The global laser sanding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision surface finishing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, furniture, and electronics. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global laser processing equipment market—encompassing laser sanding, cutting, and engraving—was valued at USD 14.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further supported by advancements in laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing, and the need for non-contact, high-accuracy finishing solutions. Mordor Intelligence projects similar momentum, citing increased adoption of Industry 4.0 practices and smart manufacturing systems as key drivers for laser-based surface treatment equipment. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, reliability, and scalability to meet evolving industrial needs. Here are the top 10 laser sanding machine manufacturers shaping the future of precision surface finishing.
Top 10 Laser Sanding Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Processing Solutions
Website: novantaphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover laser processing solutions by Novanta, experts in advanced Laser technology. Learn more about our industrial & medical laser solutions….
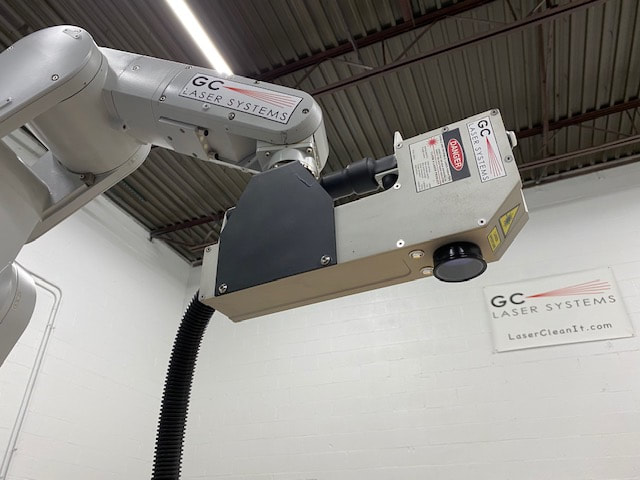
#2 G.C. Laser Systems
Website: gclasers.com
Key Highlights: G.C. Laser Systems Inc. manufactures unique laser cleaning technology that offers unmatched cleaning precision and surface prep. Our laser systems are ……
#3 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#5 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: Specializing in the production of premium-quality, Belgian-made industrial laser cleaning equipment, we take great pride in our craftsmanship and innovative ……
#6 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Argento Lux, experts in laser cleaning, utilizing high-powered lasers to remove contamination from various surfaces. Similar to sandblasting without the ……
#7 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#8 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: LME Laser is a laser cleaning machine manufacture with 17 years experience. The Products including continuous laser cleaner and pulse laser cleaner….
#9 Sales
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL 500A is a portable pulsed laser cleaning machine designed for manual, precision-focused surface cleaning applications. Laser output: 500 W Maximum ……
#10 Powerlase Limited
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: We are innovators in the high power laser industry and offer the fastest and lowest cost laser cleaning and surface preparation systems on the market….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Sanding Machine
H2: Market Trends for Laser Sanding Machines in 2026
By 2026, the global market for laser sanding machines is projected to experience substantial growth, driven by advancements in laser technology, rising demand for precision surface finishing, and increasing automation in manufacturing sectors. These machines—utilizing high-precision lasers to ablate or smooth material surfaces without physical contact—are gaining traction across industries such as aerospace, automotive, woodworking, and medical device manufacturing.
One of the key trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the shift toward non-contact, environmentally sustainable finishing methods. Traditional sanding generates dust, consumes abrasive materials, and often requires extensive post-processing. In contrast, laser sanding offers cleaner, more consistent results with minimal waste, aligning with global sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations.
Additionally, integration with Industry 4.0 technologies is accelerating adoption. Laser sanding machines are increasingly equipped with IoT connectivity, AI-driven process optimization, and real-time monitoring systems. This enables predictive maintenance, adaptive control based on material feedback, and seamless integration into smart factory ecosystems.
Another significant trend is the expansion of application areas. While initially limited to high-value niche applications, improvements in cost-efficiency and processing speed have made laser sanding viable for mid-volume production environments. In particular, the automotive sector is adopting laser sanding for pre-painting surface preparation of composite and metal components, enhancing adhesion and finish quality.
Regionally, North America and Europe are leading in early adoption due to strong industrial bases and supportive regulatory frameworks. However, the Asia-Pacific region—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—is expected to witness the highest growth rate, fueled by investments in advanced manufacturing and rising consumer demand for high-quality finished goods.
Despite these positive trends, challenges remain. High initial investment costs and the need for specialized operator training may limit adoption among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Nevertheless, as component costs decline and user-friendly interfaces become standard, market penetration is expected to broaden.
In summary, by 2026, the laser sanding machine market will be characterized by technological innovation, sustainability-driven demand, and deeper integration into automated production lines, positioning it as a transformative force in modern surface finishing.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Sanding Machine: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing a laser sanding machine can significantly enhance surface finishing capabilities, but buyers often encounter critical pitfalls related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to costly downtime, substandard results, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common issues to avoid.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many suppliers, especially lower-cost manufacturers, use inferior materials and non-industrial-grade components to cut costs. This can result in premature wear, inconsistent performance, and frequent breakdowns. Key red flags include lightweight frames, generic laser diodes instead of certified industrial lasers, and lack of IP ratings for dust and moisture resistance in workshop environments.
Inadequate Calibration and Repeatability
A high-quality laser sander must deliver consistent results across multiple runs. Poorly assembled or uncalibrated machines suffer from beam misalignment and inconsistent power output, leading to uneven sanding, surface defects, and wasted materials. Ensure the supplier provides documented calibration procedures and performance testing reports.
Unrealistic Performance Claims
Some vendors exaggerate machine capabilities, such as sanding speed, depth control, or material compatibility. These inflated claims may not hold up under real-world conditions, leading to production delays and unmet expectations. Always request third-party validation or on-site demonstrations using your actual materials and workpieces.
Lack of Compliance with Safety Standards
Laser systems must comply with international safety regulations (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety, CE, or FDA requirements). Machines lacking proper certifications pose serious safety risks and may not be legally operable in certain regions. Verify that the supplier provides full compliance documentation and integrated safety features like enclosures, interlocks, and emergency stops.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Service Network
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers without local service teams or clear SLAs (Service Level Agreements) can leave you stranded during critical operations. Evaluate the availability of spare parts, software updates, and remote troubleshooting support before purchase.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Purchasing machines that incorporate patented technologies without proper licensing exposes your business to legal liability. Some manufacturers reverse-engineer or copy proprietary designs, particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement. Conduct due diligence by requesting proof of IP ownership, patent registrations, or licensing agreements for core technologies.
Proprietary Software and Data Ownership Issues
Many laser sanding systems rely on proprietary control software. Hidden pitfalls include restrictive licensing terms, lack of data export options, or vendor lock-in that limits your ability to modify or integrate the machine into existing workflows. Clarify software rights, update policies, and data access terms before finalizing the purchase.
Inadequate Documentation and Training
Poorly documented machines with minimal user manuals or training programs increase operational risks and reduce efficiency. Ensure the supplier offers comprehensive documentation, multilingual support, and hands-on training for operators and maintenance personnel.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, technical evaluations, and legal review of contracts and IP clauses. Prioritize transparency, certifications, and long-term support to ensure a reliable and legally secure investment.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Sanding Machine
Product Classification & Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the laser sanding machine under the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) Code, typically falling within Chapter 84 or 85 depending on technical specifications. Common classifications may include 8465.99 (machines for working wood, cork, bone, hard rubber, or hard plastics) or 8515.21 (laser welding, cutting, or soldering machines). Confirm the final classification with a customs broker or national tariff authority. Required documentation includes a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or air waybill, certificate of origin, and technical specifications. Include safety data sheets (SDS) if applicable and a CE or other regional conformity certificate.
Export & Import Regulations
Verify export controls based on the country of origin. The laser sander may be subject to dual-use or laser-specific export regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S. under ECCN 2B201 or 3A001). Obtain any necessary export licenses prior to shipment. For import, confirm compliance with destination country requirements, including conformity assessments, labeling, and registration. Some countries may require pre-shipment inspection (PSI) or special permits for industrial laser equipment. Always consult local customs authorities or legal counsel for jurisdiction-specific obligations.
Safety & Regulatory Compliance
Laser sanding machines must comply with international safety standards such as IEC 60825 (laser product safety) and IEC 61400 (safety of machinery). In the European Union, compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) is mandatory, requiring CE marking. In the U.S., adherence to OSHA standards and FDA/CDRH laser product regulations (21 CFR 1040.10–1040.11) is required. Provide a Declaration of Conformity (DoC), technical construction file, and user manuals in the local language of the destination market.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Use robust, export-standard packaging to protect the machine during transit. Secure all moving parts, optics, and control panels with anti-vibration materials and moisture barriers. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include a detailed packing list inside each container. For large units, provide lifting points and comply with ISPM 15 for wooden packaging materials if shipping internationally. Ensure the machine is clean and free from contaminants to meet biosecurity regulations.
Transportation & Shipping
Choose a freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial machinery and hazardous or regulated goods (if applicable). Clearly declare the presence of laser components during booking. Sea freight is typical for heavy machinery; use FCL (Full Container Load) for better protection. For air freight, ensure compliance with IATA regulations, especially if batteries or laser components are classified as dangerous goods. Confirm insurance coverage for full replacement value, including transit risks.
Customs Clearance & Duties
Prepare all documents in advance to avoid delays. Assign a reliable customs broker at the destination to manage clearance. Provide detailed technical descriptions to facilitate accurate duty assessment. Be aware that laser equipment may be subject to higher tariffs or additional inspections. Confirm duty rates, VAT/GST, and any anti-dumping measures that may apply. Retain all compliance records for a minimum of five years.
Post-Import Requirements
Upon arrival, the machine may require on-site inspection or registration with local industrial safety or environmental agencies. In some countries, end-users must register laser equipment with national radiation or occupational safety authorities. Provide installation, operator training, and maintenance support in compliance with local labor laws. Maintain records of post-sale compliance activities to support warranty and liability management.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Sanding Machine
After thorough evaluation of available technologies, market offerings, and specific application requirements, sourcing a laser sanding machine presents a strategic investment for enhancing surface finishing precision, efficiency, and consistency. Laser sanding technology offers significant advantages over traditional mechanical sanding methods, including non-contact processing, minimal material waste, reduced tool wear, and superior control over surface texture—particularly beneficial for delicate, complex, or high-value components.
The decision to procure a laser sanding system should be guided by production volume, material types, surface quality standards, and long-term automation goals. While the initial investment may be higher than conventional alternatives, the long-term benefits—such as lower maintenance costs, improved repeatability, and integration potential with digital manufacturing workflows—justify the expenditure for operations seeking to upgrade quality and competitiveness.
Additionally, partnering with reputable suppliers offering technical support, training, and service agreements is crucial to ensure smooth implementation and sustained performance. Pilot testing and vendor demonstrations are recommended to validate machine capabilities against specific use cases.
In conclusion, sourcing a laser sanding machine aligns with modern manufacturing trends toward precision, sustainability, and digital integration. When selected and deployed appropriately, it can significantly improve product quality, reduce operational downtime, and provide a strong return on investment over time.