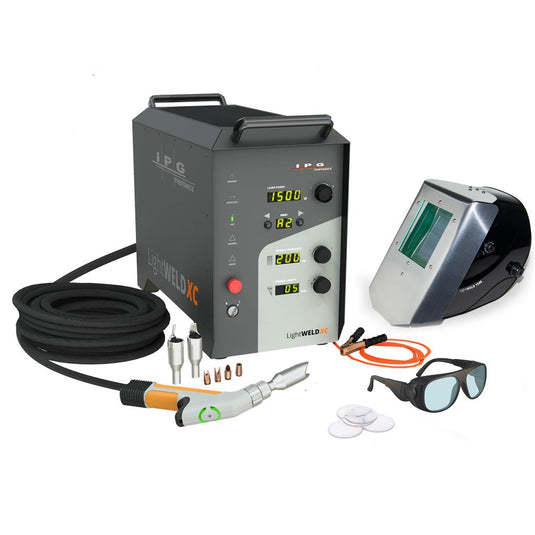
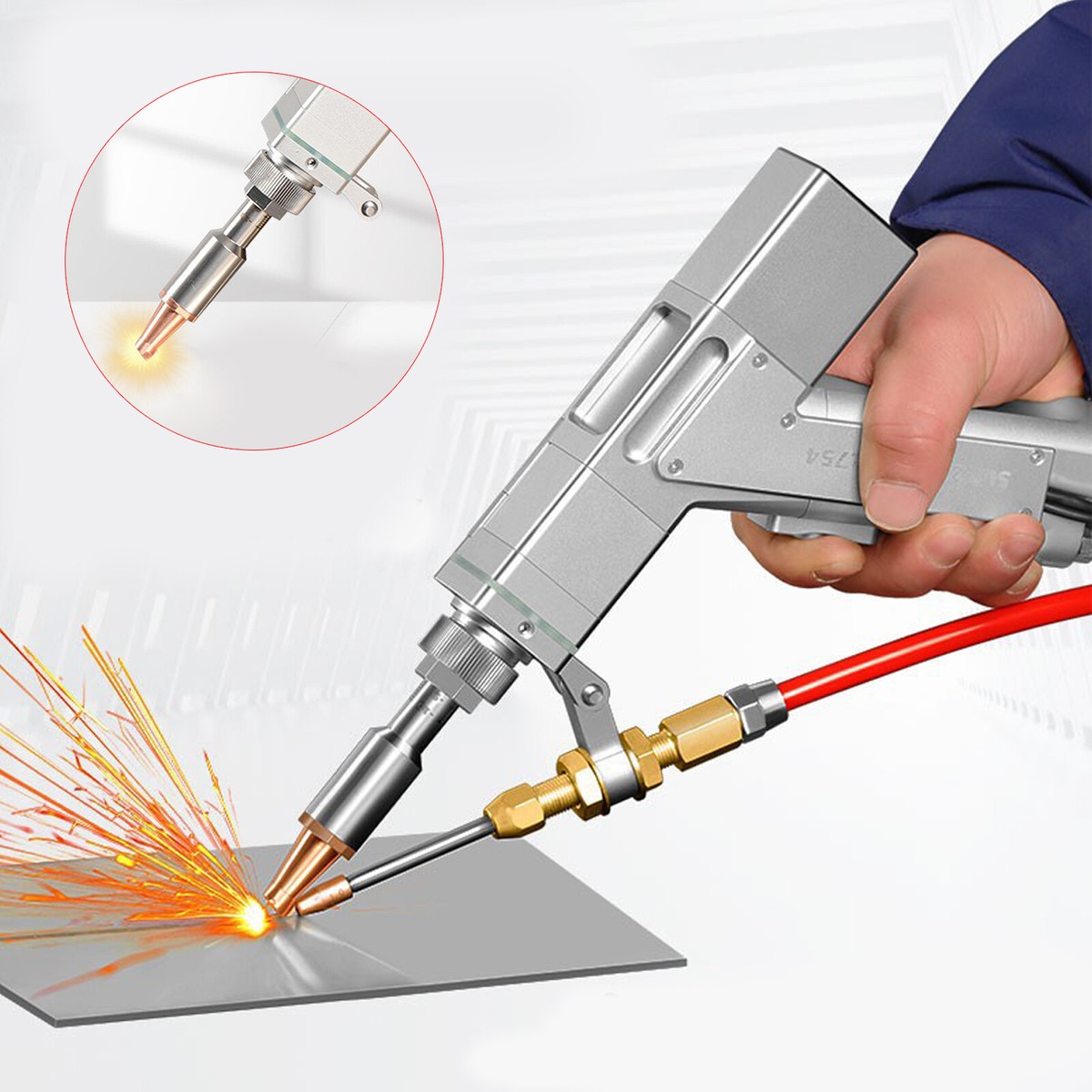
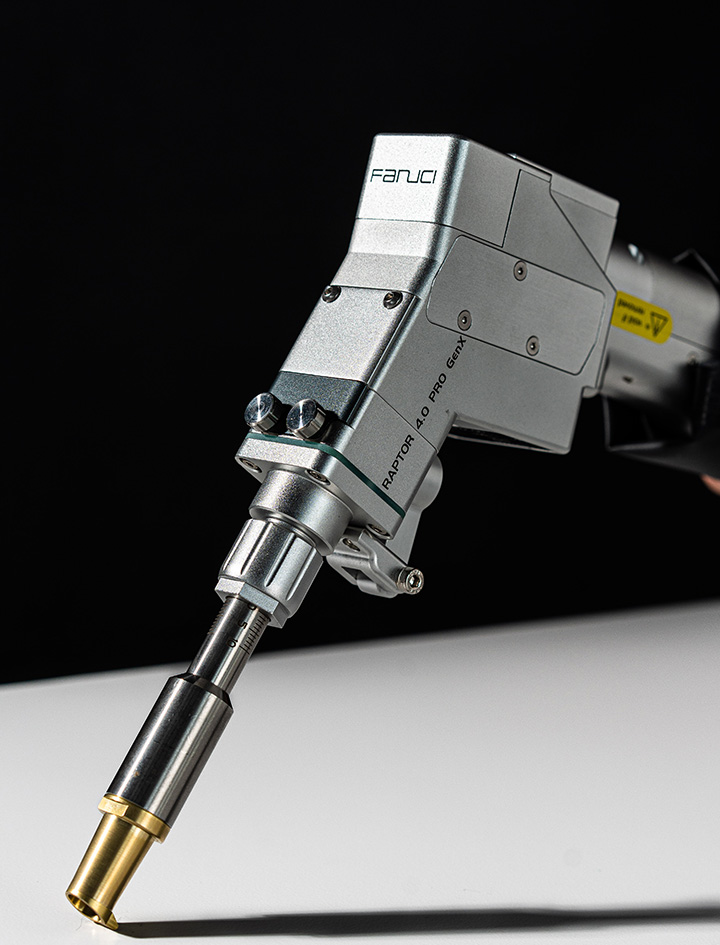
The global laser welding equipment market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision, efficiency, and automation across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 1.37 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.9% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of high-power fiber lasers, advancements in robotic integration, and the shift toward lightweight materials requiring high-precision joining technologies. Handheld laser welder guns, in particular, have gained significant traction due to their mobility, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness in both small-scale and industrial applications. As manufacturers seek to capitalize on these trends, a competitive landscape has emerged, with innovation centering on power output, beam quality, cooling efficiency, and user ergonomics. In this evolving market, nine manufacturers stand out for their technological leadership, product reliability, and global reach—setting the benchmark for performance and shaping the future of portable laser welding.
Top 9 Laser Welder Gun Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#2 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a pioneer in the field of mobile laser welding, ALPHA LASER GmbH offers a wide range of high-quality laser welding devices. This includes laser welding ……
#3 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: Laser welders are incredibly versatile and essential in any fabrication shop or factory welding parts from sheet metal….
#4 Everlast Inverter Welders Equipment
Website: everlastgenerators.com
Key Highlights: Everlast Power Equipment, manufacturers of MIG, TIG & Stick welders. For reliable welding machines and supplies shop Everlast Power Equipment….
#5 Portable Laser Welder
Website: fslaser.com
Key Highlights: In stock $1,550 deliveryHandheld laser welding is easy to learn, simple and fast to set up and provides consistent high-quality results across a wide range of materials and ……
#6 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#7 Handheld Laser Welding Machine, Handheld Laser Cleaning …
Website: kaihuanlaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a high-precision process using a focused laser beam to melt and join materials, known for its versatility and low heat impact in diverse ……
#8 Strong & Reliable Laser Welding Solutions
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar firearm welding systems deliver strong, reliable laser welding solutions for gun repair, assembly, and customization with ……
#9 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welder Gun
2026 Market Trends for Laser Welder Gun
The global laser welder gun market is poised for substantial evolution by 2026, driven by technological innovation, increased industrial automation, and growing demand for precision welding in advanced manufacturing sectors. This analysis explores key trends expected to shape the laser welder gun industry over the coming years.
Rising Adoption in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The automotive industry, particularly the electric vehicle (EV) segment, is expected to be a primary growth driver for laser welder guns by 2026. As automakers transition to lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel to improve energy efficiency and battery range, traditional welding methods are being replaced by laser-based solutions. Laser welder guns offer superior precision, speed, and weld quality, making them ideal for battery pack assembly, body-in-white construction, and powertrain components. With EV production expanding globally, demand for high-efficiency laser welding systems will surge, especially in regions like North America, Europe, and China.
Advancements in Portable and Handheld Laser Welding Technology
A major trend emerging by 2026 is the rapid development and commercialization of portable and handheld laser welder guns. These compact systems provide flexibility for on-site welding, maintenance, and repair operations in industries such as construction, shipbuilding, and aerospace. Innovations in fiber laser technology have enabled higher power outputs in smaller packages, improving weld penetration and quality even in manual applications. The ease of use, reduced need for specialized operators, and lower operational costs are making handheld laser welder guns increasingly attractive to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Integration with Automation and Industry 4.0
Laser welder guns are increasingly being integrated into automated production lines and smart manufacturing ecosystems. By 2026, the convergence of laser welding systems with robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms will enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control of welding parameters. This integration enhances repeatability, reduces defects, and increases overall production efficiency. Manufacturers are investing in modular laser welding solutions that can be easily incorporated into existing assembly systems, further accelerating adoption across high-volume industries.
Growth in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors are expected to contribute significantly to market expansion by 2026. Laser welder guns are being adopted for their ability to join complex geometries and high-performance alloys with minimal heat distortion. Applications include turbine engine components, airframe structures, and satellite systems. Stringent quality and safety standards in these industries favor the precision and consistency offered by laser welding, reinforcing long-term demand.
Regional Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the laser welder gun market by 2026, led by China, Japan, and South Korea. The region’s robust manufacturing base, government support for industrial modernization, and rising investments in automation are key growth enablers. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on next-generation laser technologies, including blue and green wavelength lasers for highly reflective materials like copper and aluminum.
Key market players such as IPG Photonics, TRUMPF, Han’s Laser, and Coherent are intensifying R&D efforts to improve beam quality, energy efficiency, and system integration. Partnerships with robotics companies and software developers are becoming common strategies to offer turnkey welding solutions.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Trends
As industries prioritize sustainability, laser welder guns are gaining favor due to their lower energy consumption and reduced material waste compared to conventional welding. Fiber laser systems, in particular, offer high wall-plug efficiency, contributing to lower carbon footprints in manufacturing. By 2026, eco-design and energy certification standards are expected to influence procurement decisions, further boosting demand for advanced laser welding equipment.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser welder gun market will be defined by technological sophistication, broader industrial adoption, and deeper integration with digital manufacturing systems. Driven by demand from EVs, aerospace, and automated production, the market is set for sustained growth. Companies that invest in innovation, user-friendly designs, and sustainable solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Welder Gun (Quality and IP)
Sourcing a laser welder gun involves navigating several critical challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can result in operational inefficiencies, safety risks, legal disputes, and financial losses. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Many suppliers—especially low-cost manufacturers—offer laser welder guns with substandard materials and imprecise manufacturing tolerances. These units often suffer from poor beam alignment, inadequate cooling systems, and fragile components, leading to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent weld quality, and increased downtime. Without proper quality certifications (such as ISO 9001) or verifiable test reports, buyers risk integrating unreliable equipment into critical production processes.
Lack of IP Due Diligence
Purchasing laser welding technology from suppliers without clear IP ownership can expose buyers to legal risks. Some manufacturers may use patented optical designs, control systems, or software without proper licensing, particularly in regions with lax IP enforcement. If your company uses such equipment, you could face infringement claims, product seizures, or costly litigation, even if you were unaware of the violation. Always require proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements before procurement.
Inadequate Technical Documentation and Support
Low-quality or counterfeit laser welder guns often come with incomplete or inaccurate technical documentation. Missing calibration records, safety certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, IEC), or software source code restricts maintenance, compliance audits, and integration with existing systems. Additionally, limited after-sales support or unresponsive suppliers can leave you stranded during critical operations.
Hidden Costs from Non-Compliance and Repairs
Initially low-priced laser welder guns may lead to higher total cost of ownership due to frequent repairs, downtime, or non-compliance with industry standards. Using equipment that fails to meet safety or emissions regulations (e.g., laser class certifications) can result in fines or shutdowns. Moreover, replacing counterfeit or poorly performing parts often costs more than investing in a reputable, compliant system upfront.
Supply Chain and Long-Term Availability Risks
Choosing a supplier without a proven track record or stable production can jeopardize long-term maintenance and spare parts availability. If the manufacturer disappears or discontinues the model, sourcing replacements or upgrades becomes difficult, potentially halting production. Ensure the supplier has a reliable supply chain and offers service agreements and part warranties.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough supplier vetting, request product samples, verify certifications, perform IP audits, and consider partnering with established manufacturers or authorized distributors with transparent supply chains and strong reputations in industrial laser technology.
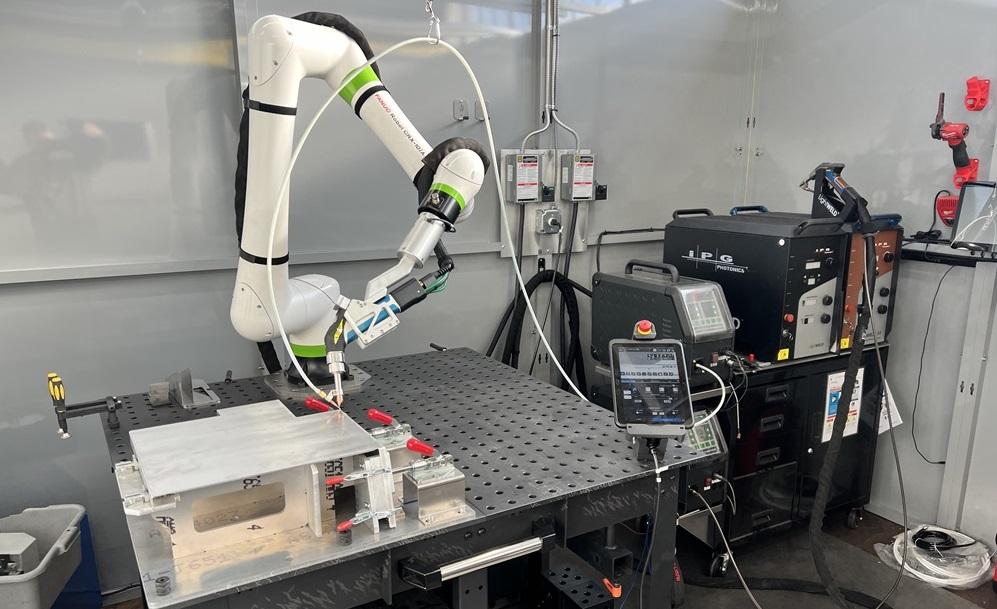

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welder Gun
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
Laser welder guns are industrial tools that combine high-powered laser technology with precision welding capabilities. Due to their technical complexity and potential safety risks, they are subject to multiple international and national regulations. Proper classification under Harmonized System (HS) codes, adherence to safety standards, and compliance with export controls are essential for legal import/export and operational use.
HS Code Classification
The Harmonized System (HS) code for laser welder guns typically falls under:
– 8515.31 – Electrical welding machines using lasers, whether or not capable of cutting.
Specific sub-codes may vary by country (e.g., 8515.31.00 in the U.S. HTS). Confirm the exact classification with the destination country’s customs authority, as misclassification can lead to delays, fines, or shipment rejection.
Safety & Technical Standards Compliance
Laser welder guns must comply with international safety and performance standards, including:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
– ISO 11553-1: Safety of machinery – Laser processing machines – Part 1: General safety requirements.
– ANSI Z136.1: Safe use of lasers (U.S. standard).
Ensure the equipment bears relevant certifications (e.g., CE, UKCA, FCC, RoHS) where applicable. Non-compliant units may be denied entry or require costly retrofitting.
Laser Safety & Hazard Communication
Laser welder guns are classified based on laser power and potential hazard (Class 1 to Class 4). Most industrial laser welders are Class 4 lasers, posing risks of eye/skin injury and fire. Compliance requires:
– Proper labeling with laser warning signs (per IEC 60825).
– Provision of safety interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency shutoffs.
– Inclusion of a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) program in operational environments (per ANSI Z136).
Documentation must include user manuals, safety instructions, and maintenance protocols in the local language.
Export Control Regulations
Laser systems may be subject to export controls due to dual-use potential (civilian and military applications). Key regulations include:
– U.S. EAR (Export Administration Regulations): Controlled under ECCN 6A003 or 6A005, depending on power, wavelength, and beam quality.
– Wassenaar Arrangement: International agreement monitoring transfer of conventional arms and dual-use goods.
– ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations): Applies if the laser meets defense-related criteria.
Verify licensing requirements before export. Unauthorized export may result in severe penalties.
Packaging & Transportation Requirements
Due to sensitivity and safety concerns, laser welder guns must be:
– Packaged in shock-resistant, anti-static containers with immobilized components.
– Shipped with protective covers over optical elements and secured power units.
– Labeled with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Radiation” warnings.
Air and sea freight must comply with IATA (air) or IMDG (sea) regulations for machinery and electrical equipment. Avoid temperature and humidity extremes during transit.
Import Documentation & Customs Clearance
Required documentation typically includes:
– Commercial invoice (with full technical specs and HS code).
– Packing list.
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, UL, etc.).
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill.
– Export license (if applicable).
Some countries may require additional permits or pre-shipment inspections. Engage a licensed customs broker familiar with laser equipment.
End-Use & Installation Compliance
Upon arrival, ensure the end-user:
– Operates the laser welder in a controlled environment with proper ventilation and fire suppression.
– Trains personnel in laser safety and emergency procedures.
– Registers the equipment with local occupational health and safety authorities if required (e.g., OSHA in the U.S.).
– Maintains compliance with local environmental and electrical codes.
Recordkeeping & Audit Trail
Maintain detailed records for at least 5 years, including:
– Export licenses and approvals.
– Product certifications and test reports.
– Shipping and customs documentation.
– End-user statements (for controlled exports).
These records may be required for regulatory audits or compliance verification.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of laser welder guns requires a proactive approach to classification, safety, export controls, and documentation. Engage regulatory experts and freight forwarders with experience in high-tech industrial equipment to ensure smooth and lawful international trade.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Welder Gun
After a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and long-term operational needs, sourcing a laser welder gun represents a strategic investment in improving manufacturing precision, productivity, and product quality. Laser welding technology offers superior control, reduced heat distortion, and higher weld strength compared to traditional methods, making it ideal for high-precision applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
Key factors in the sourcing decision include selecting a reliable supplier with proven technical support, ensuring compatibility with existing production systems, and factoring in total cost of ownership—including maintenance, training, and integration. Additionally, prioritizing safety features, ease of operation, and scalability will support long-term efficiency and adaptability.
In conclusion, the acquisition of a laser welder gun aligns with goals of technological advancement and operational excellence. By carefully selecting the right equipment and supplier, organizations can achieve significant improvements in weld quality, throughput, and competitiveness in the market. Proper implementation, coupled with workforce training and process optimization, will ensure maximum return on investment and sustainable manufacturing growth.