The global paint and coating removal market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient, eco-friendly solutions in industrial maintenance, restoration, and woodworking. According to Grand View Research, the global paint stripper market was valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by the rising need for non-abrasive, precision-based methods such as laser paint removal, particularly in sensitive applications involving wood surfaces where traditional chemical or mechanical stripping can cause damage. As sustainability and worker safety become key priorities, laser-based systems offer a solvent-free, precise, and increasingly cost-effective alternative. With industries ranging from heritage restoration to furniture manufacturing adopting advanced laser technologies, the demand for specialized equipment has spurred innovation among manufacturers. Based on market presence, technological capability, and customer adoption, the following eight companies have emerged as leading manufacturers of laser systems designed specifically for paint removal from wood.
Top 8 Laser To Remove Paint From Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: The SHARK P CL series is suitable for removing rust, paint, soot, carbon, mold, mildew, grease, weld residues, varnish, graffiti and other surface contaminants….
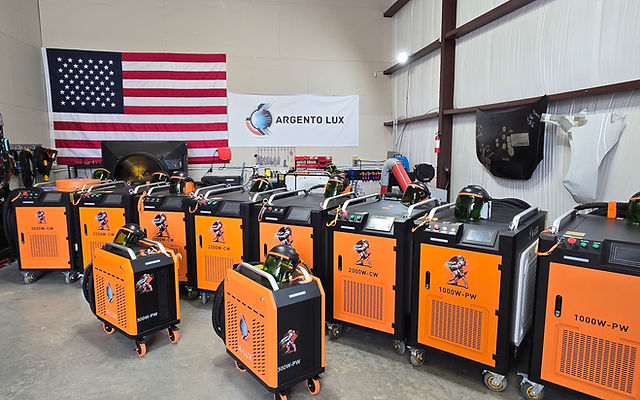
#2 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning removes paint, contaminants, rust, and residues with a high-energy laser beam which leaves the substrate untouched. Our Laser Ablation is the ……
#3 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: The technology can effectively remove corrosion, coatings, paint, and other substances without damaging the underlying substrate. This process is non-contact, ……
#4 Laser cleaning
Website: narran.cz
Key Highlights: We can design and integrate a laser cleaning system into production, build a robotic workstation or supply a mobile laser for a wide range of applications….
#5 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: A laser wood stripping machine is a tool that uses laser technology to remove contaminants, such as paint, oil, dirt, or coatings, from wooden surfaces without ……
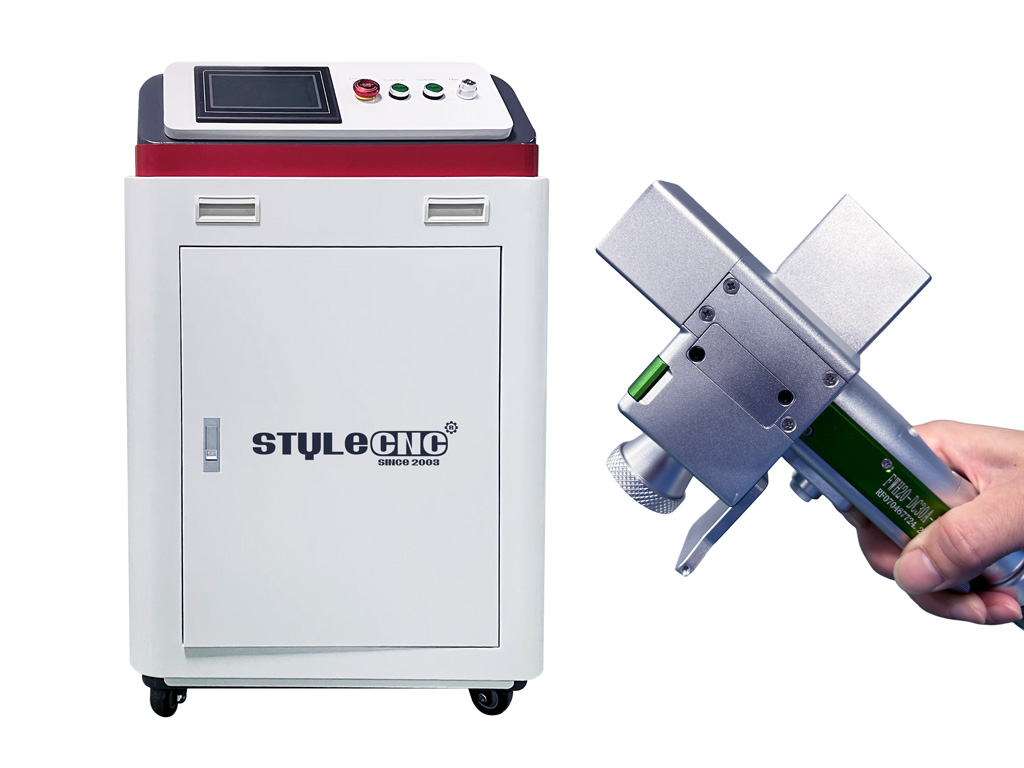
#6 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: The pulse laser cleaning machine have 100w, 200w, 300w, 500w, 1000w, Mainly used to rust, thin paint layer, wood, oil removal, It will no impact on the surface….
#7 Laser Paint Removal from Metals with Laser Cleaning
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser paint removal is a process through which paint is removed from a surface without damaging the material. The process can be applied to any metals….
#8 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping is incredibly precise, removing layers of paint, varnish, or other coatings without damaging the underlying wood….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser To Remove Paint From Wood

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Paint Removal from Wood
The global market for laser-based paint removal from wood is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by increasing environmental regulations, advancements in laser technology, and a growing preference for non-abrasive, precision-based restoration techniques. This analysis explores key trends expected to shape the industry in the coming years.
-
Rising Demand for Eco-Friendly Solutions
Environmental concerns over traditional paint removal methods—such as sandblasting and chemical strippers—are accelerating the adoption of laser technology. By 2026, stricter emissions and waste disposal regulations in North America and Europe will push restoration companies, heritage conservation projects, and furniture manufacturers toward cleaner alternatives. Laser systems produce no chemical runoff and minimal particulate matter when paired with effective filtration, making them a sustainable choice. -
Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency
Ongoing innovations in fiber and pulsed laser technology are improving the speed, precision, and affordability of laser paint removal systems. By 2026, expect wider availability of handheld and robotic-integrated laser units tailored for intricate wood surfaces, such as carved furniture or historical timber frames. Adaptive control systems using AI and real-time monitoring will allow lasers to distinguish between paint layers and delicate wood substrates, minimizing damage. -
Growth in Heritage and Restoration Projects
The preservation of historical buildings and artifacts is a major driver for laser adoption. By 2026, increased government and private funding for heritage restoration—particularly in Europe and North America—will boost demand for non-invasive paint removal. Lasers offer conservators the ability to selectively remove centuries-old paint without harming original woodwork, a capability unmatched by mechanical methods. -
Expansion into Commercial and Residential Refinishing
Beyond niche restoration, the laser paint removal market is expanding into commercial woodworking and residential renovation. Furniture refinishers, flooring contractors, and custom woodworkers are beginning to invest in mid-range laser systems to improve quality and reduce labor time. As equipment costs decline and training becomes more accessible, small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) are expected to adopt this technology more widely by 2026. -
Regional Market Growth and Investment
Europe currently leads in laser paint removal adoption due to strong heritage conservation policies and early technological integration. However, North America and parts of Asia-Pacific (notably Japan and South Korea) are projected to see the highest growth rates by 2026. Increased R&D investments, particularly in the U.S. and Germany, will likely result in more compact, user-friendly systems suitable for diverse applications. -
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite positive momentum, high initial equipment costs and the need for skilled operators remain barriers. Additionally, laser effectiveness varies with paint type and wood species, requiring optimization. However, by 2026, leasing models, modular systems, and enhanced training programs are expected to lower entry barriers and improve ROI for end users.
In summary, the 2026 market for laser paint removal from wood will be characterized by technological innovation, regulatory pressure, and expanding application across restoration, commercial, and residential sectors. As sustainability and precision become paramount, laser systems are set to transition from a specialized tool to a mainstream solution in wood surface preparation and conservation.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser to Remove Paint from Wood (Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns)
When sourcing a laser system for removing paint from wood, especially for restoration or precision applications, several critical pitfalls can compromise both the quality of the outcome and expose buyers to intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these challenges helps ensure a safe, effective, and legally compliant investment.
1. Compromised Laser Quality and Performance
-
Inadequate Power and Wavelength: Not all lasers are suitable for wood surfaces. Using a laser with incorrect power settings or wavelength may damage the wood grain or fail to remove paint efficiently. CO₂ lasers (typically 10.6 μm wavelength) are commonly effective, but low-quality systems may lack precision control.
-
Poor Beam Control and Focus: Inferior laser systems may lack advanced optics or software for beam shaping and focal control, leading to uneven paint removal, scorching, or surface degradation.
-
Lack of Cooling and Stability Mechanisms: Low-quality lasers may overheat during extended use, reducing accuracy and potentially damaging the equipment or workpiece.
-
Absence of Safety Features: High-end lasers include interlocks, ventilation, and protective enclosures. Budget systems may omit these, increasing fire risk or operator exposure to fumes and radiation.
2. Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
-
Overstated Capabilities: Some suppliers exaggerate removal speed, depth control, or compatibility with various paint types. Independent verification or third-party testing data is crucial.
-
Generic Branding Without Certification: Equipment marketed under white-label brands may lack ISO, CE, or FDA compliance, indicating poor manufacturing standards or unverified safety protocols.
3. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Use of Counterfeit or Cloned Technology: Some manufacturers, particularly in less-regulated markets, replicate patented laser designs or control software without licensing. Purchasing such systems may expose users to legal liability or IP infringement claims.
-
Lack of Documentation and Licensing: Reputable suppliers provide detailed technical documentation, software licenses, and proof of IP ownership. Omitting these may signal unauthorized use of proprietary technology.
-
Proprietary Software Dependence: Some systems rely on closed-source software with restrictive licensing. Buyers risk losing access to updates or technical support, especially if the supplier violates IP laws and faces litigation.
4. Inadequate After-Sales Support and Calibration
-
Limited Technical Assistance: Low-cost suppliers may offer minimal training or support, making it difficult to maintain optimal performance or troubleshoot issues.
-
No Calibration or Maintenance Services: High-precision laser systems require regular calibration. Without access to certified technicians, performance degrades over time, affecting removal quality and safety.
5. Regulatory and Compliance Gaps
-
Non-Compliance with Environmental and Safety Standards: Laser paint removal produces hazardous particulates and fumes. Poor-quality systems may lack proper filtration or fail to meet OSHA, EPA, or REACH regulations.
-
Export/Import Restrictions: Some laser technologies are subject to trade controls (e.g., ITAR or dual-use regulations). Sourcing from unauthorized vendors may lead to customs issues or legal penalties.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should prioritize suppliers with verifiable product quality, full compliance certifications, transparent IP licensing, and robust technical support. Conducting due diligence—such as requesting customer references, reviewing independent test reports, and verifying patent status—can mitigate risks and ensure a reliable, legally sound investment in laser paint removal technology for wood.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Paint Removal from Wood
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations when using laser technology to remove paint from wooden surfaces. Proper planning and adherence to regulations ensure operational safety, environmental responsibility, and legal compliance.
Equipment Selection and Transportation
Choose a laser system specifically designed for paint ablation on wood, considering factors such as power output, wavelength (typically fiber lasers around 1064 nm), scanning speed, and automation capabilities. Ensure the equipment is portable or modular for site access if work is off-premises. During transportation, secure all components to prevent damage, especially sensitive optical elements. Use shock-absorbing packaging and climate-controlled vehicles if necessary to protect electronics from moisture and extreme temperatures.
Site Preparation and Access
Conduct a site survey to evaluate workspace dimensions, electrical supply (voltage, amperage, grounding), ventilation options, and proximity to combustible materials. Ensure clear access routes for equipment delivery and setup. Prepare the work area by removing flammable debris, covering nearby surfaces, and demarcating a controlled laser zone with appropriate signage. Confirm stable power sources or arrange for industrial-grade generators if required.
Personnel Training and Safety Protocols
Personnel must receive certified training in laser operation, safety standards (e.g., ANSI Z136.1), and emergency response procedures. All operators should wear appropriate PPE, including laser safety goggles with the correct optical density for the laser wavelength, flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection. Implement strict access control to the laser operation zone and establish lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures for maintenance.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Adhere to federal, state, and local regulations governing laser use and hazardous material handling. Key compliance areas include:
- OSHA Standards: Follow 29 CFR 1910 Subpart K (Medical and First Aid) and Subpart I (Personal Protective Equipment), along with general duty clauses for workplace safety.
- FDA/CDRH Regulations: Comply with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 for laser product performance standards if the equipment is manufactured or imported in the U.S.
- Environmental Regulations: If paint contains lead or other hazardous substances (common in pre-1978 structures), comply with EPA’s Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) Rule (40 CFR Part 745). This includes certified renovators, containment procedures, and waste disposal protocols.
- Air Quality Standards: Monitor and control airborne particulates using HEPA-filtered vacuum extraction systems. Comply with local air pollution control district rules regarding emissions.
Waste Management and Disposal
Laser ablation produces particulate matter, including removed paint and degraded wood fibers. Collect all debris using integrated or external filtration systems. Test waste for hazardous components (e.g., lead, chromates) before disposal. If hazardous, dispose of waste through licensed hazardous waste handlers in accordance with RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act) guidelines. Maintain records of waste manifests and disposal certifications.
Emissions Monitoring and Ventilation
Install real-time particulate monitors and fume extraction systems with HEPA and activated carbon filters to capture airborne contaminants. Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent buildup of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or pyrolysis byproducts. Conduct periodic air quality testing, especially in enclosed spaces, and document results for compliance audits.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records, including equipment maintenance logs, operator training certifications, safety inspection reports, waste disposal manifests, and air monitoring data. Documentation supports regulatory compliance and facilitates audits by OSHA, EPA, or other authorities.
Emergency Preparedness
Develop and communicate an emergency response plan addressing laser malfunctions, fire hazards, and exposure incidents. Equip the site with fire extinguishers (Class ABC), first aid kits, and emergency eyewash stations. Conduct regular drills and ensure all personnel know evacuation routes and reporting procedures.
By following this logistics and compliance framework, organizations can safely and legally leverage laser technology for paint removal on wood while protecting workers, the public, and the environment.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser system for paint removal from wood offers a precise, non-abrasive, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods such as sanding or chemical stripping. Laser technology effectively removes paint layers without damaging the underlying wood, preserving its integrity and texture. Although the initial investment and operational costs may be higher, the long-term benefits—such as reduced labor time, minimal waste, and elimination of harmful chemicals—make it a compelling option for restoration projects, especially in heritage conservation and high-end woodworking. When sourcing a laser system, it is essential to select equipment with appropriate power, wavelength, and pulse control tailored for wood substrates, along with proper safety certifications and training support. Ultimately, laser paint removal represents a technologically advanced solution that combines efficiency, sustainability, and superior finish quality for wood restoration applications.