
Without defined inspection criteria and documentation, defects may go undetected until final assembly or in-field failure. Avoid suppliers who skip destructive testing (e.g., microsectioning, tensile tests) or fail to maintain batch-level traceability. Demand comprehensive quality reports and implement a right-to-audit clause.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Ambiguous Ownership of Process Parameters and Fixturing
The laser welding process often involves proprietary parameter sets, custom tooling, and unique fixturing developed during setup. If contracts do not explicitly assign IP ownership, the supplier may claim rights to these assets—limiting your ability to switch vendors or scale production. Clearly define in agreements that all process-specific IP developed for your components belongs to your organization.
Inadequate Protection of Sensitive Product Designs
Sharing detailed CAD models or product specifications with a laser welding supplier increases exposure to IP theft or unauthorized replication. Ensure robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are in place and limit data access to a “need-to-know” basis. Consider using data masking or providing only necessary cross-sections instead of full assemblies when possible.
Failure to Secure Know-How and Trade Secrets
The expertise behind successful laser welding—such as beam oscillation strategies or multi-pass sequencing—may constitute valuable trade secrets. If not protected through employment agreements and supplier contracts, this knowledge can be transferred to competitors. Implement confidentiality clauses that extend beyond the contract term and cover subcontractors.
Overlooking Export Controls and Compliance
Laser welding technology may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR), especially in defense or aerospace applications. Sourcing from international vendors without verifying compliance can lead to legal penalties. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s export licensing status and include compliance obligations in procurement agreements.
Conclusion
To mitigate risks when sourcing laser welding, organizations must prioritize both technical quality controls and legal IP safeguards. Establish clear specifications, audit supplier capabilities, and formalize IP ownership in contracts. Proactive management of these pitfalls ensures reliable production outcomes and protects competitive advantages.
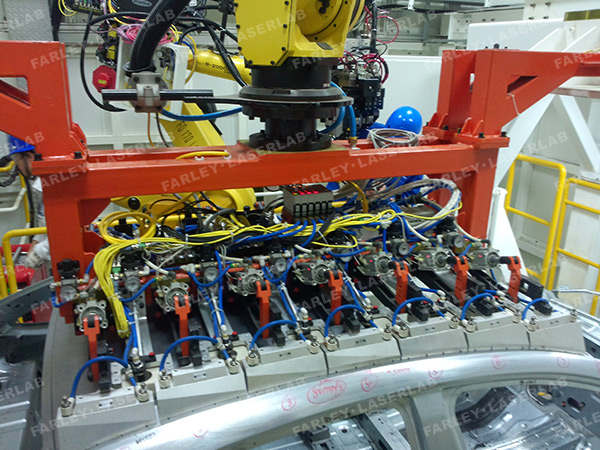
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding Process
Overview of Laser Welding and Regulatory Context
Laser welding is a high-precision manufacturing process that uses a focused laser beam to join materials, primarily metals and thermoplastics. Due to its high energy output, potential for hazardous emissions, and precision requirements, the process is subject to various logistical and compliance considerations. Ensuring adherence to safety, environmental, and quality standards is essential for operational success and regulatory compliance.
Safety and Health Compliance
Laser welding systems are classified under international safety standards such as IEC 60825-1 (Safety of Laser Equipment) and ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers). Key compliance actions include:
– Conducting a laser hazard classification assessment (Class 1 to Class 4).
– Installing appropriate engineering controls: interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency stop mechanisms.
– Requiring personnel to use certified laser safety eyewear with the correct optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength.
– Implementing controlled access zones (Laser Controlled Areas) with warning signs and barriers.
– Providing documented laser safety training for all operators and maintenance personnel.
Environmental and Emission Controls
Laser welding generates particulate matter, fumes, and occasionally hazardous gases (e.g., ozone from high-power lasers). Compliance with environmental regulations such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) standards is mandatory.
– Install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems with HEPA filtration to capture welding fumes and airborne particles.
– Monitor air quality regularly and maintain records of exposure levels (e.g., permissible exposure limits for metals like chromium or nickel).
– Follow hazardous waste disposal procedures for used filters and contaminated materials according to RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act).
Equipment and Facility Requirements
Logistical planning for laser welding must account for facility layout, power supply, and environmental conditions.
– Ensure stable electrical supply with surge protection and grounding to prevent equipment damage.
– Maintain ambient temperature and humidity within manufacturer specifications to protect laser optics and electronics.
– Allocate space for the laser cell, material handling systems, and safety buffer zones.
– Conduct regular preventive maintenance and calibration per ISO 12100 (Safety of Machinery) and manufacturer guidelines.
Quality Assurance and Process Validation
Laser welding processes must comply with industry-specific quality standards such as ISO 9001, AS9100 (aerospace), or ISO 13485 (medical devices).
– Implement documented welding procedures (WPS) and qualify personnel (e.g., per AWS D10.10 or ISO 15614).
– Use in-process monitoring systems (e.g., weld seam tracking, thermal imaging) to ensure consistency.
– Perform non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic, radiographic, or visual inspection as required.
– Maintain traceability of materials, parameters, and inspection results through a quality management system (QMS).
Regulatory Documentation and Audits
Compliance requires thorough documentation and readiness for audits.
– Keep records of safety training, maintenance logs, emission monitoring, and incident reports.
– Maintain laser safety program documentation, including standard operating procedures (SOPs) and risk assessments.
– Prepare for internal and external audits by regulatory bodies, clients, or certification agencies (e.g., TÜV, CSA).
Transportation and Handling of Materials
Logistics for raw materials and finished components must minimize contamination and damage.
– Store materials in dry, clean environments to prevent oxidation or surface contamination that affects weld quality.
– Use appropriate handling equipment (e.g., non-marring fixtures) to protect precision parts.
– Label and segregate materials by alloy type and grade to prevent mix-ups.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
Depending on the application, additional compliance may be required:
– Automotive: IATF 16949, VW 60139 (laser welding standards)
– Medical: FDA 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation)
– Aerospace: Nadcap AC7107 (special process: laser beam welding)
– EU: CE marking per Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMF Directive 2013/35/EU
Conclusion
A robust logistics and compliance framework for laser welding ensures operational safety, product quality, and regulatory alignment. Organizations must integrate safety protocols, environmental controls, quality systems, and documentation practices into daily operations. Regular training, equipment maintenance, and compliance audits are essential for sustained adherence and continuous improvement.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Welding Process:
Sourcing a laser welding process presents a strategic opportunity to enhance manufacturing efficiency, precision, and product quality. Its ability to produce high-strength, consistent welds with minimal heat-affected zones makes it ideal for industries requiring tight tolerances and superior finish, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. While the initial investment in laser welding equipment and skilled personnel is higher compared to conventional welding methods, the long-term benefits—including reduced post-processing, increased automation capability, and improved production throughput—justify the cost for high-volume or high-precision applications.
Careful evaluation of internal capabilities, production volume, material types, and part complexity is essential when deciding to outsource or in-source the laser welding process. Partnering with experienced suppliers offers access to advanced technology and expertise without significant capital expenditure, while in-house implementation provides greater control and faster iteration for proprietary products.
Ultimately, the decision to source laser welding should align with the organization’s broader manufacturing strategy, quality requirements, and scalability goals. With proper planning and partner selection, laser welding can serve as a key enabler of innovation, competitiveness, and operational excellence.