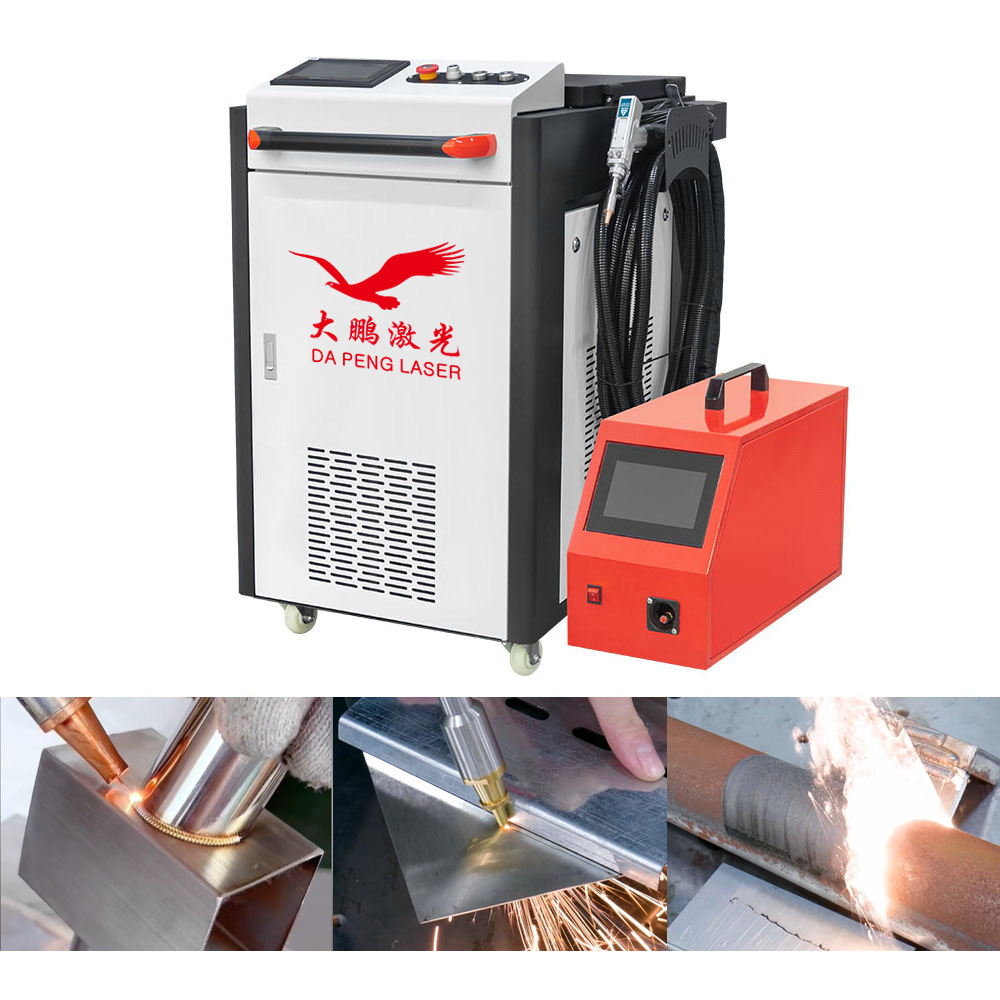
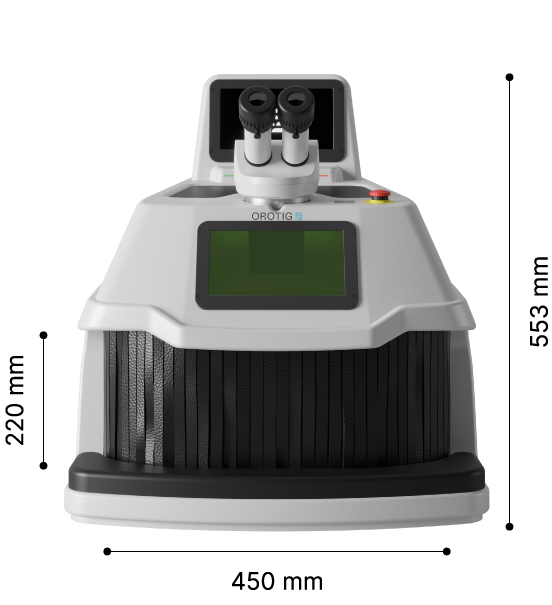
The global laser welding and cutting equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the laser cutting market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology and rising adoption of automation in production processes. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 6.08 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 8.1% through 2030. With rapid technological innovation and increased investments in industrial laser systems, identifying the leading manufacturers has become critical for businesses seeking high-performance, reliable solutions. Based on market presence, technological capabilities, and global reach, the following are the top 10 laser welder and cutter manufacturers shaping the future of advanced manufacturing.
Top 10 Laser Welder Cutter Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine and CO2 Laser Cutter Manufacturer …
Website: gwklaser.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer of laser cutting machine, CO2 laser cutter, laser welding machine, laser bending machine and laser cleaning machine, etc….
#3 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered by the most experienced engineers and ……
#5 Everlast Inverter Welders Equipment
Website: everlastgenerators.com
Key Highlights: Everlast Power Equipment, manufacturers of MIG, TIG & Stick welders. For reliable welding machines and supplies shop Everlast Power Equipment….
#6 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#7 Full Spectrum Laser
#8 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#9 Fiber laser cutting machine
Website: hsglaser.com
Key Highlights: HSG LASER is an international company dedicated to R&D, production, sales of laser cutting, bending, welding machines, automatic loading & unloading and ……
#10 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Welder Cutter

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Welder Cutters
The global market for laser welder cutters—hybrid systems combining precision cutting and welding in a single platform—is poised for transformative growth and evolution by 2026. Driven by technological advances, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives, several key trends are shaping the trajectory of this sector.
H2: Technological Convergence and Hybridization
A dominant trend is the deepening integration of cutting and welding functionalities into unified systems. By 2026, laser welder cutters will increasingly feature intelligent process switching, adaptive optics, and shared robotic arms, enabling seamless transitions between operations without retooling. Fiber and blue laser technologies will converge, allowing a single machine to handle diverse materials—from steel and aluminum to copper and dissimilar metals—boosting throughput and reducing footprint in high-mix manufacturing environments.
H2: Rise of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 Integration
By 2026, laser welder cutters will be central nodes in smart factories. Embedded IoT sensors, real-time process monitoring (e.g., melt pool imaging, spatter detection), and AI-driven predictive maintenance will become standard. Cloud connectivity will enable remote diagnostics, performance analytics, and over-the-air software updates. Digital twins will allow virtual simulation of welding and cutting parameters, optimizing production planning and minimizing material waste.
H2: Demand Surge in EV and Battery Manufacturing
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution will be a primary growth engine. Laser welder cutters are critical for high-precision battery tab welding, busbar connections, and structural cutting of lightweight EV components. As global EV production scales, manufacturers will require high-speed, high-reliability laser systems capable of processing aluminum, copper, and coated materials. By 2026, dedicated laser solutions for battery module assembly will dominate R&D and capital expenditure in the sector.
H2: Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will push demand for energy-efficient laser systems. By 2026, manufacturers will prioritize lasers with higher wall-plug efficiency (especially fiber and disk lasers) and reduced consumables. Closed-loop fume extraction and recyclable component designs will become standard. Additionally, the ability to process recycled metals with consistent quality will enhance the sustainability value proposition of advanced laser welder cutters.
H2: Expansion in Aerospace and Medical Device Sectors
High-precision industries will increasingly adopt laser welder cutters for complex, mission-critical components. In aerospace, these systems will support lightweighting through titanium and Inconel processing. In medical devices, micro-welding and cutting capabilities will enable production of intricate implants and surgical tools. Regulatory compliance and traceability features (e.g., laser marking integration) will be embedded to meet stringent quality standards.
H2: Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the largest market due to robust manufacturing and EV adoption. However, North America and Europe will see accelerated growth due to reshoring initiatives and investments in clean tech. By 2026, localized production of laser systems and components will reduce supply chain risks, with regional service hubs offering faster support and customization.
H2: Competitive Landscape and Innovation Pressure
The market will witness intensified competition between established players (e.g., TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, Han’s Laser) and agile startups. Differentiation will come from software intelligence, ease of integration, and total cost of ownership. Pay-per-use models and leasing options may emerge, lowering entry barriers for SMEs. Open-architecture platforms allowing third-party integration will gain traction, fostering ecosystem-driven innovation.
H2: Workforce Transformation and Skill Development
As laser welder cutters become more autonomous, demand will shift from manual operators to technicians skilled in robotics, data analysis, and system programming. By 2026, VR/AR training platforms and certification programs will be essential for workforce readiness, ensuring manufacturers can fully leverage advanced capabilities without operational bottlenecks.
In summary, by 2026, the laser welder cutter market will be defined by intelligent, integrated, and sustainable systems tailored to high-growth industries. Success will hinge on innovation in automation, software, and energy efficiency, positioning these machines as indispensable tools in the future of advanced manufacturing.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Welder Cutter (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a laser welder cutter involves significant investment and technical complexity. Overlooking key factors related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to costly setbacks, operational inefficiencies, and legal risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Assessment of Build Quality and Components
Many buyers focus solely on price or advertised power output, neglecting the actual build quality. Low-cost machines may use substandard optics, motors, cooling systems, or structural frames, leading to poor beam quality, inconsistent welds, frequent breakdowns, and shorter service life. Always verify the quality of core components such as the laser source (e.g., IPG, Raycus), motion control systems, and chiller units.
Ignoring Compliance and Certification Standards
Laser equipment must comply with international safety and performance standards (e.g., CE, FDA, ISO 13849). Some suppliers, especially from less-regulated markets, may provide machines that appear compliant but lack genuine certification. This can result in facility shutdowns, legal penalties, or insurance issues. Request verifiable documentation and test reports before purchase.
Overlooking After-Sales Support and Service Accessibility
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers with limited local presence or poor service networks can result in extended downtime. Ensure the supplier offers timely technical assistance, spare parts availability, and on-site service options—critical for minimizing production interruptions.
Falling for Misrepresented Laser Power and Performance
Some suppliers inflate laser power ratings (e.g., advertising a 3kW laser that performs like a 2kW unit) or provide performance data under ideal lab conditions. This leads to mismatched expectations and underperformance in real-world applications. Request third-party test results or conduct on-site demonstrations using your actual materials and weld/cut parameters.
Risk of IP Infringement from Copycat Machines
Many low-cost laser systems are reverse-engineered or outright copies of original designs, infringing on patents and trademarks. Purchasing such machines exposes your company to IP litigation, customs seizures, or reputational damage. Always vet the manufacturer’s legitimacy and ensure they hold proper IP rights or licenses for their technology.
Lack of Transparency in Software and Control Systems
Proprietary control software is a critical part of laser systems. Some suppliers use unlicensed or pirated software, which can lead to instability, lack of updates, or legal exposure. Confirm that the CNC or laser control software (e.g., CypCut, Cynexis, or proprietary systems) is fully licensed and supports future upgrades and integration.
Underestimating Training and Knowledge Transfer
Even advanced machines underperform without proper operator training. Some suppliers minimize training to cut costs, leaving your team unable to optimize or troubleshoot the system. Ensure comprehensive training is included in the purchase agreement, covering operation, maintenance, and safety protocols.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, technical evaluations, and vetting suppliers for both product quality and IP integrity. Prioritizing long-term reliability and legal compliance over initial cost savings leads to a more successful and sustainable investment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welder Cutter
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the laser welder cutter under the Harmonized System (HS) Code for international shipping. Typical classifications fall under HS Code 8456.20 (Machines for laser working of metals). Confirm the exact code with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker. Prepare essential documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin. Include detailed technical specifications such as laser power, wavelength, beam delivery system, and safety features.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser welder cutters are subject to strict safety regulations due to their classification as Class 4 lasers. Comply with international standards such as IEC 60825-1 (Safety of Laser Products) and ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers). The equipment must bear appropriate warning labels and include a key-controlled power switch, emergency stop, and interlocks on protective enclosures. Ensure the manufacturer provides a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for CE marking (EU), FDA registration (USA), or other regional requirements (e.g., KC mark for South Korea, PSE for Japan).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Package the laser welder cutter securely using export-grade materials to prevent damage during transit. Use wooden crates or heavy-duty pallets with shock-absorbing materials to protect sensitive optical and electronic components. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators. Secure all moving parts and optics per manufacturer instructions. Include desiccants if shipping to high-humidity environments to prevent condensation.
Import/Export Controls and Permits
Verify if the laser welder cutter is subject to export controls under regimes such as the Wassenaar Arrangement, particularly for high-power systems capable of precision material processing. Obtain necessary export licenses from national authorities (e.g., BIS in the U.S.). Some countries may require import permits or pre-shipment inspections. Check destination country restrictions—some may limit or ban high-power lasers without special authorization.
Transportation and Carrier Selection
Use freight carriers experienced in handling industrial machinery and hazardous or controlled goods. For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if applicable (e.g., for embedded batteries or high-pressure components). For sea freight, ensure proper containerization and stowage to avoid moisture, vibration, and temperature extremes. Track shipments in real-time and maintain insurance coverage for the full replacement value.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Upon delivery, ensure installation is performed by qualified technicians in compliance with local electrical, fire, and occupational safety codes. The installation site must have proper grounding, ventilation, and laser-safe enclosures. Conduct a safety audit before operation, including interlock verification and emergency procedures. Provide operators with training and maintain records for compliance with OSHA (U.S.), HSE (UK), or other national workplace safety standards.
After-Sales and Maintenance Compliance
Maintain compliance throughout the product lifecycle. Keep records of maintenance, safety inspections, and any modifications. Provide end-users with updated manuals and safety guidelines. For cross-border service, ensure service technicians comply with local work visa requirements and carry necessary documentation for spare parts. Dispose of end-of-life units according to local environmental regulations, especially for laser diodes and electronic waste.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Welder Cutter:
Sourcing a laser welder cutter is a strategic decision that significantly impacts manufacturing efficiency, product quality, and long-term operational costs. After evaluating various suppliers, technologies, and specifications, it is clear that selecting the right laser system requires a balanced consideration of precision, power, reliability, and after-sales support. Fiber laser systems have emerged as the preferred choice due to their superior energy efficiency, low maintenance, and excellent performance in both welding and cutting applications.
Key factors such as automation compatibility, material thickness requirements, and integration into existing production lines must be carefully assessed. Additionally, total cost of ownership—including initial investment, maintenance, training, and consumables—should guide the procurement decision rather than price alone.
Ultimately, partnering with a reputable supplier that offers comprehensive service, technical expertise, and scalable solutions will ensure long-term success. Investing in a high-quality laser welder cutter not only enhances productivity and precision but also strengthens competitive advantage in demanding markets. Therefore, a well-informed sourcing decision today lays the foundation for innovation, quality, and growth in the future.