The global laser wood processing market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision, speed, and eco-friendly manufacturing techniques in woodworking industries. According to Grand View Research, the global laser system market was valued at USD 15.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030, with industrial applications in wood engraving, cutting, and surface treatment contributing significantly to this expansion. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence reports that rising automation in furniture, architectural detailing, and customized wood products is accelerating the adoption of laser stripping and engraving technologies across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. As manufacturers seek non-contact, high-accuracy methods to remove coatings or create intricate designs on wood surfaces, the need for reliable laser stripping wood equipment has surged. This growing demand has led to the emergence of specialized manufacturers offering advanced CO₂ and fiber laser systems tailored for wood applications. Below are the top 8 manufacturers leading innovation, performance, and market presence in laser stripping wood technology.
Top 8 Laser Stripping Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: With over 35 years of expertise in surface treatment and more than 450 systems installed worldwide, P-Laser is at the forefront of industrial laser cleaning ……
#2 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#3 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: A laser wood stripping machine is a tool that uses laser technology to remove contaminants, such as paint, oil, dirt, or coatings, from wooden surfaces without ……
#4 Laser cleaning wood
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A laser cleaner is a device that uses high-intensity light to remove dirt, grime and stains from wood surfaces. It is a non-abrasive method of cleaning….
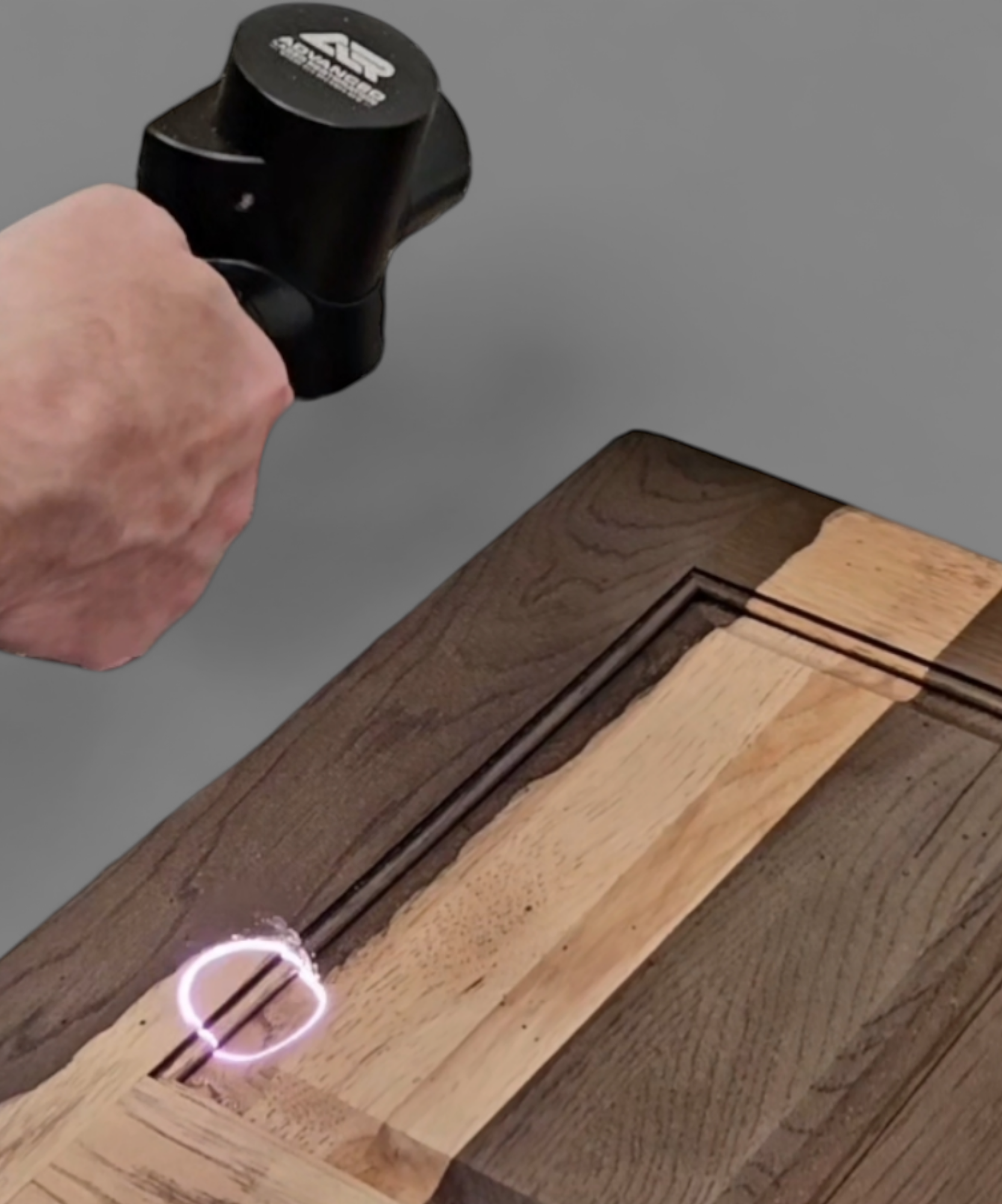
#5 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping is incredibly precise, removing layers of paint, varnish, or other coatings without damaging the underlying wood….
#6 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#7 Professional Laser Wood Stripping Machine
Website: lybylaser.com
Key Highlights: Discover the cutting-edge laser stripping machine for wood processing, featuring precision control, eco-friendly operation, and versatile applications for ……
#8 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: LME Laser is a laser cleaning machine manufacture with 17 years experience. The Products including continuous laser cleaner and pulse laser cleaner….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Stripping Wood
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Stripping Wood
As we approach 2026, the market for laser stripping wood is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental consciousness, and shifting industrial demands. This analysis explores the key trends shaping the landscape of laser-based wood stripping solutions.
1. Accelerated Adoption in Heritage Restoration and High-Value Manufacturing:
By 2026, laser stripping is expected to become the preferred method in heritage conservation and luxury woodworking. Its precision allows for the selective removal of paint, varnish, or fire-damaged layers without harming delicate carvings or original wood grain—critical for preserving historical artifacts and high-end furniture. Institutions and restoration firms are increasingly investing in laser systems to meet stringent conservation standards, fueling market growth in this niche.
2. Advancements in Pulsed Fiber and Ultrafast Lasers:
Technological innovation is a core driver. Pulsed fiber lasers, known for their efficiency and lower operational costs, are becoming more accessible. Simultaneously, ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) lasers are gaining ground in high-precision applications. These advanced systems offer superior control, minimal heat-affected zones, and the ability to process complex wood surfaces without charring—making them ideal for sensitive or intricate workpieces.
3. Integration with Automation and Robotics:
The integration of laser stripping systems into automated production lines is accelerating. By 2026, expect to see more robotic arms equipped with laser heads for consistent, high-throughput surface preparation in industries like automotive (wood trim), aerospace (interior components), and prefabricated luxury interiors. This trend enhances repeatability, reduces labor costs, and improves workplace safety.
4. Sustainability and Regulatory Pressure as Market Catalysts:
Environmental regulations are tightening globally, restricting the use of chemical strippers and abrasive blasting methods due to VOC emissions and hazardous waste. Laser stripping, as a dry, chemical-free, and low-waste process, aligns with green manufacturing goals. Companies seeking ISO 14001 certification or aiming for ESG compliance will increasingly adopt laser technology, boosting demand across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia.
5. Cost Reduction and Broader Market Accessibility:
While initially high-cost, laser systems are becoming more affordable due to improved component efficiency and economies of scale. By 2026, mid-range industrial lasers suitable for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are expected to enter the market, expanding adoption beyond large corporations. Cloud-based monitoring and predictive maintenance will also reduce downtime and total cost of ownership.
6. Growth in Customization and Smart Manufacturing:
The rise of Industry 4.0 is influencing laser stripping through the use of AI and machine vision. Systems are being developed that can scan wood surfaces in real time, detect coating types and thickness, and automatically adjust laser parameters for optimal stripping. This intelligence enables mass customization and enhances quality control, particularly in bespoke woodworking and architectural millwork.
Conclusion:
In 2026, the laser stripping wood market will be characterized by deeper technological integration, stronger environmental drivers, and expanding application scope. While challenges remain—such as initial investment costs and the need for skilled operators—the trajectory points toward widespread adoption across restoration, luxury manufacturing, and sustainable industrial sectors. Companies that embrace this technology early will gain a competitive edge in precision, efficiency, and environmental compliance.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Laser-Stripped Wood (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser-stripped wood can yield stunning, unique results, but it comes with significant risks related to both material quality and intellectual property (IP). Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to project delays, legal disputes, and compromised product integrity.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Laser Settings and Results
Laser stripping (also called laser ablation or laser cleaning) removes surface layers like paint, stain, or sealer to reveal the natural wood beneath. Inconsistent laser power, speed, or focus across batches can result in uneven depth, charring, or incomplete stripping. This leads to visual and textural inconsistencies, especially problematic in high-end furniture or architectural applications.
Wood Species and Grain Variability
Different wood species react differently to laser treatment. Softer woods (e.g., pine) may scorch or pit easily, while dense hardwoods (e.g., walnut) may require higher energy, risking surface degradation. Suppliers unfamiliar with laser processes may not account for grain direction or moisture content, leading to warping, cracking, or unpredictable finish outcomes.
Post-Processing and Finishing Challenges
Laser stripping alters the wood’s surface chemistry and porosity. Without proper post-treatment—such as sanding, sealing, or conditioning—the wood may absorb finishes unevenly, leading to blotchiness or reduced durability. Some suppliers skip these steps to cut costs, jeopardizing the final product quality.
Lack of Quality Control and Documentation
Reputable suppliers should provide batch testing, laser parameter logs, and material certifications. Sourcing from vendors without standardized QC processes increases the risk of receiving subpar or non-compliant materials, particularly for commercial or regulated projects.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Protected Designs
Laser stripping is often used to create intricate patterns, textures, or brand logos on wood surfaces. Sourcing components featuring copyrighted or trademarked designs (e.g., geometric motifs, brand emblems) from third-party suppliers without proper licensing can expose your business to IP infringement claims. This is especially common with overseas manufacturers who replicate popular designs without authorization.
Ambiguous Design Ownership
When collaborating with suppliers on custom laser patterns, it’s critical to define IP ownership in writing. Without a clear agreement, the supplier may claim rights to the design, limiting your ability to reuse, modify, or scale production. This can result in legal disputes or unexpected licensing fees.
Reverse Engineering and Design Theft
Suppliers with access to your design files may misuse them by replicating or selling similar products to competitors. This risk is heightened when working with manufacturers in jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement. Always use NDAs and limit file access to essential personnel.
Lack of Traceability and Compliance
For commercial or export projects, traceability of design origin and material sourcing is essential. Failing to verify that a supplier isn’t using stolen or plagiarized designs can damage brand reputation and lead to product recalls or customs seizures.
Mitigation Strategies
- Audit suppliers for laser capabilities, quality control, and IP compliance history.
- Require sample batches and test for consistency, durability, and finish compatibility.
- Use formal contracts that specify design ownership, usage rights, and confidentiality.
- Verify design originality—ensure patterns are either licensed or developed in-house.
- Apply watermarks or digital rights management (DRM) to design files shared externally.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, businesses can leverage laser-stripped wood safely and effectively while protecting their investments and brand integrity.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Stripping Wood
Regulatory Compliance
Environmental Regulations
Laser stripping wood may generate airborne particulates, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and potentially hazardous byproducts depending on the wood treatment (e.g., paints, varnishes, or preservatives). Compliance with environmental regulations is essential. Key requirements include:
– Emissions Control: Use of local exhaust ventilation (LEV) and high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration systems to capture fumes and particulates.
– EPA Standards: Adherence to U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations under the Clean Air Act, particularly if hazardous coatings are being removed.
– Waste Disposal: Proper handling and disposal of collected residue as hazardous or non-hazardous waste, based on material safety data sheets (MSDS) and local regulations. Conduct waste characterization testing if required.
Occupational Health & Safety
Worker safety is paramount when operating laser stripping equipment. Comply with:
– OSHA Standards: Follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910 guidelines for respiratory protection (e.g., N95 or P100 respirators), eye protection (laser safety goggles with appropriate wavelength filtering), and machine guarding.
– Laser Safety: Comply with ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers) by implementing controlled access zones, interlocks, and proper signage. Class 4 lasers require a designated Laser Safety Officer (LSO).
– Exposure Monitoring: Conduct air quality testing to ensure worker exposure to wood dust and fumes remains below permissible exposure limits (PELs).
Chemical & Material Regulations
When stripping treated or finished wood, be aware of regulated substances:
– Lead-Based Paint: If lead is present, comply with EPA’s Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) Rule and OSHA’s Lead Standard (29 CFR 1910.1025).
– Wood Preservatives: Arsenic (CCA-treated wood), creosote, or pentachlorophenol require special handling and disposal per RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act).
– Chemical Inventory: Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for any coatings or contaminants removed during the process.
Equipment & Operational Logistics
Laser System Requirements
- Laser Type: Fiber or CO₂ lasers are commonly used for wood stripping. Select based on wood type, coating thickness, and desired precision.
- Ventilation & Filtration: Integrate a fume extraction system with HEPA and activated carbon filters to manage particulates and VOCs.
- Automation & Control: Use CNC or robotic arms for consistent results, especially in industrial settings. Include emergency stop functions and safety interlocks.
Facility Setup
- Designated Work Area: Establish a dedicated, well-ventilated space with non-combustible flooring and fire suppression systems.
- Fire Prevention: Keep Class D fire extinguishers nearby and monitor for hot spots; laser processing can ignite wood.
- Noise Control: Some systems generate noise; use enclosures or hearing protection as needed.
Transportation & Handling
Material Handling
- Incoming Inspection: Screen wood materials for hazardous treatments (e.g., labels, known sources). Segregate contaminated wood.
- Storage: Store wood in dry, organized areas to prevent moisture absorption and maintain processing consistency.
- Post-Processing Handling: Cleaned wood should be stored separately; residue must be contained in sealed, labeled containers.
Shipping & Disposal Logistics
- Hazardous Waste Transport: If residue is classified as hazardous, use licensed waste transporters and manifest all shipments per DOT and EPA rules.
- Documentation: Maintain records of waste disposal, including manifests, test results, and compliance certifications.
- Non-Hazardous Waste: May be disposed of in approved landfills or recycled, depending on local regulations.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
- Compliance Records: Retain copies of SDS, air monitoring reports, worker training logs, and laser safety audits.
- Permits: Keep active permits for air emissions, hazardous waste handling, and facility operations.
- Training Logs: Document training for operators on laser safety, PPE use, and emergency procedures.
Conclusion
Laser stripping wood offers precision and efficiency but requires strict adherence to environmental, health, and safety regulations. Implementing comprehensive logistics and compliance protocols ensures operational safety, regulatory conformity, and sustainable waste management. Regular audits and staff training are recommended to maintain compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Wood Stripping:
Sourcing laser stripping for wood surfaces presents a highly effective, precise, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional wood finishing and restoration methods. The technology offers superior control, minimal substrate damage, and the ability to selectively remove finishes, coatings, or contaminants without the use of harsh chemicals. When sourcing laser stripping services or equipment, it is essential to consider factors such as laser type (e.g., fiber or CO₂), power requirements, material compatibility, safety certifications, and the expertise of service providers.
For businesses or restoration projects seeking sustainable and high-quality results, investing in professional laser stripping—either through in-house equipment or specialized contractors—can significantly improve efficiency and finish quality. As laser technology continues to advance and become more accessible, its adoption in woodworking, conservation, and industrial applications is expected to grow. Ultimately, sourcing laser wood stripping solutions represents a forward-thinking approach that balances precision, sustainability, and long-term value.