The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2023 to 2030. A key driver of this growth is the increasing adoption of laser welding for aluminum—a lightweight, high-conductivity material favored in electric vehicles (EVs) and high-performance engineering. With aluminum’s challenging thermal and reflective properties, only advanced laser systems can deliver consistent, high-quality welds. This has positioned specialized manufacturers at the forefront of innovation. As demand intensifies, particularly in sectors prioritizing energy efficiency and structural integrity, the ability to precisely weld aluminum has become a competitive differentiator. The following list highlights the top nine manufacturers leading this niche through technological expertise, global reach, and proven performance in real-world applications.
Top 9 Laser Welding Aluminium Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer of mobile, flexible, and high-performance laser systems for laser welding, laser hardening, powder deposit welding and additive metal ……
#2 Laser Company for Industrial Laser Solutions
Website: laserline.com
Key Highlights: The leading laser company for integrated & customized diode laser manufacturing solutions for various industries & applications….
#3 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: We offer comprehensive solutions in cleaning, welding and laser marking. At LC Lasers we seek laser solutions for our customers and distributors….
#4 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: Laser welders are incredibly versatile and essential in any fabrication shop or factory welding parts from sheet metal….
#5 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding creates exceptionally high-quality joints with excellent physical and electrical properties, even when joining challenging materials like aluminum ……
#6 Laser Welding Aluminum
Website: ebindustries.com
Key Highlights: Laser beam welding is one of our most popular services for welding aluminum. The process is ideal for fast, clean welds….
#7 Welding aluminum – as fast and as easy as steel
Website: kuka.com
Key Highlights: In laser hybrid welding, the laser welding process is combined with a gas metal-arc welding process, usually MIG welding. Since a filler wire is normally used ……
#8 Laser Welding Machine
Website: varisigns.com
Key Highlights: Our handheld fiber laser welder, with a power of 2000 watts, can weld aluminum letters up to 3mm thick. We can now supply a small weld head for 3D channel ……
#9 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welding Aluminium

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding of Aluminium
The market for laser welding aluminium is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and sustainability imperatives. Key trends shaping this landscape include:
1. Dominance of High-Power and Multi-Kilowatt Fiber Lasers: By 2026, high-power (10 kW+) and ultra-high-power (20 kW+) fiber lasers will solidify their position as the dominant technology. Their superior beam quality, efficiency, reliability, and ability to perform deep-penetration keyhole welding at high speeds make them ideal for demanding aluminium applications in automotive and aerospace. The shift towards remote welding with scanning optics, enabled by these powerful lasers, will accelerate, increasing throughput and flexibility.
2. Surge in Hybrid Laser-Arc Welding (HLAW) Adoption: Recognizing the challenges of welding thicker aluminium sections and bridging gaps, Hybrid Laser-Arc Welding will experience substantial growth. By combining the precision and speed of the laser with the gap-bridging capability and filler metal addition of an arc process (like MIG), HLAW offers improved tolerance to fit-up variations, reduced porosity, and the ability to weld thicker materials efficiently. This makes it highly attractive for automotive structural components and heavy fabrication.
**3. Advancements in Process Monitoring and Closed-Loop Control: To ensure weld quality and consistency, especially with aluminium’s sensitivity to defects, integrated, real-time process monitoring will become standard. Technologies like high-speed imaging, plasma monitoring, and acoustic emission sensors will be increasingly coupled with AI-powered analytics for predictive quality control. Closed-loop systems adjusting laser power, focus, and speed in real-time based on sensor feedback will enhance reliability and reduce scrap rates.
4. Focus on Overcoming Aluminium-Specific Challenges: Targeted R&D and process optimization will continue to address inherent aluminium difficulties:
* Porosity Mitigation: Improved understanding of hydrogen solubility and vaporization, combined with optimized beam oscillation (wobble) techniques and tailored shielding gas strategies (e.g., Ar+He mixtures), will significantly reduce pore formation.
* Crack Susceptibility: Development of specialized filler wires (e.g., Al-Si-Mg variants) and precise thermal management strategies (preheat control, travel speed optimization) will minimize hot cracking risks, particularly in high-strength alloys.
* Reflectivity Management: While less critical with modern fiber lasers, process designs will continue to incorporate strategies like precise beam positioning and optimized start/stop routines to handle initial reflectivity and spatter.
5. Expansion Driven by Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Lightweighting: The explosive growth of the EV market remains the primary growth engine. Laser welding is critical for manufacturing lightweight aluminium battery housings, motor components, and structural parts to maximize EV range. Demand will also increase in aerospace (airframes, fuel tanks) and consumer electronics (enclosures, heat sinks) where weight reduction and precision are paramount.
6. Automation and Digital Integration (Industry 4.0): Laser welding cells will become more deeply integrated into automated production lines. Seamless connectivity with MES/ERP systems, digital twins for simulation and optimization, and remote diagnostics will enhance productivity, traceability, and operational efficiency, making laser welding a cornerstone of smart manufacturing.
7. Sustainability as a Key Driver: The inherent energy efficiency of modern fiber lasers aligns with decarbonization goals. Furthermore, the ability to use less material through optimized joint designs and reduced heat-affected zones contributes to overall product sustainability, a growing concern for end-users.
In summary, the 2026 market for laser welding aluminium will be characterized by the widespread adoption of powerful, intelligent, and integrated systems. The focus will shift beyond just achieving the weld to ensuring maximum quality, consistency, and efficiency, driven by the demanding requirements of the EV revolution and advanced manufacturing. Hybrid processes, sophisticated monitoring, and solutions specifically engineered for aluminium’s unique properties will be key differentiators for market leaders.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Welding for Aluminium (Quality & IP)
Sourcing laser welding services for aluminium presents unique challenges due to the material’s properties and the complexity of the process. Overlooking these critical areas can lead to significant quality failures and intellectual property (IP) risks.
H3: Quality Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Process Parameter Control:
- Pitfall: Laser welding aluminium is highly sensitive to parameters (power, speed, focus, shielding). Suppliers without deep expertise or robust process validation often fail to optimize these, leading to defects.
- Consequences: Porosity (gas entrapment), lack of fusion, excessive spatter, inconsistent penetration, and poor bead geometry. This results in weak, unreliable welds prone to failure.
- Mitigation: Demand evidence of validated welding procedures (WPS/PQR), parameter windows, and real-time process monitoring (e.g., weld pool monitoring).
-
Poor Surface Preparation & Cleaning:
- Pitfall: Aluminium’s native oxide layer (Al₂O₃) has a much higher melting point than the base metal and impedes fusion. Suppliers neglecting rigorous pre-weld cleaning (mechanical, chemical) will have inconsistent results.
- Consequences: Unstable keyhole, increased porosity, lack of fusion, poor wetting, and inconsistent weld quality.
- Mitigation: Specify strict cleaning protocols (e.g., solvent degreasing, wire brushing with stainless steel, chemical etching) and verify supplier adherence. Insist on cleanliness verification.
-
Insufficient Shielding Gas Management:
- Pitfall: Aluminium readily oxidizes and absorbs hydrogen when molten. Inadequate shielding gas flow (type, purity, flow rate, nozzle design, coverage) allows atmospheric contamination.
- Consequences: Severe porosity (especially hydrogen-induced), surface oxidation, reduced mechanical properties, and poor aesthetics.
- Mitigation: Require high-purity inert gas (Argon, Helium, or mixtures), optimized delivery systems (trailing shields for deep joints), and proper gas curtain setup. Monitor gas quality.
-
Lack of Material & Joint Design Expertise:
- Pitfall: Not all aluminium alloys are equally laser-weldable. Suppliers may lack knowledge of alloy-specific challenges (e.g., hot cracking susceptibility in 6xxx series) or fail to optimize joint fit-up and design.
- Consequences: Hot cracking, distortion, incomplete penetration, mismatched strength.
- Mitigation: Engage suppliers with proven experience on your specific alloy. Ensure they review and approve joint designs for laser welding feasibility.
-
Inadequate Post-Weld Inspection & Testing:
- Pitfall: Relying solely on visual inspection. Laser welds can have internal defects invisible to the eye. Suppliers without proper NDT capabilities miss critical flaws.
- Consequences: Undetected porosity, cracks, or lack of fusion lead to in-service failures.
- Mitigation: Specify required NDT methods (e.g., Radiographic Testing (RT), Ultrasonic Testing (UT), Dye Penetrant Testing (PT)) and acceptance criteria based on the application’s criticality. Verify supplier NDT accreditation.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Inadequate or Non-Existent IP Agreements:
- Pitfall: Failing to establish clear, legally binding contracts defining IP ownership before sharing designs, processes, or specifications.
- Consequences: Ambiguity over who owns the final product design, the welding procedure developed for your part, or improvements made by the supplier. Risk of supplier claiming rights or using knowledge for competitors.
- Mitigation: Implement comprehensive IP clauses in the contract: Explicitly state that all customer-provided IP remains the customer’s property. Define ownership of new IP (typically, customer owns IP developed for them; supplier may retain background IP). Include strong confidentiality clauses.
-
Over-Disclosure of Sensitive Information:
- Pitfall: Sharing excessive technical details, schematics, or proprietary manufacturing knowledge without a clear “need-to-know” basis.
- Consequences: Exposure of core product innovations, trade secrets, or unique design features beyond what is necessary for the welding task.
- Mitigation: Provide only the minimum information required for the supplier to perform the welding (e.g., part drawings with weld locations, material specs, required tolerances). Use NDAs rigorously.
-
Lack of Control Over Process Development:
- Pitfall: Allowing the supplier to develop the optimal laser welding parameters and procedures without defining ownership or access rights.
- Consequences: The supplier owns the valuable, optimized process knowledge. You may be locked into that supplier or face high costs to replicate it elsewhere. Risk of the supplier using the learnings on similar competitor parts.
- Mitigation: Contractually stipulate that any process development, parameter optimization, or tooling created specifically for your product is the customer’s IP, or at minimum, grant the customer irrevocable, royalty-free rights to use it.
-
Weak Confidentiality & Security Measures:
- Pitfall: Assuming the supplier has adequate IT security, physical security, and employee confidentiality training.
- Consequences: Unauthorized access to digital designs (CAD files), process data, or physical parts. Data breaches or leaks.
- Mitigation: Assess the supplier’s security protocols. Require secure data transfer methods (encryption), controlled access to work areas, and ensure their employees sign confidentiality agreements. Include audit rights in the contract.
-
Failure to Address Background IP:
- Pitfall: Not clarifying the boundaries between the customer’s IP, the supplier’s standard processes/background IP, and new IP created during the project.
- Consequences: Disputes over the use of the supplier’s standard techniques or tools on your project, or ambiguity about licensing fees.
- Mitigation: Clearly define and document the supplier’s background IP in the contract. Specify the license granted to the customer to use the supplier’s background IP only for the purpose of fulfilling the order.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls through rigorous supplier selection, detailed specifications, and robust contractual agreements, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with sourcing laser welding services for aluminium.
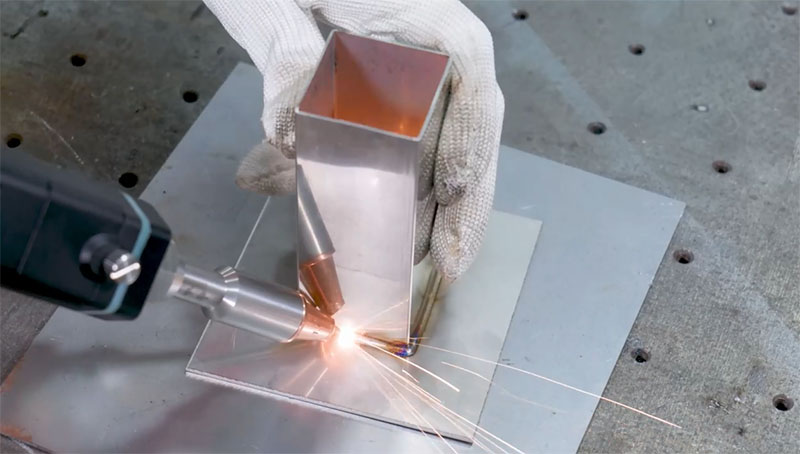
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding Aluminium
Material Handling and Storage
Aluminium used in laser welding requires careful handling and storage to maintain material integrity and ensure welding quality. Store materials in a clean, dry, and temperature-controlled environment to prevent oxidation and moisture absorption. Use protective packaging such as plastic wrap or desiccant-lined containers to minimize surface contamination. Segregate different aluminium alloys to avoid mix-ups and clearly label all stock with alloy type, temper, and batch number. Handle materials with clean gloves or tools to prevent oil and dirt transfer, which can compromise weld quality.
Transportation Requirements
When transporting aluminium components or raw materials for laser welding, secure loads to prevent movement and surface damage. Use non-abrasive padding and avoid contact with dissimilar metals to prevent galvanic corrosion. For international or inter-state shipments, ensure compliance with transportation regulations such as IMDG (for sea freight), IATA (for air), or ADR (for road in Europe). Declare materials appropriately, especially if they are classified under specific commodity codes. Maintain documentation including material safety data sheets (MSDS) and transport declarations.
Safety and Workplace Compliance
Laser welding aluminium presents specific safety hazards, including intense optical radiation, fumes, and fire risks. Implement engineering controls such as enclosed laser cells with interlocks, fume extraction systems, and beam shielding. Operators must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles with the correct wavelength filtration (typically for 1 µm or 1064 nm for fiber lasers), flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection if fume extraction is insufficient. Conduct regular risk assessments and comply with OSHA (USA), HSE (UK), or other local occupational safety standards. Ensure all personnel are trained in laser safety (e.g., ANSI Z136.1 compliance in the U.S.).
Emission and Environmental Regulations
Laser welding aluminium produces metal fumes, primarily aluminium oxide and trace alloying elements (e.g., magnesium, silicon), which are regulated under environmental and health standards. Install high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration or fume extraction systems to capture airborne particles. Monitor workplace air quality regularly and ensure exposure levels remain below permissible exposure limits (PELs) set by OSHA or threshold limit values (TLVs) by ACGIH. Dispose of collected particulate waste as hazardous or non-hazardous depending on composition and local regulations (e.g., EPA, REACH, or local waste authorities). Maintain records of emission controls and air monitoring.
Quality and Process Compliance
Ensure laser welding processes adhere to industry standards such as ISO 15614 (welding procedure qualification), ISO 3834 (quality requirements for fusion welding), and AWS D1.2 (Structural Welding Code – Aluminium). Document welding parameters including laser power, travel speed, shielding gas type (typically high-purity argon or argon-helium mix), and joint fit-up. Conduct non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic testing (UT) or radiographic testing (RT) as required. Maintain traceability through weld logs, material certifications, and operator qualifications. Regular audits should verify compliance with internal quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
Regulatory Documentation and Traceability
Maintain comprehensive documentation for regulatory compliance and traceability. This includes material test reports (MTRs), welding procedure specifications (WPS), procedure qualification records (PQR), and welder certification records. For industries such as aerospace, automotive, or pressure vessels, additional certifications (e.g., NADCAP, AS9100) may be required. Ensure digital or physical records are stored securely and retrievable for audits. Label finished components with unique identifiers linking to process data, materials used, and inspection results.
International Trade and Customs Compliance
When exporting or importing laser-welded aluminium components, comply with customs regulations, including accurate HS (Harmonized System) code classification—typically under 8424.30 for machinery parts or 7616.99 for aluminium articles. Provide certificates of origin, export licenses (if applicable), and conformity declarations (e.g., CE marking in Europe). Be aware of trade restrictions or tariffs related to aluminium products in target markets. Ensure compliance with REACH (EU), RoHS, or other substance restrictions that may apply to coatings or residual elements in the base or filler materials.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Welding for Aluminum
Sourcing laser welding services for aluminum requires careful consideration of several critical factors to ensure high-quality, reliable, and cost-effective results. Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity, reflectivity, and susceptibility to porosity and cracking demand specialized expertise and advanced laser technologies, such as fiber or disk lasers with precise control over parameters.
When selecting a supplier, key criteria should include technical capability, proven experience with aluminum alloys, appropriate equipment (e.g., high-power lasers with beam delivery systems suited for reflective materials), and robust quality control processes such as in-process monitoring and post-weld inspection.
Additionally, evaluating the supplier’s ability to handle joint design, fixturing, and surface preparation—critical for successful aluminum welding—is essential. Close collaboration during prototyping and process validation can mitigate risks and optimize weld quality.
In summary, successful sourcing of laser welding for aluminum hinges on partnering with experienced, technologically equipped vendors who understand the material-specific challenges. A strategic, quality-focused approach ensures durable welds, improved production efficiency, and long-term cost savings in demanding applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.