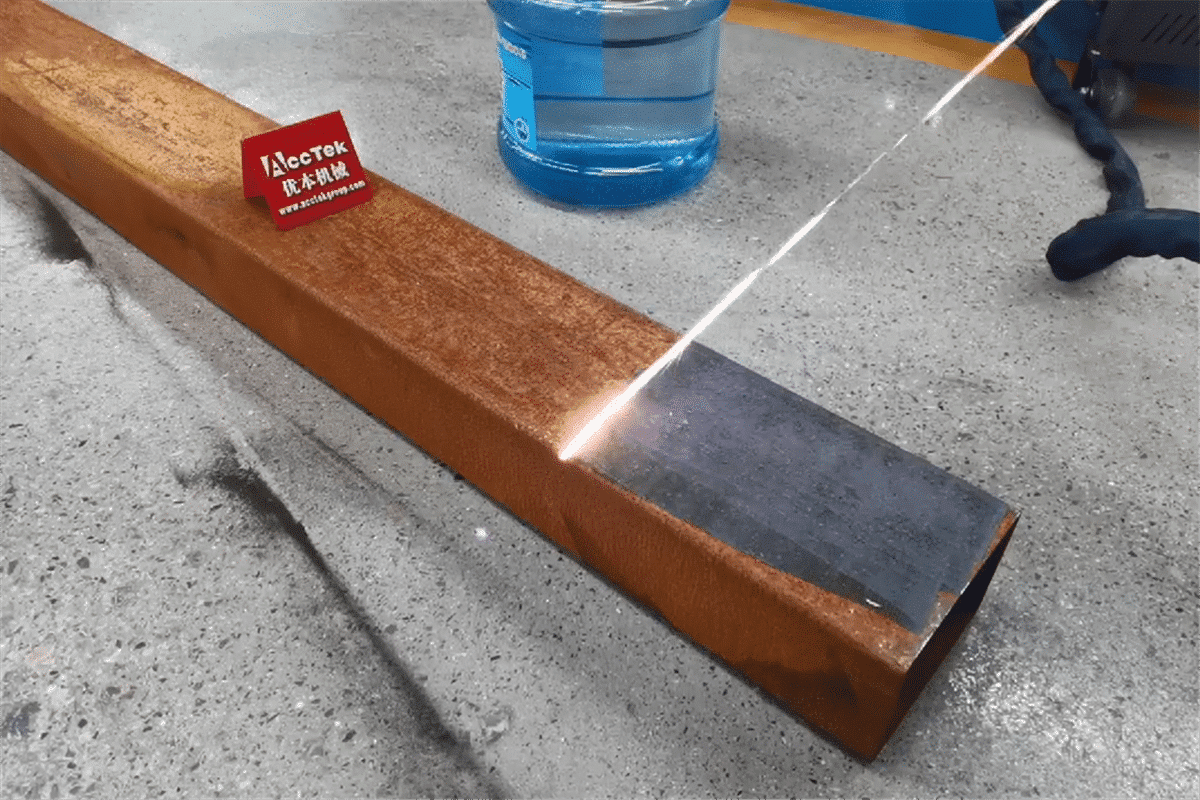
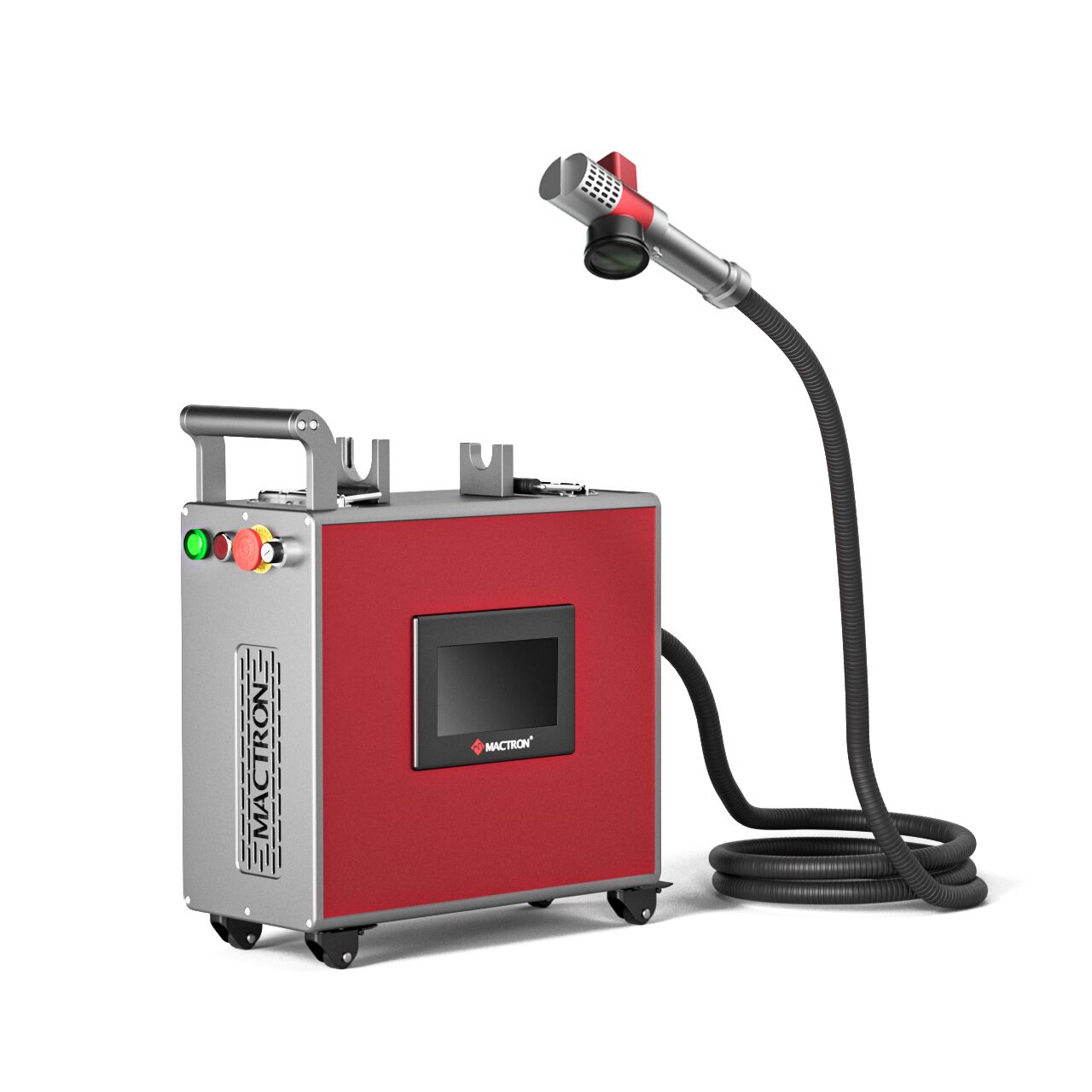
The global market for rust removal technologies has seen robust expansion in recent years, driven by increasing industrial maintenance needs and growing emphasis on asset longevity. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial cleaning equipment market was valued at USD 13.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. A key segment within this space—laser rust removal—is gaining traction due to its precision, eco-friendliness, and reduced labor costs compared to traditional methods like sandblasting or chemical treatments. Mordor Intelligence projects that the laser cleaning equipment market will grow at a CAGR of over 10% during the forecast period (2023–2028), with increasing adoption in automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation sectors. As demand surges, manufacturers specializing in laser-based rust removal solutions are innovating rapidly to deliver higher efficiency, portability, and cost-effectiveness. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top players becomes crucial for businesses seeking reliable and scalable cleaning technologies. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 manufacturers leading the charge in laser rust removal innovation and market impact.
Top 10 Laser To Clean Rust Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
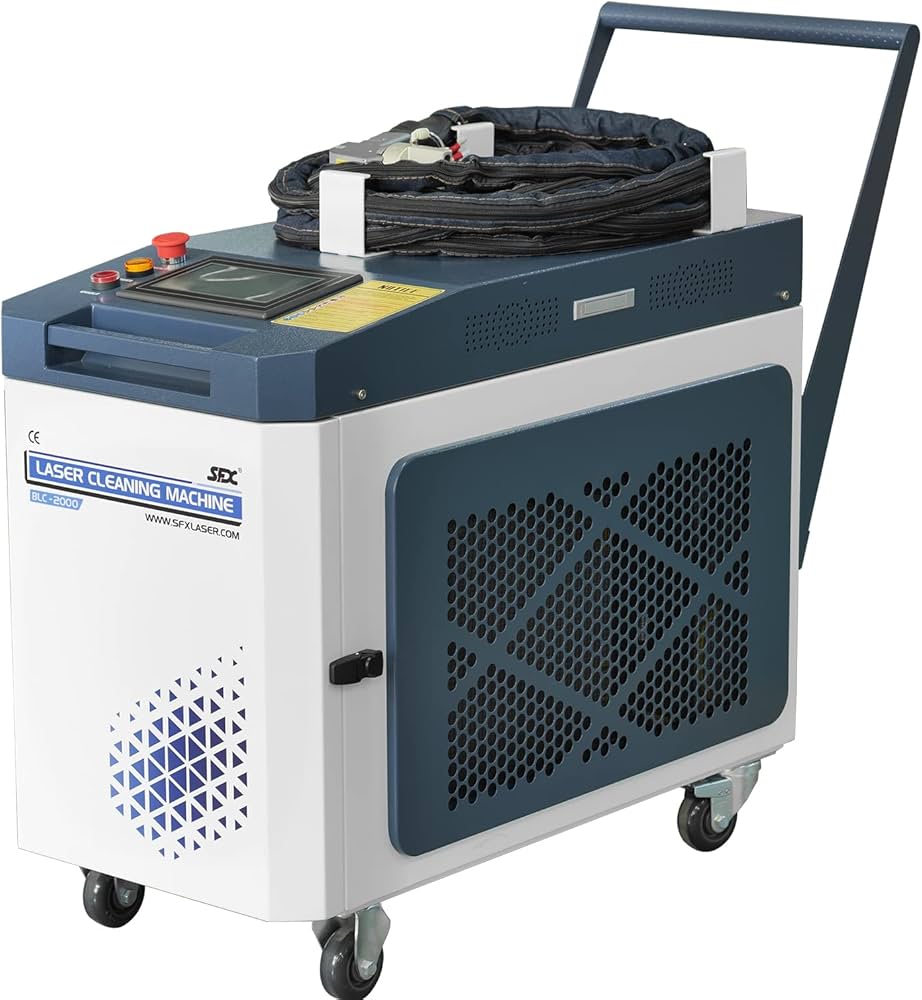
#1 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
#2 Laser Rust Removal
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: Achieve super fast rust removal rates with out lasers. Watch this super fast rust removal from carbon steel panel with the new ultra-lightweight Vulcan handheld …Missing: clean …
#3 Laser Cleaning Rust Removal
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Our equipment uses pulsating lasers to blast away any contaminants from metal surfaces. This process is eco-friendly, as you won’t need any …Missing: clean manufacturer…
#4 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Cleaning Optimizes A Wide Variety of Applications · Clean contaminants like rust, oil, and combustion deposits · Strip coatings like paint, e-coat, ceramics ……
#5 Laser Cleaning Systems
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser systems can remove all types of contaminants from metals, including oxides, coatings, rust, dust, oils, and electrolytes….
#6 Laser Rust Removal
Website: adapt-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning offers a safe and much faster way to remove rust from metal without the need of any harsh media or chemicals. Learn more….
#7 Laser Rust Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: KEYENCE offers two laser machines that can remove rust—the hybrid laser marker and the fiber laser marker. Both machines offer a non-abrasive way to remove rust ……
#8 Top Laser Rust Cleaning Machines for Efficient Rust Removal
Website: woodrowscientific.com
Key Highlights: Laser rust cleaning zaps away rust with light—no chemicals, no abrasion, just pure precision. Rust literally vaporizes while the clean metal ……
#9 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: sltl.com
Key Highlights: This futuristic laser cleaning solution can capably remove rust, oil, paint, grease, colour and other particles from the surface of the metals….
#10 Laser Rust Removal Guide
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A practical guide for professionals and entrepreneurs using PULSAR Laser systems to remove rust safely, efficiently and without abrasives….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser To Clean Rust
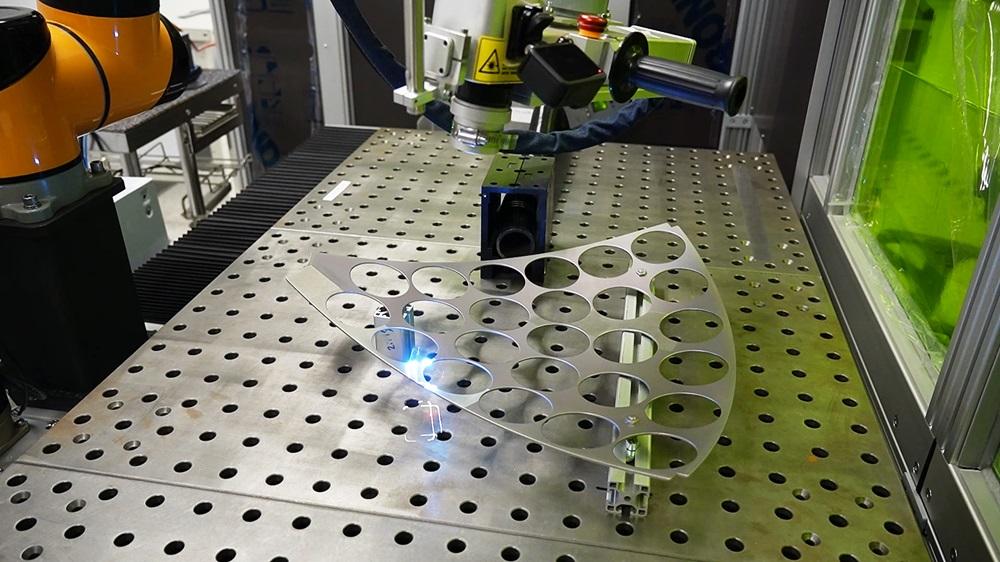

H2: Market Trends for Laser Rust Cleaning in 2026
The global market for laser-based rust cleaning technologies is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing environmental awareness, and increasing industrial automation. As industries shift toward sustainable and precision-based maintenance solutions, laser rust cleaning is emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional abrasive and chemical methods. Below are key market trends expected to shape the laser rust cleaning sector in 2026:
-
Rising Demand in Manufacturing and Automotive Sectors
By 2026, the automotive and heavy manufacturing industries are projected to be the largest adopters of laser rust cleaning systems. The need for non-contact, high-precision surface preparation in vehicle restoration, welding pre-treatment, and mold maintenance is accelerating investment in laser cleaning equipment. Manufacturers are prioritizing processes that minimize downtime and improve part longevity, giving laser technology a competitive edge. -
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Stringent global regulations on chemical waste and air emissions are pushing industries to adopt eco-friendly alternatives. Laser rust cleaning produces no secondary waste, chemicals, or wastewater, aligning with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. In regions like the European Union and North America, compliance with environmental standards is expected to boost adoption, particularly in aerospace and marine industries. -
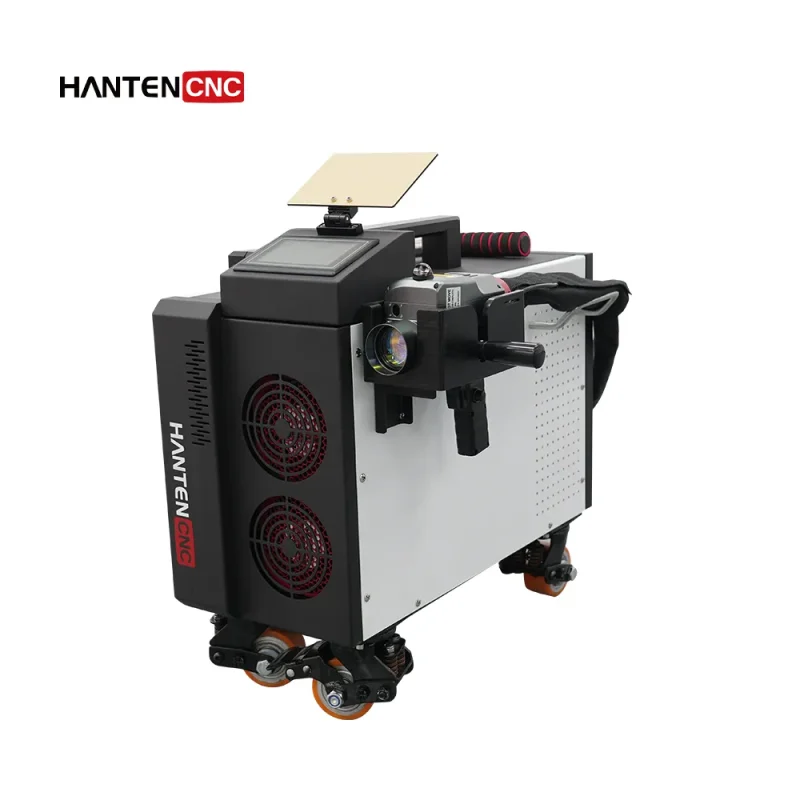
Advancements in Portable and Fiber Laser Systems
By 2026, portable fiber laser cleaning systems are expected to dominate the market due to their ease of use, energy efficiency, and improved beam quality. Innovations in handheld laser devices with intelligent control systems—such as real-time rust detection and automatic power adjustment—are making the technology accessible to smaller workshops and field service operations. -
Integration with Robotics and Industry 4.0
Laser rust cleaning is increasingly being integrated into automated production lines and robotic systems. In smart factories, these systems are connected via IoT platforms, enabling predictive maintenance and remote monitoring. This convergence with Industry 4.0 principles enhances operational efficiency and process repeatability, particularly in large-scale infrastructure and energy sectors. -
Cost Reduction and Broader Market Penetration
As production scales and component costs decline—especially in diode and fiber lasers—the upfront cost barrier for laser cleaning systems is expected to decrease. This will open up opportunities in emerging markets such as Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America, where industrial modernization efforts are gaining momentum. -
Growth in Niche Applications
Beyond heavy industry, laser rust cleaning is finding new applications in cultural heritage preservation, where delicate artifacts require non-abrasive restoration. The oil and gas sector is also adopting the technology for offshore platform maintenance, reducing risks associated with traditional sandblasting in confined or hazardous environments. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
The market is witnessing increased competition among laser equipment manufacturers, leading to strategic partnerships with system integrators and service providers. By 2026, bundled solutions—combining hardware, software, and training—are expected to become the norm, improving customer adoption and reducing implementation complexity.
In conclusion, the 2026 laser rust cleaning market will be characterized by technological maturity, environmental compliance, and expanding application scope. As industries prioritize sustainability, precision, and automation, laser-based cleaning is set to transition from a niche solution to a mainstream industrial standard.
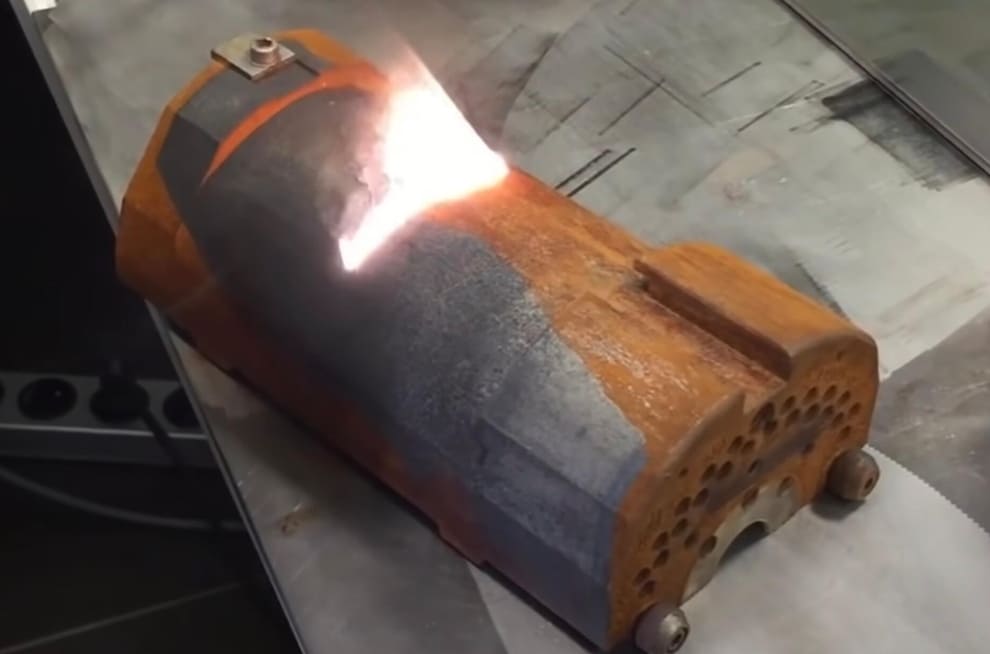

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Systems to Clean Rust (Quality and IP)
Sourcing laser systems for rust removal can offer significant advantages over traditional methods, but it also comes with several critical pitfalls—especially concerning quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these issues is essential to ensure you invest in a reliable, effective, and legally secure solution.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Underpowered or Inadequate Laser Specifications
Many suppliers offer lasers with inflated or misleading power ratings (e.g., advertised peak power vs. actual average power). A system that lacks sufficient power density or beam quality may fail to remove rust effectively, especially on thick or pitted corrosion. This leads to longer processing times, inconsistent results, and potential damage to the underlying substrate.
Tip: Verify real-world performance with third-party test reports and request on-site demonstrations using your actual rusted components.
2. Poor Beam Quality and Pulse Control
Effective rust removal requires precise control over pulse duration, frequency, and beam focus. Low-quality lasers may suffer from unstable pulse output or poor beam profiles, resulting in uneven cleaning, surface pitting, or unintentional substrate ablation.
Tip: Ask for M² (beam quality factor) values and pulse parameter ranges. Systems with fiber lasers (e.g., pulsed Yb-doped fiber) typically offer better stability and control.
3. Inadequate Cooling and Duty Cycle
Some budget systems lack robust thermal management, leading to overheating during continuous operation. This reduces laser efficiency, shortens component lifespan, and increases downtime—especially in industrial environments.
Tip: Confirm the system’s duty cycle and cooling mechanism (air vs. liquid cooling). Industrial-grade units should support 24/7 operation without performance degradation.
4. Substandard Safety Features and Compliance
Laser cleaning involves Class 4 lasers, posing serious safety risks. Some suppliers cut corners on safety interlocks, enclosures, fume extraction, or compliance with standards like IEC 60825 or FDA/CDRH regulations.
Tip: Ensure the system includes full safety certifications, interlocks, and integrated fume management. Verify compliance documentation before purchase.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Some low-cost suppliers use cloned or reverse-engineered laser sources, control boards, or software, infringing on original manufacturers’ IP. This not only risks legal exposure but also leads to poor reliability and lack of technical support.
Tip: Source from reputable manufacturers and verify component origins. Ask for proof of licensing for key technologies (e.g., IPG Photonics or nLIGHT laser modules).
2. Proprietary Software and Firmware Lock-In
Many laser systems rely on proprietary software for parameter control and diagnostics. Suppliers may restrict access to source code or charge exorbitant fees for updates, limiting your ability to customize or maintain the system in-house.
Tip: Negotiate access to API documentation or open communication protocols (e.g., Ethernet/IP, Modbus). Avoid vendors that lock you into closed ecosystems.
3. Lack of IP Ownership in Custom Solutions
If you commission a custom laser cleaning system (e.g., robotic integration), the supplier may retain IP rights to the design, software, or process parameters. This restricts your ability to modify, replicate, or scale the solution.
Tip: Include clear IP ownership clauses in contracts. Ensure you retain full rights to custom developments unless licensing is explicitly agreed upon.
4. Risk of Infringing Patented Processes
Certain laser cleaning techniques (e.g., selective ablation algorithms or multi-wavelength approaches) may be covered by active patents. Using a system that implements patented methods without a license could expose your company to litigation.
Tip: Conduct a freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis, especially for high-volume or commercial applications. Work with legal counsel to assess potential IP risks.
Conclusion
Sourcing a laser system for rust removal demands careful evaluation beyond price and specifications. Prioritize vendors with proven quality control, transparent component sourcing, and clear IP practices. Investing time in due diligence helps avoid costly downtime, legal issues, and performance shortfalls—ensuring a safe, effective, and sustainable rust removal solution.
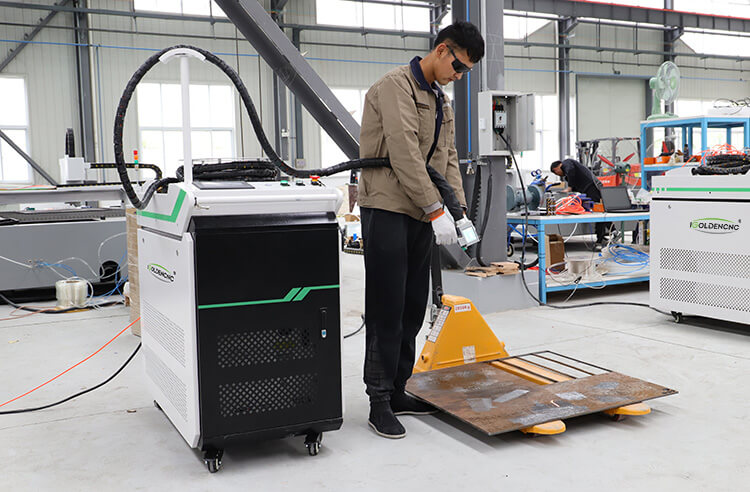

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Rust Cleaning Equipment
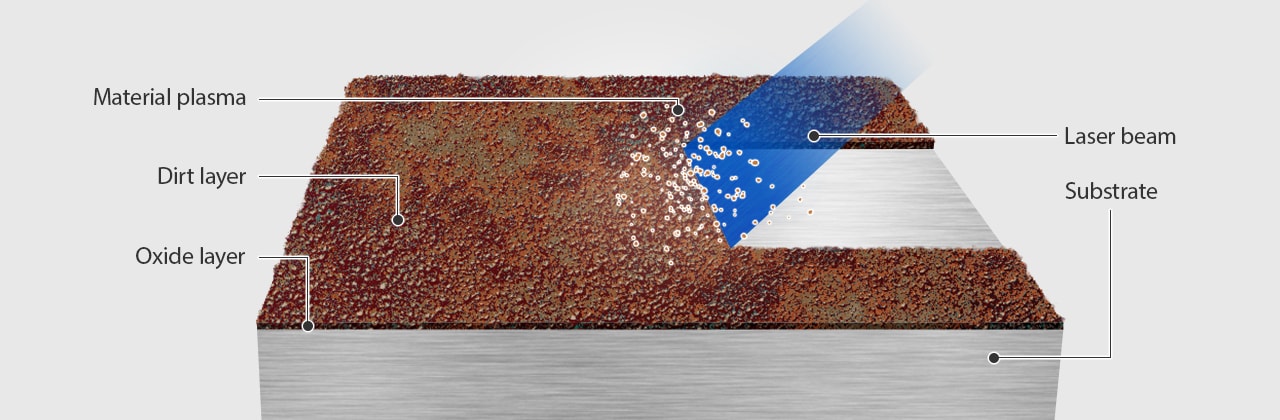
Laser rust cleaning (also known as laser cleaning or laser surface decontamination) is an advanced, eco-friendly technology used to remove rust, paint, oxides, and other contaminants from metal surfaces without damaging the underlying material. As this technology gains traction across industries like automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, and heritage restoration, it is essential to understand the logistics and compliance requirements associated with its deployment.
This guide outlines key considerations under the H2 heading “Logistics & Compliance” to ensure safe, legal, and efficient use of laser rust cleaning systems.
1. Regulatory Compliance
a. Laser Safety Standards
Laser cleaning systems typically fall under Class 4 laser classification (high-power lasers), which are subject to strict safety regulations.
- IEC 60825-1: International standard for laser product safety. Requires proper labeling, interlocks, and protective housings.
- ANSI Z136.1 (USA): U.S. standard for safe use of lasers. Mandates a Laser Safety Officer (LSO), controlled access, and safety training.
- Local Regulations: Ensure compliance with national regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK, DGUV in Germany).
b. Workplace Safety
- Eye and Skin Protection: Provide certified laser safety goggles (OD 5+ at the relevant wavelength, typically 1064 nm for fiber lasers).
- Controlled Access Zones: Establish and mark laser operation areas with warning signs.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Laser ablation produces particulate matter (metal fumes, oxides). Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems and HEPA filters to meet air quality standards (e.g., OSHA PELs or EU Directive 2004/37/EC).
c. Environmental Regulations
- Waste Management: Unlike chemical or abrasive methods, laser cleaning generates minimal waste—primarily particulate residue. Collect and dispose of debris according to local hazardous waste rules (e.g., EPA regulations if heavy metals are present).
- No Chemical Disposal: One of the key advantages—eliminates need for solvents or blasting media, reducing environmental liability.
2. Transportation & Logistics
a. Shipping and Import/Export
- Laser Classification: High-power lasers may be subject to export controls under:
- Wassenaar Arrangement (dual-use goods)
- U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL) – ECCN 6A003.b (laser systems)
- ITAR (if used in defense applications)
- Documentation: Maintain technical specs, end-user declarations, and export licenses where required.
- Customs Clearance: Clearly declare the equipment as a laser cleaning system. Include safety certifications (CE, FCC, RoHS).
b. Packaging and Handling
- Use shock-resistant, moisture-proof packaging.
- Include handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
- Secure optical components and power units separately to prevent damage.
c. Installation Logistics
- Power Requirements: Most industrial laser cleaners require 3-phase power (200–400V). Verify site compatibility.
- Space Requirements: Allow minimum 2–3 meters around the unit for safe operation and fume extraction.
- Cooling Systems: Air- or water-cooled lasers need proper thermal management infrastructure.
3. Operational Compliance
a. Operator Training
- Mandatory training on:
- Laser safety procedures
- Emergency shutdown protocols
- PPE use and maintenance
- Waste handling
- Certification records should be maintained (e.g., ANSI Z136.8 for training programs).
b. Risk Assessments
- Conduct site-specific risk assessments before deployment.
- Address hazards such as reflection risks, fume inhalation, electrical safety, and fire risk (from hot particles).
c. Maintenance & Calibration
- Follow manufacturer’s schedule for:
- Optics cleaning and alignment
- Cooling system checks
- Laser output calibration
- Keep logs for audits and compliance verification.
4. Certifications & Documentation
Ensure the following are available and up to date:
– CE Marking (for EU market) including Declaration of Conformity
– FDA Registration (for U.S. market, under 21 CFR 1040.10)
– ISO 9001 (Quality Management)
– ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) – beneficial for sustainability claims
– Safety manuals, technical drawings, and user guides in local language
5. Insurance & Liability
- Product Liability Insurance: Covers risks from equipment malfunction.
- Workers’ Compensation: Required if employees operate the laser.
- Environmental Liability: Though minimal, contamination from displaced rust particles should be considered.
Summary Checklist
| Item | Requirement |
|——|————-|
| Laser Safety Officer (LSO) | Required for Class 4 lasers |
| PPE (goggles, gloves, respirators) | Mandatory |
| Fume extraction system | Required |
| Export license | If shipping internationally |
| Site power compatibility | 3-phase, 200–400V |
| Training records | Maintain for all operators |
| Waste disposal plan | For collected particulates |
By adhering to this Logistics & Compliance Guide, organizations can safely and legally deploy laser rust cleaning technology, minimizing risk while maximizing efficiency and environmental benefits. Always consult local authorities and equipment manufacturers for site-specific guidance.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser for rust cleaning offers a highly effective, precise, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cleaning methods such as sandblasting or chemical treatments. Laser rust removal minimizes substrate damage, reduces waste, and eliminates the need for consumables, making it a sustainable and cost-efficient solution in the long term. When selecting a laser system, key factors to consider include laser power, wavelength, pulse duration, portability, and compatibility with your specific materials and production environment. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of operational efficiency, lower maintenance costs, and improved safety make laser cleaning a worthwhile investment for industries such as automotive, aerospace, maritime, and heritage restoration. Proper supplier vetting, after-sales support, and operator training are essential to ensure optimal performance and return on investment. As laser technology continues to advance, it is becoming increasingly accessible and represents the future of non-contact, precision surface cleaning.