The global laser rust removal equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision cleaning technologies in aerospace, automotive, and cultural heritage preservation industries. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the industrial laser cleaning market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 9.5% from 2023 to 2028, with laser-based rust and surface treatment solutions accounting for a significant share. This expansion is fueled by the advantages of laser cleaning—such as environmental sustainability (eliminating chemical solvents and reducing waste), improved worker safety, and high repeatability—over traditional methods like sandblasting or chemical stripping. As industries prioritize automation and eco-friendly practices, manufacturers are investing heavily in advanced laser systems capable of efficiently removing rust, oxides, and coatings without substrate damage. In this competitive landscape, a select group of innovators are leading the charge in performance, reliability, and technological integration. Here are the top 10 laser rust removal equipment manufacturers shaping the future of industrial surface treatment.
Top 10 Laser Rust Removal Equipment Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FOX P CL – laser for removing rust
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: An innovative laser cleaner that revolutionizes the maintenance and restoration of large vehicles and industrial equipment….
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: For over 10 years, we have produced laser marking and laser cleaning machines … Laser Rust Removal · Laser Oxide Removal · Laser Paint Removal · Battery Modules ……
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#4 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#5 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#6 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#7 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our Laser Ablation is the most cost-effective, efficient, and safest method of industrial cleaning, rust removal, paint removal, and surface preparation….
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#9 Laser Rust Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: The laser rust removal machine uses a focused laser beam with high peak power and short pulse to heat the external surface (the rust) to its evaporation point….
#10 Laser cleaning
Website: p-laserusa.com
Key Highlights: Our laser machines are mainly used to remove the following contaminants: Rust – Paint – Coatings – Release Agents – Grease, Oils – Soot – Rubber- Organic ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Rust Removal Equipment
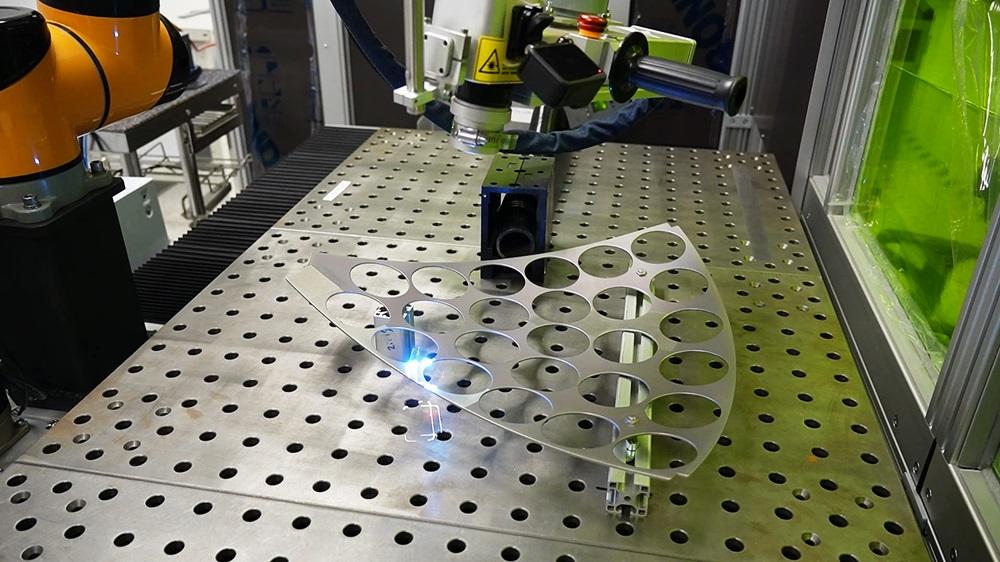

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Rust Removal Equipment
The global market for laser rust removal equipment is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and expanding industrial adoption. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Technological Advancements:
By 2026, expect widespread deployment of higher-power fiber lasers (2,000W–6,000W+) enabling faster cleaning speeds and deeper rust removal on heavy industrial components. Integration of AI and machine learning will enhance precision through real-time surface analysis and adaptive beam control. Portable and handheld laser systems will become more robust and user-friendly, expanding applications beyond fixed workstations.
2. Strong Growth in Automotive and Aerospace Sectors:
These industries will be primary growth drivers as manufacturers adopt laser cleaning for surface preparation prior to welding, coating, and inspection. The non-abrasive, chemical-free nature of laser rust removal aligns with stringent quality and environmental standards, particularly in aircraft maintenance (MRO) and electric vehicle (EV) production.
3. Rising Environmental and Regulatory Pressure:
With increasing global focus on sustainability and chemical use reduction (e.g., REACH, EPA guidelines), industries are shifting from sandblasting and chemical stripping to eco-friendly alternatives. Laser rust removal produces no secondary waste or hazardous runoff, making it a preferred solution in regulated markets across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia.
4. Expansion in Emerging Markets:
Countries like India, Vietnam, and Brazil are expected to see rising demand due to industrial modernization and infrastructure development. Lower-cost, entry-level laser systems will become more accessible, broadening adoption among small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in shipbuilding, rail, and energy sectors.
5. Focus on Automation and Integration:
Laser rust removal systems will increasingly be integrated into automated production lines, especially with robotic arms and IoT-enabled monitoring. This trend will improve throughput, consistency, and data traceability—critical for industries requiring compliance and quality assurance documentation.
6. Competitive Pricing and Market Consolidation:
As production scales and component costs (especially fiber lasers) decrease, equipment prices will become more competitive. This may lead to market consolidation, with larger players acquiring innovative startups to expand their product portfolios and geographic reach.
In summary, by 2026, the laser rust removal equipment market will be defined by smarter, faster, and more sustainable technologies, driven by regulatory tailwinds and growing recognition of long-term operational benefits over traditional methods.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Rust Removal Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing laser rust removal equipment offers significant advantages in precision and environmental safety, but buyers must navigate several critical pitfalls—particularly related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Overlooking these factors can lead to poor performance, legal exposure, or financial loss.
Overestimating Equipment Performance and Underestimating Quality Variance
One of the most frequent pitfalls is assuming that all laser rust removal systems deliver the same results. Low-cost suppliers, especially from regions with less stringent manufacturing oversight, often exaggerate technical specifications such as laser power, cleaning speed, and beam quality. In reality, these systems may use substandard components—lower-grade optical fibers, inefficient cooling systems, or poorly calibrated scanners—leading to inconsistent rust removal, premature wear, or safety risks. Buyers should insist on third-party testing reports, on-site demonstrations, and verifiable performance data before purchase.
Lack of IP Verification and Risk of Infringement
Many laser cleaning systems on the market, particularly from certain manufacturers, may incorporate technologies protected by patents held by original innovators. Sourcing equipment without verifying its intellectual property status exposes buyers to potential legal action for patent infringement. This is especially true when purchasing from suppliers who offer strikingly similar designs or unusually low prices—common red flags for reverse-engineered or copied technology. Conducting due diligence on the supplier’s R&D background, patent portfolio, and certification history is essential to avoid costly IP disputes.
Absence of After-Sales Support and Technical Documentation
Low-quality or IP-compromised equipment often comes with inadequate technical support, missing user manuals, or non-compliant safety certifications. Without proper documentation and service networks, maintenance becomes difficult, downtime increases, and compliance with industry safety standards (such as laser safety Class 1 enclosure requirements) may be jeopardized. Always confirm that the supplier provides comprehensive training, spare parts availability, and firmware/software updates—key indicators of legitimate, sustainable products.
Choosing Based on Price Alone
While budget considerations are important, prioritizing cost over quality and IP integrity frequently results in higher total cost of ownership. Inferior systems may require frequent repairs, deliver slower throughput, or fail to meet production demands, ultimately undermining return on investment. A reputable supplier with transparent IP ownership and proven quality control typically offers better long-term value, even at a higher initial price.
By carefully evaluating both the technical quality and IP legitimacy of laser rust removal equipment, buyers can avoid these common pitfalls and make a secure, effective investment.
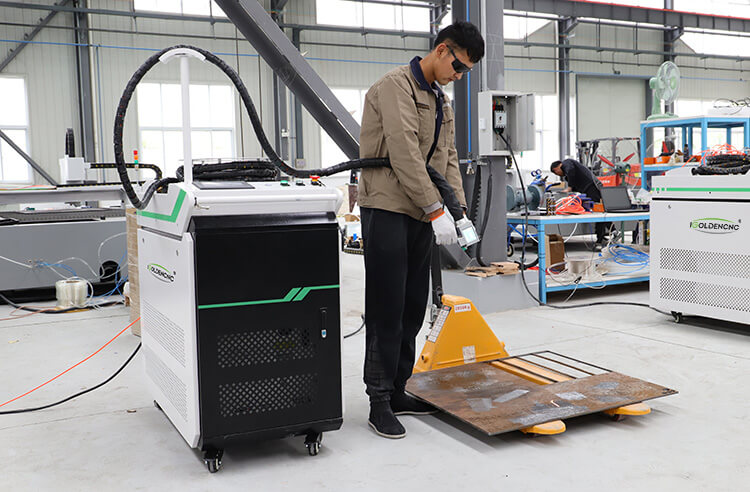

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Rust Removal Equipment
Overview and Importance
Laser rust removal equipment utilizes high-intensity laser beams to ablate rust, paint, and contaminants from metal surfaces without damaging the underlying substrate. As an advanced industrial cleaning solution, its deployment involves strict compliance and logistical considerations due to its classification as a Class 4 laser system. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance requirements for the safe transportation, import/export, operation, and maintenance of laser rust removal systems.
Regulatory Classification and Standards
Laser rust removal equipment is classified under international laser safety standards, primarily IEC 60825-1, which defines safety requirements for laser products. Most industrial laser cleaning systems fall under Class 4 lasers, indicating a high risk of eye and skin injury, as well as fire hazard. Compliance with regional regulations such as FDA/CDRH (USA), CE marking (European Union), and local laser safety authorities (e.g. Health Canada, TÜV in Germany) is mandatory. Operators must ensure equipment bears appropriate warning labels, safety interlocks, and complies with emission limits.
Transportation and Shipping Requirements
Transporting laser rust removal equipment requires adherence to international hazardous material regulations due to its laser classification and associated components. While the laser itself is not classified as dangerous goods under IATA/IMDG if powered off and secured, accompanying batteries (e.g., lithium-ion for portable units) may be regulated. Proper packaging, shock protection, moisture barriers, and secure crating are essential. Documentation should include a safety data sheet (SDS) if applicable, packing list, commercial invoice, and a declaration confirming compliance with laser safety standards. Air freight may require additional verification with carriers regarding laser equipment policies.
Import and Export Controls
Export and import of laser equipment may be subject to dual-use and strategic trade controls. In the United States, high-powered lasers may be listed under the Commerce Control List (CCL), requiring an export license from the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) depending on power, wavelength, and destination country. Similarly, the EU’s Dual-Use Regulation (EU) 2021/821 governs exports of laser systems with potential military applications. Exporters must conduct classification assessments (e.g., ECCN determination) and obtain necessary licenses. Importers must verify local customs requirements, including tariffs, conformity assessments (e.g. CE, UKCA), and registration with national laser safety authorities.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Upon delivery, installation must follow manufacturer guidelines and local safety regulations. The equipment should be set up in a controlled environment with restricted access, proper ventilation (to manage fumes from ablated materials), and fire suppression systems. A Laser Controlled Area must be established, marked with warning signs, and equipped with interlocks and emergency stop mechanisms. Operators must undergo certified laser safety training, and a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) should be designated where required by regulation (e.g. OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK).
Operational Safety and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Safe operation of laser rust removal equipment demands strict adherence to safety protocols. Operators must wear appropriate PPE, including laser safety goggles with optical density (OD) rated for the specific laser wavelength (commonly 1064 nm for fiber lasers), protective clothing, and respiratory protection if fumes are generated. Enclosures or fume extraction systems should be used to minimize airborne particulates. Regular equipment inspections and maintenance logs are required to ensure ongoing compliance and performance.
Waste and Environmental Compliance
Laser rust removal produces particulate waste, including metal oxides and surface contaminants. This waste may be classified as hazardous depending on substrate composition (e.g. lead-based paint, cadmium coatings). Operators must comply with environmental regulations (e.g. EPA in the U.S., REACH in the EU) for collection, handling, and disposal of residue. Use of HEPA-filtered vacuum systems and proper waste segregation is essential. Documentation of waste disposal through licensed facilities should be maintained for audit purposes.
Training and Documentation Requirements
Compliance requires comprehensive documentation, including equipment manuals, safety data sheets, maintenance logs, operator training records, and risk assessments. All personnel must complete laser safety training programs recognized by national standards (e.g. ANSI Z136.1 in the U.S.). Training should cover hazards, emergency procedures, PPE use, and equipment operation. Records must be retained and updated regularly to demonstrate due diligence during regulatory inspections.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Successful deployment of laser rust removal equipment relies on integrating logistics planning with regulatory compliance at every stage—from procurement and shipping to operation and disposal. Key best practices include early engagement with regulatory bodies, use of certified suppliers, continuous staff training, and implementation of a site-specific laser safety program. By following this guide, organizations can ensure legal compliance, operational safety, and environmental responsibility when using laser cleaning technology.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Rust Removal Equipment
Sourcing laser rust removal equipment represents a forward-thinking investment in advanced, sustainable, and efficient surface cleaning technology. As industries increasingly prioritize precision, environmental compliance, and operational safety, laser rust removal offers significant advantages over traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical treatments—eliminating media waste, reducing secondary contamination, and minimizing operator exposure to hazardous materials.
When sourcing this equipment, key considerations include laser power, pulse frequency, portability, cooling systems, safety features, and after-sales support. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on technical reliability, industry experience, training offerings, and warranty terms. Additionally, aligning the equipment specifications with specific application needs—such as industrial maintenance, heritage restoration, or automotive refurbishment—ensures optimal performance and return on investment.
While the initial cost of laser rust removal systems may be higher than conventional tools, the long-term savings in labor, media, disposal, and reduced downtime justify the investment. Furthermore, the technology supports compliance with stringent environmental regulations and enhances workplace safety.
In conclusion, sourcing laser rust removal equipment should be approached strategically, focusing on quality, support, and application fit. With the right supplier and system, organizations can achieve superior cleaning results, improve sustainability, and gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.