The global laser welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 6.2 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8.4% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, rising automation trends, and the superior accuracy and efficiency offered by laser welding over conventional methods. As industries prioritize high-quality, repeatable welds with minimal thermal distortion, manufacturers are investing heavily in next-generation laser welding systems. In this competitive landscape, nine key players have emerged as leaders, commanding significant market share through innovation, global reach, and comprehensive product portfolios. These manufacturers are shaping the future of industrial joining processes and setting new benchmarks in speed, reliability, and integration capabilities.
Top 9 Laser Welding Machine Used Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Machine – Laser Equipment Manufacturer
Website: dplaser.com
Key Highlights: DPLASER is a leading manufacturer & factory of industrial laser welding, laser cutting, laser marking and laser cleaning machines….
#2 Handheld Laser Welding Machine, Handheld Laser Cleaning …
Website: kaihuanlaser.com
Key Highlights: Added safety protection ensures laser focus only on the metal being welded. Easy operation and maintenance, suitable for both industrial and household use….
#3 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#5 Used Laser Welding for sale on Machineseeker.com
Website: machineseeker.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding machine with 3 kW laser power, laser components from Siemens – welding machine with genuine CE and therefore also German manual, risk analysis….
#6 Used Laser Welding Machines For Sale
Website: surplusrecord.com
Key Highlights: Find new and used Laser Welding Machines for sale from suppliers near you. Ipg, Trumpf, Branson and more….
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
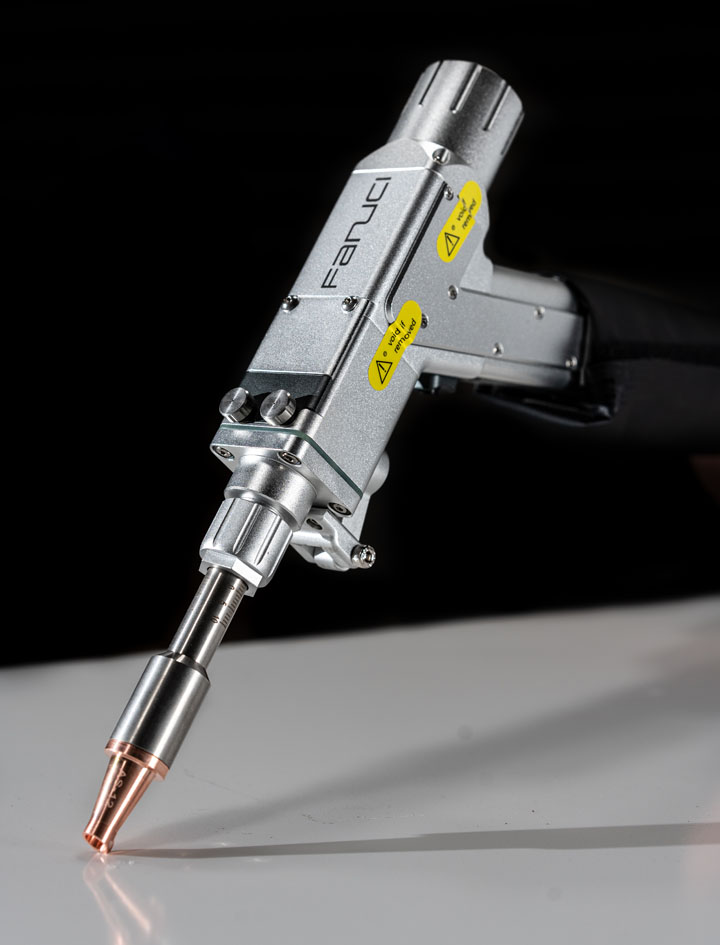
#8 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
#9 Reci Laser
Website: reci-laser.com
Key Highlights: Air-Cooled Fiber Laser Welder. This series products can be widely used in fine cutting, metal welding, surface treatment, 3D printing and rapid prototyping ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding Machine Used
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Used Laser Welding Machines
The global market for used laser welding machines is expected to witness significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and growing emphasis on cost-effective manufacturing solutions. As industries strive for precision, efficiency, and sustainability, the demand for high-performance yet affordable laser welding equipment is fueling a robust secondary market. Below are key trends shaping the 2026 landscape for used laser welding machines:
-
Increased Adoption in Emerging Economies
Developing regions in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are increasingly investing in advanced manufacturing technologies. Used laser welding machines offer a cost-efficient entry point for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking automation. Countries like India, Vietnam, and Mexico are expected to drive demand due to expanding automotive, electronics, and metal fabrication sectors. -
Rise in Automation and Industry 4.0 Integration
As factories adopt smart manufacturing practices, used laser welding systems equipped with IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, and compatibility with robotic arms are gaining favor. Buyers are actively seeking refurbished machines that can integrate seamlessly into digital production lines, boosting the value of technologically upgraded pre-owned units. -
Focus on Sustainability and Circular Economy
Environmental concerns and corporate sustainability goals are encouraging companies to opt for refurbished industrial equipment. Reusing and repurposing laser welding machines reduces electronic waste and carbon footprint associated with manufacturing new units. By 2026, lifecycle extension of industrial machinery is expected to become a key selling point. -
Growth in Refurbishment and Certification Services
The reliability of used laser welding machines is improving due to the rise of certified refurbishment programs. Leading manufacturers and third-party vendors now offer remanufactured systems with warranties, performance guarantees, and updated software. This trend is increasing buyer confidence and expanding the market for premium-grade used equipment. -
Impact of Technological Obsolescence and Upgrades
Rapid innovation in fiber and disk laser technologies is accelerating the turnover of older models. As manufacturers upgrade to higher-efficiency systems, a steady supply of well-maintained, second-hand machines enters the market. This creates opportunities for buyers to access near-state-of-the-art technology at a fraction of the cost. -
Expansion of Online Marketplaces and Global Trade
Digital platforms specializing in used industrial machinery are enhancing accessibility and transparency. By 2026, online auctions, global logistics networks, and digital diagnostics will streamline the buying process, enabling cross-border transactions and broader market reach for used laser welding equipment. -
Sector-Specific Demand Shifts
The automotive and aerospace industries continue to be major users of laser welding, but growing applications in medical device manufacturing, battery production for electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy systems are creating new demand streams. Used machines suitable for thin-sheet welding and high-precision tasks are particularly sought after.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for used laser welding machines is poised for growth, supported by economic, technological, and environmental drivers. As the line between new and refurbished equipment blurs due to quality upgrades and digital integration, the used segment will play an increasingly strategic role in global manufacturing ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Used Laser Welding Machines (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a used laser welding machine can offer significant cost savings, but it comes with critical risks related to both machine quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to downtime, safety hazards, legal exposure, and compromised production quality.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Lack of Maintenance and Service History
Used machines often come without comprehensive maintenance logs, making it difficult to verify if critical components like the laser source, optics, cooling system, and motion controls have been properly serviced. Hidden wear or undocumented repairs can result in unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs post-purchase.
Degraded Laser Source Performance
Laser sources degrade over time. Without proper documentation or testing, it’s challenging to verify the remaining lifespan or current output power and beam quality. A weakened laser may not meet your welding requirements, leading to inconsistent welds or production delays.
Worn or Damaged Optics and Consumables
Optics (lenses, mirrors) and consumables (nozzles, protective windows) are sensitive to contamination and wear. Used machines may have scratched or coated optics that reduce beam efficiency and increase maintenance costs. These components can be expensive to replace if not included in the sale.
Obsolete or Unsupported Control Systems
Older laser welders may run on outdated software or control hardware that is no longer supported by the manufacturer. This can make integration into modern production lines difficult, limit access to technical support, and increase cybersecurity risks.
Hidden Mechanical or Electrical Faults
Without a thorough inspection, internal electrical issues, worn linear guides, or alignment problems in the robotic arm (if applicable) may go unnoticed. These faults can compromise precision, repeatability, and safety.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unauthorized Software or Firmware Modifications
Used machines may contain pirated, cracked, or illegally modified control software. Using such software exposes the buyer to legal liability, voids any remaining warranties, and may prevent legitimate software updates or technical support.
Embedded Proprietary Technology Without Licensing
Some laser welding systems include proprietary algorithms, automation routines, or process libraries protected by IP rights. If the previous owner transferred the machine without proper licensing, continued use could constitute copyright or patent infringement.
Data Residue and Security Risks
Previous users may have stored sensitive production data, customer information, or proprietary welding parameters on the machine’s control system. Failing to perform a secure data wipe risks exposing confidential information and violating data protection regulations.
Lack of Documentation and Licensing Verification
Missing or incomplete software licenses, user manuals, and calibration certificates not only hinder operation but also create compliance gaps. Without verified ownership of software licenses, the new buyer may be held responsible for unauthorized use.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: request full service records, inspect the machine in person or via third-party experts, verify software authenticity and licensing, and ensure data sanitization before commissioning. Whenever possible, purchase from reputable dealers or original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) offering certified pre-owned programs with warranties and IP assurances.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Used Laser Welding Machine
Transporting and importing a used laser welding machine requires careful planning to ensure legal compliance, safety, and smooth customs clearance. This guide outlines key considerations for logistics and regulatory compliance.
Classification & Documentation
Accurate classification and complete documentation are foundational for international shipments.
- HS Code Determination: Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the used laser welding machine (typically under Chapter 84, e.g., 8456.20 for laser cutting/welding machines). This affects import duties and regulations.
- Commercial Invoice: Include detailed machine specifications (make, model, year, serial number), purchase price, and clear indication that it is used equipment.
- Packing List: List all components, accessories, and packaging materials. Specify weights and dimensions accurately.
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Ensure the carrier’s transport document reflects the actual shipment details and terms of sale (e.g., Incoterms® 2020).
- Certificate of Origin: May be required to determine eligibility for preferential tariffs under trade agreements.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): Some countries (e.g., in Africa, Middle East) require third-party inspection reports to verify condition and value.
Regulatory Compliance & Safety Standards
Used industrial lasers are subject to strict safety and environmental regulations.
- Laser Safety Certification (IEC 60825-1): Confirm the machine complies with international laser safety standards. Provide documentation such as a Declaration of Conformity or test report. Non-compliant units may be denied entry.
- Electrical & EMC Compliance: Verify adherence to local electrical safety (e.g., CE, UL, CCC) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards of the destination country.
- RoHS/REACH Compliance: Ensure the machine meets environmental directives restricting hazardous substances, especially when shipping to the EU or other regulated markets.
- FDA Registration (USA): For shipments to the United States, used laser products must be reported to the FDA under 21 CFR 1002 and 1040. Importers may need to file an electronic pre-shipment notification (ePSN).
- Local Import Permits: Check if the destination country requires specific permits for used industrial machinery or laser equipment.
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging ensures machine integrity and safety during transit.
- Secure Crating: Use a sturdy, wooden export crate with internal bracing to prevent movement. Seal against moisture and dust.
- Laser Protection: Disable or secure the laser source. Cover optics and sensitive components to prevent damage.
- Labeling: Clearly mark the crate with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Radiation” warning labels as applicable.
- Weight Distribution: Ensure even weight distribution and use forklift notches for ease of handling.
Transportation & Logistics
Selecting the right carrier and route minimizes delays and damage.
- Mode of Transport: Choose sea freight for large/heavy machines (FCL or LCL); air freight for urgent, smaller units.
- Incoterms® Agreement: Define responsibilities (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) between buyer and seller for transport, insurance, and customs clearance.
- Insurance: Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering damage, loss, and delays.
- Customs Broker: Use a licensed broker in the destination country familiar with industrial machinery and laser product regulations.
Import Procedures & Duties
Be prepared for customs inspections and potential delays.
- Duty & VAT/Tax Calculation: Duties on used machinery may differ from new equipment. Some countries apply higher rates or restrictions.
- Customs Inspection: Authorities may inspect the machine for safety compliance, especially laser and electrical components.
- Environmental or Recycling Fees: Some jurisdictions impose fees for importing used electrical equipment.
- Local Registration: After import, the machine may require registration with local safety or industrial authorities.
End-of-Life & Environmental Responsibility
Ensure compliance with waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) rules.
- Disposal Documentation: If decommissioning, follow local WEEE regulations for proper recycling.
- Hazardous Components: Identify and manage batteries, coolants, or electronic boards containing hazardous materials.
Summary Checklist
- [ ] Confirm HS code and import regulations
- [ ] Prepare complete shipping documents
- [ ] Verify laser and electrical safety certifications
- [ ] Secure machine and package for transit
- [ ] Arrange compliant transportation and insurance
- [ ] Engage customs broker in destination country
- [ ] Plan for post-import registration or inspection
Adhering to these logistics and compliance steps will help ensure a successful and lawful import of a used laser welding machine.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, sourcing a used laser welding machine can be a cost-effective and efficient solution for businesses aiming to enhance their manufacturing capabilities without the significant investment required for new equipment. Through careful evaluation of machine specifications, condition, service history, and vendor reliability, it is possible to acquire a high-performing system that meets production needs. Factors such as technological compatibility, maintenance requirements, warranty availability, and after-sales support must be thoroughly assessed to ensure long-term reliability and operational efficiency. When properly vetted, a used laser welding machine offers excellent value, enabling companies to leverage advanced welding technology while optimizing capital expenditure. Ultimately, a strategic and informed approach to purchasing pre-owned equipment can deliver substantial benefits, supporting productivity and competitiveness in today’s demanding industrial environment.