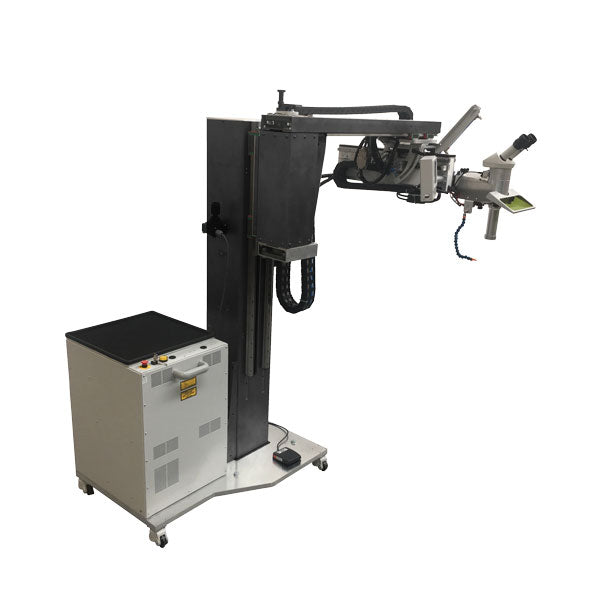
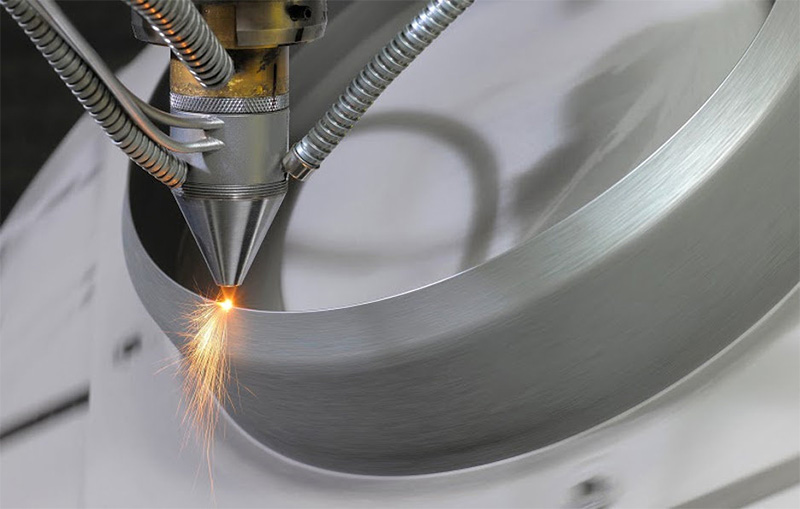
The global laser spot welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision joining technologies in automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 5.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing adoption of laser welding in electric vehicle (EV) battery production, where high accuracy, minimal heat distortion, and strong weld integrity are critical. Mordor Intelligence also highlights a similar upward trajectory, forecasting a CAGR of over 8% through 2029, with Asia-Pacific emerging as the fastest-growing region due to rapid industrialization and expanding manufacturing capabilities in China, Japan, and South Korea.
In this evolving landscape, laser spot welding—known for its ability to deliver localized, high-energy welds with minimal impact on surrounding materials—has become a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking automation, repeatability, and quality consistency. As industries shift toward lightweight materials and advanced assembly techniques, leading manufacturers are investing in high-power fiber lasers, real-time monitoring systems, and integrated robotics. The following list highlights the top 10 laser spot welding manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, reliability, and market reach, shaping the future of precision joining solutions.
Top 10 Laser Spot Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#2 Laser Welding Machine, Spot Welding Machine Manufacturer
Website: pdkjwelder.com
Key Highlights: PDKJ is China manufacturer & supplier who mainly produces Spot welding machine, Laser welding machine, Automatic welding machine with years of experience….
#3 LaserStar Spot & Seam Welding
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Spot & Seam Welding solutions provide precise, high-strength laser welding for industrial applications, ensuring durability and ……
#4 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Welding Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#5 Sunstone Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone designs and manufactures high-tech micro welding and engraving solutions for many different industries. In short, wherever a very small spot weld ……
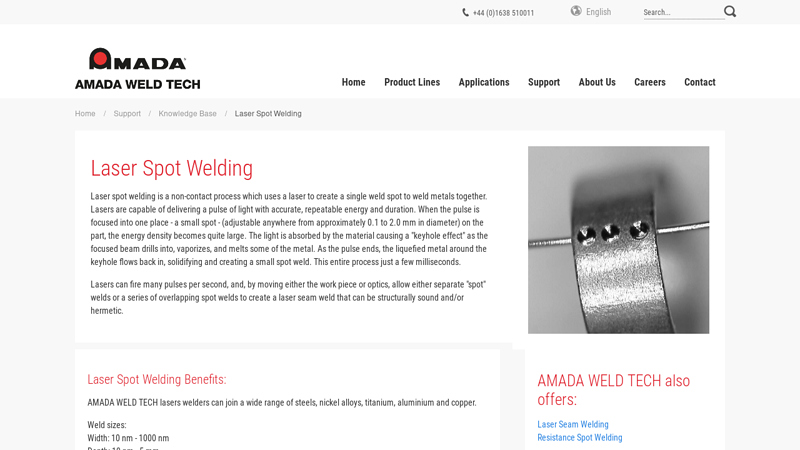
#6 Laser Spot Welding
Website: amadaweldtech.eu
Key Highlights: Laser Spot Welding Benefits: AMADA WELD TECH lasers welders can join a wide range of steels, nickel alloys, titanium, aluminium and copper….
#7 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#8 Spot welding and seam welding with lasers
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: With laser welding, you can create single joining spots or weld in continuous wave mode. The weld geometry describes how the parts fit together….
#9 Fives laser systems for welding and cutting
Website: fivesgroup.com
Key Highlights: Fives’ laser systems are proven for success. We have expertise in all aspects of laser processing, including welding, 3D cutting, cleaning and marking….
#10 Laser Welding Machine
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: Model:200W YAG laser jewelry welding machine BK-JW200 Voltage:110V/220V Laser Type:1064nm YAG Laser Small size Low weight Easy to operate Stabl……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Spot Welding
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Spot Welding
The global laser spot welding market is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising demand for precision joining solutions, and the expansion of high-tech industries such as electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, and medical devices. Key trends shaping the market include technological innovation, increased automation, material diversification, regional growth dynamics, and sustainability initiatives.
1. Rising Adoption in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Battery Manufacturing
A major driver of laser spot welding growth through 2026 is its critical role in EV production, particularly in battery pack assembly. Laser spot welding offers high precision, speed, and minimal heat-affected zones, making it ideal for joining thin copper and aluminum components in lithium-ion batteries. As global EV production scales to meet climate targets, manufacturers are increasingly relying on laser welding for reliable, scalable, and high-quality interconnects. This trend is expected to accelerate demand for pulsed fiber and solid-state laser systems optimized for micro-welding applications.
2. Technological Advancements and Process Integration
By 2026, laser spot welding systems are becoming smarter and more integrated with Industry 4.0 frameworks. Innovations such as real-time process monitoring, adaptive feedback control, and AI-driven quality assurance are enhancing weld consistency and reducing defects. Hybrid welding systems that combine laser spot welding with other technologies (e.g., resistance welding) are also emerging to optimize performance across diverse materials. Additionally, advancements in beam delivery systems, including scanning optics and remote welding heads, are increasing flexibility and throughput in high-volume production environments.
3. Expansion into Consumer Electronics and Medical Devices
The miniaturization trend in consumer electronics—especially smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices—is fueling demand for micro-laser spot welding. These applications require non-invasive, precise joining of small, heat-sensitive components. Similarly, in the medical sector, laser spot welding is becoming the preferred method for assembling surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment due to its cleanliness, repeatability, and biocompatibility. Growth in these high-margin industries is expected to open new revenue streams for laser system providers.
4. Regional Market Shifts and Manufacturing Localization
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, remains the dominant region for laser spot welding adoption due to its robust electronics and automotive manufacturing base. However, North America and Europe are witnessing rapid growth due to reshoring initiatives, increased EV investments, and strict quality standards in aerospace and medical manufacturing. Government incentives for clean energy and advanced manufacturing are further stimulating regional demand, encouraging local deployment of laser welding solutions.
5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability is becoming a key consideration in manufacturing processes. Laser spot welding consumes less energy compared to traditional welding methods and produces fewer emissions, aligning with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize energy-efficient laser systems with longer lifespans and lower maintenance requirements. Recycling and reuse of laser components are also gaining attention, contributing to a more sustainable industrial ecosystem.
6. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The laser spot welding market is seeing increased competition and consolidation among key players such as TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, Coherent, and Han’s Laser. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop compact, modular, and user-friendly systems tailored to specific industry needs. Strategic partnerships with robotics and automation firms are enabling turnkey solutions that integrate seamlessly into smart factories. This trend is likely to continue, with smaller innovators being acquired to accelerate technological deployment.
In conclusion, the 2026 outlook for laser spot welding is highly positive, characterized by expanding applications, technological sophistication, and strong cross-industry demand. As manufacturing evolves toward greater precision, automation, and sustainability, laser spot welding is set to become an indispensable technology in modern production systems.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Spot Welding (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser spot welding systems—especially for high-precision applications—introduces significant risks related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to subpar performance, supply chain vulnerabilities, and legal exposure.
Quality Risks in Laser Spot Welding Systems
One of the primary concerns when sourcing laser spot welding equipment is ensuring consistent, high-quality output. Poor quality can stem from inadequate component selection, lack of calibration standards, or insufficient process validation. Key quality pitfalls include:
- Inconsistent Weld Strength and Penetration: Low-cost or poorly calibrated systems may deliver variable pulse energy or misaligned optics, leading to weak or inconsistent welds. This is especially problematic in safety-critical industries like medical devices or automotive.
- Lack of Process Monitoring and Feedback: Advanced laser welding requires real-time monitoring (e.g., via photodiodes or cameras) to ensure weld quality. Sourcing from suppliers without integrated quality assurance systems risks undetected defects.
- Substandard Optics and Consumables: The quality of lenses, focusing heads, and fiber delivery systems directly impacts beam stability and longevity. Suppliers using inferior materials may result in frequent downtime and increased maintenance costs.
- Insufficient Validation and Documentation: Reputable suppliers provide traceable test results, weld validation reports, and compliance with standards (e.g., ISO 13849). Absence of such documentation raises red flags about reliability and repeatability.
Intellectual Property (IP) Exposure Concerns
Sourcing laser welding technology, especially from overseas or third-party integrators, can expose sensitive manufacturing processes and proprietary designs:
- Reverse Engineering Risk: Sharing detailed part geometries or process parameters with external suppliers increases the chance of IP theft, particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement.
- Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts: Failure to define ownership of custom tooling, software, or process know-how in supply agreements can lead to disputes or loss of control over critical manufacturing IP.
- Embedded Software and Firmware Vulnerabilities: Laser systems often include proprietary control software. Sourcing from untrusted vendors may introduce backdoors or undocumented features that compromise process security.
- Dependency on Supplier for Process Know-How: Some integrators develop unique welding parameters tailored to your product. If IP rights are not clearly assigned, you may become locked into a single supplier or lose the ability to replicate the process in-house.
Mitigating these risks requires due diligence: vetting suppliers for technical capability and IP ethics, conducting on-site audits, and establishing strong contractual protections around quality standards and intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Spot Welding
Overview and Scope
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for implementing and operating laser spot welding systems in industrial environments. It addresses equipment handling, installation, safety protocols, regulatory standards, and documentation practices to ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations.
Equipment Transportation and Handling
Laser spot welding systems are precision instruments requiring careful handling during transport. Use manufacturer-approved packaging and crating to prevent damage. Ensure all optical components and electronic subsystems are secured and protected from shock, moisture, and temperature extremes. Coordinate with certified freight carriers experienced in sensitive industrial equipment, and verify environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature) during transit to prevent condensation or thermal stress.
Installation and Facility Requirements
Install laser spot welding systems in a controlled environment with stable power supply, adequate ventilation, and minimal vibration. The facility must provide sufficient space for operation, maintenance access, and required safety clearances. Ensure grounding and electrical specifications meet the manufacturer’s recommendations. Laser systems typically require clean, dry compressed air and may need chiller units for thermal management—confirm utility availability prior to installation.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Laser spot welding systems are classified under international laser safety standards, primarily IEC 60825-1 and ANSI Z136.1. Class 4 lasers—common in industrial welding—require strict engineering and administrative controls. Implement:
- Laser Protective Housing: Ensure all beam paths are enclosed.
- Interlocks: Install door and access interlocks on enclosures.
- Laser Warning Signs: Post appropriate signage at entrances to laser-controlled areas.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide laser safety eyewear with correct optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength (typically 1064 nm for Nd:YAG or fiber lasers).
Compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulations in the U.S. or equivalent local authorities (e.g., HSE in the UK, DGUV in Germany) is mandatory. Conduct a site-specific laser hazard analysis and maintain a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) if required by local regulations.
Operational Documentation and Training
Maintain comprehensive documentation, including equipment manuals, safety data sheets (SDS), maintenance logs, and compliance certifications. All operators and maintenance personnel must undergo certified laser safety training covering system operation, emergency procedures, and hazard recognition. Training records must be kept on file and updated with refresher courses as required.
Environmental and Waste Compliance
Laser spot welding typically produces minimal waste, but metal fumes and particulates may be generated. Install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems compliant with OSHA or local air quality regulations. Filter and dispose of collected particulates as hazardous waste if applicable, based on material composition (e.g., welding coated or galvanized metals). Ensure fume extraction systems are regularly tested and maintained.
Quality and Process Control Standards
Adhere to relevant quality management systems such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific standards like AWS C8.9 (Recommended Practices for Laser Beam Welding) or ISO 15614 (Welding Procedure Qualification). Implement process validation, including weld peel testing, visual inspection, and non-destructive testing (NDT) as appropriate. Maintain traceability of welding parameters (power, pulse duration, spot size) and material lot numbers for critical applications.
Emergency Procedures and Incident Reporting
Establish emergency protocols for laser-related incidents, including accidental exposure, fire, or equipment malfunction. Post emergency contact numbers and evacuation routes. Provide accessible first aid kits and eyewash stations. Report all incidents to the appropriate internal and regulatory bodies as required (e.g., OSHA recordable incidents). Conduct regular drills and system safety audits.
Maintenance and Calibration Compliance
Follow the manufacturer’s preventive maintenance schedule. Calibrate laser power meters, beam alignment tools, and monitoring sensors at prescribed intervals using traceable standards. Document all maintenance and calibration activities with dates, personnel, and results. Retain records for audit purposes—typically a minimum of five years depending on jurisdiction.
International Shipping and Import Compliance
When transporting laser spot welding equipment across borders, comply with export control regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or EU Dual-Use Regulation. Laser systems may be subject to licensing due to their potential dual-use nature. Accurately classify the system under the Harmonized System (HS) code and prepare required documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and laser product certification). Verify import requirements in the destination country, including electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and safety certifications (e.g., CE, UKCA, CCC).
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain a centralized compliance file including equipment certifications (e.g., CE, FDA/CDRH for U.S. market), safety training records, inspection reports, and maintenance logs. Ensure all documentation is readily available for internal audits or regulatory inspections. Digitize records where possible for improved traceability and version control.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for laser spot welding ensures operational safety, regulatory adherence, and product quality. By following this guide, organizations can mitigate risks, avoid penalties, and support sustainable manufacturing practices. Always consult local regulations and involve qualified safety and compliance professionals during system deployment and operation.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Spot Welding
Sourcing laser spot welding technology represents a strategic investment for manufacturers seeking precision, speed, and high-quality welds in applications requiring minimal heat distortion and superior repeatability. When evaluating suppliers and systems, it is essential to consider factors such as laser type (e.g., fiber, pulsed Nd:YAG), power requirements, integration capabilities with existing production lines, and the level of automation needed.
Key benefits of laser spot welding—including narrow weld zones, strong joint integrity, and compatibility with dissimilar and highly conductive materials—make it ideal for industries such as automotive, medical devices, electronics, and aerospace. Successful sourcing involves selecting a reliable supplier with technical expertise, robust service support, and the ability to customize solutions for specific production needs.
Ultimately, organizations that carefully assess their welding requirements and partner with experienced providers can achieve significant improvements in product quality, operational efficiency, and long-term cost savings. As laser technology continues to advance, sourcing decisions today should also account for future scalability and evolving manufacturing demands.