The global wood treatment and surface finishing market has witnessed steady expansion, fueled by rising demand for high-quality, durable wood finishes in furniture, flooring, and cabinetry. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global wood coating market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029, driven by advancements in eco-friendly and precision-finishing technologies. As manufacturers prioritize efficiency and sustainability, laser varnish removal has emerged as a transformative solution—offering precise, chemical-free, and heat-controlled stripping of coatings without damaging the underlying wood. Unlike traditional sanding or chemical strippers, laser technology enables selective varnish removal with minimal waste and reduced labor costs. In this evolving landscape, selecting the right laser varnish remover is critical for maintaining production quality and competitiveness. Based on performance metrics, customer reviews, and suitability for industrial applications, here are the top eight laser varnish removers tailored for wood manufacturers in 2024.
Top 8 Laser Varnish Remover For Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: With over 35 years of expertise in surface treatment and more than 450 systems installed worldwide, P-Laser is at the forefront of industrial laser cleaning ……
#2 Laser cleaner machine prices
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaner machine prices and parameters, download our Catalogue….
#3 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning removes paint, contaminants, rust, and residues with a high-energy laser beam which leaves the substrate untouched. Our Laser Ablation is the ……
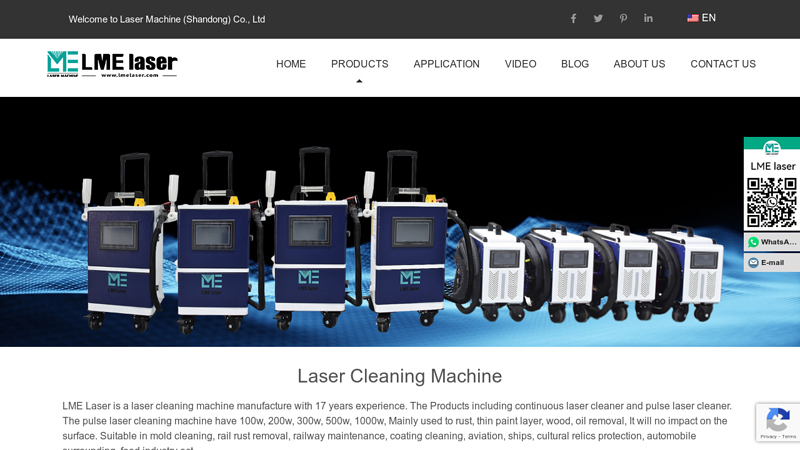
#4 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: The pulse laser cleaning machine have 100w, 200w, 300w, 500w, 1000w, Mainly used to rust, thin paint layer, wood, oil removal, It will no impact on the surface….
#5 Clean Laser Technologies
Website: cleanlasertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Discover advanced laser cleaning machines and rust removal systems trusted by industries across the USA. Eco-friendly, precise, and OSHA-compliant surface ……
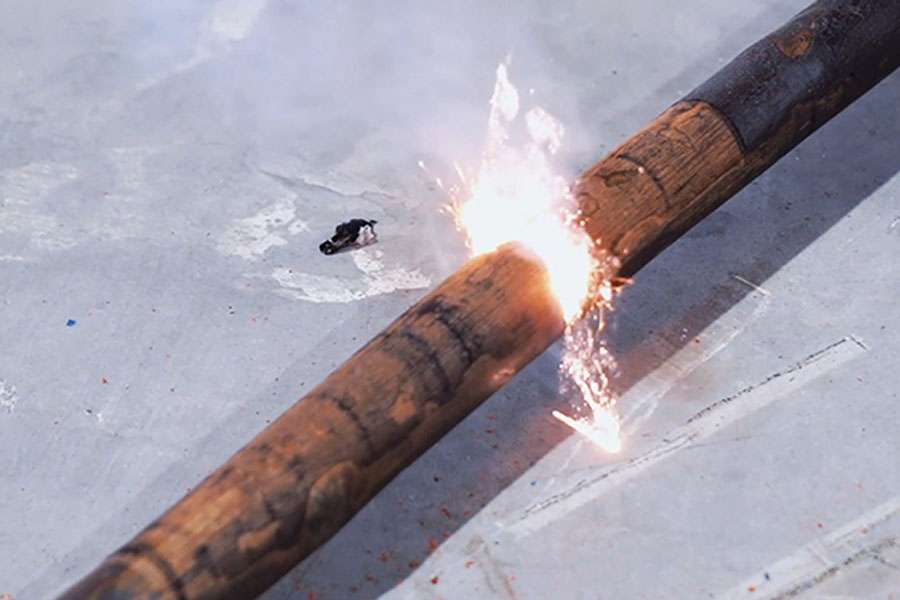
#6 Application Of Laser Paint Stripping For Wood
Website: chutian-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripper for wood offers precise control over the amount of energy used, allowing for targeted paint removal without damaging the wood….
#7 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#8 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: Our customer feedback confirms that HANTENCNC’s 500W laser stripper delivers high efficiency, effortless operation, and flawless paint removal—making it the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Varnish Remover For Wood

2026 Market Trends for Laser Varnish Remover for Wood
Rising Demand for Precision and Non-Destructive Restoration
By 2026, the market for laser varnish removers in wood applications is expected to see significant growth, primarily driven by a heightened demand for precision in restoration and conservation projects. Traditional methods such as chemical stripping or sanding often risk damaging delicate wood surfaces, especially on antique furniture, historic buildings, and intricate woodwork. Laser technology offers a non-contact, highly controllable alternative that removes varnish layer by layer without harming the underlying wood grain. As both professional restorers and high-end woodworking industries prioritize preservation and accuracy, laser systems will become increasingly favored, particularly in heritage conservation sectors across Europe and North America.
Advancements in Portable and User-Friendly Laser Systems
A key trend shaping the 2026 landscape is the rapid development of portable, compact, and more user-friendly laser varnish removal tools. Early laser systems were large, expensive, and required specialized operators. However, ongoing innovations are leading to lighter, handheld devices with intuitive interfaces and improved safety features. These advancements are lowering the entry barrier for small workshops, artisan woodworkers, and on-site restoration teams. As manufacturers integrate features like adjustable power settings, real-time monitoring, and enhanced cooling systems, adoption is expected to expand beyond industrial applications into niche and commercial markets.
Growing Environmental and Safety Regulations Driving Adoption
Environmental regulations and workplace safety standards are becoming stricter globally, particularly concerning the use of chemical solvents in varnish removal. Many traditional strippers contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that pose health risks and environmental hazards. In response, industries are seeking sustainable alternatives. Laser varnish removal produces minimal waste—primarily vaporized varnish captured by filtration systems—making it a cleaner and safer method. By 2026, compliance with green building standards and environmental certifications is likely to accelerate the shift toward laser-based solutions, especially in regions with stringent environmental policies like the EU and parts of North America.
Integration with Automation and Smart Technologies
The convergence of laser technology with automation and digital control systems will be a defining trend in 2026. Advanced laser varnish removers are increasingly being integrated with CAD-guided robotics and AI-driven pattern recognition, enabling automated, repeatable processes in large-scale woodworking and furniture manufacturing. These smart systems can detect varnish thickness and adjust laser intensity accordingly, optimizing efficiency and consistency. This trend is particularly relevant in high-volume production environments where precision and throughput are critical, further expanding the market beyond restoration into industrial finishing applications.
Price Reductions and Broader Market Accessibility
While laser varnish removers have traditionally been high-cost investments, increased competition, technological maturity, and economies of scale are expected to drive price reductions by 2026. As more manufacturers enter the space and production processes become more efficient, mid-range laser systems will become more accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Rental and service-based models may also emerge, offering cost-effective access to laser technology without the need for large upfront capital. This democratization of access is anticipated to broaden the user base significantly, including independent craftsmen, restoration startups, and educational institutions.
Expansion into Emerging Applications and Geographies
By 2026, the application scope of laser varnish removers is expected to extend beyond traditional furniture and architectural woodwork into areas such as musical instrument restoration, luxury interior design, and museum curation. Additionally, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing growing interest in high-quality restoration techniques, fueled by increasing heritage preservation efforts and rising disposable incomes. As awareness grows and training programs become more widespread, these regions are poised to become key growth areas for laser-based wood finishing technologies.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser varnish removers for wood will be characterized by increased adoption due to technological advancements, environmental compliance, and expanding accessibility. As the industry evolves, laser systems are set to become a standard tool in both conservation and modern woodworking, offering unmatched precision, safety, and sustainability.
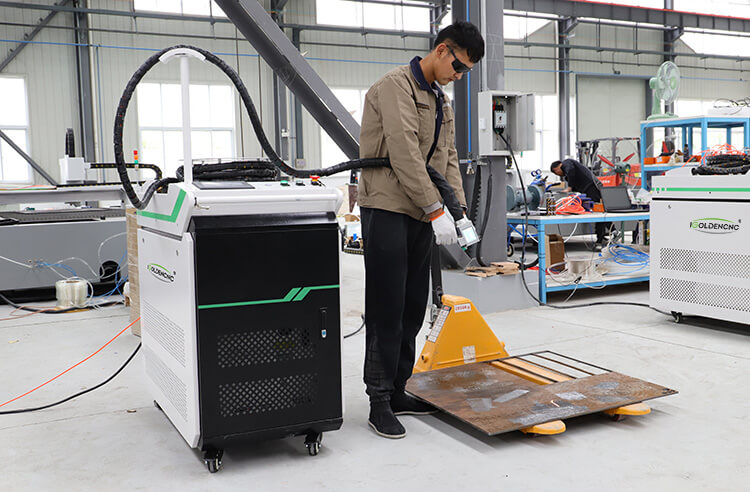

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Varnish Remover for Wood (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a laser varnish remover for wood requires careful attention to both technical performance and legal compliance. Overlooking key aspects can lead to subpar results, operational delays, or legal complications. Below are critical pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Beam Quality and Inconsistent Removal Performance
Low-quality laser systems often suffer from inconsistent beam focus, power fluctuations, or inadequate wavelength precision. This results in uneven varnish removal, wood charring, or incomplete stripping. Ensure the laser offers stable output, appropriate pulse control (for pulsed lasers), and compatibility with common wood finishes. Always request sample testing on your specific wood and varnish types before procurement.
Inadequate Power and Speed Specifications for Your Application
Not all laser removers are created equal. Systems underpowered for the task will require excessive pass runs, reducing efficiency and increasing heat buildup—which risks damaging the wood substrate. Conversely, overly powerful lasers may ablate the wood itself. Match the laser’s wattage, scanning speed, and duty cycle to your production volume and material requirements.
Lack of Cooling and Safety Features
Laser systems generate significant heat, especially during prolonged use. Units without proper cooling (e.g., air or water cooling) can overheat, leading to premature component failure. Additionally, missing safety interlocks, protective enclosures, or fume extraction compatibility increase operational risks. Always verify integration with ventilation systems to handle wood and varnish particulates.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Rights and Licensing
Using or sourcing laser equipment that incorporates patented technologies without proper licensing exposes your business to legal action. Some laser configurations, control software, or scanning mechanisms may be protected under IP laws. Verify that the supplier owns or legally licenses the technology and provides documentation to confirm compliance, especially when importing equipment internationally.
Choosing Non-Compliant or Unverified Equipment
Equipment that lacks necessary certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, or IEC standards) may not meet safety or electromagnetic compatibility requirements. This can result in regulatory delays or operational shutdowns. Ensure the laser system complies with regional safety and environmental regulations, particularly regarding laser class (e.g., Class 1 or 4) and operator protection.
Overlooking Software and User Interface Limitations
The effectiveness of a laser varnish remover heavily depends on its control software. Poorly designed interfaces, limited programmability, or lack of integration with CAD/CAM systems hinder precision and repeatability. Verify that the software allows for customizable removal patterns, depth control, and easy parameter adjustments tailored to different wood grain densities and varnish thicknesses.
Underestimating Maintenance and Support Requirements
Some suppliers offer low upfront pricing but lack reliable technical support or spare parts availability. Laser optics, mirrors, and diodes require periodic maintenance. Choose a supplier with a proven service network, accessible documentation, and training support to minimize downtime and maintain consistent quality over time.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures you source a reliable, efficient, and legally compliant laser varnish removal solution that preserves wood integrity and supports long-term operational success.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Varnish Remover for Wood
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal handling, transport, storage, and use of a laser-based system designed to remove varnish from wood surfaces. Note that this document refers to the laser system itself—not a chemical product—and therefore compliance focuses on machinery safety, radiation, and electrical standards.
Regulatory Classification & Jurisdiction
Laser Varnish Removers for Wood are classified as industrial laser systems and fall under various regulatory frameworks depending on the region. Key classifications include:
- IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
- 21 CFR 1040.10 & 1040.11 (FDA/CDRH): U.S. regulations for laser products, including performance standards and reporting.
- Directive 2014/35/EU (Low Voltage Directive) and 2014/30/EU (EMC Directive): Applicable in the European Union for electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility.
- Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC (EU): Applies if the laser is integrated into a machine system.
- ANSI Z136.1: Safe Use of Lasers (U.S. consensus standard).
Ensure the equipment carries appropriate certifications (e.g., CE, FDA registration, RoHS, REACH) prior to distribution.
Safety & Risk Mitigation
Laser systems pose significant hazards that must be addressed through engineering controls and operational procedures:
- Laser Radiation (Class 3B or 4): Most wood varnish removal lasers are Class 4—capable of causing skin and eye injuries, and fire hazards. Interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency stop mechanisms are mandatory.
- Fume and Particulate Emissions: Laser ablation generates airborne particulates and potentially toxic fumes (e.g., from varnish pyrolysis). Local exhaust ventilation (LEV) and HEPA filtration are required.
- Fire Risk: High-powered lasers can ignite wood or residue. Fire suppression systems, non-combustible work surfaces, and continuous monitoring are essential.
- Electrical Safety: High-voltage components require grounding, insulation, and protection against shock (per IEC 60335 or similar).
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators must use laser safety goggles (wavelength-specific), protective clothing, and respiratory protection if ventilation is insufficient.
Packaging & Transportation
Due to sensitivity and regulatory status, proper packaging and shipping protocols are critical:
- Secure Packaging: Use shock-absorbent materials and rigid containers to prevent damage. Include immobilization for mirrors and optical components.
- Labeling Requirements:
- “Laser Radiation – Avoid Direct Exposure to Beam” (per IEC 60825).
- Class 4 Laser Product warning label.
- Fragile, This Way Up, and moisture-sensitive indicators if applicable.
- Transport Regulations:
- Not classified as hazardous material under IATA/IMDG/ADR if no batteries or hazardous substances are included.
- Lithium batteries (if used in portable units) must comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (PI 966 or PI 967).
- Documentation must include technical specifications, laser class, and safety instructions.
Storage & Handling
Proper storage ensures equipment longevity and safety:
- Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled area (typically 10°C–40°C), free from dust and corrosive agents.
- Security: Restrict access to authorized personnel only. Use lockable enclosures if stored in shared spaces.
- Orientation: Follow manufacturer guidelines—some systems must be stored upright to prevent misalignment.
- Optical Components: Keep lenses and mirrors covered and protected from contamination.
Import/Export Compliance
International movement of laser systems is tightly regulated:
- Export Controls:
- Check EAR (U.S. Export Administration Regulations) – Some high-power lasers may be controlled under ECCN 6A003.
- EU Dual-Use Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2021/821) may apply for high-power or precision systems.
- Customs Documentation:
- Commercial invoice with HS Code (e.g., 8515.21 – Laser welding, cutting or soldering machines).
- Certificate of Conformity (CE, FDA, etc.).
- Technical specifications and user manual.
- Import Requirements:
- Verify local laser registration or approval requirements (e.g., Health Canada, ANVISA in Brazil).
- Some countries require pre-approval for Class 3B/4 lasers.
End-of-Life & Disposal
Environmental and safety considerations extend to decommissioning:
- Electrical Components: Dispose of power supplies and circuit boards per WEEE (EU) or local e-waste regulations.
- Optical Parts: Lenses and mirrors may contain coatings requiring special handling; consult local hazardous waste guidelines.
- Batteries (if applicable): Recycle per battery directive (e.g., EU Battery Directive 2006/66/EC).
- Manufacturer Take-Back Programs: Utilize if available for responsible recycling.
Training & Documentation
Compliance also requires robust operational support:
- User Training: Operators must be trained in laser safety, emergency procedures, and maintenance.
- Required Documentation:
- User manual with safety instructions.
- Declaration of Conformity (DoC).
- Laser safety data (wavelength, power, divergence).
- Maintenance and service records.
Summary & Best Practices
To ensure compliant and safe operations:
- Verify all regulatory certifications before sale or import.
- Implement engineering controls (enclosures, ventilation, interlocks).
- Train personnel and enforce PPE use.
- Ship with proper labeling and documentation.
- Monitor changes in regulations (e.g., updates to IEC, FDA, or EU directives).
- Maintain records of compliance, training, and maintenance.
Always consult local authorities and the equipment manufacturer for region-specific requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser varnish remover for wood requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure effectiveness, safety, and value. First, assess the specific type of wood and varnish you are working with, as different lasers vary in compatibility with materials and finish types. Fiber or CO₂ lasers are commonly used, with CO₂ lasers generally preferred for wood due to their precision and non-contact removal process.
When sourcing, prioritize reputable suppliers that offer technical support, safety certifications, and training—especially since laser equipment involves operational and safety risks. Evaluate machine specifications such as power output, beam control, cooling systems, and ease of integration into existing workflows. Automated or handheld options should be chosen based on project scale and required precision.
Cost is an important factor, but it should be balanced against long-term durability, maintenance needs, and energy efficiency. Additionally, consider environmental benefits, as laser removal is a chemical-free, low-waste alternative to traditional stripping methods.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality laser varnish remover from a trusted provider can significantly enhance restoration outcomes, reduce labor time, and offer a sustainable solution for wood refinishing projects. Proper research, supplier vetting, and pilot testing will ensure a successful implementation tailored to your specific needs.