The global laser surface treatment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision cleaning solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and cultural heritage restoration. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cleaning equipment market size was valued at USD 625.8 million in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.4% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of eco-friendly, non-abrasive technologies like laser varnish removal, which offer superior accuracy and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional methods. As industries prioritize efficiency and sustainability, laser systems are becoming the preferred solution for delicate surface restoration. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in developing high-performance lasers specifically designed for varnish removal. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and customer application success, here are the top 8 manufacturers shaping the future of laser-based surface cleaning.
Top 8 Laser That Removes Varnish Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 Laser cleaner machine prices
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaner machine prices and parameters, download our Catalogue….
#3 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning removes paint, contaminants, rust, and residues with a high-energy laser beam which leaves the substrate untouched. Our Laser Ablation is the ……
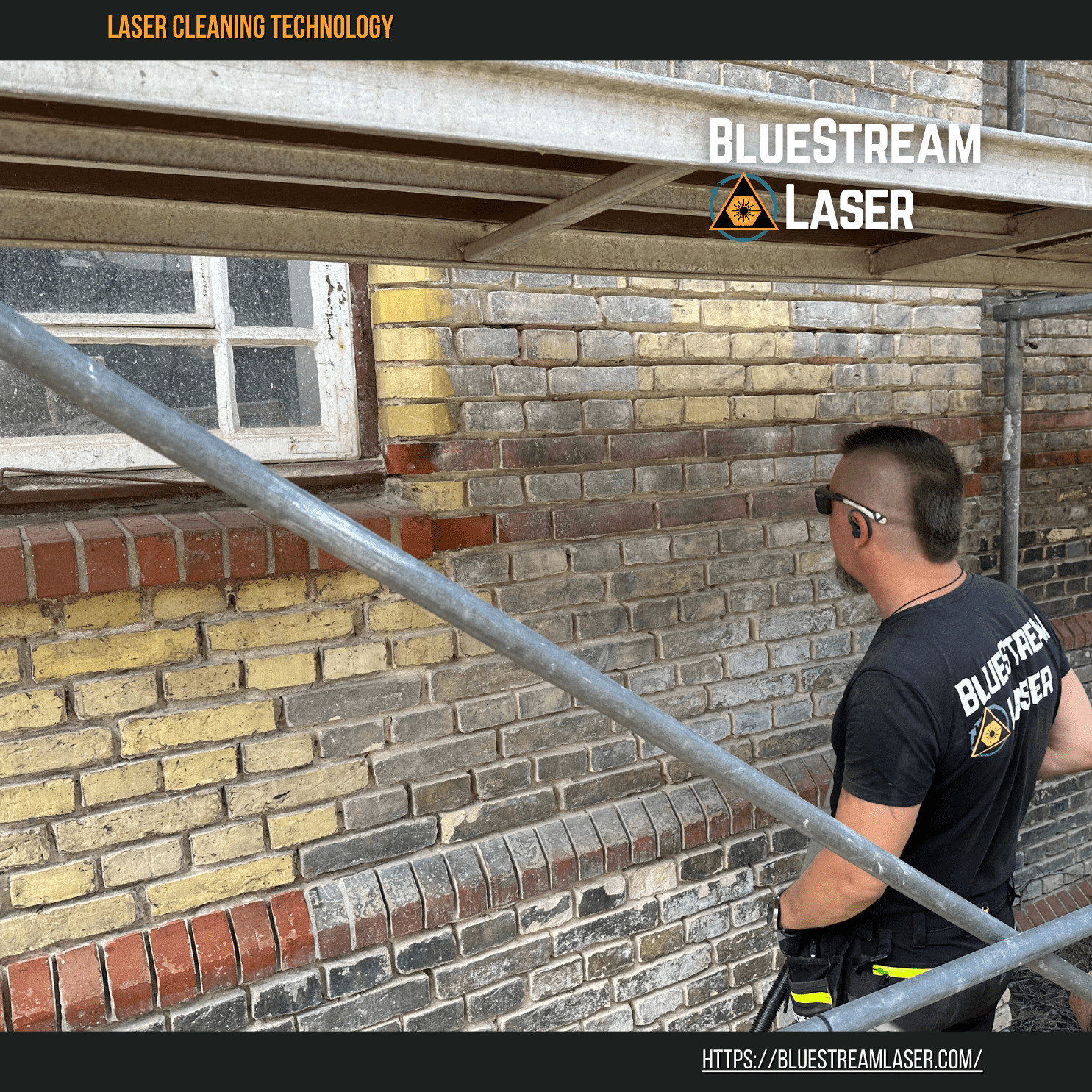
#4 Bluestream Laser Cleaning, restoration of monuments, industrial …
Website: bluestreamlaser.com
Key Highlights: The laser removes up to 98% of surface impurities, ensuring the highest standard of cleanliness of all available methods. No use of abrasives allows cleaning ……
#5 Industrial Laser Systems
#6 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#7 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: LME Laser is a laser cleaning machine manufacture with 17 years experience. The Products including continuous laser cleaner and pulse laser cleaner….
#8 Clean Laser Technologies
Website: cleanlasertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: STAIN/VARNISH REMOVAL. Precise stain and varnish removal revitalizes surfaces with effective cleaning. Commercial Kitchen Cleaning. Simplify and Streamline ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser That Removes Varnish

2026 Market Trends for Lasers That Remove Varnish
The market for lasers designed specifically for varnish removal is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental and safety regulations, and expanding applications across diverse industries. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends shaping this niche but growing sector:
Advancements in Laser Technology and Precision
By 2026, expect significant improvements in laser systems tailored for delicate varnish ablation. The focus will shift towards ultra-precise, wavelength-tunable lasers (particularly in the UV and short-pulse IR spectrum) that can selectively target varnish layers without damaging underlying substrates like wood, metal, or canvas. Innovations in beam delivery systems and real-time monitoring (using integrated sensors and AI) will enhance control, enabling automated, consistent results and minimizing operator skill dependency. This precision will be crucial for high-value applications in art restoration and aerospace.
Growing Emphasis on Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Solutions
Environmental regulations are increasingly restricting traditional chemical stripping methods due to hazardous waste and VOC emissions. By 2026, laser varnish removal will gain substantial market traction as a cleaner, solvent-free alternative. The “green” credentials of laser technology—producing minimal waste (primarily vaporized material captured by filtration) and eliminating toxic chemicals—will be a major driver, particularly in Europe and North America. This trend aligns with corporate sustainability goals and stricter industrial compliance standards.
Expansion into New and Diverse Application Sectors
While art restoration and heritage conservation remain core markets, 2026 will see broader adoption. Key growth areas include:
* Aerospace & Automotive: Precise removal of coatings from sensitive components (e.g., turbine blades, composite parts) without substrate damage.
* Electronics Manufacturing: Delicate stripping of conformal coatings from circuit boards for rework or repair.
* Industrial Maintenance: Efficient cleaning of machinery, molds, and tools coated with protective varnishes or release agents.
* Marine Industry: Eco-conscious hull and deck maintenance, replacing harsh chemical cleaners.
Increasing Automation and Integration
Laser varnish removal systems will become more integrated into automated production and maintenance lines by 2026. Robotic arms equipped with laser heads, guided by CAD/CAM software or vision systems, will enable high-throughput, consistent processing for batch applications (e.g., restoring furniture sets or maintaining industrial equipment). This shift towards automation will improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance process repeatability.
Cost Reduction and Accessibility
While high initial investment remains a barrier, the cost of laser systems (especially fiber lasers) is expected to decrease gradually by 2026 due to economies of scale and technological maturation. Concurrently, operational costs (energy efficiency, minimal consumables) will highlight the long-term economic advantage over chemical methods. This improved cost-benefit analysis will make laser technology accessible to a wider range of businesses, including smaller restoration workshops and mid-sized manufacturers.
Focus on Safety and Operator Protection
As adoption grows, safety standards for laser operations will become more stringent. Systems in 2026 will feature enhanced safety interlocks, improved fume extraction and filtration (addressing potential nanoparticle generation), and comprehensive operator training modules. User-friendly interfaces and remote operation capabilities will further reduce risks, making the technology safer and easier to deploy in various work environments.
Rising Demand in Art and Heritage Conservation
The art restoration sector will remain a critical driver, with conservators increasingly relying on lasers for their unparalleled precision and non-contact nature. By 2026, advancements will allow for even safer treatment of fragile, multi-layered historical artifacts and paintings. The ability to document and verify the cleaning process digitally will also enhance the credibility and acceptance of laser methods in prestigious institutions and museums worldwide.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lasers for Varnish Removal: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Poor Beam Quality and Inconsistent Performance
A frequent issue is sourcing lasers with substandard beam quality, leading to uneven varnish removal, thermal damage to the underlying material, or incomplete stripping. Low-quality lasers may lack precise wavelength control or stable pulse durations, which are critical for selective ablation. Buyers often overlook specifications like M² factor, beam profile, and pulse-to-pulse stability, resulting in unreliable performance and increased rework or material waste.
Lack of Proper Cooling and System Integration
Many cost-effective lasers skimp on integrated cooling systems or robust housing, causing overheating during continuous operation. This reduces laser lifespan and can lead to frequent downtime. Additionally, poor mechanical and software integration with existing production lines can hinder automation, requiring costly custom engineering solutions post-purchase.
Inadequate Safety Features and Compliance
Some suppliers offer lasers that do not meet international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825), lacking proper enclosures, interlocks, or emission indicators. This exposes users to health risks and potential regulatory non-compliance, especially in industrial or medical environments. Always verify certification documentation before procurement.
Misrepresentation of IP Ownership and Design Originality
A significant intellectual property (IP) pitfall is sourcing from vendors who falsely claim ownership of laser technology. Some manufacturers rebrand or slightly modify designs protected by others’ patents, exposing buyers to legal liability. For instance, using diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) or fiber laser architectures that infringe on existing patents can lead to infringement claims, especially in markets like the EU or U.S.
Use of Counterfeit or Substandard Components
Lower-cost lasers may incorporate counterfeit or out-of-spec optical components (e.g., laser diodes, mirrors, or crystals), which degrade quickly and compromise output quality. These components often lack traceability and warranty support, making maintenance difficult and increasing total cost of ownership.
Insufficient Technical Support and Documentation
Many suppliers, particularly in less-regulated markets, provide inadequate technical documentation, software SDKs, or post-sale support. This hampers integration, troubleshooting, and process optimization. Absence of clear maintenance guidelines or training can lead to improper use and premature system failure.
Hidden IP Licensing Requirements
Even if a laser appears compliant, underlying technologies (such as pulse modulation algorithms or scanning systems) may be patented. Buyers may unknowingly violate licensing agreements by using the laser in certain applications. Always conduct due diligence on third-party IP dependencies and request indemnification clauses in supply contracts.
Failure to Verify Real-World Application Suitability
Suppliers may advertise lasers based on ideal lab conditions, not real-world varnish types or substrate materials. Without application-specific testing, buyers risk investing in systems that underperform on actual production workloads. Always request sample processing trials using your specific materials before finalizing a purchase.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser That Removes Varnish
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, and operation of industrial lasers designed specifically for varnish removal. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and efficient deployment.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Determine the correct classification of the laser system under international and national regulations. Most varnish-removal lasers are Class 4 lasers due to their high power, capable of removing coatings through ablation. Required documentation includes:
– FDA/CDRH compliance (in the U.S.) including product report and variance (if applicable)
– CE marking with conformity to EU directives (e.g., Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, and Laser Product Safety EN 60825-1)
– IEC 60825-1 certification for laser safety
– Technical File and Declaration of Conformity
Ensure all manuals (user, service, safety) are provided in local languages for target markets.
Export and Import Compliance
Verify export control classifications, such as ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) under the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL). High-power lasers may be subject to export restrictions under dual-use regulations (e.g., Wassenaar Arrangement). Required actions:
– Obtain export licenses if necessary (e.g., for certain destinations or power levels)
– Complete accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin
– Comply with destination country import requirements (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC Mark in South Korea)
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Use robust, shock-resistant packaging suitable for heavy industrial equipment:
– Secure the laser head, power unit, and control panel in custom foam inserts
– Include desiccants to prevent moisture damage during transit
– Clearly label packages with:
– “Fragile”
– “This Side Up”
– “Laser – Do Not Expose to Light or Heat”
– Class 9 miscellaneous hazardous material label (if applicable, depending on battery or component classification)
Follow IATA/IMDG regulations if shipping by air or sea, especially when lithium batteries are included.
Transportation and Handling
- Use freight carriers experienced in handling sensitive industrial equipment
- Ensure lift-gate service and forklift availability at delivery points
- Train personnel in safe uncrating and movement using appropriate PPE and equipment
- Avoid tilting or dropping the unit; maintain manufacturer-recommended orientation
On-Site Installation and Safety Compliance
Prior to operation, ensure:
– Installation in a controlled environment with stable temperature and low humidity
– Proper grounding and electrical supply meeting specifications (voltage, phase, amperage)
– Implementation of a designated laser-controlled area with:
– Interlocks and warning signs (e.g., “Laser Radiation – Avoid Eye or Skin Exposure”)
– Physical barriers or enclosures to contain beam and debris
– Emergency stop buttons within reach
– Installation of fume extraction systems to capture particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during varnish ablation
Operational Safety and Training
Mandate laser safety training compliant with ANSI Z136.1 (U.S.) or IEC 60825 standards. Training must cover:
– Laser classification and hazards (eye/skin exposure, fire risk)
– Proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles with correct OD rating for the laser wavelength
– Safe work procedures and emergency response
– Designation of a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) for Class 4 systems
Environmental and Waste Management
Varnish removal produces waste in the form of ablated particles and fumes. Comply with environmental regulations by:
– Using certified filtration or HEPA vacuum systems to capture debris
– Disposing of collected waste as hazardous or non-hazardous based on varnish composition (check MSDS/SDS)
– Monitoring air quality and ensuring ventilation meets OSHA or local standards
– Maintaining logs of maintenance and waste disposal activities
Maintenance and Regulatory Audits
- Schedule regular maintenance per manufacturer guidelines
- Keep records of calibration, repairs, and safety inspections
- Prepare for compliance audits by maintaining up-to-date documentation including:
- Laser registration (if required by local authorities)
- Employee training records
- Safety protocols and risk assessments
Adherence to this logistics and compliance framework ensures safe, legal, and efficient use of laser varnish removal systems across global operations.
Conclusion:
Laser technology presents a highly effective, precise, and environmentally friendly solution for removing varnish from a variety of surfaces, particularly in delicate applications such as art restoration, historical preservation, and fine woodworking. Unlike traditional chemical or mechanical methods, laser ablation selectively targets the varnish layer without damaging the underlying material, preserving the integrity and details of the substrate.
When sourcing a laser system for varnish removal, key considerations include wavelength (commonly Nd:YAG at 1064 nm or frequency-doubled at 532 nm), pulse duration, energy density, beam control, and cooling mechanisms. Systems should offer adjustable parameters to accommodate different varnish types and substrate sensitivities. Safety features, ease of use, and compliance with regulatory standards are also crucial.
Ultimately, investing in a specialized laser for varnish removal offers long-term benefits through improved precision, reduced material waste, and minimized exposure to hazardous chemicals. For conservators, restorers, and industrial users alike, selecting the right laser system ensures efficient, non-invasive, and sustainable results.