The global laser stripping market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision wire processing across aerospace, defense, medical device manufacturing, and the automotive industries. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser wire stripping market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in laser technology and the rising need for contactless, high-accuracy stripping solutions. Additionally, Grand View Research estimates that the broader industrial laser market—under which laser stripping falls—was valued at over USD 15 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.2% through 2030, supported by automation trends and Industry 4.0 adoption. As manufacturers seek to eliminate mechanical wear, reduce material waste, and enhance repeatability, laser-based stripping systems have become mission-critical in high-reliability applications. In this competitive landscape, nine companies have emerged as leaders, combining technical innovation, global reach, and a strong track record of performance in industrial environments.
Top 9 Laser Stripping Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
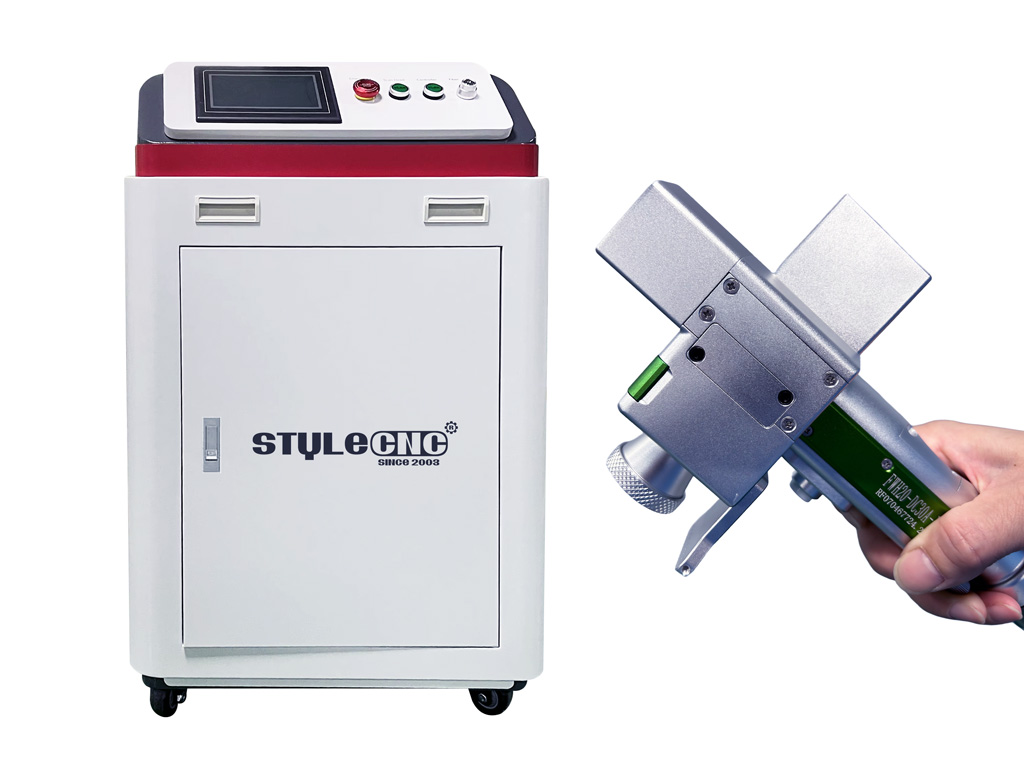
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#4 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#5 Laser cleaner machine prices
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaner machine prices and parameters, download our Catalogue….
#6 The 4JET Group
Website: 4jet.de
Key Highlights: 4JET develops innovative laser systems for cleaning, patterning, marking, cutting and modifying materials to achieve high-quality component surfaces….
#7 Laser Coating Removal Solutions for Industry
Website: surclean.com
Key Highlights: SurClean manufactures laser coating removal and surface preparation equipment that is precise, safe and clean. Our systems replace current methods of chemical, ……
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Non-Contact Process Laser cleaning is a remote process that enables precision material removal, virtually eliminating damage to the underlying material….
#9 to Sciton Medical & Aesthetic Laser Technologies
Website: sciton.com
Key Highlights: A leader in energy-based medical aesthetics. Sciton was founded to build exceptional lasers and light sources to improve people’s lives….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Stripping

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Stripping
The laser stripping market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing industrial automation, and growing demand for precision and sustainability. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Accelerated Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Battery Manufacturing:
The rapid expansion of the EV industry is a primary growth driver. Laser stripping offers unmatched precision for removing insulation from delicate high-voltage battery cables and busbars without damaging conductive materials. By 2026, laser systems will be increasingly integrated into automated battery module and pack assembly lines, ensuring consistent quality, enhanced safety, and improved production throughput. Demand for lasers capable of handling diverse wire types (e.g., aluminum, copper) and complex geometries (e.g., rectangular busbars) will surge.
2. Advancement of Ultrafast and Pulsed Laser Technologies:
Ultrafast lasers (picosecond and femtosecond) will gain prominence due to their minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ), enabling the clean stripping of sensitive materials like enameled magnet wire, aerospace-grade composites, and micro-coaxial cables. By 2026, expect wider adoption driven by decreasing costs and improved reliability. Pulsed fiber lasers will dominate high-throughput industrial applications due to their robustness, efficiency, and lower operating costs compared to older CO2 or Nd:YAG systems.
3. Integration with Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0:
Laser stripping systems will become fully integrated nodes within smart factories. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of:
* Real-time monitoring and control: Integrated sensors (e.g., vision systems, power monitors) providing closed-loop feedback for process optimization and defect detection.
* Predictive maintenance: IoT connectivity enabling remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime.
* Digital twin integration: Simulation and optimization of stripping processes before physical deployment.
* Seamless PLC/SCADA integration: For centralized control and data logging within automated production lines.
4. Focus on Sustainability and Reduced Environmental Impact:
Regulatory pressure and corporate sustainability goals will push laser stripping as the preferred alternative to chemical or mechanical methods. By 2026, the market will emphasize:
* Elimination of hazardous chemicals: Reducing environmental disposal costs and safety risks.
* Reduced waste generation: Precise material removal minimizes scrap compared to mechanical stripping.
* Energy efficiency: Continued development of more efficient laser sources and system designs.
5. Expansion into New Materials and Applications:
Beyond traditional copper wires, laser stripping will see increased use with:
* Fiber-reinforced polymers (FRP) and composites: For aerospace and automotive lightweighting.
* Medical devices: Precision stripping of miniature, biocompatible wires and catheters.
* Photovoltaics: Processing of solar cell ribbons and connectors.
* Recycling: Selective separation of materials in end-of-life electronics and cables.
6. Growth of Automated and Robotic Solutions:
Demand for fully automated laser stripping cells, often integrated with robotics for part handling and positioning, will accelerate. By 2026, modular, flexible systems capable of handling high-mix/low-volume production will be crucial for industries like medical device manufacturing and aerospace, driving the need for user-friendly programming and quick changeover capabilities.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the laser stripping market will be characterized by smarter, faster, more precise, and more sustainable solutions. Driven by the EV revolution, advancements in laser technology, and the demands of Industry 4.0, laser stripping will transition from a niche high-precision tool to a mainstream industrial process across diverse sectors, offering superior quality, efficiency, and environmental benefits over traditional methods.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Stripping Services: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser stripping services—commonly used in electronics, medical devices, and aerospace for precision wire and cable insulation removal—two critical risk areas are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) vulnerabilities. Failing to address these can lead to product failures, compliance issues, or loss of competitive advantage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Strip Accuracy and Repeatability
Laser stripping requires high precision to remove insulation without damaging the underlying conductor. Inexperienced or poorly calibrated service providers may produce inconsistent results, leading to nicks, burns, or incomplete stripping. This variability can compromise electrical performance and reliability, especially in high-frequency or high-reliability applications.
Material Compatibility Issues
Not all laser systems handle diverse insulation materials (e.g., PTFE, polyimide, or fluoropolymers) equally. Vendors may lack the proper laser wavelength or process parameters for specific materials, resulting in charring, melting, or residue. Without material-specific validation, performance and safety standards may not be met.
Lack of Process Validation and Documentation
Reputable suppliers should provide process capability studies (e.g., Cp/Cpk), first-article inspections, and traceable quality records. Sourcing from vendors without robust quality systems increases the risk of undetected defects and challenges during audits or regulatory reviews (e.g., ISO 13485, AS9100).
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Inadequate IP Protection Agreements
Sharing detailed designs, materials, or process requirements with a third-party laser stripping provider exposes sensitive technical data. Without comprehensive non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear IP ownership clauses, companies risk unauthorized use, replication, or leakage of proprietary information.
Subcontracting Without Oversight
Some suppliers outsource laser stripping to subcontractors without informing the client. This creates a blind spot in IP protection and quality control. If the subcontractor lacks equivalent security measures, confidential designs could be exposed to additional parties.
Lack of Data Security Protocols
Digital files for laser programming (e.g., CAD or G-code) often contain embedded design intelligence. Vendors without secure data handling practices (e.g., encrypted transfers, access controls) can inadvertently expose IP to cyber threats or insider misuse.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, companies should:
– Audit potential suppliers for quality certifications and in-house process controls.
– Require documented process validation for specific materials and geometries.
– Establish strong legal agreements covering IP ownership, confidentiality, and restrictions on subcontracting.
– Verify data security practices and ensure file sharing occurs through secure channels.
– Conduct on-site assessments or request sample runs before full-scale engagement.
Proactively managing quality and IP concerns ensures reliable performance and protects innovation when outsourcing laser stripping operations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Stripping
Overview of Laser Stripping Technology
Laser stripping is a non-contact, precision method used to remove insulation, coatings, or surface layers from wires, cables, and components. It utilizes focused laser energy to ablate material without damaging the underlying substrate. This technology is widely used in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, telecommunications, and electronics industries due to its accuracy, repeatability, and minimal mechanical stress.
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Laser stripping systems must be transported and handled in accordance with manufacturer specifications. Units should be securely packaged in shock-absorbent materials and transported in climate-controlled environments to prevent damage from moisture or extreme temperatures. Prior to installation, verify that all components (laser source, optics, motion stages, cooling system) are intact. Only trained personnel should unpack and install equipment using proper lifting techniques and tools.
Facility Requirements and Installation
Installation of laser stripping equipment requires a dedicated, controlled environment. The facility must provide stable electrical power (typically 208–480 V, 3-phase), adequate ventilation, and sufficient space for machine operation and maintenance access. Installations must comply with local building codes and industrial safety standards. Laser safety interlocks, emergency stops, and proper grounding must be verified during commissioning. A certified technician should perform the initial setup and calibration.
Laser Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser stripping systems are classified under international laser safety standards (IEC 60825-1). Equipment must be labeled with appropriate warning signs and operated within a designated Class 1 or interlocked Class 4 enclosure. Personnel must undergo laser safety training and wear appropriate protective eyewear when engineering controls are bypassed. Compliance with OSHA (29 CFR 1910.97), ANSI Z136.1, and applicable regional regulations is mandatory. Maintain a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) role to oversee safety protocols and audits.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Considerations
Laser ablation produces fumes and particulate matter that may contain hazardous materials, especially when processing fluorinated or chlorinated insulation (e.g., PTFE, PVC). Install certified fume extraction systems with HEPA and activated carbon filtration. Conduct air quality monitoring as needed. Used filters and waste material must be handled and disposed of in compliance with EPA, REACH, or local environmental regulations. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for processed materials should be maintained on file.
Operational Procedures and Quality Control
Develop and document standard operating procedures (SOPs) for laser stripping operations, including machine startup, parameter selection, in-process inspection, and shutdown. Implement a quality control plan that includes periodic verification of strip length accuracy, insulation removal completeness, and conductor integrity using microscopy or electrical testing. Maintain logs for equipment maintenance, calibration, and process validation (e.g., per AS9100 or ISO 13485 requirements).
Regulatory Documentation and Traceability
Ensure full traceability of materials, processes, and personnel qualifications. Maintain records of equipment calibration, operator certifications, and lot-specific processing parameters. For regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, medical), documentation must support compliance with FAA, FDA 21 CFR Part 820, or equivalent standards. Implement a document control system to manage revisions and ensure access to current versions.
Training and Personnel Certification
Only personnel who have completed formal training in laser safety, equipment operation, and emergency procedures may operate laser stripping systems. Training records must be maintained and updated annually. Certification should include hands-on competency assessment and refresher courses. Access to the laser area should be restricted to authorized personnel.
Waste Management and Disposal
Waste generated from laser stripping—including removed insulation debris, used filters, and contaminated consumables—must be classified according to local and international hazardous waste regulations (e.g., EPA, RoHS, WEEE). Segregate waste streams appropriately and use licensed disposal vendors. Maintain manifests and disposal records for audit purposes.
Emergency Response and Incident Reporting
Establish emergency procedures for laser malfunctions, fire, fume release, or personnel exposure. Provide accessible emergency shut-offs, fire extinguishers (Class C for electrical fires), and eyewash stations. Report incidents involving laser exposure, environmental release, or safety system failure to the LSO and relevant regulatory bodies as required. Conduct periodic drills and review response effectiveness.
Audits and Continuous Improvement
Schedule regular internal audits to verify compliance with safety, quality, and environmental standards. Use audit findings to update procedures, enhance training, and improve system performance. Engage external auditors for certification maintenance (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 14001). Foster a culture of continuous improvement through employee feedback and process optimization.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Stripping
Sourcing laser stripping technology represents a strategic advancement in precision wire processing, offering significant benefits over traditional mechanical and thermal stripping methods. Its ability to deliver high accuracy, minimal damage to conductors, and clean, consistent results makes it ideal for applications in high-reliability industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and advanced electronics.
When sourcing laser stripping solutions, it is essential to evaluate key factors including laser type (e.g., UV, fiber), automation integration, material compatibility, and vendor support. Investing in a system that aligns with current production requirements while allowing scalability ensures long-term operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, partnering with experienced suppliers who offer technical expertise, training, and maintenance support is crucial for maximizing return on investment.
In conclusion, laser stripping is a superior choice for high-precision wire preparation, and thoughtful sourcing—balancing performance, reliability, and total cost of ownership—will enable organizations to enhance product quality, reduce waste, and maintain a competitive edge in demanding markets.