The global wood treatment and surface restoration market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for aesthetic preservation and longevity in wood products. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global wood coatings market was valued at USD 21.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% through 2029, fueled by advancements in finishing technologies and rising consumer preference for sustainable, high-quality wood finishes. As manufacturers seek efficient, non-abrasive solutions to maintain product integrity, laser stain removers have emerged as a precision-driven alternative to traditional sanding and chemical stripping. These systems offer targeted removal of contaminants, discoloration, and surface defects without damaging the underlying grain—making them increasingly vital in high-end furniture, flooring, and cabinetry production. In this context, selecting the right laser stain remover is no longer just a technical consideration, but a competitive advantage. Here are the top 9 laser stain removers setting new benchmarks for performance, reliability, and integration in modern wood manufacturing.
Top 9 Laser Stain Remover For Wood Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#2 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Argento Lux, experts in laser cleaning, utilizing high-powered lasers to remove contamination from various surfaces. Similar to sandblasting without the ……
#3 Wood Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: laserchina.com
Key Highlights: These innovative tools utilize precision laser technology to lift away years of dirt, grime, paint, and more without damaging your wood surfaces….
#4 Laser cleaning wood
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A laser cleaner is a device that uses high-intensity light to remove dirt, grime and stains from wood surfaces. It is a non-abrasive method of cleaning….
#5 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: The pulse laser cleaning machine have 100w, 200w, 300w, 500w, 1000w, Mainly used to rust, thin paint layer, wood, oil removal, It will no impact on the surface….
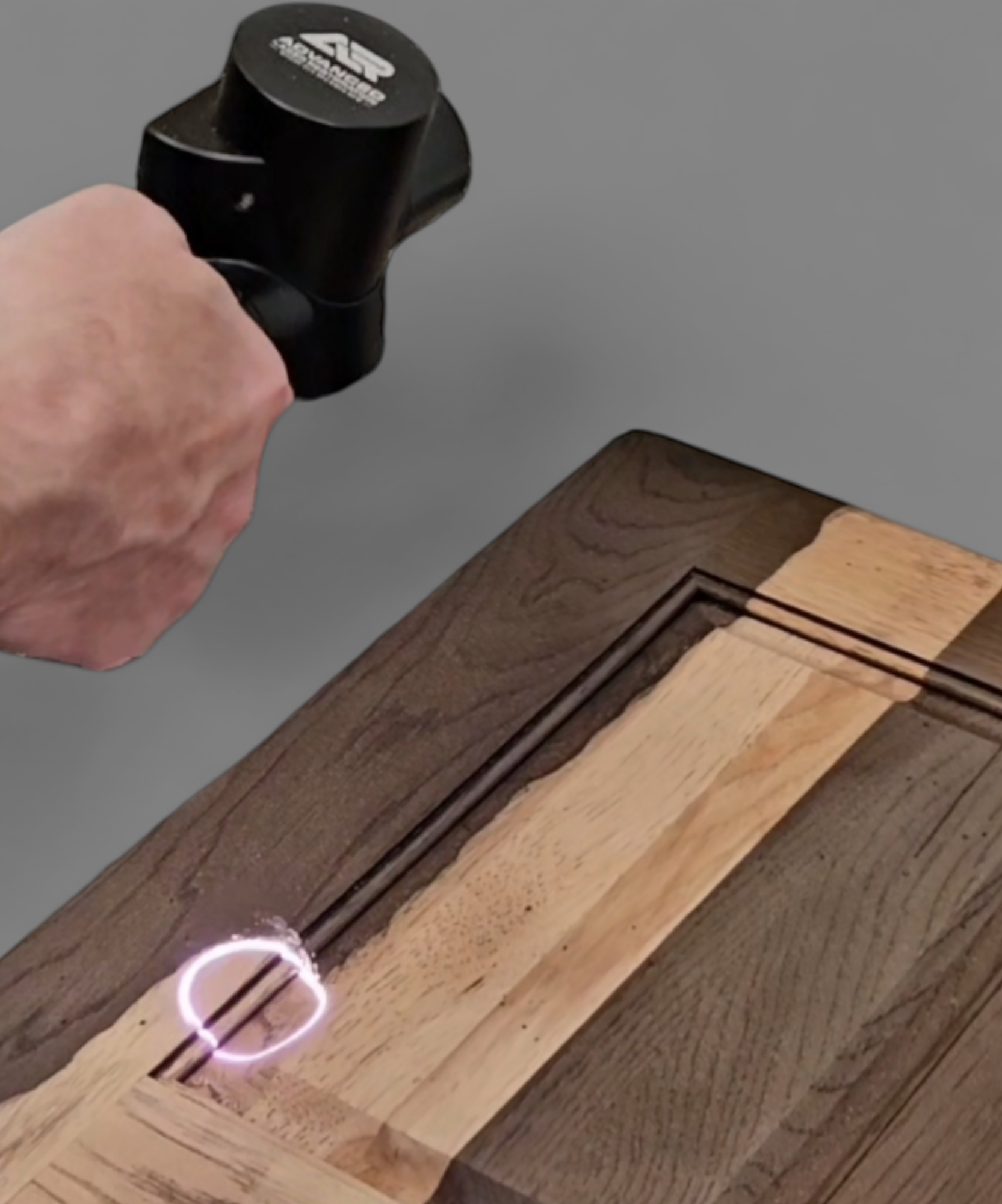
#6 Laser Wood Cleaning & Restoration
Website: advancedlaserrestoration.com
Key Highlights: Advanced Laser Restoration offers eco-friendly laser wood cleaning for cabinets, floors, beams, and decks. Remove paint, stain, mold, soot, ……
#7 Does the Laser Wood Stripping Machine Really Work?
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: This article first introduces the functions of laser wood stripping machine and then focuses on some successful cases of HANTENCNC laser wood stripping….
#8 Laser Cleaning Machine – LaserBlast Systems
Website: alliedscientificpro.com
Key Highlights: An ideal laser surface cleaner for building restoration projects; compatible with stone, metals, wood, and many other materials. Gentle enough for art, ……
#9 Transform Wood with a Laser Wood Stain Removal Tool
Website: umw.top
Key Highlights: The laser wood stain removal tool offers a modern, non-invasive solution that is transforming the way we approach wood restoration….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Stain Remover For Wood

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Stain Remover for Wood
The global market for laser stain removers for wood is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and evolving consumer and industrial preferences. As industries shift toward eco-friendly and precision-based solutions, laser-based wood restoration is emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional chemical and mechanical methods. The following analysis outlines key market trends expected to shape the landscape of laser stain removers for wood in 2026.
-
Growing Adoption in Restoration and Heritage Conservation
By 2026, the use of laser stain removers is expected to expand significantly in the restoration of historical wooden artifacts, furniture, and architectural elements. Cultural heritage institutions and preservation agencies are increasingly investing in non-abrasive, precise cleaning technologies. Laser systems offer controlled removal of stains, smoke damage, and biological growth without harming the underlying wood structure, making them ideal for delicate conservation projects. -
Advancements in Portable and User-Friendly Systems
Manufacturers are focusing on developing compact, portable laser devices suitable for on-site applications. In 2026, we anticipate a surge in handheld or mobile laser units tailored for furniture restorers, antique dealers, and restoration contractors. These devices will feature intuitive interfaces, adjustable power settings, and safety mechanisms, broadening accessibility beyond large industrial users. -
Integration of Smart Technology and AI
Laser stain removal systems are expected to incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms by 2026. These technologies will enable real-time surface analysis, automatic stain detection, and adaptive power modulation, optimizing cleaning efficiency and minimizing human error. AI integration will enhance precision, reducing the risk of wood damage and improving overall treatment outcomes. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Appeal
With increasing regulatory pressure on the use of chemical solvents and abrasive materials, laser-based cleaning is gaining favor as a green alternative. The process eliminates the need for toxic chemicals, reduces waste, and conserves water—key factors that align with global sustainability goals. By 2026, environmental certifications and carbon footprint disclosures will likely influence procurement decisions in both public and private sectors. -
Expansion into Residential and DIY Markets
While currently dominated by professional and industrial applications, the market is expected to see growth in the residential and do-it-yourself (DIY) segments by 2026. As prices decrease and safety improves, homeowners and hobbyists may adopt smaller-scale laser tools for restoring wooden floors, furniture, and decks. Marketing efforts will likely emphasize ease of use, safety, and long-term cost savings over conventional methods. -
Rising Demand in Furniture and Flooring Industries
The furniture manufacturing and hardwood flooring sectors are anticipated to be major growth drivers. Laser technology enables manufacturers to efficiently remove stains and defects during production, improving yield and product quality. In flooring restoration, lasers offer a fast, non-invasive method to refurbish surfaces without sanding, reducing downtime and material waste. -
Regional Market Growth and Investment
Europe and North America are expected to lead market adoption due to strong heritage conservation initiatives and strict environmental regulations. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—will witness rapid growth, fueled by urban redevelopment projects and rising interest in high-end wood craftsmanship. Government and private sector investments in laser technology R&D will further accelerate market penetration. -
Challenges and Barriers
Despite positive trends, high initial equipment costs, limited awareness, and the need for skilled operators remain challenges. In 2026, market expansion will depend on effective training programs, leasing models, and partnerships between technology providers and industry stakeholders to lower entry barriers.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser stain removers for wood will be characterized by technological sophistication, environmental consciousness, and broader application reach. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, it is expected to redefine wood restoration standards across multiple industries.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Stain Remover for Wood (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a “Laser Stain Remover for Wood” presents unique challenges, especially concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP). This emerging technology often lacks standardized definitions and testing, making careful evaluation critical. Here are the key pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Unproven or Exaggerated Performance Claims
Many suppliers, particularly online or from regions with less stringent regulations, make dramatic claims about removing deep-set stains, ink, paint, or even restoring antique finishes without damage. These claims are often unsupported by independent testing or real-world data. Be wary of:
- Lack of Specificity: Vague terms like “instant,” “effortless,” or “works on anything” without concrete details on stain types (water, ink, oil, pet, dye) or wood species.
- Absence of Demonstrated Results: No high-quality before-and-after photos or videos on known stain types and wood types under controlled conditions.
- Ignoring Safety Parameters: Claims that ignore the inherent risks of laser interaction with wood (charring, ignition, VOC release) suggest a lack of genuine engineering.
Underestimating Safety and Fire Hazards
Lasers powerful enough to ablate or alter wood stain are Class 3B or Class 4 devices, posing significant risks:
- Fire Risk: The primary pitfall. Inadequate power control, poor beam focusing, or operator error can easily ignite dry wood dust or the wood itself. Verify if the device incorporates essential safety features like automatic shut-off, enclosed beam paths, or integrated vacuum extraction.
- Eye and Skin Damage: High-powered infrared lasers (common in these tools) are invisible and can cause severe retinal injury. Ensure the device has proper safety interlocks, key switches, and requires certified laser safety goggles (OD rating appropriate for the laser wavelength).
- Fume Emission: Burning wood stain and finish releases toxic fumes (VOCs, formaldehyde, etc.). Devices lacking effective fume extraction systems pose serious health risks.
Neglecting Laser Specifications and Build Quality
The actual laser parameters determine effectiveness and safety. Pitfalls include:
- Ambiguous Wavelength & Power: Suppliers may state “laser” without specifying the crucial wavelength (e.g., 1064nm fiber laser, 10.6µm CO2 laser) or accurate average/peak power output. Different stains absorb different wavelengths; wrong wavelength = ineffective. Inflated power claims are common.
- Poor Beam Quality & Focus: A poorly collimated or focused beam reduces cleaning efficiency, increases processing time, and heightens fire risk by spreading energy unevenly.
- Inferior Construction: Devices made with cheap components, inadequate cooling, or flimsy housings fail prematurely under continuous use and compromise safety.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
This is a critical, often overlooked pitfall:
- Sourcing from Copycat Manufacturers: Many suppliers, especially in certain regions, replicate designs patented by legitimate innovators. Purchasing such devices may:
- Infringe Patents: You could be liable for using a product that violates existing patents (utility, design, or method patents) covering the laser system, safety mechanisms, or application technique.
- Lack Technical Support & Updates: Copycats rarely offer genuine support, firmware updates, or spare parts, leading to device abandonment.
- Undermine Innovation: Supporting IP theft discourages future R&D investment in better, safer tools.
- Unclear IP Status: Reputable suppliers should be transparent about their IP ownership or licensing. Be suspicious of companies unwilling or unable to discuss this.
Failing to Validate Real-World Usability
A device might work in a lab but fail practically:
- Complex Operation & Training: High-power lasers require significant operator skill and training. Overly complex interfaces or lack of proper training materials lead to poor results and accidents.
- Slow Processing Speed: Removing stains over large areas can be impractically slow with low-power or inefficient systems, negating any time-saving benefits.
- Lack of Wood-Specific Calibration: Wood varies greatly in density, grain, and moisture. A one-size-fits-all setting won’t work. Look for devices with adjustable parameters and proven settings for different wood types.
Disregarding Regulatory Compliance
Ensure the device meets safety standards for its intended market (e.g., FDA/CDRH in the US, IEC standards internationally):
- Laser Safety Certification: Verify the device has the required safety certifications (e.g., FDA 21 CFR 1040.10/1040.11 in the US). Lack of certification is a major red flag.
- Electrical Safety: Certification like CE (EMC & LVD), UL, or CSA is essential for electrical components.
In summary, sourcing a reliable and safe Laser Stain Remover for Wood requires rigorous due diligence. Prioritize suppliers who provide verifiable technical specifications, demonstrable real-world results, comprehensive safety documentation, clear IP status (preferably legitimate ownership or licensing), and adherence to international safety standards. Cutting corners on any of these aspects risks financial loss, safety incidents, legal liability, and ineffective results.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Stain Remover For Wood
Product Classification and Identification
The Laser Stain Remover For Wood is categorized as a wood surface treatment product designed to remove stains using non-chemical, laser-based technology. It is typically a handheld or benchtop device utilizing focused light energy to ablate or vaporize surface contaminants without damaging the underlying wood grain.
Key Product Attributes:
– Type: Non-chemical, laser-based surface restoration tool
– Intended Use: Removal of stains, discoloration, and surface imperfections on wood
– Power Source: Electric (plug-in or battery-operated)
– Hazard Classification: Low chemical hazard; classified primarily as an electronic device with laser components
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser Safety Standards (IEC/EN 60825-1)
The device must comply with international laser safety standards, particularly IEC 60825-1 (or its regional equivalents such as EN 60825-1 in the EU). Compliance ensures that the laser emission is within safe limits for consumer or professional use.
Key Requirements:
– Laser Class: Must be classified correctly (typically Class 1, 1M, 2, or 2M for consumer devices; higher classes require controlled environments)
– Labeling: Visible laser warning labels, including class, wavelength, and output power
– Safety Interlocks: If applicable, must include protective mechanisms to prevent exposure during maintenance
Electrical Safety (IEC/UL/EN 62368-1)
As an electrical device, compliance with safety standards for audio/video, information, and communication technology equipment is required.
Applicable Standards:
– North America: UL 62368-1
– European Union: EN 62368-1 (under CE marking directive)
– Other Regions: Local equivalents (e.g., CCC in China, PSE in Japan)
Mandatory Actions:
– Certification by accredited testing laboratories
– Inclusion of safety documentation and user manuals in local languages
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
The device must not emit excessive electromagnetic interference and must be immune to common levels of interference.
Standards:
– EU: EMC Directive 2014/30/EU (EN 55032, EN 55035)
– USA: FCC Part 15, Subpart B (Class B for residential environments)
– Other Markets: CISPR 32, AS/NZS CISPR 32
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Required Labels
- CE Mark (for EU) or FCC ID (for USA)
- Laser safety class symbol and warning text
- Manufacturer/importer contact information
- Power input specifications (voltage, frequency, current)
- RoHS compliance marking (if applicable)
Packaging Considerations
- Use anti-static and shock-absorbent materials to protect sensitive optical and electronic components
- Include multilingual safety instructions and operating manuals
- Ensure packaging is recyclable and complies with regional environmental directives (e.g., EU Packaging Waste Directive)
Import/Export Documentation and Trade Compliance
Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for relevant standards (e.g., CE, FCC)
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
- Export License (if required based on destination and technology)
Import Compliance
- EU: Declaration of Conformity (DoC), CE marking, registration under EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) if applicable
- USA: FDA registration (if considered a device with laser radiation), CBP clearance, FCC compliance
- China: CCC certification if power > specific threshold, customs declaration
- Canada: ICES-003 compliance, Health Canada laser product notification
Hazardous Materials and Environmental Regulations
The Laser Stain Remover For Wood does not contain hazardous chemicals under normal operation. However, regulatory checks are required for:
- RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances in Electrical Equipment
- Ensure lead, mercury, cadmium, and other restricted substances are below thresholds
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals
- Compliance required for any substances in components (e.g., plastics, coatings)
- WEEE (EU): Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
- Must provide take-back or recycling information; label with crossed-out wheelie bin symbol
Transportation and Shipping Guidelines
Air Transport (IATA)
- Classified as “Electronic Device with Laser” – not typically considered hazardous
- No special UN number required if laser is non-hazardous (Class 1–3R)
- Packaging must prevent accidental activation
- Batteries (if included) must comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (e.g., UN 3480 for lithium-ion)
Ground and Sea Transport
- No ADR (road) or IMDG (sea) hazardous classification required for the main unit
- Lithium batteries (if present) must be shipped according to applicable dangerous goods regulations
- Secure packaging to prevent movement during transit
Market-Specific Compliance Summary
| Region | Key Requirements | Certification Body |
|——-|——————|——————–|
| European Union | CE Mark, RoHS, REACH, WEEE, EMC, LVD, Laser Safety | Notified Body (e.g., TÜV, SGS) |
| United States | FCC Part 15, FDA CDRH laser registration, UL/cUL listing | FCC, FDA, UL |
| Canada | ICES-003, Health Canada laser notification, CSA certification | ISED, Health Canada, CSA Group |
| United Kingdom | UKCA marking (post-Brexit), UKCA RoHS | UK Approved Body |
| Australia/New Zealand | RCM mark, AS/NZS 62368.1, EMC compliance | ACMA |
Best Practices for Ongoing Compliance
- Maintain technical files and conformity documentation for at least 10 years
- Monitor regulatory updates (e.g., EU AI Act if device includes smart features)
- Conduct periodic product audits and safety re-evaluations
- Train customer support and logistics teams on compliance requirements
This guide ensures safe and legal distribution of the Laser Stain Remover For Wood across global markets while minimizing compliance risks.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Laser Stain Remover for Wood
After evaluating various options and considerations for sourcing a laser stain remover for wood, it is evident that this technology offers a precise, non-abrasive, and environmentally friendly solution for restoring wooden surfaces. Laser systems provide superior control in removing stains, finishes, and contaminants without damaging the underlying wood grain, making them ideal for both delicate restoration projects and industrial applications.
When sourcing such equipment, key factors must be considered: laser type (typically fiber or CO₂), power output, portability, ease of use, safety features, and after-sales support. It is also important to assess suppliers based on reputation, technical expertise, and service availability—especially for training and maintenance.
Although the initial investment is higher compared to traditional methods, the long-term benefits—such as reduced labor time, minimal waste, and preservation of valuable wood materials—justify the cost, particularly for high-end furniture restorers, heritage conservation, or manufacturing settings.
In conclusion, sourcing a high-quality laser stain remover for wood is a strategic investment in precision, efficiency, and sustainability. By choosing a reputable supplier and the right system for specific needs, businesses and artisans can achieve superior results while advancing their capabilities in wood restoration and finishing.