The global laser equipment market, driven by increasing demand for precision in manufacturing and woodworking industries, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. With the woodworking sector increasingly adopting automated solutions for efficiency and accuracy, laser technology has emerged as a preferred method for stripping, engraving, and cutting wood without compromising material integrity. In particular, CO₂ and fiber laser systems are gaining traction due to their non-contact operation, reduced waste, and compatibility with various wood types. As industries shift toward sustainable and high-precision processing, the demand for specialized laser systems to strip wood—removing finishes, paint, or coatings with minimal substrate damage—has surged. This growing trend has catalyzed innovation among manufacturers who are enhancing power control, beam quality, and integration with CNC systems to deliver turnkey solutions. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and customer adoption, here are the top 9 manufacturers leading the development and deployment of laser systems specifically designed for wood stripping applications.
Top 9 Laser To Strip Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Machine – Laser Equipment Manufacturer
Website: dplaser.com
Key Highlights: DPLASER is a leading manufacturer & factory of industrial laser welding, laser cutting, laser marking and laser cleaning machines….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Explore PULSAR Laser P CL laser cleaning machines for industrial rust removal and paint stripping. Compare SHARK P CL, PANDA P CL and FOX P CL….
#4 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#5 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#6 Laser cleaning
Website: narran.cz
Key Highlights: We can design and integrate a laser cleaning system into production, build a robotic workstation or supply a mobile laser for a wide range of applications….
#7 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: LME Laser is a laser cleaning machine manufacture with 17 years experience. The Products including continuous laser cleaner and pulse laser cleaner….
#8 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
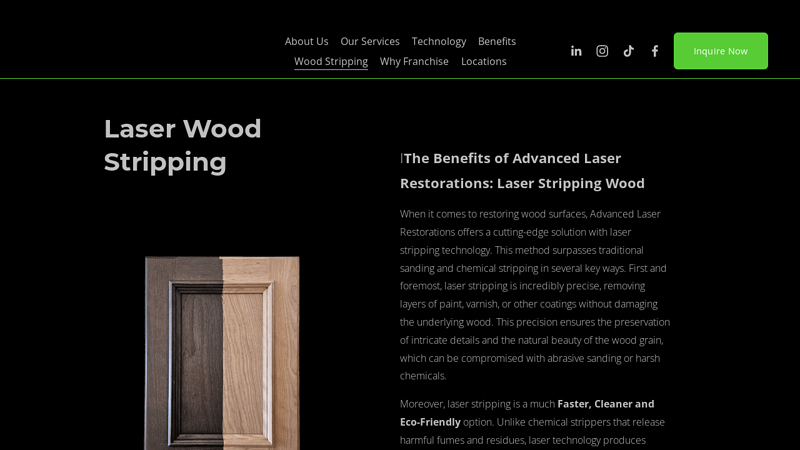
#9 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping is incredibly precise, removing layers of paint, varnish, or other coatings without damaging the underlying wood….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser To Strip Wood

2026 Market Trends for Laser to Strip Wood
The global market for laser-based wood stripping technologies is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in laser systems, rising demand for eco-friendly surface preparation methods, and growing adoption across industrial, restoration, and manufacturing sectors. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the “Laser to Strip Wood” industry, focusing on technological innovation, environmental benefits, sector-specific applications, and regional growth patterns.
Technological Advancements in Laser Stripping Systems
By 2026, laser wood stripping technology is expected to undergo substantial improvements in efficiency, precision, and accessibility. Fiber and pulsed laser systems are becoming more compact and cost-effective, enabling broader adoption beyond large industrial facilities. Innovations in beam control, real-time monitoring, and automated scanning systems allow for selective removal of paint, varnish, or coatings without damaging the underlying wood grain. Integration with robotics and AI-driven software enables adaptive stripping for complex or irregular surfaces, improving consistency and reducing labor costs. These advancements are making laser systems increasingly competitive with traditional methods like sandblasting or chemical stripping.
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Environmental sustainability is a major catalyst for the adoption of laser wood stripping. Unlike chemical solvents or abrasive techniques, laser ablation produces minimal waste, no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and eliminates the need for hazardous disposal. As global regulations tighten—particularly under EU REACH and EPA guidelines—industries are shifting toward cleaner alternatives. The non-contact nature of laser stripping also reduces secondary contamination and worker exposure to harmful substances. By 2026, companies seeking compliance with green manufacturing standards are expected to prioritize laser-based solutions, boosting market demand.
Growth in Restoration and Heritage Conservation
The cultural heritage and architectural restoration sectors are emerging as key adopters of laser wood stripping. Preservationists value the precision of lasers in removing centuries of grime, paint, or varnish from historic wooden artifacts, facades, and furniture without altering original textures. Museums, government restoration projects, and private conservators are investing in portable and tunable laser systems to handle delicate work. With increased funding for heritage conservation in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, this niche application is projected to expand significantly by 2026.
Industrial and Manufacturing Integration
Beyond restoration, industrial sectors such as furniture manufacturing, marine, and aerospace are integrating laser stripping into production lines. In marine applications, lasers are used to strip old coatings from wooden boats efficiently and without substrate damage. Furniture manufacturers are adopting the technology for high-precision refinishing, enabling customization and circular economy practices (e.g., refurbishing used wood products). The scalability of automated laser stations supports mass production needs, making this technology attractive for OEMs focused on quality and sustainability.
Regional Market Expansion
Europe currently leads the laser wood stripping market due to stringent environmental laws and a strong heritage restoration culture. Germany, France, and the UK are key markets with active R&D and deployment. North America is following closely, driven by growth in green construction and industrial automation. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) by 2026, fueled by rising industrialization in China and Japan and increasing environmental awareness in South Korea and India. Local manufacturing of laser components is also reducing equipment costs, accelerating adoption.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite positive momentum, challenges remain. High initial investment costs, limited awareness among small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs), and the need for skilled operators hinder widespread adoption. However, as laser systems become more user-friendly and rental or service-based models emerge, accessibility is expected to improve. By 2026, the global market for laser wood stripping is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 9–12%, reaching an estimated value of USD 300–400 million. Continued innovation, regulatory support, and cross-sector collaboration will be critical to unlocking the full potential of this sustainable technology.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser for Wood Stripping (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a laser system for wood stripping requires careful evaluation to avoid costly mistakes. Two critical areas where pitfalls frequently occur are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) concerns.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Beam Performance: Low-quality lasers may deliver uneven power output or poor beam focus, leading to inconsistent stripping results—such as incomplete removal, charring, or surface damage. This reduces process reliability and can compromise the finish of high-value wood products.
-
Inadequate Cooling and Duty Cycle: Poorly designed systems may overheat during extended use, especially in industrial environments. This leads to downtime, reduced laser lifespan, and potential safety hazards—particularly if the cooling system fails under continuous operation.
-
Substandard Optics and Components: Cheap lenses, mirrors, and motion systems degrade quickly when exposed to wood debris and ambient dust. This results in frequent maintenance, misalignment, and declining performance over time, increasing total cost of ownership.
-
Lack of Environmental Protection (IP Rating Mismatch): Wood processing environments generate dust, moisture, and particulates. Lasers without appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) ratings—such as IP54 or higher—risk internal contamination, electrical failure, or reduced operational life. Assuming standard industrial enclosures are sufficient without verifying IP ratings is a common oversight.
-
Poor Integration and Control Software: Inflexible or proprietary control systems can hinder integration with existing production lines. Limited software support or poor user interfaces reduce operational efficiency and increase training time.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Use of Unlicensed or Cloned Laser Technology: Some suppliers, particularly in less regulated markets, may use copied or reverse-engineered laser designs that infringe on patents. Sourcing such systems exposes buyers to legal liability, potential seizure of equipment, or forced shutdowns if IP violations are discovered.
-
Proprietary Software Lock-In: Vendors may withhold source code or restrict access to control algorithms, making it impossible to modify, maintain, or upgrade the system independently. This creates dependency on the supplier and limits long-term flexibility.
-
Lack of Documentation and Compliance Certificates: Reputable suppliers provide full technical documentation, CE/UL certification, and proof of IP ownership. Absence of these documents is a red flag indicating potential IP issues or non-compliance with safety standards.
-
Unclear Warranty and Support Terms: Limited or ambiguous warranties may exclude coverage for IP-related failures or software updates. This can leave buyers exposed if the system is later found to use infringing technology.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: verify component origins, request IP compliance statements, inspect IP ratings for environmental resilience, and prioritize suppliers with transparent technical and legal documentation.
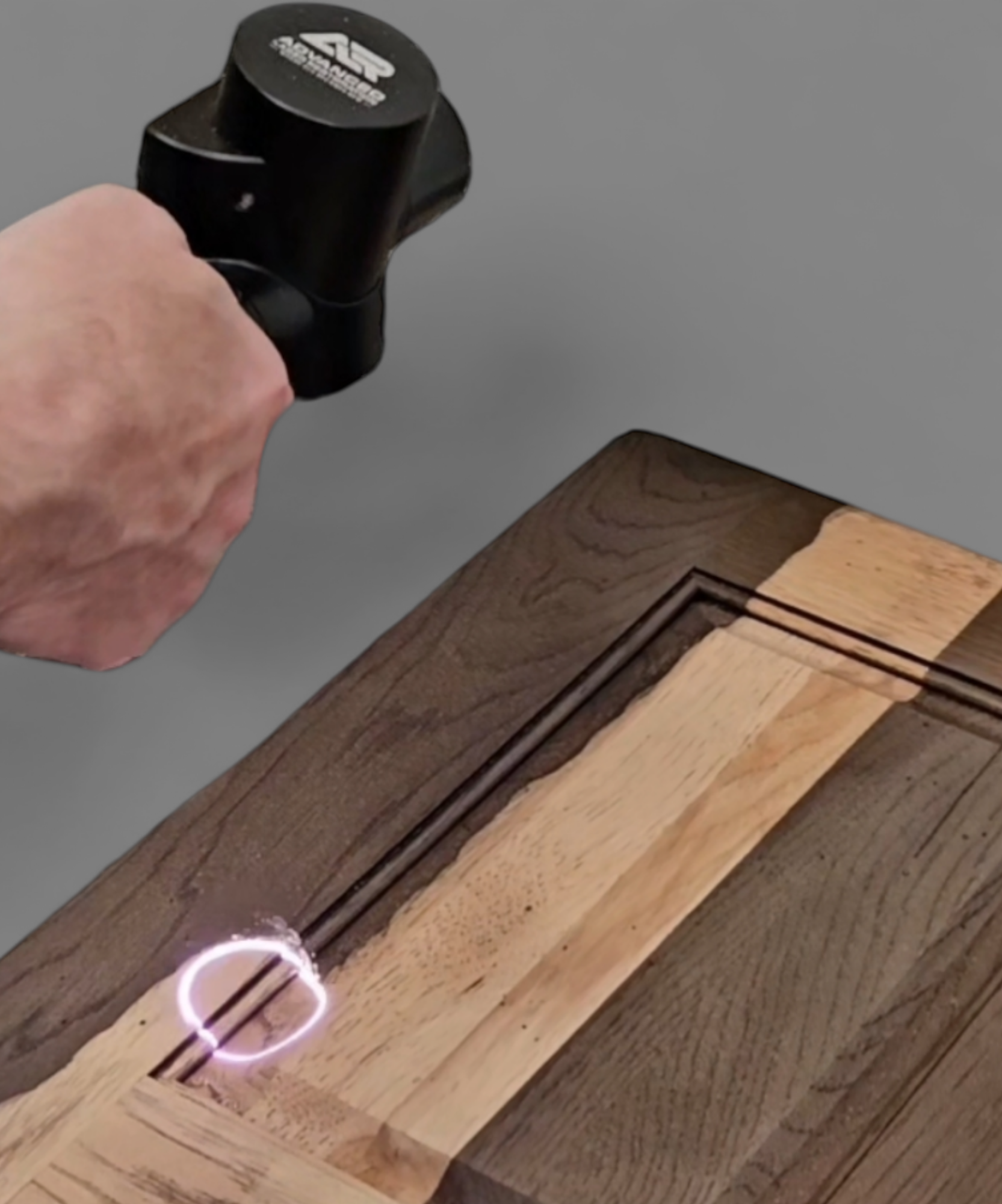

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser to Strip Wood
Overview and Purpose
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance requirements for the transportation, handling, and use of laser systems designed to strip wood surfaces. Whether used in industrial, commercial, or artisanal applications, adherence to safety, environmental, and regulatory standards is critical to ensure operational efficiency and legal compliance.
Regulatory Compliance
Laser Safety Standards
Laser systems used for wood stripping must comply with laser safety regulations established by recognized authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11, or the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60825-1 standard. Key requirements include proper classification (typically Class 4 for industrial wood-stripping lasers), installation of safety interlocks, emergency shut-offs, and appropriate labeling indicating laser class and hazard warnings.
Workplace Safety and OSHA Regulations
Operators must comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards, particularly those related to machine guarding (29 CFR 1910.212), hazard communication (29 CFR 1910.1200), and respiratory protection (29 CFR 1910.134). Adequate ventilation or fume extraction systems are required to manage airborne particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) generated during the laser stripping process.
Environmental Regulations
Wood stripping via laser may produce hazardous byproducts such as charred wood particles and chemical residues. Facilities must comply with Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations under the Clean Air Act and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) when handling, storing, and disposing of waste materials. Emissions control systems (e.g., HEPA filters and carbon scrubbers) are recommended to minimize air pollution.
Equipment Transportation and Handling
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Laser systems must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use manufacturer-recommended crates with shock-absorbing materials. Ensure sensitive optical components are protected and power units are disconnected. Documentation, including a commercial invoice, packing list, and safety data sheets (SDS), should accompany the shipment.
Import/Export Regulations
When shipping internationally, comply with export control regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or equivalent in other jurisdictions. High-powered lasers may be subject to licensing requirements. Verify Harmonized System (HS) codes for customs classification (e.g., 8515.21 for laser machinery) and ensure compliance with destination country standards (e.g., CE marking in the EU).
Installation and Operational Logistics
Site Preparation
Ensure the installation site provides stable power supply (voltage and grounding as specified), adequate ventilation, and sufficient space for safe operation and maintenance. Install physical barriers or light-tight enclosures to contain laser radiation and prevent unauthorized access.
Training and Certification
Personnel operating laser wood-stripping systems must undergo certified training in laser safety, including alignment procedures, emergency protocols, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) ratings.
Maintenance and Waste Management
Routine Maintenance
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for cleaning optics, checking cooling systems, and inspecting safety features. Keep detailed logs of all maintenance activities for compliance audits.
Waste Disposal
Collect and label all waste generated from the stripping process (wood debris, filter residues) as potentially hazardous. Test waste materials if necessary to determine disposal classification. Use licensed waste disposal services that comply with local and federal regulations.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records including equipment manuals, safety certifications, operator training logs, maintenance schedules, and waste disposal manifests. These documents may be required during regulatory inspections or insurance claims.
Emergency Preparedness
Develop and post emergency procedures for laser malfunctions, fire hazards (due to high heat), and exposure incidents. Ensure fire suppression systems (e.g., Class D extinguishers for electrical fires) are accessible and personnel are trained in their use.
Conclusion
Safe and compliant operation of laser systems for wood stripping requires strict adherence to regulatory standards, proper logistics planning, and continuous staff training. By following this guide, organizations can mitigate risks, ensure legal compliance, and promote a safe working environment.
Conclusion: Sourcing Lasers for Wood Stripping
Sourcing a laser system for wood stripping presents a highly efficient, precise, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods such as sandblasting, chemical stripping, or manual abrasion. Laser technology offers selective material removal, minimal substrate damage, and reduced waste, making it ideal for restoring historic woodwork, preparing surfaces for refinishing, or achieving detailed decorative effects.
When sourcing a laser for this application, key considerations include laser type (typically fiber or CO₂ lasers), power output, wavelength compatibility with wood and coatings, beam control systems, and safety features. Additionally, integration with automation or CNC systems can enhance repeatability and throughput for industrial applications.
While the initial investment in laser equipment may be higher than conventional tools, the long-term benefits—such as lower consumable costs, reduced labor, improved precision, and compliance with environmental regulations—justify the cost for many professionals and businesses.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser for wood stripping is a forward-thinking decision that enhances quality, efficiency, and sustainability in woodworking and restoration projects. Careful evaluation of technical requirements, operational needs, and supplier support will ensure the successful implementation of laser technology in your wood finishing or conservation workflow.