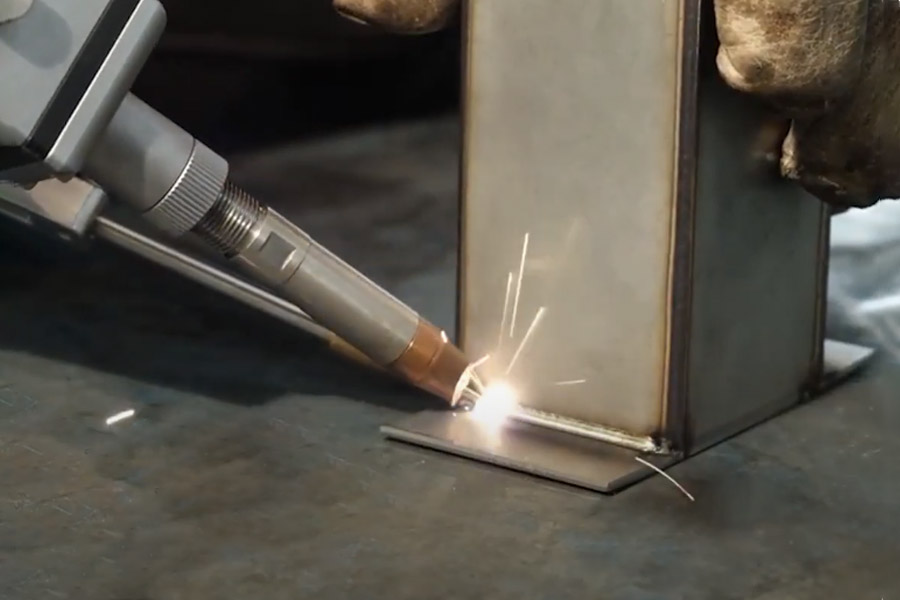
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining technologies across automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of automation, the shift toward lightweight vehicle manufacturing, and advancements in fiber laser technology. As industries prioritize efficiency, speed, and weld quality, laser welding has emerged as a cost-effective alternative to traditional methods. With intensified competition and technological diffusion, manufacturers worldwide are optimizing production costs while maintaining performance standards. This growing landscape has given rise to a new wave of cost-competitive laser welding system producers, particularly in Asia-Pacific, where lower operational costs and strong industrial ecosystems support scalable innovation. Based on market pricing trends, production capacity, and technology accessibility, we’ve identified the top 10 laser welding manufacturers delivering superior value without compromising on quality.
Top 10 Laser Welding Cost Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#3 How Much Does a Laser Welder Cost?
Website: cobot.systems
Key Highlights: Prices can range from $2,500 to $10,000 for basic models suitable for amateur use, around $21,000 to $25,000 for manufacturer-grade systems, ……
#4 Cost of Laser Welding
Website: kirinlaser.com
Key Highlights: Depending on the material and thickness, the cost per meter can range from as little as $0.80 to $2.00….
#5 All Types of Laser Welding Machines Prices for Reference
Website: megmeet-welding.com
Key Highlights: Prices generally range from $5,000 to $15,000. They are commonly used in electronics, medical, and small-scale manufacturing sectors. Mid-Range ……
#6 Laser Welding
Website: precollc.com
Key Highlights: Preco provides laser welding processes including robotics, tooling and material handling. The process can be used with just about any materials that are ……
#7 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#8 Laser Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: 6–7 day deliveryLaser Welders · Compare. Original price $5,200.00 – Original price $5,700.00 · Compare. Original price $21,900.00 – Original price $21,900.00 · Compare. Original …..
#9 How Much Does a Laser Welding machine Cost? (2024)
Website: longxinlaser.com
Key Highlights: Range: $4,700 – $26,300 · Popular models: Entry-level (1000W): $5,000 – $8,000; Mid-range (1500W): $10,000 – $15,000; High-end (2000W+): $18,000 ……
#10 Laser Welder Cost Guide
Website: fab-line.com
Key Highlights: Is Laser Welding Expensive? Your objectives will determine this. A $20K–$60K fibre laser is a wise investment for many mid-sized manufacturing firms since it:….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding Cost

2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding Cost: Key Drivers and Projections
As the manufacturing sector continues to evolve, laser welding technology is poised for significant transformation by 2026. The cost dynamics of laser welding systems and services are expected to be shaped by technological advancements, supply chain developments, and shifting industry demands. Below is an analysis of the major trends influencing laser welding costs in the coming years.
Technological Advancements Driving Cost Efficiency
By 2026, rapid improvements in fiber and diode laser technologies are expected to reduce both the capital and operational costs of laser welding systems. Fiber lasers are becoming more energy-efficient, with higher wall-plug efficiency (up to 50% or more), which reduces electricity consumption and lowers long-term operating expenses. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive maintenance systems will minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan, further improving cost-effectiveness. Automation and robotic integration will also streamline production, reducing labor costs and increasing throughput, thereby lowering the cost per weld.
Increased Adoption and Economies of Scale
Growing adoption across industries—including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics—will drive economies of scale in laser welding equipment manufacturing. As demand rises, particularly in emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, manufacturers are expected to expand production capacity, leading to lower unit costs. This widespread adoption will also encourage competition among laser system suppliers, resulting in more competitive pricing and reduced barriers to entry for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Material and Component Cost Volatility
Despite overall cost reductions, fluctuations in raw material prices—especially rare earth elements used in laser diodes and optical components—could impact system costs. Supply chain resilience will be critical; geopolitical tensions and trade policies may influence the availability and pricing of key components. However, ongoing research into alternative materials and localized manufacturing could mitigate these risks by 2026, stabilizing or even reducing input costs over time.
Shift Toward High-Power and Hybrid Systems
The trend toward high-power laser systems (10 kW and above) for applications such as electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing and heavy industrial welding may initially increase upfront costs. However, these systems offer faster processing speeds and deeper penetration, improving productivity and reducing cost per part. Additionally, hybrid laser-arc welding systems are gaining traction, combining the precision of lasers with the gap-bridging capabilities of arc welding. While hybrid systems may carry a higher initial price tag, their versatility and efficiency are expected to deliver long-term cost savings.
Service and Consumables Market Growth
As laser welding systems become more prevalent, the aftermarket for maintenance, training, and consumables (e.g., protective lenses, nozzles) will expand. By 2026, predictive analytics and remote monitoring will enable proactive service models, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Subscription-based service packages may become common, offering predictable operational expenditures and lowering total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
By 2026, the overall cost of laser welding is expected to decline on a per-unit basis due to technological innovation, economies of scale, and increased competition. While initial investment in advanced systems may remain significant, the total cost of ownership will likely decrease, making laser welding more accessible and economically viable across a broader range of applications and industries. Manufacturers who adopt these technologies early will benefit from improved efficiency, precision, and long-term cost advantages.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Welding: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser welding services or equipment, organizations often focus heavily on upfront costs while overlooking critical long-term risks related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these aspects can lead to project delays, compromised product integrity, legal disputes, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Overlooking Quality Consistency and Process Validation
One of the most frequent mistakes is assuming that all laser welding providers deliver the same level of quality. Laser welding is a precision process highly sensitive to parameters such as power density, beam alignment, material composition, and joint fit-up. Sourcing from vendors without rigorous quality controls can result in:
- Inconsistent weld strength and penetration, leading to premature product failure
- Excessive spatter or porosity that compromises structural integrity and aesthetics
- Lack of traceability and documentation, making it difficult to meet industry standards (e.g., ISO 3834, AWS D1.1)
To mitigate this, buyers must verify that suppliers have certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), conduct regular process validation (e.g., through weld procedure qualification records), and provide detailed inspection reports including non-destructive testing (NDT) results.
Insufficient Control Over Intellectual Property Rights
Laser welding often involves proprietary designs, specialized tooling, and unique process parameters developed by the client. A major pitfall occurs when sourcing agreements fail to clearly define IP ownership and confidentiality terms. Risks include:
- Unintended IP leakage if the supplier uses client designs or processes for other customers
- Lack of contractual clarity on who owns improvements or derivative works developed during the project
- Inadequate data security measures, exposing sensitive manufacturing data to unauthorized access
To protect IP, organizations should ensure contracts explicitly state that all client-provided designs, specifications, and process data remain the client’s exclusive property. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clauses restricting the use and replication of proprietary information are essential. Additionally, vetting the supplier’s cybersecurity and data handling practices is critical, especially when sharing CAD files or process parameters.
Choosing Vendors Based Solely on Low Cost
While cost is an important factor, selecting a laser welding partner based primarily on price often leads to compromised quality and hidden expenses. Low-cost providers may:
- Use outdated or poorly maintained equipment, affecting weld repeatability
- Employ undertrained personnel, increasing the risk of defects
- Cut corners on quality checks and documentation
This can result in higher total cost of ownership due to rework, warranty claims, or product recalls. A better approach is to perform a total cost analysis that includes quality metrics, delivery reliability, technical support, and compliance history.
Neglecting Long-Term Support and Service Capabilities
Laser welding systems require regular maintenance, calibration, and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers with limited after-sales service or unclear support terms can lead to extended downtime and reduced productivity. Buyers should assess the vendor’s service network, spare parts availability, response time, and training offerings before making a decision.
In summary, successful sourcing of laser welding services requires a balanced evaluation of cost, quality assurance, and IP protection. Organizations that proactively address these pitfalls are better positioned to ensure reliable, secure, and cost-effective manufacturing outcomes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding Costs
Understanding the logistics and compliance aspects tied to laser welding is essential for accurate cost forecasting, operational efficiency, and regulatory adherence. These factors influence both direct and indirect expenses across the supply chain and production lifecycle.
Transportation and Material Handling
Laser welding operations require precise delivery and storage of components, consumables, and equipment. Shipping high-precision parts or laser systems often demands specialized packaging, climate-controlled transport, and insurance against damage, increasing logistics costs. Just-in-time (JIT) delivery strategies can reduce inventory holding costs but may increase transportation frequency and associated expenses. Handling heavy or sensitive laser components may require trained personnel and safety protocols, adding labor and training costs.
Import/Export Regulations and Duties
If laser welding systems, optics, or raw materials are sourced internationally, compliance with import/export regulations becomes critical. High-powered lasers may be subject to export controls under frameworks such as the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), requiring licensing and documentation. Tariffs, customs duties, and value-added taxes (VAT) can significantly affect the landed cost of equipment and materials. Delays due to non-compliance can lead to production downtime, further increasing operational costs.
Safety and Environmental Compliance
Laser welding involves high-intensity radiation, fumes, and potential fire hazards, requiring adherence to occupational safety standards such as OSHA (U.S.) or similar regulations globally. Facilities must invest in protective enclosures, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and laser safety officers (LSO) to ensure compliance. Non-compliance risks fines, shutdowns, and increased insurance premiums. Additionally, disposal of hazardous waste (e.g., metal fumes, used filters) must follow environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, REACH), contributing to operational and compliance-related costs.
Certification and Standards Compliance
Laser welding processes may need to meet industry-specific certifications such as ISO 3834 (welding quality requirements), AS9100 (aerospace), or AWS D1.1 (structural welding). Achieving and maintaining these certifications involves audits, documentation, and process validation, all of which add to administrative and labor costs. Use of certified materials and qualified welders further influences cost structures. Non-compliant welds can result in rework, recalls, or rejection of parts, significantly increasing project expenses.
Facility and Utility Requirements
Laser welding systems require stable power supplies, cooling systems, and compressed air, which must be factored into facility planning and utility costs. Compliance with electrical safety codes (e.g., NFPA 70) and building regulations may necessitate infrastructure upgrades. Proper grounding, shielding, and fire suppression systems are mandatory in many jurisdictions, adding capital and maintenance expenses. Location-based utility rates and energy efficiency standards also impact long-term operating costs.
Documentation and Traceability
Regulated industries (e.g., medical, aerospace, automotive) require full traceability of welding parameters, materials, and operator qualifications. This necessitates digital data logging, secure storage, and audit-ready documentation systems. Investments in welding management software and data compliance tools contribute to operational costs but are essential for meeting regulatory expectations and avoiding penalties.
By proactively managing logistics and compliance requirements, organizations can mitigate risks, avoid unexpected costs, and ensure that laser welding operations remain both efficient and legally sound.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Welding Cost:
Sourcing laser welding services involves a careful evaluation of multiple cost factors, including equipment investment, labor, material compatibility, production volume, and required precision. While laser welding typically entails higher initial setup costs compared to traditional welding methods, its advantages—such as superior precision, reduced material distortion, faster processing speeds, and lower post-welding finishing requirements—can lead to significant long-term savings, especially in high-volume or high-precision applications.
Effective cost optimization can be achieved by selecting the right type of laser welding (e.g., fiber, CO₂, or pulsed laser) based on material and joint requirements, partnering with experienced suppliers who offer competitive pricing and value-added services, and considering in-house automation for scalability. Additionally, bulk production and design standardization can further reduce per-unit costs.
Ultimately, the total cost of ownership—not just the unit price—should guide sourcing decisions. A thorough cost-benefit analysis, combined with supplier evaluations and pilot testing, ensures that laser welding solutions deliver both economic efficiency and high-quality results aligned with technical and production goals.