The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing across high-value industries such as jewelry, automotive, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is particularly pronounced in the jewelry sector, where manufacturers are increasingly adopting laser welding technology to achieve superior precision, reduce material waste, and enhance production efficiency. The shift toward automation and the need for seamless, high-strength welds in delicate precious metal components have made laser welding an indispensable tool for modern jewelry production. As competition intensifies and craftsmanship standards rise, leading manufacturers are turning to advanced laser systems that offer micron-level accuracy, minimal heat distortion, and compatibility with gold, silver, platinum, and gem-embedded settings. In this evolving landscape, selecting the right laser welding solution is critical—here are the top 8 systems shaping the future of jewelry manufacturing.
Top 8 Laser Welding For Jewelry Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Sunstone Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: LASER TECHNOLOGY High-precision laser welding, engraving and cutting for perfect control and flexibility….
#3 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a pioneer in the field of mobile laser welding, ALPHA LASER GmbH offers a wide range of high-quality laser welding devices. This includes laser welding ……
#4 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals in the jewellery, ……
#5 The Italian Style in Welding DaDo
Website: dadowelder.com
Key Highlights: In jewelry DaDo is a welder that is perfectly suited to all those who need to repair small jewelry. In the dental sector, it is an indispensable tool for all ……
#6 Machinery and laser systems
Website: sisma.com
Key Highlights: More than 130 machine models for the automatic production of gold chains · Laser systems for marking, welding, cutting and engraving. · Laser systems for welding….
#7 Jewelry Laser Welding Machine
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: BK-JW60X 60W Desktop YAG Welding Machine Small Mini YAG CCD Laser Welder for Metal Stainless Steel Gold Jewelry. $3,400.00 USD $3,700.00 USD….
#8 What is the best laser welder for jewelry?
Website: stuller.com
Key Highlights: One key feature is the tri-access welding chamber. The pulse shaping technology allows for precise energy control, minimizing heat impact on delicate materials….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding For Jewelry

2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding in Jewelry
The laser welding market for jewelry is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and increasing demand for precision and sustainability in jewelry manufacturing. As jewelers seek faster, cleaner, and more efficient production methods, laser welding is emerging as a cornerstone technology in both artisanal and industrial settings. This analysis explores the key trends shaping the laser welding for jewelry sector in 2026.
Advancements in Laser Technology and Equipment
By 2026, laser welding systems for jewelry are expected to feature greater precision, improved user interfaces, and enhanced automation. Manufacturers are investing in compact, high-efficiency fiber lasers that offer finer control over weld quality—critical for delicate materials like gold, platinum, and silver. Innovations such as real-time monitoring, AI-assisted weld path planning, and integration with CAD/CAM systems are becoming standard, enabling jewelers to achieve consistent results with minimal rework. Portable and benchtop laser welders are also gaining traction, especially among small workshops and independent designers, making the technology more accessible.
Growing Demand for Customization and On-Demand Manufacturing
Consumer demand for personalized and bespoke jewelry continues to rise, and laser welding supports this trend by enabling intricate designs and quick assembly without compromising structural integrity. In 2026, laser welding is increasingly integrated into on-demand and digital manufacturing workflows, allowing jewelers to produce custom pieces efficiently. The ability to weld small components without excessive heat distortion makes laser technology ideal for setting stones, resizing rings, or repairing fine details—tasks traditionally challenging with conventional soldering.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
Sustainability is a growing priority in the luxury goods sector, and the jewelry industry is responding by adopting greener production methods. Laser welding contributes to environmental goals by reducing the need for flux and solder, minimizing material waste, and lowering energy consumption compared to traditional torch welding. As regulations tighten and consumers favor eco-conscious brands, jewelers are turning to laser welding as a clean, precise alternative that aligns with circular economy principles. Recycled gold and ethically sourced materials pair well with laser techniques, further enhancing brand sustainability narratives.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
The adoption of laser welding in jewelry manufacturing is accelerating in emerging economies such as India, China, and Southeast Asia, where skilled labor meets growing domestic and export demand. By 2026, local manufacturers in these regions are investing in laser technology to improve product quality, reduce production time, and compete globally. Government initiatives supporting advanced manufacturing and vocational training in gemology and precision craftsmanship are also facilitating technology uptake.
Integration with Digital Workflows and Industry 4.0
Laser welding systems are increasingly being integrated into broader digital jewelry ecosystems. In 2026, seamless connectivity with 3D printing, scanning, and design software enables end-to-end digital production. Smart factories and small-scale studios alike leverage IoT-enabled laser welders that collect performance data, support predictive maintenance, and ensure traceability—key for quality assurance and compliance in luxury goods. This integration represents a shift toward Industry 4.0 principles in what has traditionally been a craft-oriented industry.
Conclusion
By 2026, laser welding for jewelry will be a pivotal technology, bridging craftsmanship and innovation. Driven by advances in equipment, sustainability imperatives, and digital transformation, the market is set for sustained growth. As jewelers adopt laser welding not just for efficiency but also for creative and environmental advantages, the technology will become a standard tool in modern jewelry production across global markets.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welding for Jewelry: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser welding services or equipment for jewelry manufacturing, businesses—especially high-end or design-focused brands—must navigate several critical pitfalls. Overlooking these can lead to compromised product quality, loss of competitive advantage, or even legal disputes. Below are key challenges related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Weld Integrity
One of the most common quality issues in laser welding jewelry is inconsistent weld strength and appearance. Poorly calibrated equipment or unskilled operators can result in weak joints, porosity, or discoloration, particularly on delicate pieces like fine chains or thin gold bands. This compromises both the aesthetic and structural integrity of the jewelry.
Improper Material Compatibility
Laser welding parameters must be precisely adjusted for different alloys (e.g., 14k vs. 18k gold, white gold vs. platinum). Sourcing from providers without expertise in precious metals can lead to cracking, warping, or contamination due to incorrect power settings or shielding gas use.
Lack of Post-Weld Finishing Expertise
Even a technically sound laser weld may require expert polishing and finishing to become invisible. Sourcing partners who lack integrated finishing capabilities may deliver parts that still show seams or heat marks, undermining the value of using laser welding in the first place.
Insufficient Quality Control Processes
Vendors without robust inspection protocols—such as magnified visual checks, dye penetrant testing, or microhardness testing—risk delivering substandard work. Without documented QC steps, traceability and consistency across batches cannot be guaranteed.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unprotected Design Exposure
Sharing CAD files, wax models, or prototypes with third-party laser welding providers increases the risk of design theft or unauthorized reproduction. This is especially concerning when working with overseas or unvetted vendors who may not adhere to strict confidentiality standards.
Weak or Absent Confidentiality Agreements
Many suppliers, particularly smaller workshops, may not use comprehensive non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or may use vague terms that fail to protect specific design elements. This leaves IP vulnerable, especially in jurisdictions with lax enforcement of intellectual property rights.
Lack of Clear IP Ownership Clauses
Contracts that do not explicitly state that the client retains full ownership of designs, tooling, and any derivative works can lead to disputes. Some vendors may claim partial rights to designs developed during the manufacturing process, especially if modifications are made for weldability.
Inadequate Data Security Measures
Digital design files shared for laser welding programming are prone to unauthorized access or leaks if the supplier lacks secure data systems. Cloud storage without encryption, unsecured file transfers, or shared workstations increase the risk of IP breaches.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Vet suppliers for proven experience with precious metals and certification (e.g., ISO standards).
– Require sample welds and conduct third-party material testing.
– Use detailed contracts with strong IP clauses and jurisdiction-specific enforceability.
– Limit design file access to need-to-know personnel and use watermarked or low-resolution previews when possible.
– Invest in suppliers who offer end-to-end confidentiality and secure digital workflows.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, jewelry brands can leverage laser welding technology safely and effectively while protecting their craftsmanship and brand value.
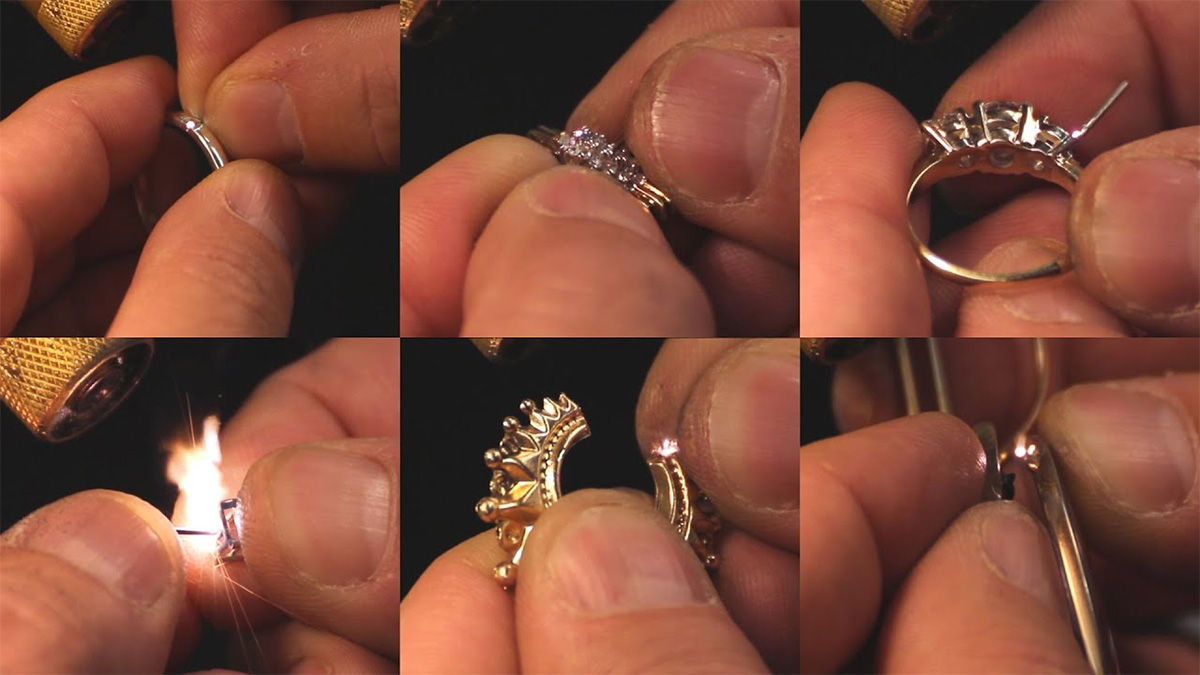

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding in Jewelry Manufacturing
Overview of Laser Welding in Jewelry Production
Laser welding has become a cornerstone technology in modern jewelry manufacturing due to its precision, minimal heat distortion, and ability to work with delicate designs. This guide outlines the logistics and compliance considerations essential for integrating and operating laser welding systems safely and legally within a jewelry production environment.
Equipment Selection and Sourcing
When procuring a laser welding system, verify that the equipment meets international safety standards such as IEC 60825-1 (laser safety) and complies with regional electrical regulations (e.g., CE in Europe, UL in North America). Choose suppliers with proven support networks to ensure timely delivery, installation, and ongoing technical assistance. Consider shipping methods, import duties, and customs documentation if sourcing equipment internationally.
Import/Export Regulations for Laser Equipment
Laser systems are often subject to export control regulations due to their dual-use potential. In the U.S., check compliance with the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) under the Department of Commerce. Classify the laser system using the appropriate Export Control Classification Number (ECCN). Documentation such as a commercial invoice, packing list, and export license (if required) must accompany shipments. For intra-EU or other regional trade zones, ensure adherence to local customs protocols.
Workplace Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser welding operations must comply with occupational health and safety standards. Install appropriate engineering controls, including interlocks, beam enclosures, and fume extraction systems. Follow OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent national guidelines (e.g., HSE in the UK) for workplace safety. Provide laser safety training certified by recognized bodies and designate a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) if required. Protective eyewear specific to the laser’s wavelength must be worn at all times.
Electrical and Facility Requirements
Ensure your facility meets the electrical specifications for the laser system, including voltage, grounding, and circuit capacity. Install dedicated power lines if necessary to prevent interference with other equipment. Maintain a clean, climate-controlled environment to protect sensitive optics and electronics. Plan workspace layout to allow safe access, ventilation, and emergency egress.
Material Handling and Traceability
Jewelry laser welding often involves precious metals (e.g., gold, platinum, silver). Establish secure logistics for receiving, storing, and tracking materials to prevent loss or contamination. Use inventory management systems that support traceability from raw material to finished product, especially for conflict-free sourcing compliance (e.g., following OECD Due Diligence Guidance).
Waste Management and Environmental Compliance
Laser welding generates fine metallic particulates and fumes. Install certified fume extraction units with HEPA or ULPA filtration. Dispose of collected waste in accordance with local environmental regulations—precious metal residues may require specialized recycling. Maintain records of waste disposal to demonstrate compliance with EPA (U.S.) or equivalent environmental agencies.
Maintenance, Calibration, and Documentation
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for optimal performance and safety. Keep detailed logs of service, calibration, and component replacements. Regular calibration ensures weld consistency and product quality, and may be required for ISO 9001 certification. Store all compliance-related documents (safety certifications, training records, maintenance logs) for audit readiness.
Quality Assurance and Industry Standards
Adopt quality control protocols aligned with jewelry industry standards. Use non-destructive testing (e.g., magnification, dye penetrant) to verify weld integrity. Maintain compliance with hallmarking laws in target markets (e.g., UK Hallmarking Act, U.S. jewelry guidelines from FTC). Document all quality checks to support traceability and customer trust.
Training and Personnel Certification
Ensure all operators are formally trained in laser welding techniques and safety procedures. Training should cover machine operation, emergency protocols, and proper handling of materials. Certifications from recognized institutions or equipment manufacturers enhance compliance and proficiency. Maintain up-to-date training records for all personnel.
Insurance and Liability Considerations
Secure appropriate business insurance coverage, including equipment, liability, and worker’s compensation. Confirm that your policy covers laser operations and associated risks such as fire or eye injury. Review contractual agreements with suppliers and clients to clarify responsibilities related to equipment use, material loss, and product defects.
Conclusion
Successfully implementing laser welding in jewelry manufacturing requires careful attention to logistics, safety, and regulatory compliance. By adhering to this guide, businesses can ensure efficient operations, legal conformity, and high-quality output while protecting personnel and assets. Regular audits and staying informed on regulatory updates are key to maintaining long-term compliance.
Conclusion: Sourcing Laser Welding for Jewelry
Sourcing laser welding technology for jewelry manufacturing offers significant advantages in terms of precision, efficiency, and design flexibility. The ability to perform highly accurate, localized welds with minimal heat distortion makes laser welding ideal for delicate and intricate jewelry pieces, preserving fine details and surrounding materials. It enables repairs and adjustments without damaging gemstones or requiring re-plating, reducing material waste and rework.
When sourcing laser welding services or equipment, it is essential to evaluate the technical capabilities of suppliers, including beam precision, pulse control, and compatibility with various metals. Partnering with experienced providers or investing in in-house systems can enhance production consistency, reduce lead times, and elevate the overall quality of finished products.
Moreover, as consumer demand grows for custom, high-quality, and sustainably produced jewelry, integrating laser welding into the workflow positions brands competitively in the market. Ultimately, sourcing laser welding—whether through outsourcing to specialized workshops or adopting the technology internally—represents a strategic investment in innovation, craftsmanship, and long-term operational efficiency within the modern jewelry industry.