The global laser marking and engraving equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision labeling across industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods. According to Grand View Research, the global laser marking machines market size was valued at USD 1.27 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising need for permanent, high-contrast markings on various materials, along with advancements in fiber and ultrafast laser technologies. As automation and traceability become critical in manufacturing, laser scriptor manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation, delivering systems with enhanced speed, accuracy, and integration capabilities. In this evolving landscape, seven key players have emerged as leaders, combining technological expertise, global reach, and strong R&D investment to shape the future of laser-based marking solutions.
Top 7 Laser Scriptor Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 High
Website: aci-laser.com
Key Highlights: As a laser manufacturer, we help you choose the right system – customized to your requirements and needs. Competent advice, sample laser marking, product demos, ……
#2 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#3 Industrial Laser Marking Machines by Domino North America
Website: domino-printing.com
Key Highlights: Domino has been a leader in industrial laser for over 40 years. Our CO2, Fiber and UV Lasers have been installed in factories all over the world. Reach out!…
#4 Wuhan Raycus Fiber Laser Technologies Co., Ltd.
Website: en.raycuslaser.com
Key Highlights: High efficiency of electro-optic conversion · Resistance to high resistance · Efficient sheet cutting · Output fiber length can be customized · Maintenance free ……
#5 Laserscript CO2 laser engraving and cutting machines and CNC …
Website: laserscript.net
Key Highlights: The Laserscipt range of machinery includes CO2 and fibre laser engraving and cutting machines, CNC routers, waterjet and pipe cutting machines….
#6 Lumentum
Website: lumentum.com
Key Highlights: Discover how Lumentum enables innovation through optical and photonic technologies for cloud networking, 3D sensing, lasers, and advanced manufacturing….
#7 Plugin to replace the extrusion g
Website: community.ultimaker.com
Key Highlights: My problem is that when i generate g-code its creates it as to think there is Extrusion happening, but what i need to do is replace this with my laser function….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Scriptor
H2: Market Trends Shaping Laser Scriptor in 2026
By 2026, the market for Laser Scriptor—a specialized software platform likely focused on laser marking, engraving, or cutting programming and control—is poised for significant evolution driven by broader industrial, technological, and economic shifts. Here’s an analysis of the key trends expected to impact its trajectory:
1. Accelerated Integration of Industry 4.0 & IIoT:
* Trend: Deepening integration of smart manufacturing principles (Industry 4.0) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) will be paramount. Laser systems are becoming central nodes in connected production lines.
* Impact on Laser Scriptor: The software will be expected to offer seamless, real-time connectivity. Key demands will include:
* Advanced Data Exchange: Robust APIs and support for protocols like OPC UA to integrate with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), ERP systems, and cloud platforms for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and production analytics.
* Remote Monitoring & Control: Enhanced capabilities for operators and managers to monitor machine status, job progress, and performance metrics remotely via web dashboards or mobile apps.
* Production Traceability: Stronger features for logging job parameters, material IDs, timestamps, and quality data directly linked to the laser process for full part traceability.
2. Rise of AI and Machine Learning for Optimization:
* Trend: AI/ML is moving beyond prediction to active process optimization and quality assurance in manufacturing.
* Impact on Laser Scriptor: Integration of AI will become a key differentiator:
* Intelligent Parameter Suggestion: AI algorithms analyzing material type, thickness, desired mark/engrave/cut quality, and historical data to automatically suggest optimal laser power, speed, frequency, and focus settings, reducing setup time and expertise barriers.
* Predictive Quality & Defect Detection: Using image recognition (potentially integrated with inline cameras) and process data to predict potential quality issues (e.g., incomplete marks, thermal damage) in real-time and suggest corrective actions or trigger automatic adjustments.
* Automated Job Optimization: AI optimizing nesting (especially for cutting) and path planning to minimize machine time and material waste.
3. Demand for Enhanced Usability and Democratization:
* Trend: The need to onboard less specialized operators and reduce reliance on highly trained technicians persists. User experience (UX) is critical.
* Impact on Laser Scriptor: The software interface will need to evolve:
* Intuitive, Guided Workflows: Simplified, step-by-step interfaces with visual guides, reducing the learning curve for new users.
* Template-Driven Operation: Extensive use of pre-defined, validated templates for common materials and applications, ensuring consistency and reducing errors.
* Cloud-Based Access & Collaboration: Growth of cloud-hosted versions enabling easier software updates, license management, and collaboration on job designs across locations.
4. Focus on Sustainability and Resource Efficiency:
* Trend: Increasing regulatory and corporate pressure to reduce energy consumption, waste, and environmental impact.
* Impact on Laser Scriptor: Software will play a direct role:
* Energy Consumption Monitoring & Reporting: Built-in tools to track and report energy usage per job, enabling users to identify savings opportunities and meet reporting requirements.
* Material Efficiency Optimization: Advanced nesting algorithms (for cutting) and path optimization (for marking/engraving) to maximize material yield and minimize scrap.
* Support for Sustainable Materials: Enhanced libraries and parameter databases specifically optimized for new or recycled materials with potentially challenging processing characteristics.
5. Expansion into New Materials and Applications:
* Trend: Lasers are being applied to increasingly diverse materials (e.g., advanced composites, new polymers, thin films, ceramics) and complex applications (e.g., micro-processing, medical device marking, battery manufacturing).
* Impact on Laser Scriptor: The software must keep pace:
* Expanded Material Libraries: Continuously updated databases with specific processing parameters for emerging materials.
* Support for Complex Geometries & 3D Marking: Enhanced capabilities for programming on curved surfaces, 3D contours, and intricate 3D structures (e.g., via galvo scanners with dynamic focus).
* Specialized Modules: Potential development of add-on modules for specific high-growth sectors like e-mobility (battery, EV components) or medical devices.
6. Cybersecurity as a Critical Concern:
* Trend: As manufacturing becomes more connected, the risk of cyberattacks on industrial control systems increases significantly.
* Impact on Laser Scriptor: Security will be non-negotiable:
* Robust Security Protocols: Implementation of strong encryption (in transit and at rest), secure authentication (e.g., multi-factor), regular security patching, and adherence to standards like IEC 62443.
* Secure Update Mechanisms: Ensuring firmware and software updates are delivered and verified securely to prevent tampering.
Conclusion for Laser Scriptor in 2026:
To thrive in 2026, Laser Scriptor must transcend its role as a mere laser control interface. It needs to evolve into an intelligent, connected, and user-centric manufacturing platform. Success will depend on seamless IIoT integration, leveraging AI for optimization and quality, offering exceptional usability, supporting sustainability goals, adapting to new materials/applications, and providing enterprise-grade cybersecurity. The software that best embodies these trends will be positioned to capture significant market share in the increasingly competitive and sophisticated industrial laser processing landscape.
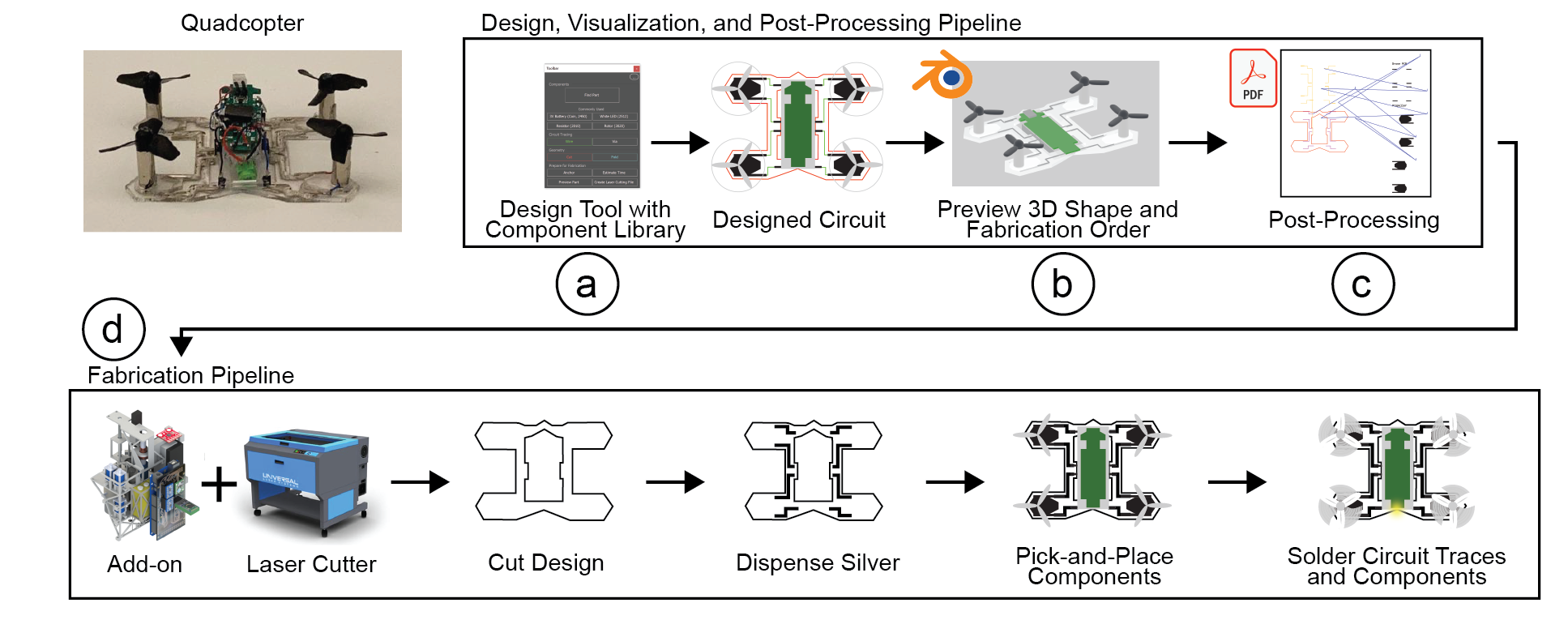
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Scriptor: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Laser Scriptor technology—whether as a finished product, component, or licensed software—introduces several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these risks is essential to avoid costly delays, legal disputes, and substandard performance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Laser Precision and Performance
One of the most common quality issues is variability in laser accuracy and engraving consistency. Low-quality or poorly calibrated Laser Scriptor units may deliver uneven depth, misaligned markings, or inconsistent line widths. This compromises product aesthetics and functionality, especially in industries requiring high tolerances (e.g., medical devices or aerospace).
Use of Substandard Components
Unreliable suppliers may cut costs by using inferior optical components, power supplies, or cooling systems. These components degrade faster, increase maintenance needs, and reduce the system’s operational lifespan. Always verify material specifications and conduct third-party durability testing.
Lack of Proper Calibration and Testing Procedures
Some suppliers fail to provide adequately calibrated systems out of the box. Without proper factory calibration and quality control documentation, end users face extended setup times and potential rework. Ensure suppliers provide calibration certificates and performance verification data.
Insufficient Software Integration and User Support
The Laser Scriptor software must be stable, intuitive, and compatible with common design tools. Poorly designed or undocumented software can lead to workflow disruptions, errors in engraving files, and difficulty troubleshooting. Evaluate software demos and support response times before committing.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unclear or Infringing IP Ownership
A major risk is sourcing Laser Scriptor technology that incorporates third-party IP without proper licensing. This could expose your business to infringement claims. Always require suppliers to disclose the origin of core technologies and provide IP warranties.
Hidden Licensing Restrictions
Some Laser Scriptor systems come with restrictive software licenses that limit usage, number of installations, or modification rights. These restrictions can hinder scalability or integration into existing production systems. Review licensing terms thoroughly before procurement.
Risk of Reverse Engineering or IP Leakage
When working with overseas or third-party manufacturers, there’s a risk that your proprietary designs or configurations could be copied or sold to competitors. Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), limit access to sensitive data, and consider legal jurisdiction when contracting.
Inadequate Documentation for Compliance and Audits
Proper IP documentation—including design records, software licenses, and component sourcing—is vital for regulatory compliance and future audits. Suppliers that fail to provide this increase your legal and operational risk.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: audit suppliers, request sample testing, verify IP clearances, and include enforceable quality and IP clauses in contracts. Engaging legal and technical experts during sourcing can significantly reduce exposure to these common risks.
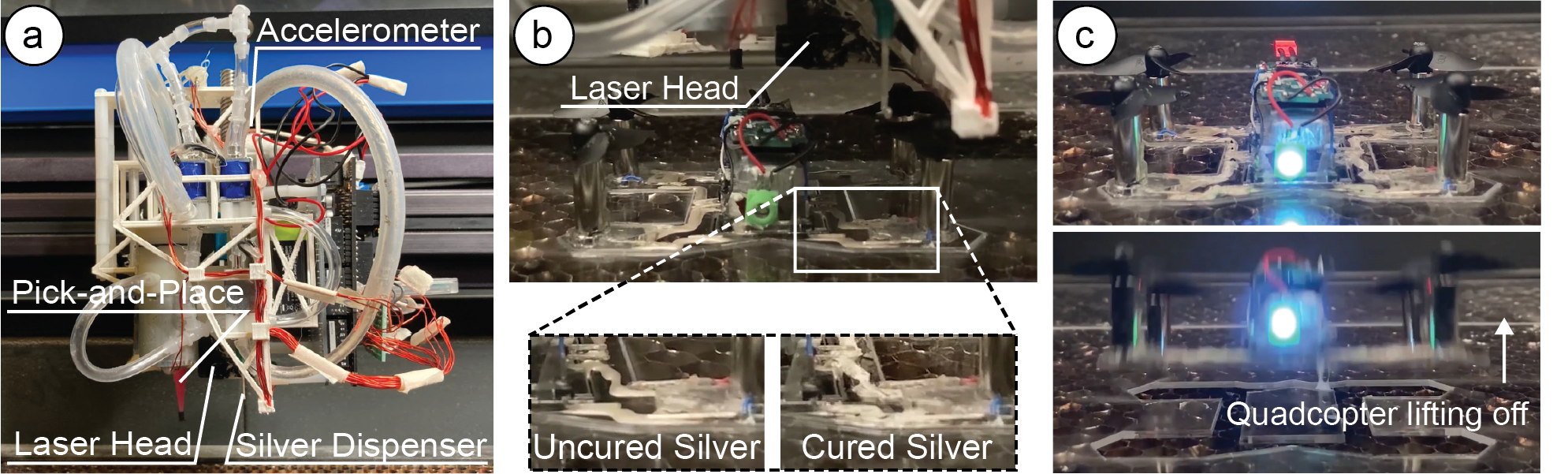
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Scriptor
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal operation, transportation, and use of the Laser Scriptor device. Adherence to these guidelines ensures user safety, regulatory compliance, and protection of equipment.
Regulatory Compliance
The Laser Scriptor must comply with all applicable national and international regulations regarding laser safety and electronic devices. Key standards include:
- FDA/CDRH (USA): Complies with 21 CFR Part 1040.10 and 1040.11 for laser products. The device is classified as a Class 1 Laser Product under normal operating conditions.
- IEC 60825-1 (International): Meets safety requirements for laser products. Users must not bypass safety interlocks or operate the device with modified optics.
- CE Marking (Europe): Conforms to the European Union’s Laser Product Safety Directive and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): The device and its components comply with restrictions on hazardous substances and chemical safety regulations.
Ensure all documentation, including the Declaration of Conformity and user manuals, are available and up to date.
Shipping & Handling
Proper packaging and handling are critical to prevent damage during transit:
- Packaging: Use the original manufacturer’s shipping container with protective foam inserts. Ensure all accessories are secured and the laser head is locked in transport mode.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.” Include compliance labels such as the Class 1 Laser Product symbol.
- Carrier Requirements: Ship via carriers experienced in handling sensitive electronic equipment. Avoid extreme temperatures and high humidity during transport.
- Documentation: Include a packing slip, commercial invoice (for international shipments), and safety data sheets (SDS) if applicable.
Import/Export Regulations
When shipping across borders, comply with customs and trade regulations:
- HS Code: Use the appropriate Harmonized System code (e.g., 9013.20 for laser machines) for accurate classification.
- Export Controls: Verify if the device or its components are subject to export restrictions (e.g., under EAR or ITAR). Most Laser Scriptors qualify for license exceptions (e.g., ENC or LVS), but confirm eligibility.
- Import Duties & Taxes: Provide accurate product descriptions and value declarations. Work with a customs broker if necessary to ensure smooth clearance.
Installation & Site Requirements
Prepare the installation environment to meet operational and safety standards:
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow or connect to an approved fume extraction system, especially when engraving certain materials.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source matching the device’s voltage and frequency requirements (e.g., 100–240 VAC, 50/60 Hz). Surge protection is recommended.
- Workspace Safety: Install in a controlled area with restricted access. Use warning signs during operation and ensure emergency shutoff is accessible.
Operational Compliance
Follow best practices during use to maintain compliance and safety:
- User Training: Only trained personnel should operate the Laser Scriptor. Training must cover emergency procedures, material compatibility, and laser safety.
- Material Restrictions: Do not process materials that produce toxic fumes (e.g., PVC, PTFE) or are flammable. Refer to the approved materials list.
- Maintenance Logs: Keep records of inspections, calibrations, and repairs. Replace consumables (e.g., lenses, mirrors) according to the maintenance schedule.
Disposal & End-of-Life
Dispose of the device and components responsibly:
- Waste Electrical Equipment (WEEE): In the EU, dispose of the Laser Scriptor through certified e-waste channels.
- Batteries & Optics: Remove and recycle batteries and optical components per local hazardous waste regulations.
- Data Security: If the device stores operational data, perform a factory reset and follow data sanitization protocols before disposal.
Adhering to this Logistics & Compliance Guide ensures safe operation, legal conformity, and environmental responsibility when using the Laser Scriptor. Always consult the latest manufacturer documentation and local regulations for updates.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Scriptor
Sourcing a laser scriptor requires careful evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, and vendor reliability. It is essential to identify the precise needs of your project—such as engraving depth, material compatibility, precision, and production speed—to select a system that delivers optimal performance and return on investment. After comparing various models and suppliers, emphasize factors such as build quality, software integration, after-sales support, and warranty terms.
Investing in a reputable laser scriptor not only ensures consistent, high-quality markings but also reduces long-term operational costs through improved efficiency and durability. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing decision will enhance production capabilities, support scalability, and contribute to overall operational excellence. Prioritizing compatibility, service support, and future-proofing will lead to a successful integration of the laser scripting solution into your workflow.