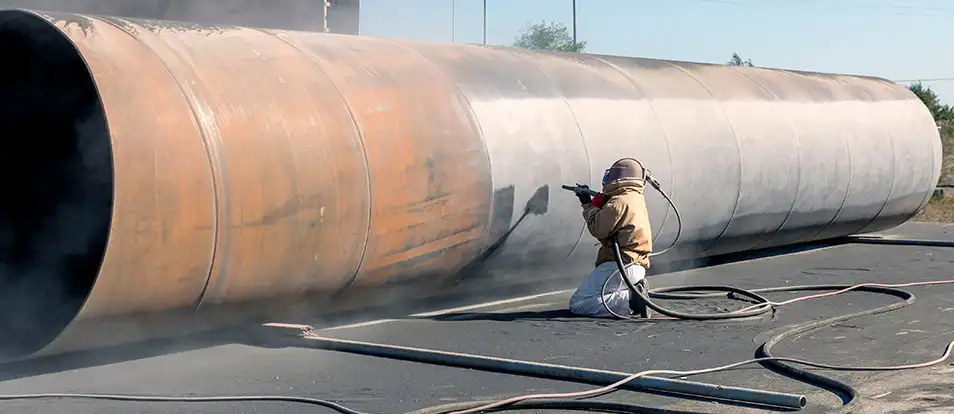
The global laser surface treatment market is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by increasing demand for precision, eco-friendly, and automated finishing solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global laser cleaning market was valued at USD 1.2 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.3% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by stricter environmental regulations and the phasing out of traditional sandblasting methods due to their harmful emissions and waste byproducts. Laser sandblasting—or laser ablation—offers a cleaner, more efficient alternative with minimal maintenance and operational costs. As industries pivot toward sustainable manufacturing, leading technology providers are scaling innovation in power output, portability, and integration with robotic systems. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and global reach, the following nine manufacturers represent the forefront of laser sandblasting innovation.
Top 9 Laser Sandblasting Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Systems
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Oem Laser Cleaning Systems. From low-power to high-power lasers, our range of products allow manufacturers to efficiently solve their surface cleaning needs….
#2 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#4 JH Norton Company Inc.
Founded: 1973
Website: nortonsandblasting.com
Key Highlights: 3-day delivery 30-day returnsSince 1973, JH Norton Company Inc. supplies many types and sizes of sandblasting equipment, abrasive blasting parts, and accessories….
#5 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Argento Lux, experts in laser cleaning, utilizing high-powered lasers to remove contamination from various surfaces. Similar to sandblasting without the ……
#6 Clean Laser Technologies
Website: cleanlasertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Clean Laser Technologies is a Mississippi-based company specializing in laser cleaning technology, providing state of the art laser cleaning machines, training ……
#7 Laser Cleaning Machine – LaserBlast Systems
Website: alliedscientificpro.com
Key Highlights: Our fiber laser cleaning system requires no blast media, consuming only electricity and utilizing a highly efficient power input. Digitally controlled, ……
#8 Laser cleaning
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: How to achieve the perfect weld seam: laser cleaning allows you to very gently clean metal components of dirt, as well as oxidation and functional layers….
#9 IKONICS
Website: ikonics.com
Key Highlights: Sandcarving & Personalization Market … IKONICS Imaging is the Total Solution Supplier for all sandcarving needs with high-quality equipment and products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Sandblasting

2026 Market Trends for Laser Sandblasting
Rising Demand in Aerospace and Defense Driving Innovation
By 2026, the laser sandblasting market is expected to experience significant growth, primarily fueled by increasing adoption in the aerospace and defense sectors. Stringent regulatory standards for surface preparation and the need for non-contact, precision cleaning methods are pushing manufacturers toward laser ablation technologies. Aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations are increasingly replacing traditional abrasive blasting with laser systems to eliminate media contamination, reduce substrate damage, and improve worker safety. This shift is accelerating R&D investments in high-power, portable laser solutions tailored for complex geometries and sensitive composite materials.
Expansion into Automotive and Heavy Industry Applications
Beyond aerospace, the automotive and heavy machinery industries are emerging as key growth segments for laser sandblasting by 2026. Manufacturers are adopting laser cleaning for rust removal, paint stripping, and weld preparation due to its environmental and efficiency advantages. As sustainability regulations tighten globally—particularly in Europe and North America—industries are seeking eco-friendly alternatives to chemical solvents and silica-based blasting media. Laser systems produce no secondary waste and consume minimal consumables, aligning with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals and reducing long-term operational costs.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Accessibility and Performance
Advancements in fiber laser technology are making laser sandblasting more accessible and cost-effective. By 2026, expect to see wider availability of mid-range power systems (500W–2kW) that balance performance with affordability for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Integration with robotics and AI-driven path planning is improving automation, enabling consistent results in high-volume production environments. Additionally, handheld laser cleaning devices are gaining traction for maintenance and restoration tasks, broadening the user base beyond large industrial facilities.
Regional Growth and Competitive Landscape
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region for laser sandblasting by 2026, led by industrial modernization in China, Japan, and South Korea. Government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing and green technology are creating favorable conditions for adoption. Meanwhile, North America and Europe remain strong markets due to mature industrial infrastructure and strict environmental compliance requirements. The competitive landscape is intensifying, with established players and new entrants focusing on product differentiation through software integration, service models, and modular system designs.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the positive trajectory, challenges remain, including high initial investment costs and the need for skilled operators. However, as technology matures and total cost of ownership improves, market penetration is expected to accelerate. By 2026, the global laser sandblasting market is poised for robust expansion, driven by environmental regulations, technological innovation, and growing recognition of its operational benefits across critical industries.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Sandblasting (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser sandblasting services, businesses often encounter challenges that can compromise project quality, timelines, and intellectual property (IP) security. Recognizing these pitfalls is crucial for successful vendor selection and project execution.
Poor Process Control Leading to Inconsistent Quality
Laser sandblasting requires precise control over parameters such as laser intensity, pulse duration, beam focus, and scanning speed. Inexperienced or poorly equipped suppliers may lack standardized operating procedures, resulting in inconsistent surface finishes, over- or under-ablation, or damage to the substrate. This variability undermines product reliability and repeatability, especially in high-precision industries like aerospace or medical devices.
Inadequate Material and Surface Compatibility Assessment
Not all materials respond the same way to laser ablation. A common pitfall is selecting a vendor who fails to conduct proper material testing or surface analysis prior to full-scale processing. This oversight can lead to unintended surface modifications, residual contamination, or compromised structural integrity—particularly with composites, coated materials, or heat-sensitive alloys.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
High-quality laser sandblasting demands rigorous process documentation, including parameter logs, pre- and post-treatment inspection reports, and batch traceability. Vendors who lack robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 certification) may not provide the necessary documentation, making it difficult to validate consistency or meet regulatory requirements in controlled industries.
Lack of Intellectual Property Protection Measures
Laser sandblasting often involves proprietary part designs, surface patterns, or treatment specifications. A critical risk arises when suppliers do not have clear IP protection protocols—such as signed NDAs, secure data handling practices, or controlled access to design files. Unauthorized use, replication, or leakage of sensitive data can result in competitive disadvantage or legal disputes.
Inexperienced Operators Without Technical Expertise
The effectiveness of laser sandblasting heavily depends on operator skill and engineering support. Sourcing from vendors with undertrained staff may lead to suboptimal parameter selection, misinterpretation of technical drawings, or inability to troubleshoot process issues, ultimately affecting final quality and delivery timelines.
Hidden Costs from Poor Pre- and Post-Processing Integration
Some suppliers focus solely on the laser process but overlook necessary pre-cleaning or post-inspection steps. This narrow scope can result in unexpected costs or delays when contaminants interfere with ablation or when additional finishing is required to meet specifications. Lack of integrated workflow planning is a frequent oversight.
Failure to Validate Equipment Calibration and Maintenance
Laser systems require regular calibration and maintenance to ensure performance accuracy. Vendors who do not adhere to strict maintenance schedules may deliver inconsistent results due to beam misalignment, power fluctuations, or optics degradation—issues that are often not immediately apparent but impact long-term quality.
Overlooking Compliance and Industry Standards
Depending on the application, laser sandblasting may need to comply with industry-specific standards (e.g., AS9100 for aerospace, FDA guidelines for medical devices). Sourcing from suppliers unfamiliar with these requirements can lead to non-compliant processes, failed audits, and product rejection.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough supplier audits, request sample validations, verify certifications, and establish clear contractual terms around quality assurance and IP protection.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Sandblasting
Laser sandblasting, more accurately referred to as laser ablation or laser surface cleaning, is an advanced technology used to remove coatings, oxides, rust, and contaminants from surfaces using high-intensity laser beams. Unlike traditional abrasive sandblasting, it produces no secondary waste media and offers precise, environmentally friendly surface preparation. However, due to its specialized nature, specific logistics and compliance considerations are essential for safe, legal, and efficient operation.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with local, national, and international regulations is critical when operating laser sandblasting equipment. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in fines, operational shutdowns, or safety incidents.
Laser Safety Standards
Laser systems are classified under international standards such as IEC 60825-1 and ANSI Z136.1. Most industrial laser sandblasting systems fall under Class 4, the highest risk category, requiring strict controls including:
- Implementation of laser-controlled areas with warning signs
- Use of interlocks on enclosures and access points
- Mandatory use of appropriate laser safety eyewear (wavelength-specific optical density)
- Appointment of a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) in larger operations
Workplace Health and Safety Regulations
Employers must comply with occupational health and safety regulations such as OSHA (US), HSE (UK), or equivalent bodies in other jurisdictions. Key requirements include:
- Conducting risk assessments for laser operations and fume exposure
- Implementing engineering controls (e.g., fume extraction, beam enclosures)
- Providing comprehensive training for operators and maintenance personnel
- Maintaining documented safety procedures and emergency protocols
Environmental Regulations
Although laser ablation generates no abrasive waste, it does produce particulate matter and fumes (especially when removing paints or coatings containing heavy metals or hazardous substances). Compliance includes:
- Installation of high-efficiency fume extraction and filtration systems (e.g., HEPA filters)
- Proper disposal of collected particulate waste as hazardous or non-hazardous based on material analysis
- Adherence to air emission standards under laws such as the Clean Air Act (US) or Industrial Emissions Directive (EU)
Electrical and Machine Safety
Laser systems require high-power electrical supplies and must conform to:
- Electrical safety standards (e.g., NFPA 70, IEC 60204)
- Machine guarding requirements to prevent access to moving parts or energized components
- Regular inspection and maintenance programs per manufacturer guidelines
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Proper logistics are essential for the installation, movement, and maintenance of laser sandblasting systems, which are often large, heavy, and sensitive.
Packaging and Shipping
– Use manufacturer-approved crates with shock-absorbing materials to protect optical components and electronics
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Equipment” warnings
– Ensure climate-controlled transport when required to prevent condensation or thermal damage
Installation Requirements
– Site must have adequate floor loading capacity to support equipment weight (often 500–2000 kg)
– Stable power supply with proper grounding, voltage regulation, and backup (UPS) if necessary
– Sufficient space for ventilation, operator access, and integration with extraction systems
– Level and vibration-free foundation, especially for high-precision applications
On-Site Movement
– Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts, cranes) with trained personnel
– Avoid tilting laser heads or optical benches beyond manufacturer limits
– Protect fiber optic cables and cooling lines during relocation
Operational Logistics
Efficient day-to-day operations depend on planning, maintenance, and coordination.
Operator Training and Certification
– Operators must be certified in laser safety and equipment-specific operation
– Training should cover startup/shutdown procedures, emergency stops, and troubleshooting
– Refresher courses and competency assessments should be conducted annually
Maintenance Scheduling
– Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance intervals for optics, cooling systems, and software
– Keep detailed logs of service history, part replacements, and calibration checks
– Schedule downtime to minimize production impact
Material Flow and Workflow Integration
– Design workflow to minimize material handling—position laser stations near pre- and post-processing areas
– Use automated conveyors or robotic arms where possible for high-volume applications
– Ensure parts are clean and fixtured properly before laser treatment
Waste Management and Disposal
Although laser sandblasting is cleaner than traditional methods, it still generates waste that must be managed responsibly.
Fume and Particulate Collection
– Use high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration systems to capture sub-micron particles
– Conduct regular filter inspections and replacements
– Monitor filter integrity with differential pressure sensors
Waste Classification
– Analyze collected residue (e.g., via XRF or lab testing) to determine if it contains hazardous materials (e.g., lead, cadmium, chromium VI)
– Classify waste as hazardous or non-hazardous per local regulations (e.g., EPA TCLP test in the US)
Disposal Protocols
– Store waste in sealed, labeled containers
– Use licensed hazardous waste disposal contractors when required
– Maintain manifests and disposal records for audit purposes
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintaining accurate documentation supports compliance, traceability, and continuous improvement.
Essential Records Include
– Laser safety program and LSO reports
– Equipment maintenance logs and calibration certificates
– Operator training records and certifications
– Risk assessments and method statements
– Waste disposal manifests and material test results
– Incident reports and corrective actions
Audit Preparedness
– Conduct internal audits at least annually
– Keep all documentation organized and readily accessible
– Prepare for inspections by regulatory agencies (e.g., OSHA, environmental authorities)
International Considerations
For global operations, additional compliance factors may apply.
Import/Export Regulations
– Laser systems may be subject to export controls (e.g., ITAR, EAR in the US) if they meet certain power or precision thresholds
– Obtain necessary permits or licenses before shipping across borders
Local Legal Requirements
– Comply with country-specific laser safety, environmental, and labor laws
– Translate safety signage and operating manuals into local languages
By adhering to this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure safe, efficient, and legally sound operations when utilizing laser sandblasting technology. Regular review and updates to procedures will help maintain alignment with evolving regulations and technological advancements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Sandblasting:
Sourcing laser sandblasting services offers a precise, efficient, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional sandblasting methods. With superior accuracy, minimal material waste, and the ability to create intricate designs on various surfaces, laser sandblasting is ideal for industries requiring high-quality surface finishing, such as aerospace, automotive, and precision manufacturing. When sourcing this technology, it is essential to evaluate vendors based on technical capabilities, experience, quality certifications, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, considering factors like lead times, scalability, and after-sales support ensures a successful partnership. As laser technology continues to advance, investing in trusted laser sandblasting solutions positions businesses at the forefront of innovation, enhancing product quality and operational efficiency in a competitive market.