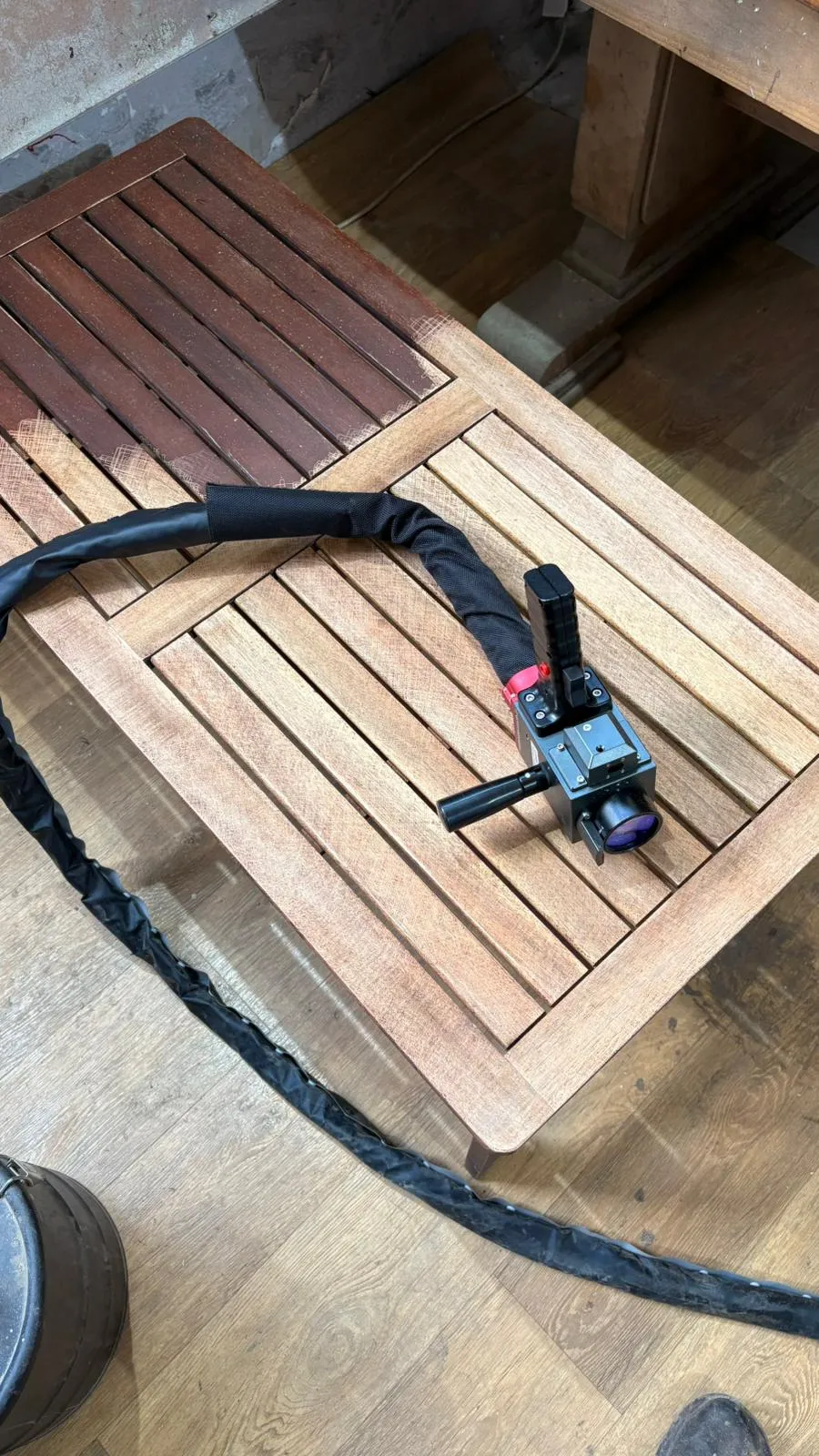
The global laser cleaning equipment market is experiencing robust growth, fueled by increasing demand for precision, non-abrasive surface treatment technologies across industries—including wood restoration. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser cleaning market was valued at USD 708.6 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1,392.4 million by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 11.9% during the forecast period. This surge is driven by the adoption of eco-friendly, chemical-free cleaning methods, with laser technology emerging as a preferred solution for delicate applications such as varnish removal from wood surfaces.
In woodworking and furniture restoration, traditional chemical strippers and mechanical sanding often risk damaging the underlying grain. Laser ablation, in contrast, offers controlled, residue-free de-coating with minimal substrate impact. As demand grows for sustainable and efficient finishing processes, manufacturers are investing in specialized laser systems tailored for organic materials. Based on market traction, technological innovation, and industry adoption, the following nine manufacturers stand out for their advanced laser solutions designed specifically to remove varnish from wood—combining precision engineering with environmental responsibility.
Top 9 Laser To Remove Varnish From Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A laser cleaning machine is an industrial system designed for the removal of rust, paint, grease, coatings and surface contaminants using precisely ……
#2 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning removes paint, contaminants, rust, and residues with a high-energy laser beam which leaves the substrate untouched. Our Laser Ablation is the ……
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: P-Laser: How does laser cleaning work? QF-2000 Laser removes almost any other kind of contamination, including grease, rust….
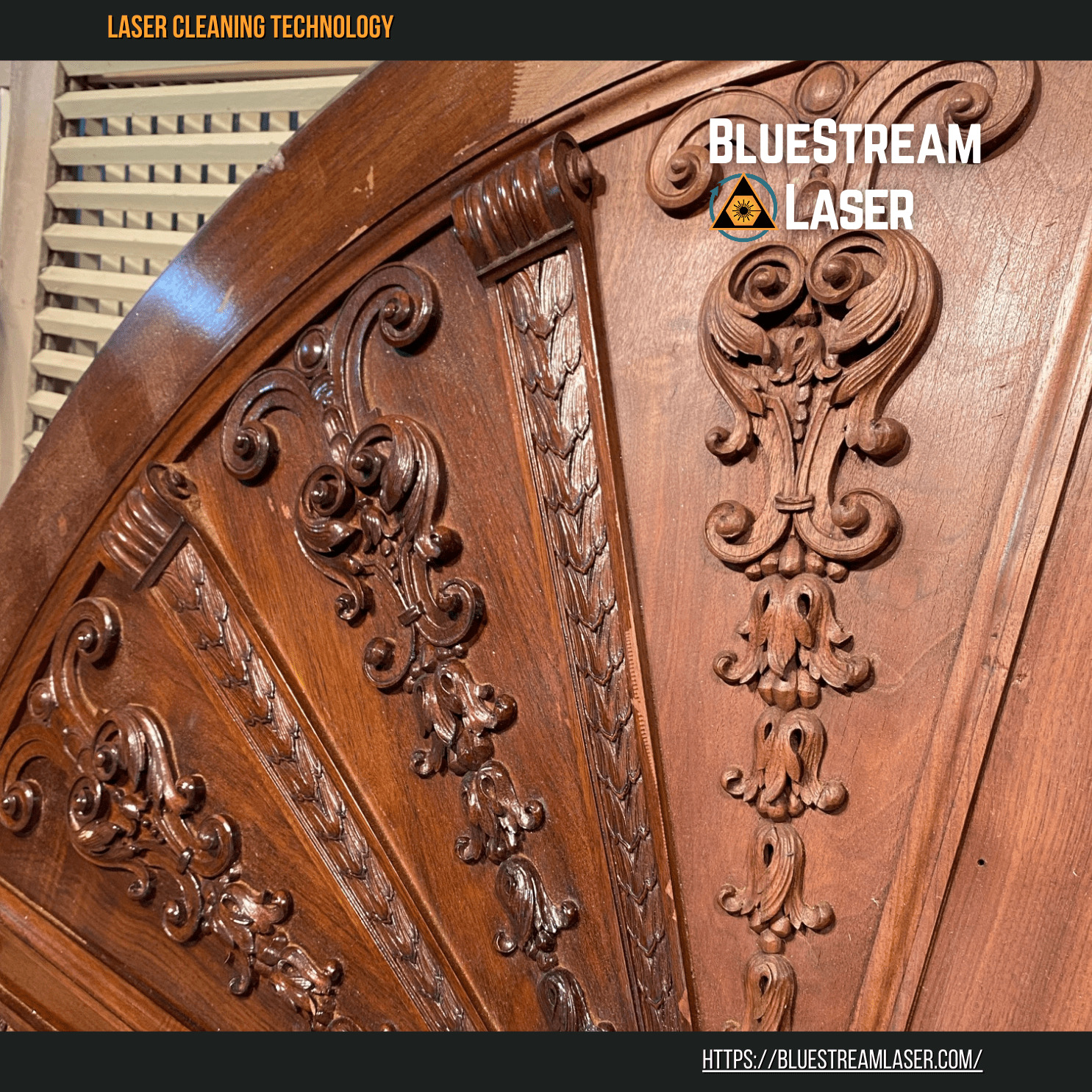
#4 Bluestream Laser Cleaning, restoration of monuments, industrial …
Website: bluestreamlaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is a non-contact process that removes only the unwanted materials, with no abrasives or secondary components involved….
#5 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: The pulse laser cleaning machine have 100w, 200w, 300w, 500w, 1000w, Mainly used to rust, thin paint layer, wood, oil removal, It will no impact on the surface….
#6 Clean Laser Technologies
Website: cleanlasertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: STAIN/VARNISH REMOVAL. Precise stain and varnish removal revitalizes surfaces with effective cleaning. Commercial Kitchen Cleaning. Simplify and Streamline ……
#7 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping is incredibly precise, removing layers of paint, varnish, or other coatings without damaging the underlying wood….
#8 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: So the laser wood stripping machine is an ideal tool for stripping paint from wooden, They offer precise and eco-friendly cleaning without damaging the base ……
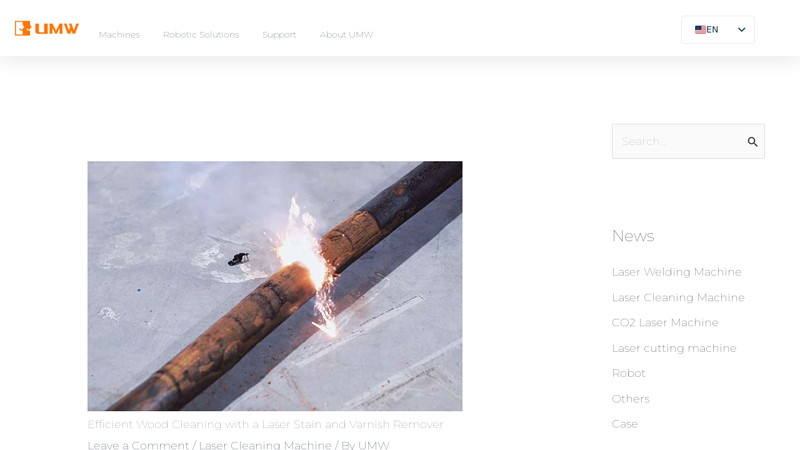
#9 Efficient Wood Cleaning with a Laser Stain and Varnish Remover
Website: umw.top
Key Highlights: Laser stain and varnish removal uses focused laser beams to remove layers of stain or varnish from wood surfaces. The laser’s energy targets the coating, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser To Remove Varnish From Wood
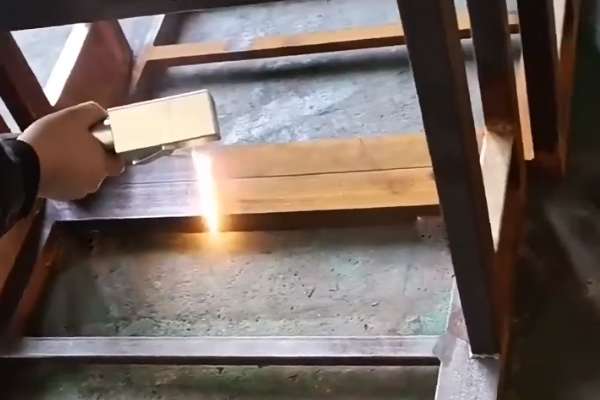

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Technology to Remove Varnish From Wood
The global market for laser-based solutions in wood restoration and surface treatment is poised for significant transformation by 2026, particularly in the niche of varnish removal. Driven by advances in laser technology, growing environmental regulations, and rising demand for non-chemical restoration methods, laser systems are increasingly being adopted as a sustainable and precise alternative to traditional sanding or chemical stripping.
-
Increased Adoption in Restoration and Heritage Conservation
By 2026, laser varnish removal is expected to gain strong traction in the restoration of historical woodwork, antiques, and heritage buildings. Conservation professionals are turning to lasers due to their precision, non-abrasive nature, and ability to selectively target varnish without damaging underlying wood. Institutions and government-funded preservation projects in Europe and North America are anticipated to drive early adoption. -
Advancements in Fiber and Pulsed Laser Technology
Technological improvements in fiber lasers and ultra-short pulsed lasers are enhancing efficiency and safety in varnish removal. These lasers offer better control over energy delivery, reducing heat damage and enabling use on delicate or intricate wood surfaces. By 2026, more compact and user-friendly systems are expected to enter the market, making the technology accessible to small workshops and independent restorers. -
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
With tightening global regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and chemical waste from traditional stripping methods, industries are under pressure to adopt eco-friendly alternatives. Laser ablation produces minimal waste and no toxic runoff, making it compliant with environmental standards such as REACH and RoHS. This regulatory push is accelerating investment in laser solutions across furniture manufacturing and renovation sectors. -
Growth in Furniture and Flooring Refinishing Markets
The furniture and hardwood flooring industries are increasingly exploring laser technology for refinishing products without sanding. By 2026, demand is projected to rise as manufacturers seek faster, cleaner, and repeatable processes. Automated laser systems integrated into production lines could enable large-scale refurbishment of wood surfaces, reducing labor costs and material waste. -
Cost Reduction and Market Expansion
Although initial equipment costs remain high, increased competition and technological maturity are expected to lower prices by 2026. Entry of new manufacturers from Asia, particularly China and South Korea, is likely to expand supply and drive affordability. This will open the market to mid-sized businesses and service providers, broadening the commercial base beyond elite restoration studios. -
Integration with Automation and AI
Future laser systems are expected to incorporate smart features such as AI-powered surface analysis and adaptive beam control. These integrations will allow real-time detection of varnish thickness and wood grain, optimizing removal efficiency and minimizing human error. By 2026, hybrid systems combining robotics and laser technology may become standard in industrial applications.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser-based varnish removal from wood is set for robust growth, underpinned by technological innovation, environmental imperatives, and expanding applications across restoration, manufacturing, and design industries. As the technology becomes more accessible and efficient, it is likely to redefine industry standards for sustainable wood surface treatment.
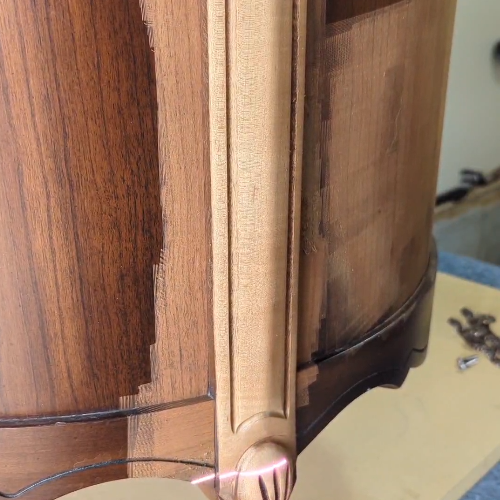

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lasers to Remove Varnish from Wood (Quality and Intellectual Property)
When sourcing laser systems for removing varnish from wood, businesses and restoration professionals must navigate several critical challenges related to both equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to subpar performance, legal risks, and financial losses.
Poor Laser Quality and Inadequate Technical Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is selecting a laser based on low cost rather than technical suitability. Not all lasers are designed for delicate wood restoration. Using lasers with incorrect wavelengths (e.g., high-power fiber lasers meant for metal) can scorch or damage the wood substrate. Additionally, systems lacking precise power modulation, beam control, and cooling mechanisms may result in inconsistent varnish removal, surface pitting, or irreversible wood degradation. Buyers should verify pulse duration, energy density, scanning speed, and spot size to ensure compatibility with wood’s thermal sensitivity.
Lack of Industry-Specific Calibration and Software
Many off-the-shelf laser systems are designed for industrial metal cleaning and lack software tuned for organic materials like wood. Without proper calibration profiles for different varnish types (oil-based, polyurethane, shellac) and wood species (oak, pine, mahogany), the laser may underperform or cause collateral damage. Vendors offering generic solutions without application-specific software or technical support increase the risk of ineffective treatment and project delays.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Training
Sourcing from overseas or unknown suppliers often results in limited technical support, delayed spare parts delivery, and inadequate training. Laser operation for wood restoration requires skilled handling; without proper training, operators may misuse the equipment, leading to poor results or safety hazards. Ensure the supplier provides comprehensive documentation, remote assistance, and on-site training as part of the sourcing agreement.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
A significant but often overlooked pitfall involves IP violations. Some low-cost laser systems, particularly from certain international manufacturers, may incorporate replicated or reverse-engineered technology protected by patents in your region. Using such equipment could expose your business to legal action for contributory infringement. Always verify that the laser system complies with regional IP laws and request proof of licensing for core technologies (e.g., laser source, control algorithms, software).
Misrepresentation of Capabilities by Suppliers
Certain vendors exaggerate their systems’ effectiveness on wood surfaces, claiming universal compatibility without real-world validation. They may provide misleading demo videos or omit limitations such as slow processing speed or inability to handle curved surfaces. Conduct independent testing with your specific wood and varnish types before finalizing procurement. Third-party validation or pilot trials can prevent costly procurement mistakes.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, prioritize suppliers with proven experience in heritage restoration or fine woodworking applications. Conduct thorough due diligence on technical specs, request IP compliance documentation, and insist on performance guarantees. Investing in a high-quality, legally sound laser system ultimately ensures better results, protects your business, and preserves the integrity of valuable wooden artifacts.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser to Remove Varnish From Wood
Product Overview
The laser system designed for removing varnish from wood is a non-abrasive, precision tool that utilizes focused laser energy to vaporize surface coatings without damaging the underlying wood. This technology is commonly used in restoration, furniture refinishing, and woodworking industries. Due to its technical nature and potential safety hazards, proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential.
Regulatory Compliance
Laser Safety Standards
The laser system must comply with international and national laser safety regulations, including:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
– 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11: U.S. FDA regulations for laser products, administered by the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH).
– ANSI Z136.1: Safe Use of Lasers (U.S. standard for laser safety practices).
Users must ensure the laser is properly classified (typically Class 1, 3B, or 4) and labeled with appropriate warning signs. Class 3B and 4 lasers require safety interlocks, key-controlled operation, and a designated controlled area.
Electrical and Equipment Standards
The device must meet electrical safety standards such as:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
– UL/CSA (North America): Certification for electrical safety and performance.
– RoHS and REACH (EU): Restrictions on hazardous substances in electrical equipment.
Environmental and Workplace Safety
- OSHA (U.S.) / HSE (UK) / Local Regulations: Employers must provide training and implement safety measures for laser operations, including ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and fire prevention.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Varnish removal produces hazardous fumes (e.g., isocyanates, solvents). Systems must include HEPA and activated carbon filtration in accordance with NIOSH and ACGIH guidelines.
- Waste Management: Residue and filter waste may be classified as hazardous; disposal must comply with EPA (U.S.) or Environment Agency (UK) regulations.
Transportation and Logistics
Packaging and Handling
- The laser system must be shipped in robust, shock-resistant packaging with internal bracing to protect optical and electronic components.
- Include desiccants to prevent moisture damage during transit.
- Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Equipment – Do Not Open” warnings.
Shipping Documentation
Ensure all shipments include:
– Commercial invoice with product description, value, and Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 8543.70 for laser-based machinery).
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for any consumables or hazardous components.
– FCC or CE Declaration of Conformity.
– Export licenses if applicable (especially for high-power lasers under ITAR or EAR regulations).
Import/Export Compliance
- Export Controls: High-powered lasers may be subject to export restrictions under the Wassenaar Arrangement or U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Verify if a license is required for the destination country.
- Customs Clearance: Accurately declare the product’s technical specifications (wavelength, power output) to avoid delays.
- Duty and Tax Considerations: Research local tariffs, VAT, or GST requirements in the importing country.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Site Requirements
- Adequate power supply (voltage, grounding) as specified by the manufacturer.
- Controlled environment: stable temperature, low humidity, minimal dust.
- Dedicated workspace with restricted access and laser safety signage.
Personnel Training and Certification
Operators must receive formal training on:
– Laser safety procedures
– Emergency shutdown protocols
– PPE usage (laser safety goggles with correct optical density for the laser wavelength)
– Maintenance and troubleshooting
Maintain training records and conduct periodic safety audits.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
- Follow the manufacturer’s preventive maintenance schedule.
- Document all service activities, safety inspections, and incident reports.
- Retain compliance certificates, calibration records, and operator training logs for audit purposes.
Conclusion
Operating a laser system for varnish removal from wood requires strict adherence to safety, environmental, and regulatory standards. Proper logistics planning, documentation, and compliance protocols ensure safe transportation, legal import/export, and responsible use. Always consult local authorities and the equipment manufacturer to remain up to date with evolving regulations.
In conclusion, laser technology presents a highly effective, precise, and environmentally friendly solution for removing varnish from wood. Unlike traditional methods that involve harsh chemicals or mechanical abrasion—which can damage the wood surface or pose health and safety risks—laser ablation selectively targets the varnish layer while preserving the underlying wood grain and integrity. Advances in fiber and pulsed laser systems have improved efficiency and control, making the process suitable for delicate restoration work, heritage conservation, and high-precision industrial applications.
While the initial investment in laser equipment is higher than conventional tools, the long-term benefits—such as reduced labor costs, minimal waste generation, and repeatability—justify the cost for professional restorers and woodworking operations. Additionally, laser systems require skilled operators and appropriate safety measures, including ventilation and protective eyewear.
Overall, sourcing a laser system for varnish removal offers a sustainable, accurate, and non-contact method that aligns with modern standards for quality and environmental responsibility. For businesses and conservators aiming for superior results with minimal impact on valuable wooden artifacts or surfaces, laser-based varnish removal is a compelling, future-ready solution.