The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, automated manufacturing processes across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising adoption of electric vehicles requiring complex battery and component welding, and the broader push toward industrial automation. As manufacturers seek faster, cleaner, and more energy-efficient joining solutions, laser welding has emerged as a superior alternative to traditional methods. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and technological integration—setting the benchmark for quality and performance worldwide.
Top 10 Laser Weilder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: Laser welders are incredibly versatile and essential in any fabrication shop or factory welding parts from sheet metal….
#3 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#4 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#5 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#6 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#7 Everlast Inverter Welders Equipment
Website: everlastgenerators.com
Key Highlights: Everlast Power Equipment, manufacturers of MIG, TIG & Stick welders. For reliable welding machines and supplies shop Everlast Power Equipment….
#8 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
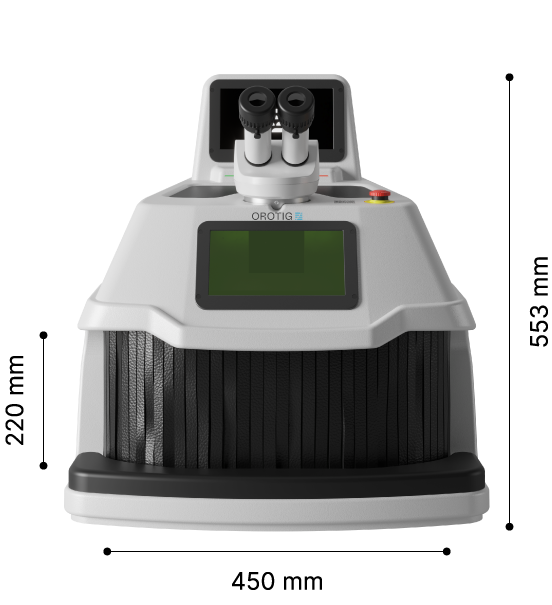
#9 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
#10 Full Spectrum Laser
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Weilder

2026 Market Trends for Laser Welding: H2 Outlook
Heading into the second half of 2026, the global laser welding market is poised for continued expansion, driven by technological advancements, increasing automation demands, and shifting industrial priorities. Key trends shaping the H2 2026 landscape include:
-
Accelerated Adoption of High-Power & Ultrafast Lasers:
- Focus: Industrial lasers exceeding 10 kW (fiber and disk) will solidify dominance in heavy-duty applications (e.g., shipbuilding, heavy machinery, thick-section welding in EVs). Simultaneously, ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers will see broader commercial use beyond R&D, particularly in medical device manufacturing, electronics, and precision battery welding, enabling clean, cold-welding processes.
- Impact: Enables faster processing speeds, deeper penetration, and welding of previously challenging materials (e.g., copper, aluminum alloys, dissimilar metals).
-
Intelligent Welding Systems & AI Integration:
- Focus: H2 2026 will see widespread deployment of AI-driven monitoring, control, and optimization systems. Real-time monitoring (using sensors like spectrometers, high-speed cameras, acoustic emission) combined with machine learning algorithms will enable predictive quality control, automatic defect detection, adaptive process parameter adjustment, and reduced scrap rates.
- Impact: Significantly improves weld consistency, reduces reliance on highly skilled operators, lowers total cost of ownership, and enhances traceability.
-
Hybrid Laser-Arc Welding (HLAW) Maturation:
- Focus: HLAW technology will move beyond niche applications into mainstream production, especially in high-volume sectors like automotive (especially chassis and body-in-white) and heavy equipment. Improved system integration and control software will make HLAW more user-friendly and reliable.
- Impact: Combines the speed and precision of lasers with the gap-bridging and tolerance forgiveness of arc welding, offering cost-effective solutions for demanding applications.
-
Sustainability & Green Manufacturing Drivers:
- Focus: Energy efficiency will be a major purchasing criterion. Manufacturers will favor lasers with higher wall-plug efficiency. The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy infrastructure (solar panels, battery storage systems) will be the single largest driver, demanding high-speed, high-precision welding of battery components (tabs, busbars, casings) and power electronics.
- Impact: Laser welding’s inherent low heat input and minimal waste align perfectly with sustainability goals, boosting its adoption.
-
Expansion in Key Sectors:
- EV Battery Manufacturing: Remains the primary growth engine, demanding high-speed, high-reliability welding for prismatic, pouch, and cylindrical cells. Automation lines equipped with multiple laser welding stations will be ubiquitous.
- Electronics & Micro-Welding: Miniaturization trends drive demand for precise, low-heat-input welding in consumer electronics, semiconductor packaging, and sensors.
- Medical Devices: Growth in minimally invasive devices and implants requires the precision and cleanliness of laser welding.
- Aerospace & Additive Manufacturing: Advanced alloys and complex geometries continue to leverage laser welding for critical components and as part of hybrid manufacturing processes.
-
Regional Shifts & Supply Chain Resilience:
- Focus: While Asia-Pacific (led by China, Japan, South Korea) remains the largest market, North America and Europe are experiencing strong growth, partly driven by onshoring/nearshoring initiatives in EV and battery production. Supply chains for critical components (laser sources, optics) will focus on diversification and resilience.
- Impact: Increased regional manufacturing hubs will drive localized demand for laser welding systems.
-
Increased Competition & Cost Pressure:
- Focus: Intensifying competition, particularly in the mid-power fiber laser segment, will lead to price stabilization or even modest decreases. This will further lower the barrier to entry for smaller manufacturers.
- Impact: Wider adoption across SMEs and in cost-sensitive applications.
H2 2026 Outlook Summary:
The laser welding market in the second half of 2026 will be characterized by maturity, intelligence, and specialization. The technology will be less of a novelty and more of a standard, high-precision manufacturing tool. Success will depend on system intelligence (AI/ML), process reliability, energy efficiency, and seamless integration into automated production lines. The EV revolution will remain the dominant growth vector, but expansion into electronics, medical, and aerospace will diversify the market. Vendors focusing on integrated, intelligent solutions and supporting the sustainability transition will be best positioned for success.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welders: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser welders, especially from international or less-established suppliers, involves significant risks related to both equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for making informed procurement decisions and safeguarding your long-term operational and competitive interests.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Build Quality and Component Sourcing
Many suppliers, particularly lower-cost manufacturers, may use substandard materials or inconsistent assembly practices. Key components like laser sources, optics, cooling systems, and motion controls might be sourced from unreliable vendors, leading to premature failure, reduced precision, and increased downtime.
Lack of Rigorous Testing and Certification
Some laser welders are shipped without undergoing comprehensive performance, safety, or reliability testing. Absence of internationally recognized certifications (such as CE, FDA, or ISO standards) can indicate non-compliance with safety regulations and performance benchmarks, posing operational and legal risks.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Poor technical support, limited documentation, and difficulty sourcing spare parts—especially for proprietary components—can severely impact uptime and maintenance efficiency. This is particularly problematic when sourcing from distant or inexperienced suppliers.
Overstated Performance Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate laser power, welding speed, accuracy, or duty cycle in marketing materials. Without independent verification or on-site testing, buyers risk acquiring equipment that fails to meet production requirements, leading to costly rework or replacement.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Some manufacturers incorporate cloned or pirated laser modules, control software, or optical components in their systems. This not only affects reliability but may also expose the end user to legal liability if the original IP holder pursues infringement claims.
Embedded Proprietary Software Without Licensing
Laser welders often rely on sophisticated software for control, monitoring, and process optimization. Unauthorized or unlicensed software embedded in the system can lead to compliance issues, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, or unexpected obsolescence if the software is later challenged or withdrawn.
Lack of IP Ownership Clarity in Custom Solutions
When commissioning custom-built laser welding systems, contracts may fail to clearly define who owns the design, process parameters, or software enhancements developed during the project. This ambiguity can hinder future scalability, maintenance, or technology transfer.
Exposure to Third-Party IP Litigation
Using a system that infringes on existing patents (e.g., in beam delivery, motion control, or safety interlocks) may draw the end user into legal disputes, even if unintentional. Due diligence on the supplier’s IP clearance practices is essential to mitigate this risk.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier vetting, request third-party validation of performance claims, insist on transparent component sourcing, and include robust IP clauses in procurement contracts. On-site audits, pilot testing, and legal reviews of software and design rights can significantly reduce exposure to quality and IP-related issues.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welder
Equipment Transportation and Handling
Ensure the laser welder is securely packaged and transported on a stable, vibration-dampened platform to prevent internal component damage. Use lifting equipment rated for the machine’s weight and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for tilting and positioning. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, or dusty environments during transit. Upon arrival, perform a visual inspection and confirm all components are intact before installation.
Site Preparation and Installation Requirements
Prepare a level, clean, and well-ventilated workspace with adequate power supply matching the laser welder’s voltage, phase, and amperage specifications. Install appropriate grounding to prevent electrical hazards. Ensure sufficient clearance around the machine for maintenance, heat dissipation, and operator access. Confirm that environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) are within the manufacturer’s recommended range.
Regulatory Compliance
Comply with all local, national, and international regulations governing laser equipment use, including OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards in the U.S. or equivalent bodies such as the HSE in the UK. Adhere to IEC 60825-1 for laser safety classification and ensure the laser welder is registered with the appropriate regulatory authority if required. Maintain documentation of compliance certifications and equipment conformity (e.g., CE, UL marks).
Laser Safety Protocols
Implement engineering controls such as interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency stop mechanisms. Install appropriate laser warning signs at entry points to the work area. Require operators to wear laser safety eyewear with the correct optical density (OD) rating for the laser’s wavelength and power. Conduct regular safety training and maintain a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) if mandated by regulations.
Operational Documentation and Recordkeeping
Keep detailed logs of machine usage, maintenance, calibration, and safety inspections. Store user manuals, safety data sheets (SDS), and compliance documentation on-site or in a secure digital system. Maintain records of operator training and certification to demonstrate due diligence in compliance audits.
Waste and Byproduct Management
Safely collect and dispose of fumes and particulate matter generated during laser welding using certified fume extraction systems. Filter and maintain exhaust systems regularly to ensure effectiveness. Classify and dispose of metal residues and filters according to local hazardous waste regulations.
Import/Export and Customs Considerations (if applicable)
If shipping the laser welder across international borders, verify export control classifications (e.g., ECCN under the EAR). Obtain necessary licenses for controlled technology, especially for high-power laser systems. Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Comply with destination country’s import regulations for industrial machinery and laser products.
Maintenance and Compliance Audits
Schedule routine preventive maintenance per the manufacturer’s recommendations and document all service activities. Conduct internal compliance audits periodically to verify adherence to safety, environmental, and operational standards. Address any non-conformities promptly and update procedures as needed.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Welder
In conclusion, sourcing a laser welder requires a careful evaluation of several key factors including welding application requirements, material types and thicknesses, precision needs, production volume, and available budget. After assessing various suppliers, technologies (such as fiber, CO2, and disk lasers), and system integrations, it is evident that selecting the right laser welding solution involves balancing performance, reliability, and long-term operational costs.
Investing in a high-quality laser welder from a reputable supplier not only enhances welding accuracy and efficiency but also reduces maintenance downtime and operational waste. Automation compatibility and post-purchase support—such as training, service, and spare parts availability—are critical for ensuring seamless integration into existing production lines.
Ultimately, the decision should align with both current manufacturing demands and future scalability goals. By conducting thorough due diligence and prioritizing technical specifications alongside supplier credibility, organizations can make a strategic investment that improves product quality, increases productivity, and strengthens competitive advantage in the marketplace.