The global wood coatings removal market has seen increasing demand, driven by growth in furniture restoration, historic preservation, and industrial maintenance sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global laser systems market—encompassing industrial applications such as surface treatment and coating removal—was valued at USD 13.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% through 2029. A key driver in this expansion is the rising adoption of precision non-abrasive techniques like laser ablation, especially for sensitive applications such as removing varnish from wood without damaging the underlying grain. As sustainability and material longevity gain importance, manufacturers are shifting toward eco-friendly alternatives to chemical strippers and mechanical sanding, positioning laser-based solutions at the forefront of innovation. This shift has led to a surge in specialized laser system producers focusing on controlled, efficient, and residue-free varnish removal. Based on technological capability, market presence, and customer adoption, the following eight manufacturers have emerged as leaders in delivering laser systems tailored for wood varnish removal.
Top 8 Laser That Removes Varnish From Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL – a universal professional laser cleaning machine suitable for metal, wood, stone and mixed-material applications….
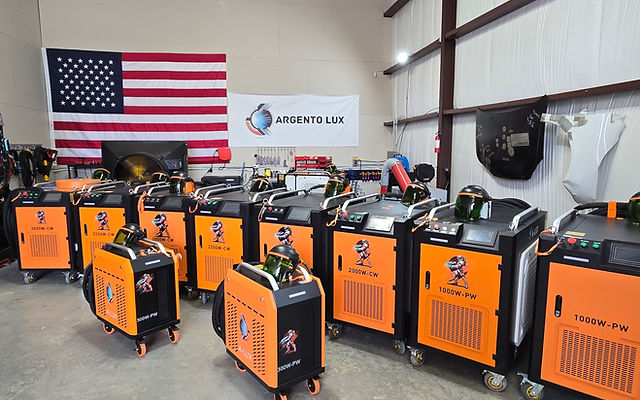
#2 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning removes paint, contaminants, rust, and residues with a high-energy laser beam which leaves the substrate untouched. Our Laser Ablation is the ……
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: LPC-100 Laserpack is a laser cleaning backpack. P-laser teambuilding. QF-2000 Laser removes almost any other kind of contamination, including grease, rust….
#4 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: The pulse laser cleaning machine have 100w, 200w, 300w, 500w, 1000w, Mainly used to rust, thin paint layer, wood, oil removal, It will no impact on the surface….
#5 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning systems from Laser Photonics effectively clean a wide range of materials, including metals, thermoplastics, composites, stone, wood, and concrete ……
#6 Clean Laser Technologies
Website: cleanlasertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Discover advanced laser cleaning machines and rust removal systems trusted by industries across the USA. Eco-friendly, precise, and OSHA-compliant surface ……
#7 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: So the laser wood stripping machine is an ideal tool for stripping paint from wooden, They offer precise and eco-friendly cleaning without damaging the base ……
#8 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping is incredibly precise, removing layers of paint, varnish, or other coatings without damaging the underlying wood….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser That Removes Varnish From Wood
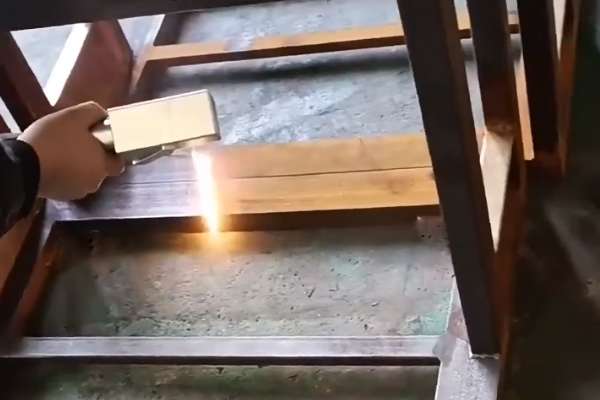

H2: Market Trends for Laser Technology in Varnish Removal from Wood (2026 Outlook)
The global market for laser-based solutions in wood restoration, particularly for varnish removal, is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by advancements in precision technology, growing environmental consciousness, and increasing demand for non-destructive restoration methods, laser systems are emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional chemical and mechanical stripping techniques.
One of the key trends shaping the 2026 market is the rising adoption of fiber and pulsed laser technologies. These systems offer selective ablation—effectively removing varnish and coatings without damaging the underlying wood grain. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating AI-driven controls and robotic automation into laser platforms, enhancing consistency and enabling real-time monitoring during the removal process. This technological evolution is expanding applications beyond niche restoration projects to include industrial-scale furniture refinishing, heritage conservation, and architectural woodwork.
Sustainability is another major driver. As regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) tighten globally, industries are seeking eco-friendly methods. Laser varnish removal produces no chemical waste and minimal particulate matter when paired with effective filtration, aligning with green manufacturing standards. This positions laser systems favorably in markets with strict environmental compliance requirements, such as the European Union and North America.
Additionally, cost dynamics are shifting. While initial investment in laser equipment remains high, decreasing prices of core components like laser diodes and improved system durability are making the technology more accessible. By 2026, industry analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 9–12% for laser-based surface treatment in woodworking, with varnish removal being a key application segment.
Finally, market expansion is being fueled by growing awareness among restoration professionals and artisan workshops. Training programs and demonstration centers are helping bridge the knowledge gap, accelerating adoption. As a result, by 2026, laser varnish removal is expected to transition from a premium option to a standard tool in high-value wood restoration, particularly in luxury furniture, museum conservation, and historic building maintenance.
In summary, the 2026 market for lasers that remove varnish from wood will be defined by technological sophistication, environmental compliance, and expanding commercial viability—positioning laser systems as a cornerstone of modern, sustainable wood surface treatment.
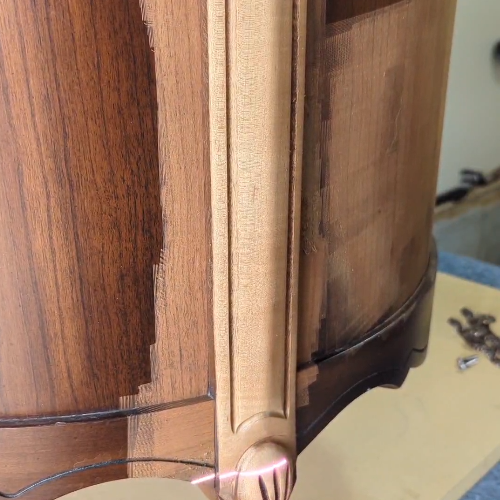

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser for Removing Varnish from Wood
Sourcing a laser system capable of effectively removing varnish from wood requires careful consideration of both technical capabilities and legal protections. Overlooking key factors can lead to poor performance, damage to substrates, or intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Laser Quality and Performance Specifications
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting a laser based on cost alone without verifying its technical suitability for wood varnish removal. Low-quality or improperly specified lasers may lack the precision, power control, or wavelength needed to ablate varnish cleanly without scorching or etching the underlying wood. Buyers should verify pulse duration, beam quality (M² factor), wavelength (typically fiber or UV lasers around 355nm or 1064nm), and power stability. Without proper specifications, the system may deliver inconsistent results, require repeated passes, or fail entirely on certain varnish types.
Insufficient Understanding of Material Interaction
Varnish types (polyurethane, acrylic, shellac, etc.) and wood species react differently to laser energy. A common pitfall is assuming one laser setting works universally. Without proper testing on actual samples or access to application expertise from the supplier, users risk damaging valuable wood surfaces. Suppliers should provide material testing reports or demo services to validate performance across expected use cases.
Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Rights and Licensing
When sourcing laser systems—especially turnkey or automated solutions—buyers may inadvertently violate IP rights if the technology incorporates patented methods for surface cleaning, scanning patterns, or control software. Using a system without proper licensing, particularly in commercial or industrial applications, can expose the buyer to legal action. Always verify that the supplier holds necessary IP rights or offers proper usage licenses, especially for proprietary ablation algorithms or integrated robotics.
Poor After-Sales Support and Technical Documentation
Many suppliers, particularly those based overseas, offer attractive upfront pricing but lack robust technical support, training, or documentation. This becomes a critical issue when troubleshooting, maintaining, or optimizing the laser process. Ensure the supplier provides comprehensive manuals, safety certifications (e.g., FDA, CE), software access, and responsive technical assistance before purchase.
Incomplete Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser systems for varnish removal often fall under Class 4 laser safety regulations. A key pitfall is sourcing equipment that lacks required safety features (interlocks, enclosures, emergency stops) or proper regulatory certifications for your region. Non-compliant systems pose safety hazards and may be prohibited from operation in commercial environments, leading to costly retrofits or shutdowns.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in evaluating both technical performance and legal safeguards when sourcing laser systems for wood varnish removal.
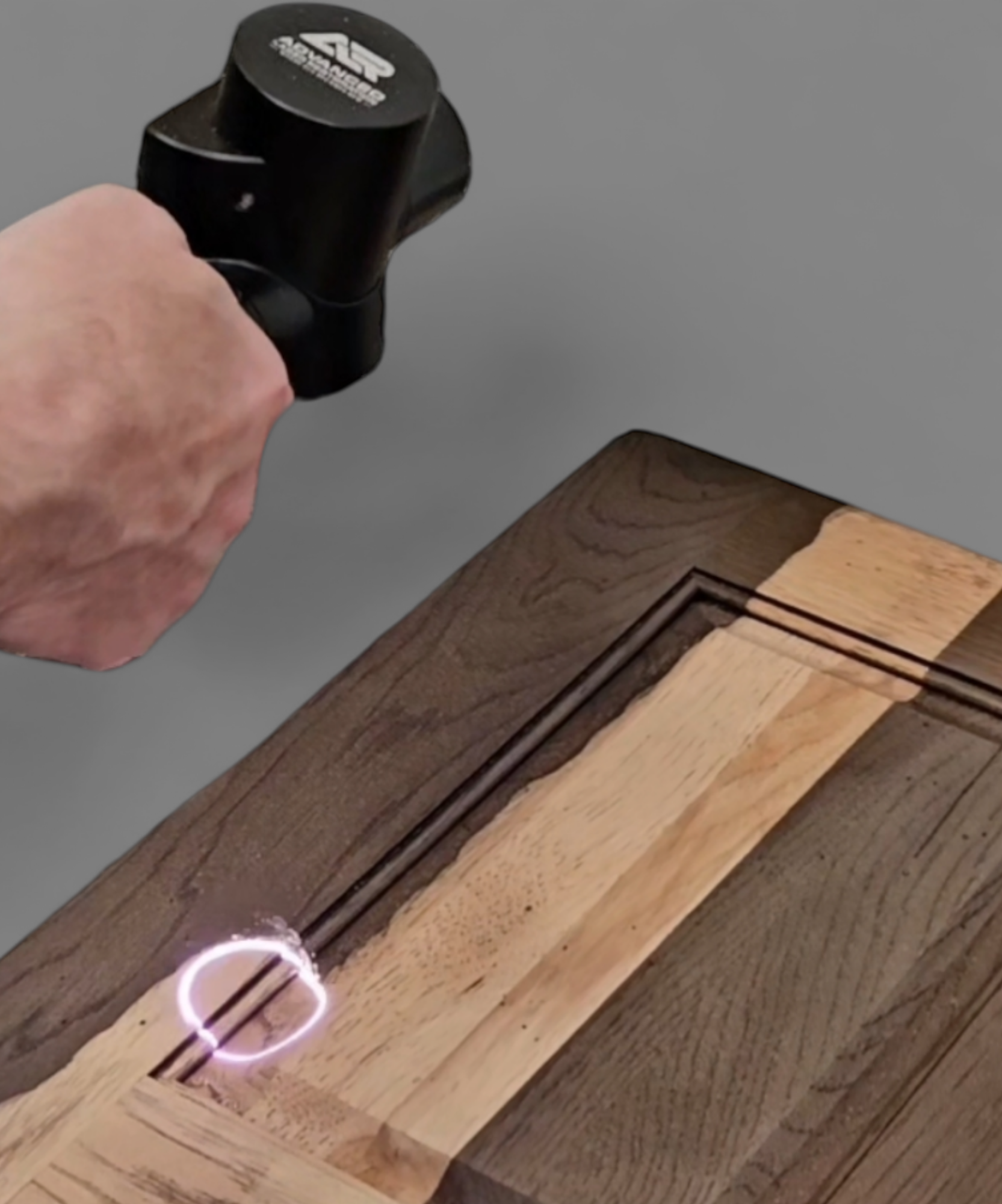

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser That Removes Varnish From Wood
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
The laser system designed to remove varnish from wood is classified as an industrial laser processing machine. It falls under the broader category of laser-based equipment used in manufacturing, woodworking, and restoration industries. Key regulatory frameworks applicable include:
- IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements
- ANSI Z136.1: Safe Use of Lasers (U.S. standard)
- Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC (for CE marking in the European Union)
- FDA/CDRH Regulations (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) for laser products in the U.S.
Ensure the laser system is properly classified (typically Class 1 or Class 4, depending on enclosure and access) and carries appropriate warning labels and safety interlocks.
Export and Import Compliance
When shipping the laser system internationally, compliance with export control and customs regulations is critical:
- Export Control Classification Number (ECCN): Determine if the laser falls under ECCN 6A003 or 6A005 based on laser power, wavelength, and intended use. Some high-powered lasers may be subject to ITAR or EAR restrictions.
- End-Use Documentation: Provide a statement of end-use if required, especially for destinations with strict technology controls.
- Customs Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, and certificate of origin. Clearly describe the product as “Laser Equipment for Wood Varnish Removal – Industrial Use.”
Verify import regulations in the destination country, as some jurisdictions may require additional certifications or local representation.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Due to the sensitive optical and electronic components, packaging must meet industrial equipment standards:
- Use shock-absorbent, anti-static materials and a rigid outer crate.
- Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
- Secure all moving parts and optics during transit.
- Include a detailed packing list and user documentation inside the shipment.
Confirm compliance with ISTA 3A or equivalent packaging performance testing standards for domestic and international freight.
Transportation and Shipping Modes
Choose appropriate shipping methods based on size, weight, and delivery urgency:
- Air Freight: Suitable for lightweight models or time-sensitive deliveries. Ensure compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries (e.g., for portable units) are included.
- Ocean Freight: Recommended for heavy or bulk shipments. Use FCL (Full Container Load) for better protection.
- Ground Transport: Ideal for regional distribution within the U.S., EU, or other land-connected markets.
Coordinate with carriers experienced in handling industrial machinery and laser equipment.
Installation, Training, and On-Site Compliance
Upon delivery:
- Require certified technicians to perform installation and safety checks.
- Provide operator training on laser safety, emergency shutdown, and PPE (laser safety goggles appropriate for the laser’s wavelength).
- Conduct a site risk assessment to ensure proper ventilation, fire prevention, and safe operation zones.
- Supply required documentation: User Manual, Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for any generated particulates, and compliance certificates (CE, FDA, etc.).
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Varnish removal via laser may produce airborne particulates and fumes:
- Equip the system with an integrated fume extraction and filtration unit compliant with OSHA or REACH standards.
- Advise users to operate the laser in well-ventilated areas or with local exhaust ventilation (LEV).
- Dispose of collected particulate waste in accordance with local hazardous waste regulations, as some varnishes contain regulated chemicals.
Maintenance and Service Logistics
Establish a service network for ongoing support:
- Stock critical spare parts regionally to minimize downtime.
- Offer remote diagnostics and on-site service contracts.
- Maintain logs of service activities for compliance audits.
Ensure all service personnel are trained and equipped to handle laser safety protocols.
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain detailed records for at least 5 years, including:
- Product compliance certifications
- Export licensing documentation
- Customer training logs
- Service and maintenance reports
These records support regulatory audits and warranty claims.
By following this guide, manufacturers and distributors can ensure safe, legal, and efficient logistics for laser systems used in wood varnish removal.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser system for removing varnish from wood requires careful consideration of laser type, power, safety features, and precision. Fiber or CO₂ lasers are typically most effective, with CO₂ lasers being particularly well-suited for organic materials like wood due to their wavelength absorption characteristics. Key factors in selecting a suitable system include consistent beam quality, adjustable settings for controlled material removal, and integrated safety mechanisms such as fume extraction and protective enclosures. Additionally, evaluating the supplier’s reputation, technical support, and after-sales service is crucial for long-term reliability and performance. When properly implemented, laser varnish removal offers a precise, non-contact, and environmentally friendly alternative to mechanical or chemical stripping methods, preserving the integrity of the underlying wood while improving efficiency and finish quality.