The global engineered wood products market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by rising demand for sustainable and aesthetically versatile materials in construction and interior design. According to Grand View Research, the global engineered wood market was valued at USD 170.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030. A key driver of this growth is the increasing popularity of decorative surface technologies such as laser striping—a precision engraving technique that imitates the natural grain and texture of solid wood on engineered boards. With architects, designers, and manufacturers prioritizing both durability and design authenticity, laser striping has emerged as a preferred solution for high-end laminate and wood-based panels. As demand surges, particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation in laser-finished wood products, combining advanced digital texturing with scalable production capabilities. The following analysis highlights the top 8 laser striping wood manufacturers shaping this dynamic segment through technological excellence, product consistency, and market reach.
Top 8 Laser Striping Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser cleaner machine prices
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaner machine prices and parameters, download our Catalogue….
#2 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#4 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping is incredibly precise, removing layers of paint, varnish, or other coatings without damaging the underlying wood….
#5 Professional Laser Wood Stripping Machine
Website: lybylaser.com
Key Highlights: Discover the cutting-edge laser stripping machine for wood processing, featuring precision control, eco-friendly operation, and versatile applications for ……
#6 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: This article first introduces the functions of laser wood stripping machine and then focuses on some successful cases of HANTENCNC laser wood stripping….
#7 Laser Stripping Machine For Wood White Paint Removal
Website: mrj-lasermark.com
Key Highlights: Look no further than our 1.5mj Laser Stripping Machine for Wood, designed specifically for the swift removal of white and other colored paints. Send Inquiry….
#8 Laser Stripping Wood: Fast, Precise & Eco
Website: heatsign.com
Key Highlights: Laser stripping wood uses lasers to take off paint or varnish from wood. Lasers are very precise and can focus on small areas….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Striping Wood
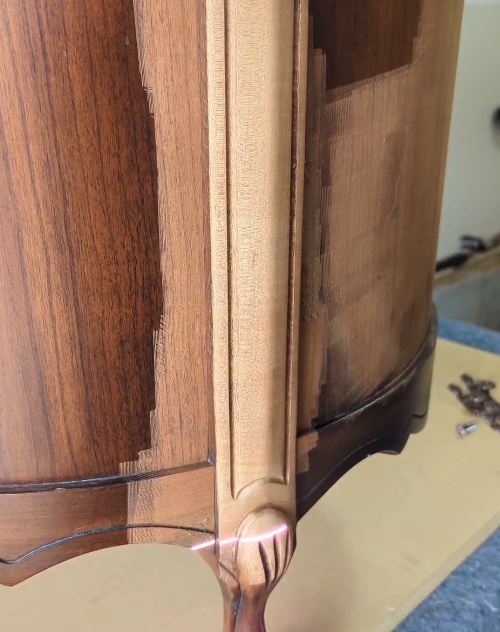

2026 Market Trends for Laser Striping Wood
As the demand for unique, sustainable, and high-precision wood finishes continues to rise, Laser Striping Wood is poised to become a leading innovation in the interior design, flooring, and furniture industries by 2026. This technique, which uses focused laser beams to create precise, decorative striping patterns on wood surfaces, is gaining significant traction due to its eco-friendliness, customization potential, and alignment with modern design trends. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the Laser Striping Wood sector in 2026.
Growing Demand for Customized and Aesthetic Wood Finishes
Consumers and designers are increasingly seeking personalized, high-end finishes for residential and commercial spaces. Laser striping allows for intricate, repeatable patterns—such as linear grooves, geometric designs, or textured gradients—that cannot be easily achieved with traditional milling or sanding. By 2026, customization will be a primary driver in the wood products market, with laser technology enabling on-demand pattern creation tailored to individual customer preferences. This trend is particularly strong in luxury interiors, high-end cabinetry, and bespoke furniture.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
With stricter environmental regulations and heightened consumer awareness, sustainable manufacturing practices are a top priority. Laser striping is a non-contact, chemical-free process that produces minimal waste and avoids the use of VOC-emitting stains or coatings. As companies strive to meet green building certifications like LEED and WELL, the adoption of laser-treated wood is expected to grow. Additionally, the ability to enhance lower-grade or reclaimed wood through aesthetic patterning supports circular economy principles, further boosting market appeal.
Integration with Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
By 2026, the wood processing industry will see deeper integration of digital technologies. Laser striping systems are increasingly being paired with CNC automation, AI-driven design software, and IoT-enabled monitoring systems. This allows for seamless production scaling, real-time quality control, and rapid prototyping. Manufacturers adopting these smart systems will benefit from reduced labor costs, improved precision, and faster turnaround times—making laser striping more accessible to mid-sized producers and niche designers.
Expansion in Commercial and Architectural Applications
Beyond residential use, laser-striped wood is finding new applications in commercial architecture, including wall paneling, ceiling features, retail fixtures, and hospitality interiors. Architects are leveraging the visual depth and texture of laser striping to create dynamic spatial experiences. The trend towards biophilic design—integrating natural elements into built environments—further supports the use of enhanced wood finishes. In 2026, expect increased adoption in office spaces, hotels, and public buildings seeking both aesthetic distinction and material authenticity.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
Ongoing improvements in laser efficiency, beam control, and software integration are lowering operational costs and expanding the range of compatible wood species. Fiber and CO₂ lasers are becoming more energy-efficient and user-friendly, enabling smaller workshops to adopt the technology. As equipment prices decline and maintenance requirements decrease, the barrier to entry for laser striping will lower, accelerating market penetration across regions, particularly in emerging economies in Asia and Eastern Europe.
Regional Market Growth and Industrial Adoption
North America and Western Europe remain the dominant markets for laser-striped wood, driven by design innovation and sustainability mandates. However, by 2026, Asia-Pacific is expected to experience the fastest growth, fueled by rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and a booming construction sector. Countries like China, India, and Vietnam are investing in advanced woodworking technologies, positioning laser striping as a premium differentiator in export-oriented furniture and flooring products.
Conclusion
The Laser Striping Wood market in 2026 will be shaped by a convergence of design innovation, environmental responsibility, and digital manufacturing. As consumer demand for unique, sustainable surfaces grows, laser technology offers a scalable and precise solution. With continued advancements and broader industry adoption, laser-striped wood is set to transition from a niche technique to a mainstream choice in high-value wood applications across global markets.
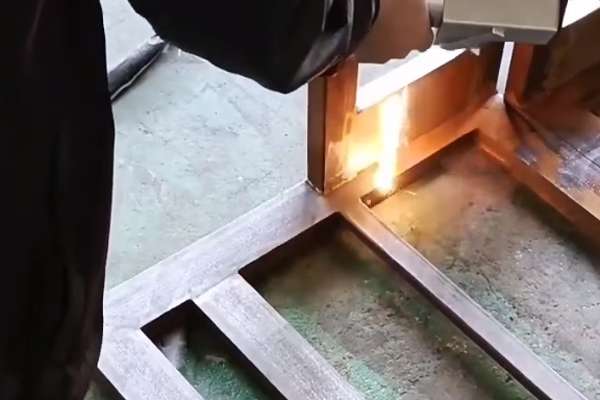

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Laser Striping Wood (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser striping wood—timber intentionally marked with laser engraving for identification, grading, or anti-theft purposes—requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to supply chain disruptions, legal risks, and compromised product integrity.
Poor Wood Quality and Inconsistent Striping
One of the most frequent pitfalls is receiving wood that fails to meet structural or aesthetic standards. Laser striping is often applied to premium hardwoods like oak, walnut, or teak, and inconsistencies can significantly devalue the material. Common quality issues include uneven grain, warping, moisture content outside acceptable ranges, or surface defects that interfere with laser readability. Additionally, inconsistent laser application—such as varying depth, alignment, or contrast—can render the markings ineffective for tracking or branding purposes. Buyers must verify supplier quality control processes and request sample batches before committing to large orders.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Laser striping often incorporates logos, certification marks, proprietary codes, or branded patterns, raising significant IP concerns. Sourcing from unauthorized or unveted suppliers increases the risk of inadvertently receiving wood marked with protected designs without proper licensing. This can expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated markets or when reselling under a private label. Furthermore, counterfeit striping may mimic legitimate certification marks (e.g., FSC or PEFC), misleading consumers and violating environmental compliance standards. To mitigate this, buyers should ensure suppliers provide documentation of IP rights and maintain transparent traceability records.
Lack of Traceability and Certification Verification
Closely tied to IP issues is the absence of verifiable traceability. Legitimate laser striping should support chain-of-custody documentation, proving sustainable sourcing and legal harvesting. However, some suppliers may apply misleading or forged striping to non-compliant wood, especially in regions with weak enforcement. Without third-party audits or certification verification, buyers risk reputational damage and regulatory non-compliance. It is essential to work with suppliers who integrate laser marking with digital tracking systems and provide access to certification data for each batch.
Inadequate Supplier Due Diligence
Failing to conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers amplifies both quality and IP risks. Some suppliers may lack the technical capability to produce consistent laser markings or operate without proper IP clearances. Buyers should assess a supplier’s equipment, staff training, compliance history, and references. Auditing facilities—either directly or through third parties—helps confirm adherence to quality and legal standards. Relying solely on price or convenience when selecting suppliers often leads to costly downstream issues.
Technological Limitations and Material Compatibility
Not all wood species or finishes respond well to laser marking. Some treatments or resins can cause charring, fading, or poor contrast, reducing the durability and legibility of striping over time. Buyers may overlook the need to test laser compatibility with specific wood types and finishes, resulting in markings that degrade during transport or processing. Confirming the laser technology used (e.g., CO2 vs. fiber lasers) and its suitability for the intended wood species is crucial to ensure long-lasting, high-quality striping.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Striping Wood
Overview of Laser Striping Wood
Laser striping wood involves using high-precision laser technology to engrave or mark wood surfaces with decorative, functional, or identification patterns. This process is commonly used in flooring, architectural millwork, and furniture manufacturing. Proper logistics and compliance are essential to ensure product quality, regulatory adherence, and safe handling throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Environmental Regulations
Laser striping operations may generate airborne particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), depending on the wood species and coatings used. Facilities must comply with local, national, and international environmental standards such as:
– EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) regulations on air emissions.
– REACH (EU Regulation on Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) for material safety.
– CARB (California Air Resources Board) Phase 2 compliance for formaldehyde emissions in composite wood products.
Ensure ventilation systems and air filtration (e.g., HEPA filters) are in place to meet permissible exposure limits (PELs) for wood dust and fumes.
Workplace Safety Standards
Adhere to occupational health and safety regulations:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines for laser safety (29 CFR 1910.97) and woodworking facilities.
– Implement Laser Safety Officer (LSO) programs where applicable.
– Provide personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles rated for laser wavelengths, respirators, and hearing protection.
Laser Equipment Certification
Laser systems must comply with:
– FDA/CDRH (U.S. Food and Drug Administration/Center for Devices and Radiological Health) regulations for laser products (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11).
– IEC 60825-1 international standard for laser safety classification and labeling.
Ensure all laser equipment is properly classified (typically Class 1 or Class 4 with interlocks) and undergoes periodic safety audits.
Material Sourcing and Handling
Sustainable Sourcing & Certification
Use wood sourced from responsibly managed forests:
– Prioritize suppliers certified by FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification).
– Maintain chain-of-custody documentation for certified wood to support green building certifications (e.g., LEED).
Wood Species Considerations
Different species react uniquely to laser processing:
– Hardwoods (e.g., oak, maple) may require higher laser power and generate more smoke.
– Avoid woods treated with halogenated flame retardants or preservatives, as they can release toxic fumes when lasered.
– Confirm material safety data sheets (MSDS/SDS) are available for all wood and finish types.
Packaging and Transportation
Protective Packaging
To prevent damage during transit:
– Use edge protectors and moisture-resistant wrapping for laser-striped surfaces.
– Separate panels with non-abrasive interleaving paper or foam.
– Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “This Side Up.”
Shipping Documentation
Include required compliance documentation with each shipment:
– Customs declarations for international transport.
– CITES documentation if using protected wood species (e.g., certain tropical hardwoods).
– Compliance certificates (FSC, CARB, REACH) upon request.
Hazardous Materials Considerations
While untreated wood is generally non-hazardous, laser processing residues (dust, off-gassing) may classify waste as hazardous in some jurisdictions. Label and dispose of waste per:
– DOT (U.S. Department of Transportation) regulations for combustible dust.
– Local waste management codes for industrial byproducts.
Import/Export Compliance
Tariff Classifications
Classify products under the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) codes, such as:
– 4418.79 – Other builders’ joinery and carpentry of wood.
– 8456.10 – Laser machines for working wood.
Verify classifications with customs brokers to avoid delays or penalties.
Country-Specific Requirements
- European Union: Ensure CE marking for machinery and compliance with the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) if used in building applications.
- United States: Comply with Lacey Act requirements for legal wood sourcing.
- China, Australia, and others: Check for import restrictions on wood products and phytosanitary certificates.
Quality Control and Traceability
In-Process Inspections
Implement quality checks at key stages:
– Pre-laser inspection for grain consistency and surface defects.
– Post-laser verification of stripe accuracy, depth, and finish quality.
– Use digital imaging systems to ensure pattern consistency.
Batch Traceability
Maintain records linking:
– Wood batch numbers.
– Laser machine settings and operators.
– Compliance documentation.
This supports recalls, audits, and sustainability claims.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for laser striping wood require a holistic approach integrating environmental stewardship, regulatory adherence, and supply chain transparency. By following this guide, manufacturers and distributors can ensure safe, sustainable, and legally compliant operations from raw material sourcing to final delivery.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Striping for Wood
Sourcing laser striping for wood involves a careful balance of technology, material compatibility, and supplier expertise. Laser striping—achieved through controlled laser ablation or engraving—offers a precise, repeatable, and customizable method for adding decorative or functional patterns to wooden surfaces. When sourcing this service, it is essential to partner with experienced providers that utilize high-quality laser systems capable of handling various wood types without causing excessive charring or structural damage.
Key considerations include the type of wood (hardwood vs. softwood), desired depth and pattern complexity, finishing requirements, and production volume. Suppliers should offer sample testing to ensure compatibility and aesthetic satisfaction. Additionally, evaluating turnaround time, cost-efficiency, sustainability practices, and post-processing capabilities (such as sealing or staining) contributes to a successful outcome.
In conclusion, laser striping presents a modern, aesthetically appealing solution for enhancing wood products, and effective sourcing depends on selecting a technically proficient and reliable partner who can deliver consistent quality while meeting project-specific needs.