The global laser welding and cutting machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the laser cutting machine market was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the broader industrial laser systems market, which includes both welding and cutting applications, will expand at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology and increasing automation in production environments. As manufacturers prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and energy savings, the adoption of high-performance laser systems continues to accelerate. Within this expanding landscape, a select group of leading manufacturers are spearheading innovation, delivering next-generation solutions that redefine manufacturing capabilities. Here are the top 9 laser welding and cutting machine manufacturers shaping the future of industrial fabrication.
Top 9 Laser Welding And Cutting Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
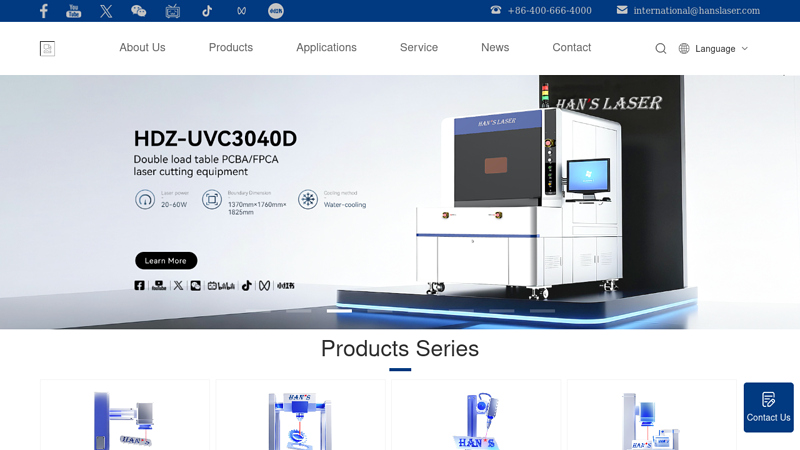
#1 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now become the flagship of Chinese national laser ……
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine and CO2 Laser Cutter Manufacturer …
Website: gwklaser.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer of laser cutting machine, CO2 laser cutter, laser welding machine, laser bending machine and laser cleaning machine, etc….
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered by the most experienced engineers and design ……
#5 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#6 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
#8 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
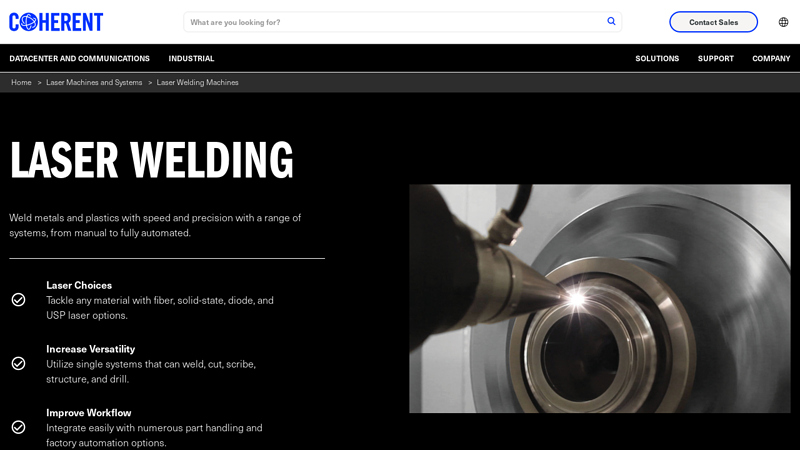
#9 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: MPS Series are integrated systems for laser welding, cutting, structuring, and drilling, as well as for numerous high-precision USP laser-enabled applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding And Cutting Machine
H2: Market Trends for Laser Welding and Cutting Machines in 2026
The global market for laser welding and cutting machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving industrial demands, and macroeconomic shifts. As industries prioritize automation, precision, and sustainability, laser-based manufacturing solutions are becoming central to modern production systems. This analysis explores key H2-level trends expected to shape the laser welding and cutting machine market in 2026.
1. Increased Adoption of Fiber Lasers
Fiber laser technology continues to dominate the market due to its superior efficiency, lower maintenance, and higher beam quality compared to CO₂ lasers. By 2026, fiber lasers are projected to account for over 75% of new laser cutting and welding machine installations. Their ability to cut reflective metals like copper and aluminum with minimal energy loss makes them ideal for electric vehicle (EV) and battery manufacturing, two rapidly expanding sectors.
2. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Laser systems are increasingly being integrated into smart factories through IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven process optimization. In 2026, most high-end laser machines will feature predictive maintenance algorithms, cloud-based diagnostics, and digital twin capabilities. This integration improves uptime, reduces operational costs, and enables remote supervision across global supply chains.
3. Growth in Electric Vehicle and Battery Production
The surge in EV adoption is directly fueling demand for precision laser welding in battery pack assembly, motor components, and lightweight frame structures. Laser welding offers the speed and consistency required for high-volume battery production. By 2026, automotive and battery manufacturing are expected to be the largest end-use sectors for laser welding machines, particularly in China, Europe, and North America.
4. Expansion in Emerging Markets
Countries in Southeast Asia, India, and Eastern Europe are investing heavily in advanced manufacturing infrastructure. Government initiatives to boost local production (e.g., India’s “Make in India”) are accelerating the adoption of laser systems. By 2026, these regions will represent over 30% of incremental market growth, driven by rising labor costs and the need for higher production quality.
5. Advancements in Ultrafast and High-Power Lasers
Ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers are gaining traction in high-precision applications such as medical device manufacturing and electronics. Simultaneously, high-power lasers (10 kW and above) are enabling faster cutting of thick metals in heavy industries like shipbuilding and construction. By 2026, hybrid systems combining multiple laser types in a single platform are expected to emerge, offering greater flexibility.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient technologies. Modern laser machines consume up to 30% less energy than older models and reduce material waste through precision processing. In 2026, energy efficiency will be a key differentiator in procurement decisions, with OEMs emphasizing low total cost of ownership (TCO) and carbon footprint metrics.
7. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market is witnessing increased consolidation, with major players like TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, Han’s Laser, and Bystronic acquiring niche technology firms to expand their portfolios. By 2026, partnerships between laser manufacturers and robotics companies (e.g., KUKA, Fanuc) will become more common, enabling turnkey automated solutions for SMEs.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser welding and cutting machine market will be characterized by technological convergence, sector-specific customization, and global geographic diversification. The integration of AI, fiber laser dominance, and alignment with green manufacturing will define competitive advantage. Companies that invest in smart, scalable, and sustainable laser solutions will lead the next phase of industrial transformation.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welding and Cutting Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser welding and cutting machines involves significant investment and technical complexity. While cost and delivery time are important considerations, overlooking quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to severe long-term consequences, including safety hazards, production downtime, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Lack of Certifications
One of the most common mistakes is selecting suppliers based solely on price without verifying their technical capabilities or quality management systems. Reputable manufacturers should possess recognized certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management, CE marking (for EU compliance), or FDA registration (if applicable). Failure to confirm these credentials increases the risk of receiving substandard equipment with inconsistent performance, poor beam quality, or unreliable component integration.
Poor Component Quality and Hidden Substitutions
Some suppliers may advertise high-end components (e.g., IPG or TRUMPF lasers, Siemens CNC systems) but substitute them with lower-quality alternatives during assembly. This bait-and-switch practice often goes unnoticed until after installation. Buyers should insist on component-level documentation, conduct factory inspections, and include contractual clauses specifying exact brands and models.
Inconsistent Machine Calibration and Performance Testing
Laser machines require precise calibration for optimal performance. Machines shipped without proper factory acceptance testing (FAT) or comprehensive performance validation may exhibit issues such as misaligned optics, inaccurate beam focus, or unstable power output. Ensure suppliers perform standardized tests—like cutting/welding precision trials, thermal stability checks, and safety interlock verification—before shipment.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and spare parts. Sourcing from suppliers with weak or nonexistent local support networks can result in prolonged downtime and inflated repair costs. Evaluate the supplier’s service infrastructure, response time guarantees, and long-term spare parts availability before finalizing a purchase.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Risk of Infringing Third-Party Patents
Laser technology is heavily patented, covering aspects like beam delivery systems, cooling mechanisms, and control software. Purchasing a machine from a supplier that uses patented technology without licensing exposes the buyer to potential infringement lawsuits. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP compliance and request documentation proving legitimate use of core technologies.
Use of Counterfeit or Pirated Software
Some low-cost machines come with unauthorized or cracked versions of control software (e.g., licensed CNC or laser processing software). Using such software not only violates copyright laws but can also introduce security vulnerabilities and limit future upgrades. Verify software licenses and insist on genuine, traceable software installations.
Lack of IP Ownership Clauses in Contracts
When customizing machines or developing proprietary processes, buyers may assume they own the resulting IP. However, without explicit contractual agreements, the supplier may retain rights to modifications, designs, or process parameters. Clearly define IP ownership, transfer rights, and usage limitations in procurement contracts to avoid disputes.
Exposure to Reverse Engineering and Design Theft
Working with untrusted suppliers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, increases the risk that your proprietary configurations or production methods could be copied or resold. Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), limit technical disclosures, and consider engaging legal counsel familiar with international IP law when sourcing from high-risk jurisdictions.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, buyers can ensure they acquire reliable, compliant, and legally sound laser welding and cutting systems that support long-term operational success.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding and Cutting Machines
General Overview
Laser welding and cutting machines are high-precision industrial tools that utilize focused laser beams for metal processing. Due to their complexity, power requirements, and safety implications, their international logistics and regulatory compliance require careful planning. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, legal, and efficient transport and deployment.
Classification & Regulatory Framework
Laser welding and cutting machines are classified under various international and national regulatory systems. Key classifications include:
– HS Code (Harmonized System): Typically 8456.11 or 8456.12 (Machines using laser or other light/photonic radiation for working metal).
– Export Controls: Subject to dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation, U.S. EAR – Export Administration Regulations) if power output exceeds thresholds or if intended for military applications.
– Laser Safety Classification: Classified under IEC 60825-1 (international) or FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 (U.S.) as Class 1, 3B, or 4 lasers. Most industrial machines fall under Class 4 and require safety interlocks, warning labels, and protective housings.
Export Documentation
Ensure the following documentation is prepared and accurate:
– Commercial Invoice (with technical specifications, value, and HS codes)
– Packing List (including gross/net weights, dimensions, and packaging type)
– Certificate of Origin
– Technical Data Sheet and User Manual (including laser class, power, wavelengths)
– Compliance Certificates (CE, UKCA, FCC, RoHS, REACH if applicable)
– Export License (if required by destination country or based on power/application)
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Industrial laser machines are sensitive to shock, moisture, and temperature. Proper packaging is essential:
– Use sturdy, wooden export crates with internal bracing and vibration-dampening materials.
– Secure all optical components, gantries, and moving parts with transit locks or brackets.
– Include desiccant packs to prevent condensation during transit.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” warnings.
– Remove or securely cover laser optics; store lenses and mirrors separately if advised.
Transportation Logistics
- Mode of Transport: Ocean freight is common for full machines; air freight may be used for urgent or high-value components.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection: Conduct quality and safety checks before crating.
- Customs Clearance: Ensure all documents are in order to avoid delays. Use a licensed customs broker familiar with industrial machinery.
- Insurance: Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering damage, loss, and delays.
Import Compliance by Region
European Union (EU):
– CE Marking required per Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
– Compliance with EN standards (e.g., EN 12100, EN 60204-1).
– Registration under REACH and RoHS directives for hazardous substances.
United States:
– FDA CDRH (Center for Devices and Radiological Health) registration required for Class III and IV lasers.
– Compliance with OSHA safety standards (e.g., 29 CFR 1910.133 for eye protection).
– FCC Part 18 compliance for electromagnetic interference.
China:
– CCC (China Compulsory Certification) may apply depending on configuration.
– GB standards compliance (e.g., GB/T 18975 for laser safety).
– Customs clearance via China Electronic Port system.
Other Regions:
– Canada: CSA Z462 and ICES-001 compliance.
– Australia: RCM mark and compliance with AS/NZS IEC 60825.
– Japan: PSE mark and compliance with MHLW Ordinance 144.
On-Site Installation & Safety Compliance
- Verify local electrical supply compatibility (voltage, phase, frequency).
- Ensure proper grounding and installation in a well-ventilated area with fume extraction.
- Conduct laser safety audits and install protective barriers, interlocks, and warning signs.
- Train operators on laser safety (ANSI Z136.1 in the U.S. or IEC 60825 internationally).
- Maintain records of maintenance, safety checks, and operator training.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Laser cutting produces hazardous fumes (e.g., metal oxides); install certified filtration systems.
- Used coolant, filters, and contaminated materials must be disposed of per local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, EEA).
- End-of-life equipment should be recycled through certified e-waste handlers.
Summary & Best Practices
- Verify regulatory requirements for both origin and destination countries.
- Partner with experienced freight forwarders and compliance consultants.
- Maintain detailed technical and compliance documentation.
- Prioritize safety in packaging, transport, and installation.
- Stay updated on changes in international trade and laser safety regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, sourcing a laser welding and cutting machine requires a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors, including application requirements, machine specifications, budget constraints, service and support, and long-term operational goals. Investing in the right laser system can significantly enhance manufacturing precision, productivity, and product quality. It is crucial to partner with reputable suppliers who offer reliable technology, technical expertise, and after-sales support to ensure optimal performance and minimal downtime. By carefully assessing your needs and conducting thorough market research, you can select a laser solution that delivers both immediate benefits and sustainable value, positioning your operations for long-term success in a competitive industrial landscape.