The global laser soldering market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision joining technologies in electronics, automotive, and telecommunications industries. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market—of which laser soldering is a critical subset—was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of automated and high-precision manufacturing processes, particularly in miniaturized electronic components where traditional soldering methods fall short. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that advancements in diode and fiber laser technologies, coupled with growing investments in smart manufacturing and electric vehicles, are accelerating the uptake of laser soldering systems. As industries prioritize efficiency, repeatability, and thermal control, leading manufacturers are innovating to meet stringent quality standards. In this evolving landscape, the following nine companies have emerged as key players, shaping the future of laser soldering through technological leadership and strategic market presence.
Top 9 Laser Soldering Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Han’s Laser Technology co., ltd.
Domain Est. 2020
Website: hanslaserus.com
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser has more than 200 machine models, including Laser Engraving / Marking / Etching Series, Laser Welding Series, Laser Cutting Series, Sub-Surface ……
#2 Indium Corporation Global Solder & PCB Assembly Materials Supplier
Domain Est. 1995
Website: indium.com
Key Highlights: Explore our wide range of offerings, including solder pastes and powders, metals and compounds, flux and epoxies, thermal interface materials, and more….
#3 Laser soldering – Automated solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kuka.com
Key Highlights: KUKA laser soldering enables you to achieve high-quality bonded connections. Automate your soldering process with the help of our experts….
#4 Laser
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fancort.com
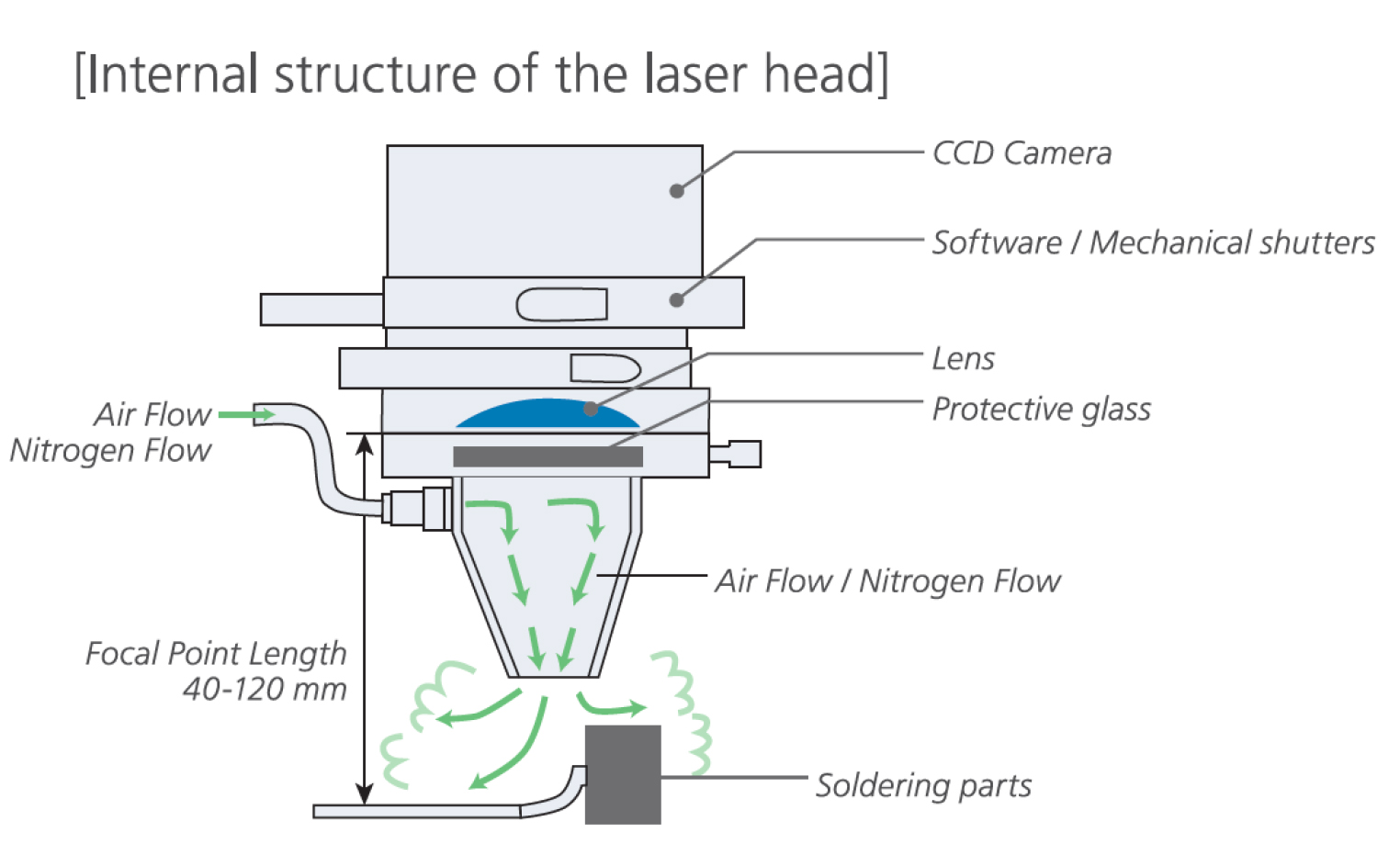
Key Highlights: The ULD-H4 Laser Head is designed to deliver precise heat to specific solder joints, making it ideal for fine-pitch components and intricate PCB designs….
#5 Laser Soldering
Domain Est. 2000
Website: apolloseiko.com
Key Highlights: Laser soldering is a non-contact process that eliminates the risk of marring or damaging sensitive components….
#6 Laser Soldering Machine
Domain Est. 2005
Website: us.hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Laser soldering includes pasting laser soldering, wire laser soldering and ball laser soldering. Solder paste, tin wire and solder ball are often used as filler ……
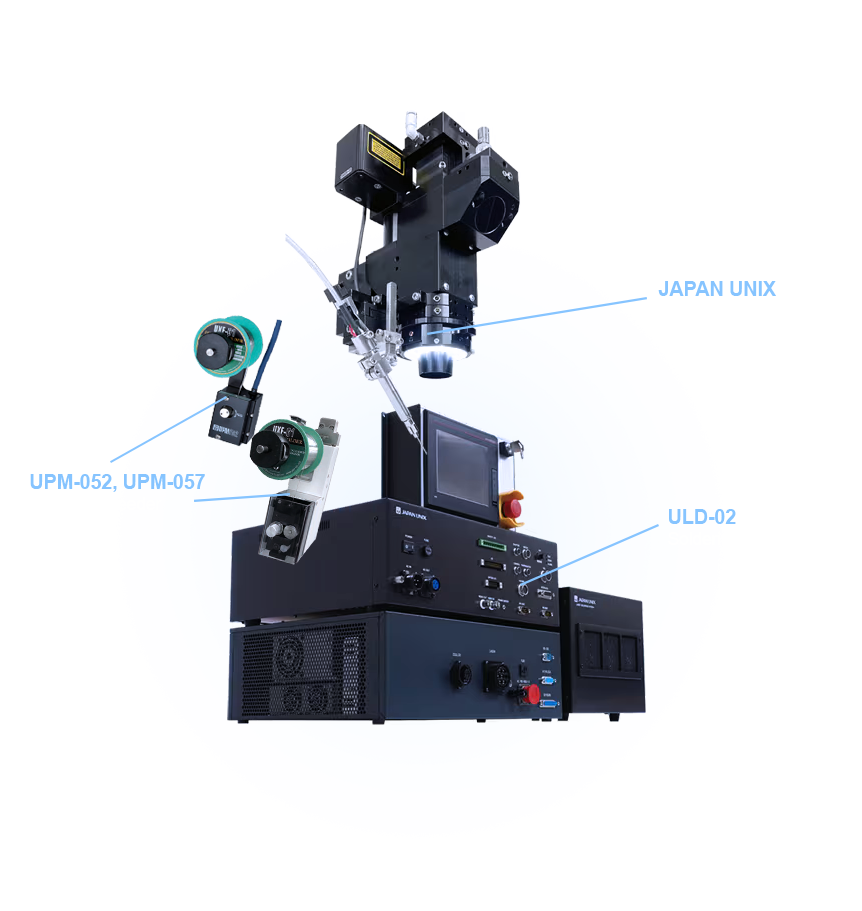
#7 Laser Soldering
Domain Est. 2006
Website: japanunix.com
Key Highlights: Laser soldering enables precise soldering in ultra-fine areas that are difficult or impossible to reach with conventional soldering irons….
#8 Laser Soldering
Domain Est. 2010
Website: kurtzersa.com
Key Highlights: Laser soldering is a special, contactless soldering process with a very high energy density which can be focused on very small geometries….
#9 Laser Soldering Power Supplies
Domain Est. 2019
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Browse our product selection of laser soldering equipment for laser micro soldering which uses selective heat solder with laser irradiation to form bonds….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Soldering
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Soldering
The laser soldering market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by relentless demands for miniaturization, precision, and automation across key industries. Here are the dominant trends shaping the market:
1. Accelerated Demand in Electronics Miniaturization & High-Density Packaging:
* Microelectronics & Advanced Packaging: The proliferation of 5G/6G devices, IoT sensors, wearables, and advanced semiconductor packaging (e.g., Fan-Out Wafer Level Packaging – FOWLP, System-in-Package – SiP) necessitates soldering at micron-level precision. Laser soldering, with its non-contact, localized heat input, is becoming essential for joining tiny components (<01005, 0201) and fine-pitch leads without damaging surrounding elements or substrate warping. This segment will be the primary growth engine.
* Flexible & Rigid-Flex PCBs: The rise of flexible electronics in consumer devices, medical implants, and automotive applications demands gentle joining techniques. Laser soldering minimizes mechanical stress and heat exposure, making it ideal for these delicate substrates.
2. Automotive Electrification & Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS):
* EV/HEV Power Electronics: High-reliability soldering of power modules (IGBTs, SiC, GaN), battery management system (BMS) components, and charging connectors is critical. Laser soldering offers superior process control, repeatability, and reduced thermal stress on heat-sensitive power semiconductors, enhancing long-term reliability crucial for safety.
* ADAS & Sensor Integration: The dense, complex circuitry in radar, LiDAR, camera modules, and sensor fusion units requires precise, reliable interconnections. Laser soldering enables high-yield production of these mission-critical systems.
3. Advancements in Laser Technology & Process Control:
* Wider Adoption of Blue & Green Lasers: While IR lasers dominate, blue (450nm) and green (532nm) lasers offer significantly higher absorption in copper and gold, the primary metals used in electronics. This translates to faster processing, lower required power, reduced heat-affected zones (HAZ), and better process stability, especially for challenging materials. Expect wider commercialization and cost reduction by 2026.
* Smarter Systems (AI/ML Integration): Real-time process monitoring using pyrometry, machine vision, and spectral analysis will become standard. AI/ML algorithms will analyze this data for predictive process control, automatic defect detection, adaptive parameter adjustment, and predictive maintenance, boosting yield and reducing scrap.
* Increased Automation & Robotics: Laser soldering heads will be seamlessly integrated into high-speed pick-and-place lines and collaborative robot (cobot) cells, enabling fully automated, lights-out manufacturing for high-volume applications.
4. Focus on Sustainability & Cost Efficiency:
* Reduced Energy Consumption: Compared to traditional hot iron or convection reflow, laser soldering is highly energy-efficient, targeting only the joint area. This aligns with growing corporate sustainability goals.
* Less Waste & Rework: Precise control minimizes solder spatter, bridging, and tombstoning, reducing material waste and costly rework. Closed-loop control further enhances first-pass yield.
* Lead-Free & Alternative Solder Challenges: As lead-free solders (e.g., SAC alloys) with higher melting points become standard, the precise thermal control of laser soldering becomes even more advantageous for managing thermal profiles and avoiding damage.
5. Expansion into New Application Areas:
* Medical Devices: Growth in minimally invasive devices, implantable electronics, and diagnostic equipment drives demand for ultra-clean, reliable, and hermetic soldering in sterile environments – a perfect fit for laser processes.
* Aerospace & Defense: High-reliability requirements for avionics, satellite components, and communication systems will increase adoption for critical interconnects.
* Photovoltaics (PV): Potential for precise interconnection of next-generation solar cell technologies (e.g., perovskite, tandem cells) requiring delicate handling.
Challenges & Considerations for 2026:
* Higher Initial Investment: Cost of advanced laser systems (especially blue/green) and integration remains a barrier for some manufacturers, though TCO is improving.
* Process Development & Expertise: Optimizing parameters (power, speed, spot size, solder paste/form) requires expertise. Standardization and easier programming interfaces will be key.
* Solder Paste/Form Material Development: Formulations specifically optimized for rapid laser heating (e.g., low oxidation, controlled flux activation) will be crucial for wider adoption.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the laser soldering market will be characterized by mainstream adoption in high-value, high-precision electronics manufacturing, driven by irreplaceable advantages in miniaturization, reliability, and process control. The convergence of advanced laser wavelengths (blue/green), AI-powered process intelligence, and deeper integration into automated production lines will solidify its position as a critical enabling technology for the next generation of electronic devices, particularly in automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. While cost and expertise remain hurdles, the compelling technical benefits ensure sustained market growth.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Soldering (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser soldering technology—whether as equipment, services, or integrated solutions—organizations often encounter significant challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, and compromised product integrity.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Process Control
Laser soldering requires precise control over parameters such as laser power, pulse duration, beam focus, and solder feed rate. Sourcing from vendors without proven process validation can result in inconsistent joint quality, leading to weak connections, solder bridging, or thermal damage to sensitive components. Lack of standardized process documentation and real-time monitoring capabilities increases the risk of undetected defects.
Insufficient Equipment Calibration and Maintenance
Low-quality or poorly maintained laser systems may drift out of specification, affecting solder joint reliability. Vendors that do not provide regular calibration logs, preventive maintenance plans, or traceable service records can compromise long-term production yield and product lifespan.
Inadequate Material Compatibility Testing
Not all solder alloys and substrate materials respond uniformly to laser energy. Sourcing solutions without comprehensive compatibility testing (e.g., for thermal expansion mismatch or wetting behavior) may result in premature joint failure, especially under thermal cycling or mechanical stress.
Lack of Skilled Operators and Training
Even high-end laser soldering systems require skilled personnel for setup, monitoring, and troubleshooting. Vendors who fail to include operator training or technical support in their offering may leave buyers with underutilized equipment and increased downtime.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Ambiguous IP Ownership in Custom Solutions
When working with suppliers to develop customized laser soldering processes or tooling, contracts that do not clearly define IP ownership can lead to disputes. Without explicit agreements, the supplier may retain rights to process innovations, limiting the buyer’s freedom to use, modify, or scale the technology.
Risk of IP Infringement
Sourcing laser soldering systems from vendors using third-party technologies (e.g., patented beam delivery optics or control algorithms) without proper licensing exposes the buyer to potential infringement claims. Buyers may unknowingly adopt equipment that violates existing patents, leading to costly litigation or forced redesigns.
Inadequate Protection of Proprietary Processes
Sharing sensitive product designs or manufacturing parameters with suppliers increases the risk of IP leakage. Vendors without strong confidentiality agreements (NDAs), secure data handling practices, or restricted access controls may inadvertently or deliberately expose critical know-how.
Reverse Engineering and Technology Cloning
In regions with weak IP enforcement, there is a heightened risk that sourced equipment or processes could be reverse-engineered and replicated by competitors. This is especially concerning when transferring technology to offshore partners or contract manufacturers.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on supplier quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949).
– Require detailed process validation reports and in-line quality monitoring capabilities.
– Define IP ownership, usage rights, and confidentiality terms in legally binding agreements.
– Perform patent landscape analyses to ensure sourced technology is non-infringing.
– Limit disclosure of proprietary information and use tiered access controls.
Proactively addressing quality and IP concerns during the sourcing phase ensures reliable, defensible, and scalable laser soldering integration.
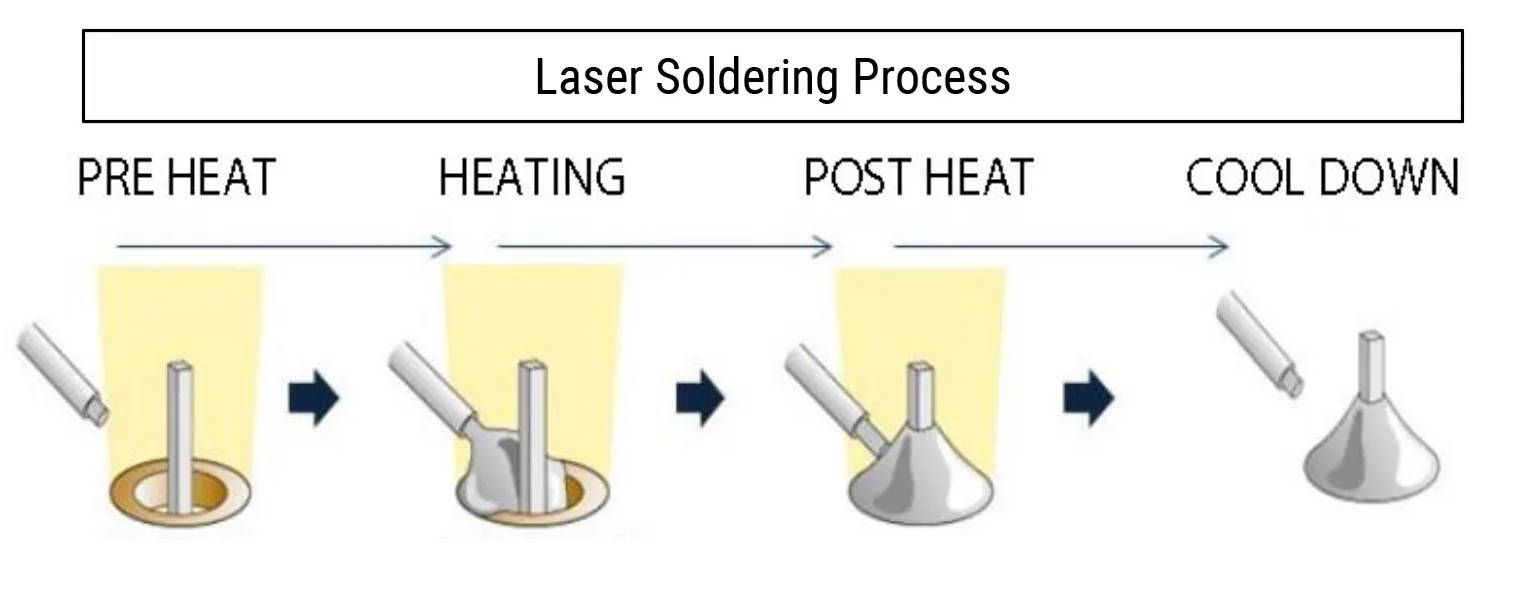
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Soldering
Overview
Laser soldering is a precise, non-contact joining process used primarily in electronics manufacturing, medical device assembly, and other high-precision industries. This guide outlines essential logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements to ensure safe, efficient, and lawful operations involving laser soldering systems.
Equipment Procurement and Installation
Ensure that laser soldering systems are sourced from certified suppliers compliant with international standards such as IEC 60825-1 (Safety of Laser Products) and ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers). Confirm that equipment includes necessary safety interlocks, beam enclosures, and emission indicators. Coordinate with suppliers for site assessment, including power requirements, ventilation, and workspace layout. Schedule professional installation by qualified technicians and conduct a post-installation safety audit before operation begins.
Facility Requirements
Laser soldering must be performed in a designated, controlled area with appropriate environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, ESD protection). The workspace should be clearly marked with laser warning signs (per ANSI Z535 and ISO 3864 standards) and access restricted to authorized personnel. Install appropriate fume extraction systems to capture soldering byproducts, especially when lead-free or rosin-based solders are used, complying with OSHA and local air quality regulations.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to all applicable regulations, including:
– Laser Safety: Comply with FDA/CDRH (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) in the U.S., or equivalent national laser safety regulations. Appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) if required.
– Chemical Handling: Follow OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) for solder materials and fluxes. Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and ensure proper labeling and storage.
– Environmental Regulations: Manage waste solder tips, used filters, and cleaning solvents according to EPA or local environmental codes (e.g., RCRA for hazardous waste).
– Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Ensure equipment meets EMC directives (e.g., EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU) to prevent interference with other devices.
Operator Training and Certification
All personnel operating or maintaining laser soldering systems must undergo documented training covering laser safety, emergency procedures, equipment operation, and hazard recognition. Training should align with ANSI Z136.3 (Safe Use of Lasers in Health Care) or equivalent industry-specific standards. Maintain training records and require periodic refresher courses. Implement a competency assessment process prior to granting operational authorization.
Maintenance and Calibration
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule for laser delivery systems, optics, fume extractors, and safety features. Use only manufacturer-recommended replacement parts. Calibrate laser power output and temperature sensors at regular intervals (e.g., quarterly) using traceable standards. Document all maintenance and calibration activities for audit purposes.
Shipping and Transportation
When transporting laser soldering equipment, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries or high-power components are included. Secure optical components and disable lasers during transit. Label packages with appropriate handling instructions and laser warnings. Retain shipping documentation, including export licenses if applicable under ITAR or EAR (U.S. regulations) for dual-use technologies.
Documentation and Auditing
Maintain comprehensive records, including equipment logs, operator certifications, maintenance reports, safety inspections, and compliance audits. Establish a document control system to ensure versions are current and accessible. Conduct internal audits at least annually to verify adherence to safety and regulatory standards, and prepare for third-party inspections as required.
Incident Reporting and Emergency Procedures
Implement a clear protocol for reporting laser-related incidents, exposure events, or equipment malfunctions. Provide emergency eyewash stations and first aid kits in the vicinity. Train staff on emergency shutdown procedures and laser exposure response. Report serious incidents to relevant authorities (e.g., OSHA, FDA) as mandated by law.
Conclusion on Sourcing Laser Soldering Technology
In conclusion, sourcing laser soldering technology presents a strategic opportunity for manufacturers seeking precision, repeatability, and efficiency in high-end electronic assembly and micro-manufacturing applications. The non-contact nature of laser soldering minimizes mechanical stress on sensitive components, while the ability to deliver controlled, localized heat improves joint quality and reduces thermal damage to surrounding areas.
When sourcing laser soldering systems, it is critical to evaluate suppliers based on technical capabilities, system integration support, reliability, and after-sales service. Investing in laser soldering requires a thorough understanding of application requirements—such as power needs, beam delivery options, vision guidance, and process control—to ensure optimal performance.
Furthermore, while the initial capital investment may be higher compared to traditional soldering methods, the long-term benefits—such as increased throughput, reduced rework, and improved product reliability—justify the expenditure for high-mix, low-volume, or precision-driven production environments.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of laser soldering solutions involves collaboration with experienced vendors, proper staff training, and a clear alignment with overall manufacturing goals. As automation and miniaturization continue to advance across industries, laser soldering stands out as a future-ready technology that enhances both product quality and operational efficiency.