The global laser weld cleaning market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision surface preparation across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser cleaning market was valued at USD 1.35 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.6% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated value of USD 3.8 billion by the end of the forecast period. This expansion is largely fueled by increased adoption of automation, growing environmental regulations limiting chemical cleaning methods, and the superior efficiency of laser-based solutions in removing oxides, paint, and contaminants from welded surfaces. As industries prioritize quality, safety, and sustainability, laser weld cleaning has emerged as a preferred non-abrasive technology. This accelerating demand has led to a surge in innovation and competition, giving rise to a new generation of manufacturers specializing in high-performance, reliable laser cleaning systems. Below, we spotlight the top 10 manufacturers leading this transformation with advanced technology, broad application capabilities, and strong global footprints.
Top 10 Laser Weld Cleaning Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#3 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#4 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#5 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA….
#6 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: We offer comprehensive solutions in cleaning, welding and laser marking. At LC Lasers we seek laser solutions for our customers and distributors….
#7 HGLASER
Website: hglaserglobal.com
Key Highlights: HGLASER is a leading provider of laser cutting machine, laser marking mahcine and laser cleaning machine.Email:[email protected]….
#8 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Welding Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#9 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
#10 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: We offer, among others, laser welders, cleaning lasers, laser cutters for pipes, profiles, and sheet metal, nitrogen generators, and 3D laser printers for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Weld Cleaning
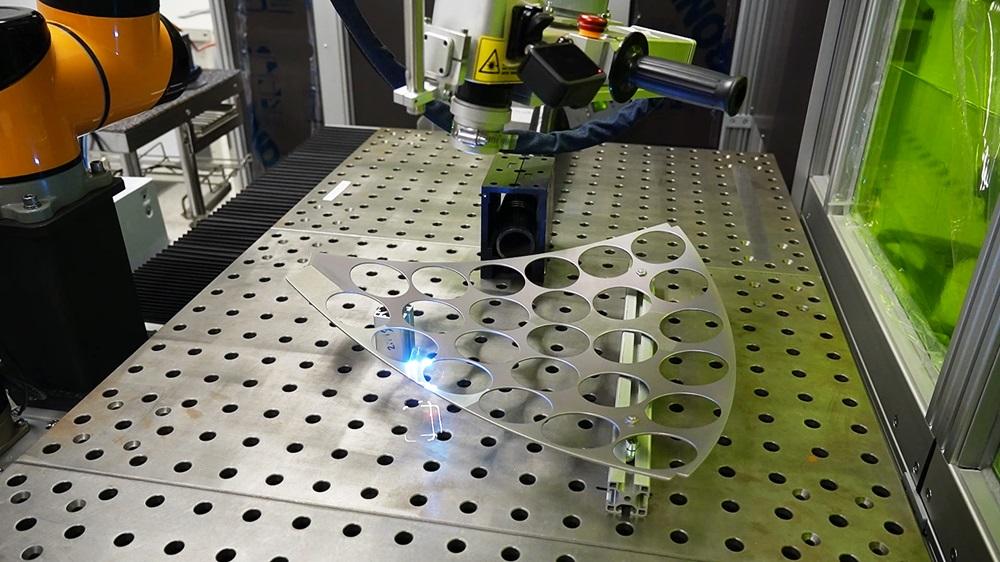

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Weld Cleaning
The laser weld cleaning market is poised for significant transformation and robust growth by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing industrial automation, and a heightened focus on sustainability and precision. Here’s a detailed analysis of the key trends shaping the market:
1. Accelerated Adoption Across Diverse Industries:
Beyond its established stronghold in heavy industries like automotive and aerospace, laser weld cleaning is rapidly penetrating sectors such as shipbuilding, power generation (especially nuclear and renewable), and precision manufacturing (medical devices, electronics). The demand for cleaner, stronger, and more reliable welds in safety-critical applications is a major catalyst. By 2026, expect broader adoption in maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations across industrial plants and infrastructure.
2. Integration with Automation and Robotics:
A dominant trend is the seamless integration of laser cleaning systems with robotic arms and automated production lines. This synergy enables fully automated, high-throughput weld prep and post-weld cleaning processes, particularly in automotive and large-scale fabrication. By 2026, “plug-and-play” robotic laser cleaning cells will become more common, improving efficiency, consistency, and worker safety by minimizing human exposure to fumes and debris.
3. Advancements in Laser Technology and Portability:
Technological evolution will focus on:
* Higher Power & Efficiency: Development of more powerful yet energy-efficient fiber lasers will enable faster cleaning of thicker oxides, rust, and spatter on larger welds.
* Improved Beam Quality & Control: Enhanced beam shaping and pulse control will allow for more precise cleaning of complex geometries and heat-sensitive materials without substrate damage.
* Increased Portability & Ergonomics: Continued miniaturization of laser sources and power supplies will lead to lighter, more maneuverable handheld and compact systems, expanding their usability in confined spaces and field applications.
4. Emphasis on Sustainability and Environmental Compliance:
Laser cleaning offers a major advantage over traditional methods (abrasive blasting, chemical solvents) by eliminating secondary waste (spent abrasives, contaminated solvents) and reducing water usage. As environmental regulations tighten globally (e.g., REACH, RoHS, EPA standards), industries will increasingly adopt laser cleaning as a “green” alternative. This regulatory push will be a significant growth driver by 2026.
5. Focus on Process Monitoring and Intelligence:
Future systems will increasingly incorporate sensors (vision systems, spectrometers) and AI-driven software for real-time monitoring. This enables:
* Automated Process Optimization: Adjusting laser parameters on-the-fly based on material and contamination levels.
* Quality Assurance: Providing immediate feedback and documentation of cleaning quality, crucial for traceability in regulated industries.
* Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring system health to prevent downtime.
6. Cost Reduction and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Justification:
While the initial investment remains higher than traditional methods, the TCO of laser cleaning is becoming increasingly favorable. By 2026, falling component costs, longer laser source lifetimes, reduced consumable costs (no abrasives/solvents), lower waste disposal fees, and improved worker productivity will strengthen the ROI argument, making adoption accessible to a wider range of manufacturers.
7. Expansion of Service Models:
Alongside equipment sales, the market will see growth in laser cleaning-as-a-service (LCaaS) models. Companies will offer mobile cleaning services or rent equipment, lowering the barrier to entry for SMEs and projects requiring occasional cleaning.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the laser weld cleaning market will be characterized by smarter, faster, more automated, and environmentally responsible solutions. Driven by industrial digitization, sustainability mandates, and the relentless pursuit of quality and efficiency, laser cleaning will transition from a niche technology to a standard process in advanced manufacturing and maintenance workflows. Success will belong to providers offering integrated, user-friendly, and cost-effective solutions backed by strong service and support.
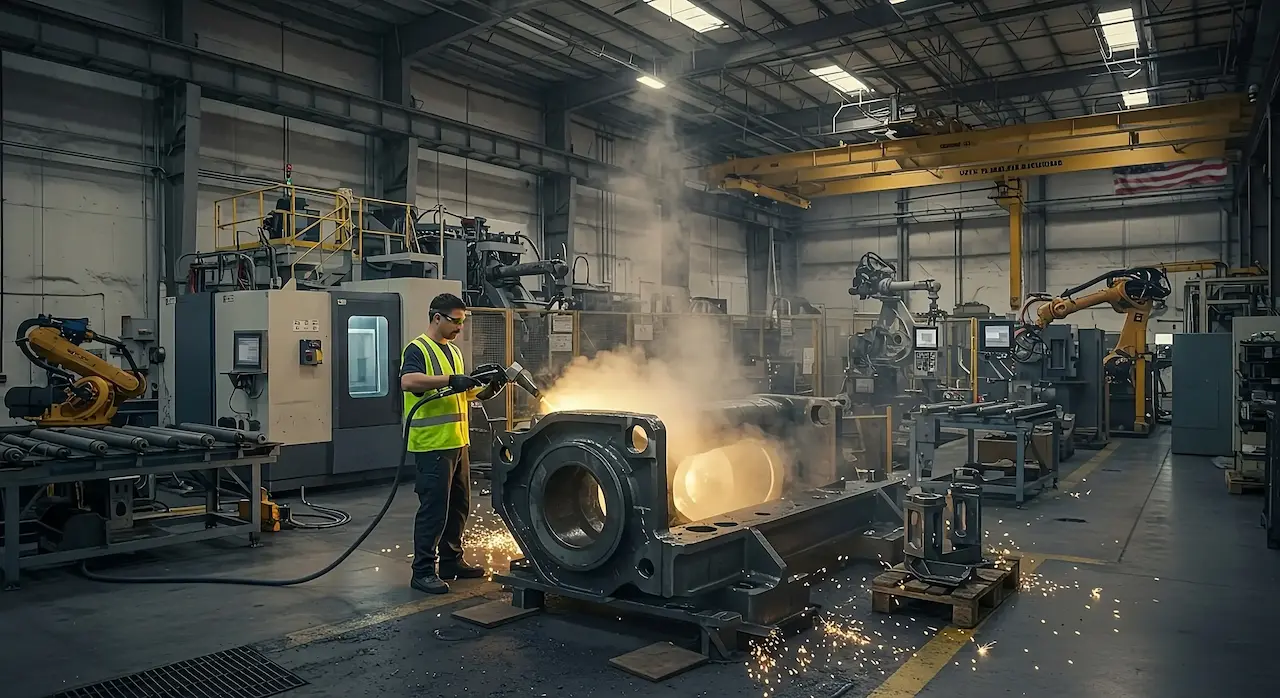

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Weld Cleaning Equipment (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing laser weld cleaning equipment presents significant challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to substandard performance, legal risks, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
H2: Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing laser weld cleaning systems—especially from less-established manufacturers—is inconsistent build quality and unreliable performance. Many suppliers, particularly in competitive low-cost markets, prioritize cost reduction over engineering rigor, resulting in systems that fail to meet promised specifications. Key indicators of poor quality include:
- Inaccurate Power Output Claims: Some suppliers overstate laser power (e.g., advertising 1000W systems that deliver significantly less), directly impacting cleaning efficiency and speed.
- Substandard Components: Use of low-grade optics, cooling systems, or fiber lasers reduces system lifespan and increases downtime.
- Lack of Certification: Absence of international safety and performance certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, IEC 60825) raises concerns about compliance and operational safety.
- Inadequate Testing and Documentation: Limited or falsified test reports make it difficult to verify real-world performance under industrial conditions.
To mitigate this, conduct thorough due diligence: request third-party test reports, perform on-site factory audits, and insist on sample testing under your specific use-case conditions.
H2: Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement and Technology Theft
Sourcing laser equipment, particularly from regions with weaker IP enforcement, carries a high risk of inadvertently acquiring systems based on stolen or copied technology. This exposes your organization to legal liability, reputational damage, and potential import bans. Key IP-related pitfalls include:
- Counterfeit or Cloned Systems: Some suppliers replicate patented laser designs, software interfaces, or control algorithms from leading brands without licensing, offering “budget” versions that infringe on IP.
- Lack of IP Transparency: Vendors may be unwilling or unable to provide documentation proving ownership or licensing of core technologies.
- Embedded Proprietary Software Risks: Cloned control software may contain malware or violate software copyright, leading to cybersecurity and compliance issues.
- Supply Chain Uncertainty: Components such as laser diodes or control boards may be sourced from suppliers with questionable IP practices, further complicating liability.
To safeguard against IP risks, require suppliers to provide IP indemnification clauses in contracts, conduct background checks on their R&D history, and consider engaging legal counsel specializing in international IP law during the sourcing process.
Addressing these H2-level pitfalls—quality control gaps and IP exposure—is essential to ensure reliable performance, legal compliance, and long-term return on investment when sourcing laser weld cleaning technology.
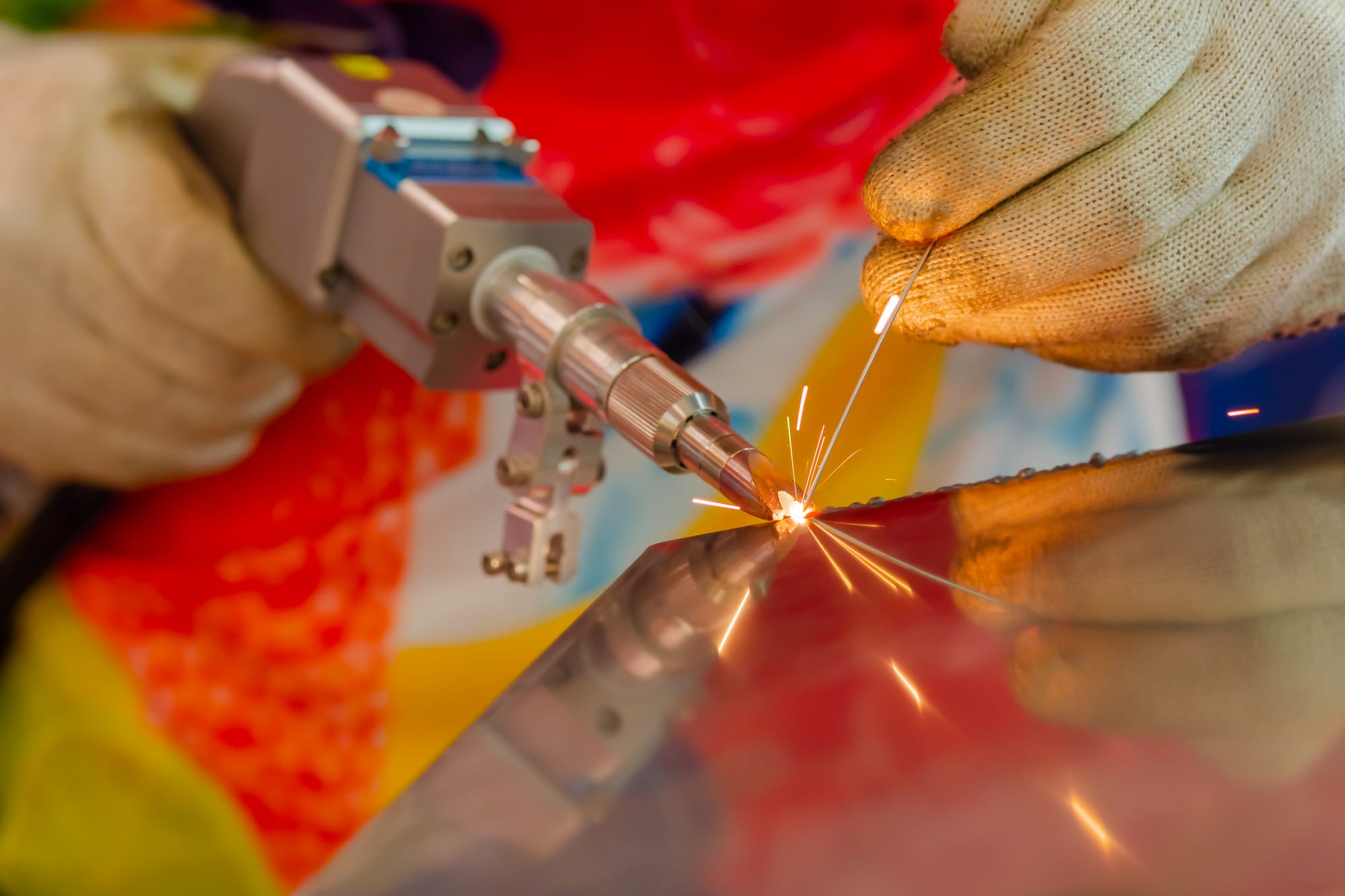

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Weld Cleaning
Equipment Transportation and Handling
Ensure laser weld cleaning equipment is transported in secure, shock-resistant packaging to prevent damage during transit. Use padded crates or specialized cases designed for sensitive optical and electronic systems. During handling, follow manufacturer guidelines for lifting and positioning—avoid tilting beyond recommended angles, especially for systems containing cooling components. Always power down and disconnect units before moving, and protect optical heads with protective caps.
Site Preparation and Setup
Before deployment, verify that the operational site meets minimum requirements for power supply (voltage, frequency, grounding), ventilation, and ambient temperature. Ensure a clean, dry workspace free of flammable materials. Position the laser unit on a stable, level surface with adequate clearance for cables, cooling systems, and operator access. Conduct a site safety assessment to identify potential hazards such as reflective surfaces, overhead obstructions, or nearby personnel zones.
Regulatory Compliance – Laser Safety
Laser weld cleaning systems typically fall under Class 4 laser classification, requiring strict adherence to laser safety standards such as ANSI Z136.1 (U.S.) or IEC 60825-1 (international). Implement engineering controls including interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency stop mechanisms. Designate a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) to oversee compliance. Operators must wear appropriate laser safety eyewear with the correct optical density (OD) rating for the laser’s wavelength and power output.
Regulatory Compliance – Workplace Safety
Comply with OSHA (or local equivalent) regulations regarding hazardous emissions. Laser cleaning generates particulate matter and fumes, including metal oxides and potentially hazardous airborne contaminants. Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) or fume extraction systems certified to capture and filter these byproducts. Conduct air quality monitoring if required. Provide operators with appropriate PPE, including respirators (NIOSH-approved), protective gloves, and flame-resistant clothing.
Environmental and Waste Management
Dispose of collected particulate waste in accordance with local environmental regulations. Classified as industrial waste, residues may contain heavy metals (e.g., chromium, nickel from stainless steel cleaning) and require hazardous waste handling procedures. Maintain records of waste disposal and use licensed waste handlers. Minimize environmental impact by using filter systems with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration and avoiding open-air cleaning near sensitive areas.
Operator Training and Certification
All personnel must complete formal training on laser safety, equipment operation, and emergency procedures. Training should include hands-on practice, hazard recognition, and response to malfunctions (e.g., beam misalignment, fire). Maintain training records and conduct periodic refresher courses. Certification may be required depending on regional regulations or internal safety policies.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive logs for equipment maintenance, safety inspections, operator training, and incident reports. Keep copies of compliance documentation, including laser classification certificates, fume extraction system specifications, and safety data sheets (SDS) for materials being cleaned. These records support audits and demonstrate due diligence in regulatory compliance.
International Shipping and Customs
For cross-border logistics, classify the equipment under the correct HS code (e.g., 9013.20 for laser devices). Provide technical specifications, safety certifications (CE, FCC, RoHS), and a laser product report as required by customs authorities. Be aware of import restrictions on high-power laser systems in certain countries. Use freight forwarders experienced in handling controlled technology shipments to ensure compliance with export regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.).
Emergency Procedures and Incident Response
Establish protocols for laser-related incidents, including eye exposure, fire, or equipment malfunction. Post emergency contacts and evacuation routes near work areas. Equip sites with Class D fire extinguishers for metal fires and first aid kits. Conduct regular drills and ensure all personnel know how to activate emergency shutdowns and report incidents to the LSO or safety supervisor.
Maintenance and Calibration
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for optics cleaning, cooling system checks, and laser alignment. Calibrate safety interlocks and sensors periodically. Keep spare parts for critical components on hand to minimize downtime. Document all maintenance activities and retain service records for compliance audits.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Weld Cleaning Equipment
Sourcing laser weld cleaning technology represents a strategic investment in advancing manufacturing and maintenance processes with sustainable, efficient, and high-precision capabilities. As industries increasingly prioritize environmental compliance, worker safety, and operational efficiency, laser cleaning emerges as a superior alternative to traditional methods such as abrasive blasting or chemical cleaning.
When sourcing laser weld cleaning systems, careful consideration should be given to factors including power output, portability, safety features, ease of integration, and supplier support. Selecting a reputable supplier with proven applications in your specific industry ensures reliability and optimal performance. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—factoring in reduced consumables, lower maintenance, and minimal downtime—reveals long-term cost benefits despite higher initial investment.
In conclusion, sourcing laser weld cleaning equipment not only enhances cleaning precision and weld quality but also supports sustainability goals and improves workplace safety. As the technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, early adoption positions businesses at the forefront of innovation, efficiency, and environmental responsibility.