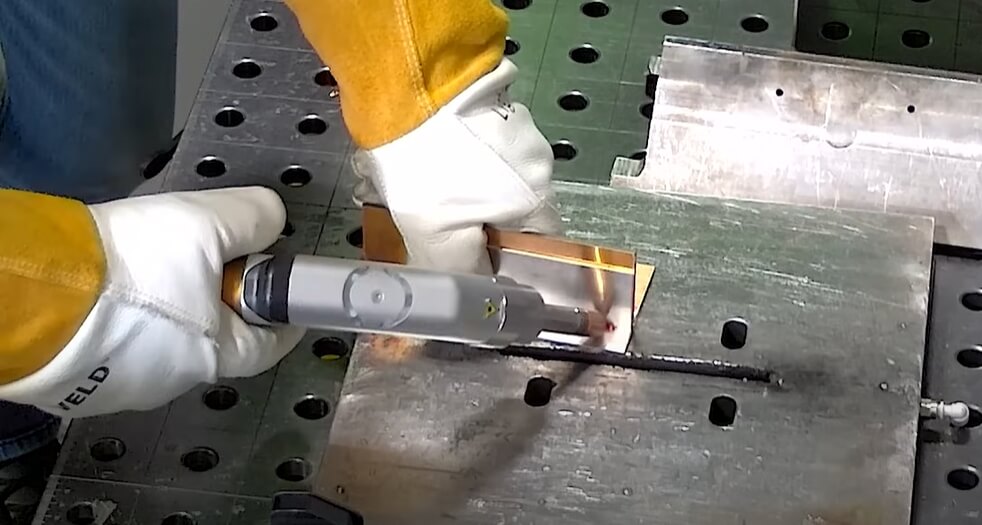
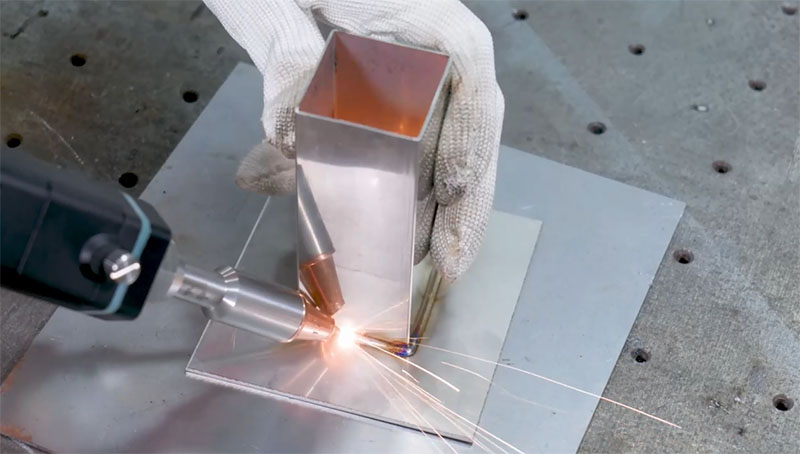
The global aluminum laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for lightweight, high-strength joints in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 4.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% from 2023 to 2030, with aluminum welding representing a significant segment due to its favorable thermal and mechanical properties. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 8.5% for the laser welding market through 2028, citing rising adoption in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing where aluminum’s weight-saving advantages are critical. As precision and automation become paramount, leading manufacturers are investing heavily in advanced laser welding technologies tailored specifically for aluminum’s unique conductivity and reflectivity challenges. In this competitive landscape, the following ten companies have emerged as pioneers, demonstrating exceptional innovation, quality, and market reach in laser welding aluminum components.
Top 10 Laser Weld Aluminum Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#3 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: Laser welders are incredibly versatile and essential in any fabrication shop or factory welding parts from sheet metal….
#4 Weldlogic Inc.
Website: weldlogic.com
Key Highlights: Weldlogic Inc Designs & Manufactures The Finest Automatic Welding & Roll Forming System in the World. Contact Us for a Free Consultation ……
#5 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding creates exceptionally high-quality joints with excellent physical and electrical properties, even when joining challenging materials like aluminum ……
#6 Laser Welding Aluminum
Website: ebindustries.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum is laser weldable. Certified ISO 13485:2016 laser welding services. Fast quote and and turn-around. Automated, semi-automated, CAD/CAM design, ……
#7 Nuburu Blue Laser Company
Website: nuburu.net
Key Highlights: NUBURU’s blue lasers uniquely deliver kW-class power with galvo scanner compatibility, enabling high speed welding with a large process window and micron-scale ……
#8 Welding aluminum – as fast and as easy as steel
Website: kuka.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding. In laser welding, a laser heats the material to melting temperature. The radiation is focused with the aid of optics. The low melt amount and ……
#9 Laser welding
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: TRUMPF lasers can create fine weld points of just a millimeter in diameter in an instant, as well as deep-welded seams stretching over several meters….
#10 Mastering Laser Welding Aluminum
Website: gwklaser.com
Key Highlights: Here you will find the knowledge and skills required for laser welding aluminum and some considerations when combined with practice….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Weld Aluminum

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding Aluminum
The global market for laser welding aluminum is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. Key trends shaping this landscape include:
1. Dominance of High-Power Fiber Lasers & Increased Process Efficiency:
By 2026, high-power (multi-kilowatt) fiber lasers will solidify their position as the dominant technology for aluminum welding. Their superior beam quality, wall-plug efficiency, reliability, and compatibility with automation will drive adoption. Key developments include:
* Single-Mode & Brightness Optimization: Wider adoption of single-mode and high-brightness fiber lasers will enable deeper penetration, higher speeds, and narrower welds, crucial for thin and thick aluminum sections alike.
* Process Speed & Throughput: Continuous improvements in laser power and beam control will significantly increase welding speeds (potentially exceeding 10 m/min for certain applications), boosting production throughput and reducing costs per part.
* Reduced Heat Input & Distortion: Advanced beam shaping (e.g., wobbling, oscillation, ring-mode beams) and process monitoring will minimize heat-affected zones (HAZ), reducing distortion and improving dimensional accuracy, especially vital for lightweight, complex aluminum components.
2. Integration of AI, Machine Learning, and Advanced Process Monitoring:
Intelligence will be deeply embedded into laser welding systems:
* Real-Time Quality Control: Integrated inline monitoring (high-speed cameras, spectroscopy, thermal imaging, acoustic sensors) combined with AI/ML algorithms will enable real-time defect detection (porosity, lack of fusion, spatter) and immediate process correction, moving towards zero-defect manufacturing.
* Predictive Maintenance & Optimization: AI will analyze operational data to predict laser source or component failures, optimize process parameters for specific alloys and joint configurations, and reduce downtime.
* Digital Twins: Wider use of digital twins for process simulation, optimization, and virtual commissioning will shorten development cycles and improve first-time-right success rates.
3. Expansion Beyond Automotive into Diverse High-Growth Sectors:
While automotive (especially EVs) remains the primary driver, significant growth will come from other industries:
* Electric Vehicles (EVs): Explosive growth in EV battery packs (busbars, cooling plates, enclosures), motors (housings, stators/rotors), and lightweight chassis/components will be the single largest driver. Aluminum’s conductivity and weight savings are critical here.
* Aerospace & Defense: Increased adoption for airframes, engine components, and UAVs due to demand for lightweight, high-strength, and reliable joints. Stringent quality requirements will accelerate the use of AI monitoring.
* Renewable Energy: Growing use in solar panel frames, trackers, and particularly in hydrogen storage and fuel cell components (tanks, bipolar plates) where aluminum offers weight and corrosion resistance advantages.
* Consumer Electronics: Miniaturization drives demand for precision laser welding of aluminum housings, heat sinks, and internal components with minimal thermal damage.
4. Focus on Sustainability and Green Manufacturing:
Environmental pressures will influence technology and material choices:
* Energy Efficiency: The inherent energy efficiency of fiber lasers compared to traditional welding (MIG/TIG) will be a major selling point, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and reducing operational costs.
* Lightweighting Imperative: Laser welding enables complex, lightweight aluminum structures, directly contributing to reduced fuel consumption in transportation (EV range extension, aircraft efficiency) and lower lifecycle emissions.
* Reduced Waste: Higher precision, fewer reworks, and less post-weld finishing (due to cleaner, narrower welds) will minimize material waste and energy consumption in secondary operations.
5. Advancements in Hybrid Processes and Automation:
Hybridization and seamless integration will enhance capabilities:
* Laser-Arc Hybrid Welding: Increased use, especially for thicker aluminum sections, combining the deep penetration of laser with the gap-bridging and filler metal addition capabilities of arc processes (e.g., MIG), improving tolerance to fit-up and reducing porosity.
* Robotic & Flexible Automation: Tighter integration of high-power lasers with advanced robotics (including collaborative robots) and flexible fixturing will enable complex 3D welding paths and high-mix, low-volume production, essential for aerospace and custom applications.
* Modular & Scalable Systems: Demand for flexible manufacturing will drive development of modular laser cells that can be easily reconfigured.
6. Addressing Material Challenges & Process Robustness:
Ongoing R&D will focus on overcoming aluminum-specific hurdles:
* Porosity & Spatter Mitigation: Further refinement of beam delivery (e.g., blue lasers for highly reflective pure Al), shielding gas strategies (optimized mixtures, gas nozzles), and real-time control will minimize defects.
* Reflectivity Management: While less critical with modern fiber lasers, process stability for highly reflective aluminum alloys (e.g., 1xxx series) will continue to improve.
* Joining Dissimilar Materials: Increased research and application of laser welding for aluminum-to-steel or aluminum-to-composites, crucial for multi-material lightweight designs, though still a significant technical challenge.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the laser welding of aluminum market will be characterized by smarter, faster, more efficient, and more sustainable processes. Driven by the EV revolution and broader industrial decarbonization, high-power fiber lasers integrated with AI and advanced automation will become the standard for high-quality, high-throughput aluminum joining. Success will depend on continuous innovation in laser sources, process control, and system integration to meet the demanding requirements of next-generation lightweight and high-performance products across multiple sectors.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welded Aluminum: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser welded aluminum components offers advantages like high precision, minimal heat distortion, and strong joints. However, it also presents specific challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to ensure reliable supply and safeguard proprietary designs.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Laser welding aluminum is technically demanding due to the material’s high thermal conductivity, reflectivity, and sensitivity to contamination. Poor execution or oversight during sourcing can lead to critical quality failures.
1. Inconsistent Weld Penetration and Porosity
Aluminum’s high reflectivity and thermal conductivity make achieving uniform laser absorption difficult. Contamination from oils, oxides, or moisture on the surface often results in unstable keyhole formation, leading to inconsistent penetration depth and porosity. Sourcing from suppliers without strict pre-weld cleaning protocols or process monitoring increases the risk of weak or defective welds.
2. Lack of Process Control and Documentation
Laser welding requires precise control over parameters such as laser power, travel speed, shielding gas flow, and beam focus. Suppliers without robust process validation (e.g., through Welding Procedure Specifications – WPS) and real-time monitoring (e.g., melt pool monitoring) may deliver inconsistent results. Without documented process controls, traceability and root cause analysis during failures become nearly impossible.
3. Poor Joint Fit-Up and Fixturing
Aluminum expands and contracts significantly during welding. Inadequate joint preparation or fixturing can lead to gaps, misalignment, or distortion. Laser welding, with its narrow weld zone, is less forgiving of poor fit-up than traditional methods. Sourcing from partners without precision tooling and alignment capabilities increases the risk of geometric inaccuracies and weld defects.
4. Inadequate Post-Weld Inspection and Testing
Many suppliers rely solely on visual inspection, missing subsurface defects like micro-cracks or porosity. Without non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic testing (UT), radiographic testing (RT), or computed tomography (CT), hidden flaws may go undetected until in-field failure. Ensure your supplier has access to and applies appropriate NDT methods based on the component’s criticality.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
When sourcing custom laser welded aluminum parts, especially for high-tech or competitive industries, protecting design and process IP is crucial.
1. Weak or Absent IP Clauses in Contracts
Generic procurement agreements often lack explicit terms defining IP ownership of designs, tooling, and process know-how. Without clear contractual language, suppliers may claim rights to improvements or reuse your designs for other clients. Always include clauses specifying that all IP developed or used for your project remains your exclusive property.
2. Risk of Design Replication or Reverse Engineering
Suppliers with access to CAD models, jigs, and welding parameters may replicate your components or sell similar designs to competitors. This is particularly concerning with offshore or low-cost suppliers. Mitigate this by using tiered information disclosure (e.g., providing only assembly-level data), watermarking documents, and requiring strict confidentiality agreements (NDAs) with audit rights.
3. Uncontrolled Sub-tier Supplier Access
Many contract manufacturers subcontract welding or machining operations. If sub-tier suppliers are not bound by the same IP protections, your designs could be exposed to multiple untrusted parties. Ensure your master supplier is contractually responsible for extending IP protections to all sub-contractors and maintains a controlled supply chain.
4. Loss of Process IP and Tacit Knowledge
The laser welding parameters and fixturing solutions developed for your product represent valuable process IP. If not formally documented and protected, suppliers may retain or exploit this knowledge. Specify in contracts that all process documentation, settings, and tooling belong to you and must be returned upon project completion.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Conduct thorough supplier audits focusing on welding certifications (e.g., ISO 3834, AWS D17.1), NDT capabilities, and IP security measures.
- Require documented Welding Procedure Qualifications (WPQ) and sample testing before full production.
- Use detailed technical specifications and acceptance criteria, including weld quality standards (e.g., ISO 13919-1 for laser welding).
- Implement strong IP protections: include IP assignment clauses, confidentiality obligations, and data handling protocols in all agreements.
- Maintain active oversight with regular quality audits and open communication channels.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP challenges, companies can effectively leverage the benefits of laser welded aluminum while minimizing risk in their supply chain.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welding Aluminum
Material Handling and Storage
Aluminum used in laser welding must be stored in a clean, dry environment to prevent oxidation and contamination. Store materials off the floor on racks or pallets, and cover them when not in use to protect against dust, oils, and moisture. Separate aluminum from ferrous metals to avoid cross-contamination, which can compromise weld integrity. Label all materials clearly with alloy type, temper, and batch number to ensure traceability throughout the production process.
Transportation Requirements
During transportation, aluminum components and raw materials must be securely fastened to prevent movement and surface damage. Use non-abrasive padding and protective films to avoid scratches or deformation. For sensitive or precision parts, climate-controlled transport may be required to minimize thermal expansion and condensation risks. Ensure shipping containers are clean and free from residues that could transfer contaminants to aluminum surfaces prior to welding.
Pre-Welding Surface Preparation Compliance
Prior to laser welding, aluminum surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned to remove oils, oxides, and particulates. Use chemical cleaning (e.g., alkaline or solvent degreasing) or mechanical methods (e.g., stainless steel wire brushing dedicated to aluminum) in accordance with ISO 14175 or AWS C5.7 standards. Document cleaning procedures and parameters to meet quality audit requirements. Only use tools and cloths designated exclusively for aluminum to avoid iron contamination.
Laser Welding Process Control and Safety Protocols
Laser welding operations must comply with safety standards such as ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers) and IEC 60825. Install interlocks, beam enclosures, and laser-safe viewing windows. Operators must wear appropriate PPE, including laser-protective eyewear rated for the specific wavelength (typically 1070 nm for fiber lasers). Maintain a controlled environment with proper fume extraction systems to capture aluminum oxide particulates, complying with OSHA PEL (Permissible Exposure Limits) and local air quality regulations.
Environmental and Emission Compliance
Fumes generated during aluminum laser welding contain fine metal particulates and may include ozone and nitrogen oxides. Install high-efficiency fume extraction systems equipped with HEPA or ULPA filters. Conduct regular emissions testing and maintain records to comply with EPA, REACH, or local environmental regulations. Dispose of collected filters and waste materials as hazardous waste where applicable, following RCRA guidelines.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Implement a documented welding procedure specification (WPS) and procedure qualification record (PQR) in accordance with AWS D1.2 or ISO 15614-12. Perform non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic testing (UT) or radiographic testing (RT) as required. Maintain traceability of materials, weld parameters, operator certifications, and inspection results. Store records digitally or physically for the required retention period (typically 10+ years for critical applications).
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Ensure compliance with applicable standards, including:
– AWS D1.2/D1.2M: Structural Welding Code – Aluminum
– ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems
– ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety
– AS9100 (if in aerospace): Quality Management for Aviation, Space, and Defense
– PED 2014/68/EU (if in pressure equipment): Pressure Equipment Directive
Regularly audit processes and update procedures to reflect changes in regulations or customer requirements.
Training and Personnel Certification
All personnel involved in laser welding aluminum must undergo certified training programs. Welders should be qualified per AWS D1.2 or ISO 9606-2. Laser safety officers (LSOs) must be appointed and trained per ANSI Z136.1. Maintain up-to-date training records and certifications, including refresher courses on safety, quality, and equipment operation.
Packaging and Final Product Shipment
After welding, finished products must be protected against corrosion and physical damage. Use VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) packaging or desiccants for long-term storage or overseas shipping. Clearly label packages with handling instructions, material specifications, and compliance markings (e.g., CE, RoHS if applicable). Include shipping documentation such as material test reports (MTRs), weld logs, and certificates of compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Weld Aluminum:
Sourcing components or services involving laser welding of aluminum requires a strategic approach that balances material quality, welding expertise, and process precision. Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity, reflectivity, and susceptibility to porosity and cracking make laser welding a technically demanding process that necessitates specialized equipment and skilled operators. Therefore, when sourcing laser weld aluminum solutions, it is critical to select suppliers with proven experience in handling aluminum alloys, access to advanced laser technologies (such as fiber or disk lasers), and robust quality control measures.
Key considerations include alloy compatibility, joint design, surface preparation, and post-weld inspection capabilities. Partnering with suppliers who adhere to industry standards and can provide consistent repeatability and metallurgical integrity ensures reliable performance in demanding applications—especially in industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics where lightweight, high-strength structures are essential.
Ultimately, successful sourcing hinges on thorough vetting of supplier capabilities, clear communication of technical requirements, and ongoing collaboration to ensure quality, cost-efficiency, and on-time delivery. Investing in the right laser welding partner enables optimal performance, durability, and innovation in aluminum-based fabricated components.