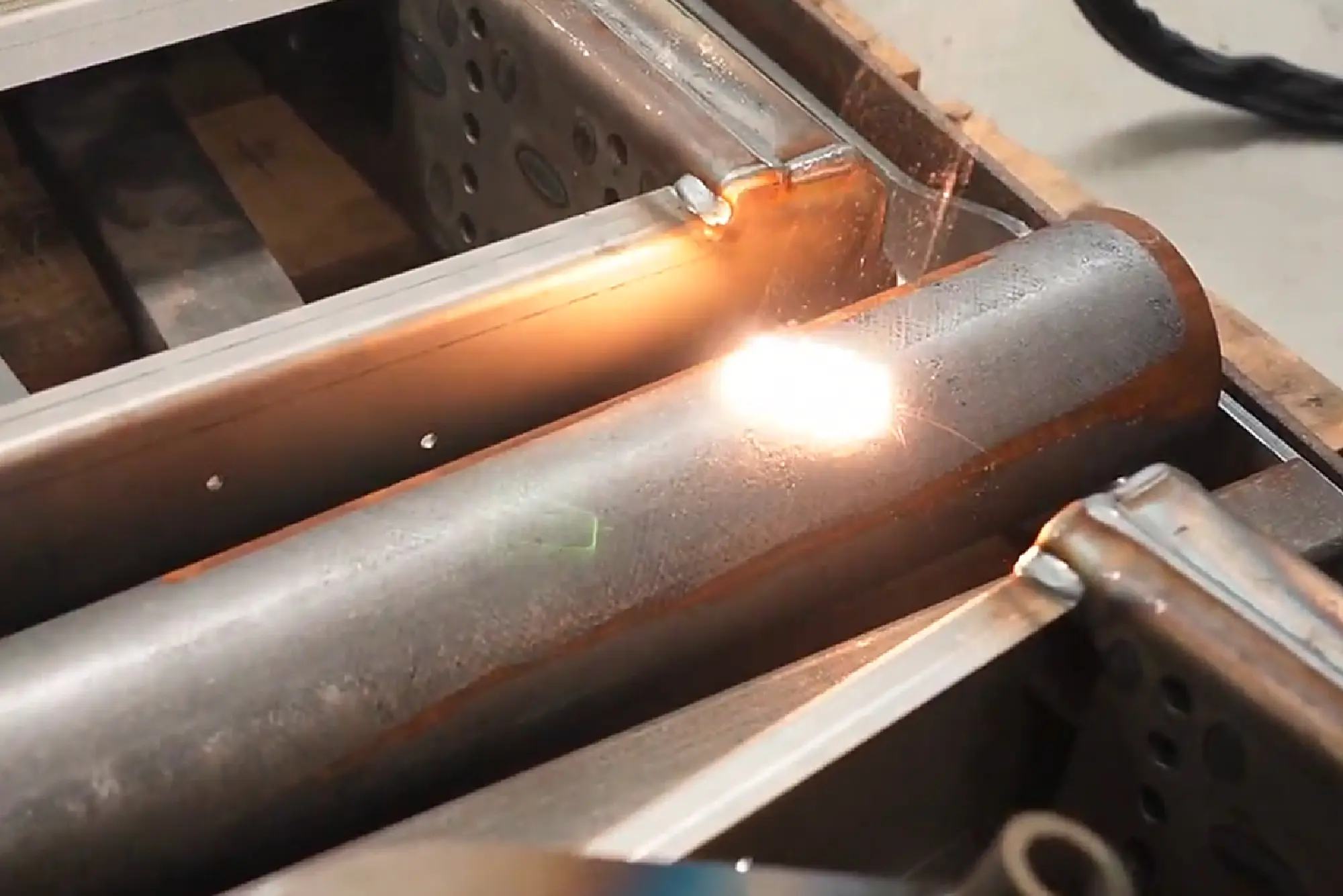
The global laser rust removal market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision cleaning solutions in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the industrial laser cleaning equipment market was valued at USD 590.4 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1,148.6 million by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 11.8% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the shift toward eco-friendly, non-abrasive cleaning methods that reduce waste and operational downtime. As manufacturers seek efficient, sustainable alternatives to traditional rust removal techniques like sandblasting and chemical treatments, laser-based solutions are gaining prominence. This growing adoption has led to a surge in innovation and competition among key players globally. The following list highlights the top 10 laser rust removal business manufacturers leading this transformation through advanced technology, scalable solutions, and strategic market positioning.
Top 10 Laser Rust Removal Business Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: With over 35 years of expertise in surface treatment and more than 450 systems installed worldwide, P-Laser is at the forefront of industrial laser cleaning ……
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#4 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#5 Top Laser Rust Cleaning Machines for Efficient Rust Removal
Website: woodrowscientific.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics brings a comprehensive lineup of industrial laser rust cleaning machines for 2025, covering everything from quick site repairs to ……
#6 Laser Rust Removal
Website: adapt-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning offers a safe and much faster way to remove rust from metal without the need of any harsh media or chemicals. Learn more….
#7 Laser Cleaning vs. Dustless Blasting
Website: dustlessblasting.com
Key Highlights: Rust Removal and Metal Cleaning: Laser rust removal is faster and more efficient than many traditional methods, eliminating the need for harsh chemicals and ……
#8 ZAC Laser Machine
Founded: 2004
Website: zaclaser.com
Key Highlights: ZAC laser is the professional manufacture since 2004 which sell many laser machines such as laser rust removal-laser cleaning machine, laser engraver-laser ……
#9 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#10 Laser Rust Removal Guide
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A practical guide for professionals and entrepreneurs using PULSAR Laser systems to remove rust safely, efficiently and without abrasives….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Rust Removal Business
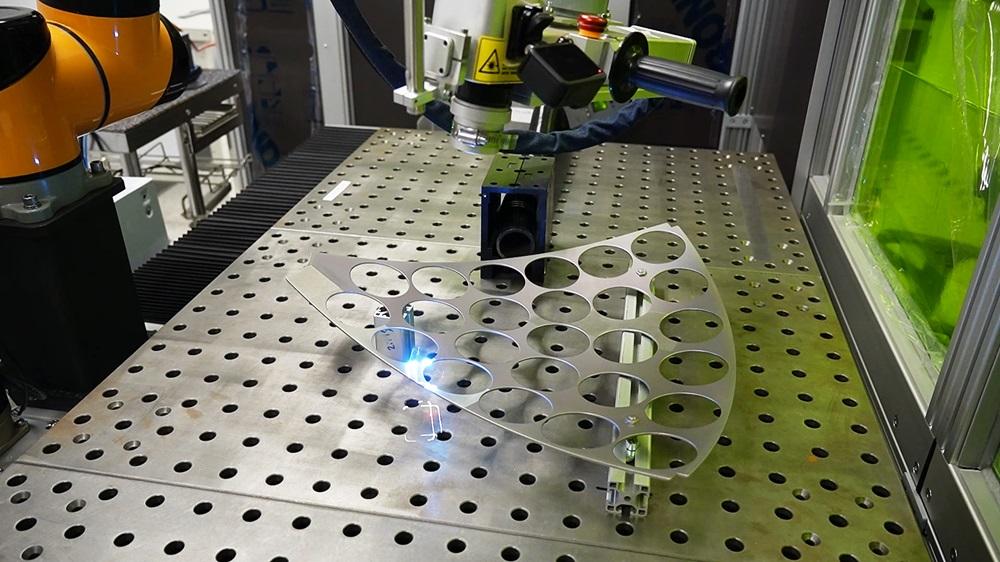

H2: Market Trends Shaping the 2026 Laser Rust Removal Business
The laser rust removal market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing environmental consciousness, and expanding industrial demand. Here’s a detailed analysis of key trends expected to shape the business landscape:
1. Accelerated Adoption Across Key Industries
By 2026, laser rust removal is projected to see widespread adoption in sectors such as automotive restoration, aerospace maintenance, maritime, and heritage preservation. The technology’s precision, non-abrasive nature, and ability to selectively remove rust without damaging underlying substrates make it ideal for high-value applications. The automotive and defense sectors, in particular, will likely increase investment in laser systems for fleet maintenance and corrosion control.
2. Technological Innovation and System Miniaturization
Laser systems are expected to become more compact, user-friendly, and energy-efficient by 2026. Advancements in fiber laser technology will lead to portable and handheld devices, enabling on-site rust removal in remote or hard-to-reach locations. Integration with robotics and automation—such as robotic arms for large-scale industrial use—will improve consistency and reduce labor costs, especially in manufacturing and shipbuilding environments.
3. Strong Push for Eco-Friendly Surface Preparation
Environmental regulations are tightening globally, and traditional rust removal methods (e.g., sandblasting, chemical strippers) face increasing scrutiny due to hazardous waste and airborne pollutants. Laser rust removal, which produces no secondary waste and requires no chemicals, aligns with sustainability goals. By 2026, companies will increasingly adopt laser solutions to comply with ESG standards and reduce their environmental footprint, bolstering market growth.
4. Cost Reduction and Improved ROI
While initial investment in laser equipment remains high, costs are expected to decline due to mass production, competition, and technological maturation. By 2026, the total cost of ownership will become more favorable compared to conventional methods, especially when factoring in reduced labor, waste disposal, and rework costs. This improved return on investment (ROI) will make the technology accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
5. Expansion of Service-Based Business Models
Alongside equipment sales, there will be a growing market for laser rust removal as a service (LRaaS). Mobile service providers offering on-demand, on-site rust removal will emerge as a dominant trend. This model lowers the entry barrier for industries reluctant to invest in capital equipment and allows flexible scaling—particularly appealing to restoration shops, infrastructure maintenance firms, and construction companies.
6. Integration with Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
By 2026, laser rust removal systems will increasingly incorporate IoT sensors, AI-driven diagnostics, and real-time monitoring. These smart features will enable predictive maintenance, process optimization, and data logging for quality assurance—critical for industries under strict regulatory oversight. Integration with digital twins and production line automation will further enhance efficiency and traceability.
7. Regulatory and Safety Standardization
As adoption grows, regulatory bodies and industry consortia are expected to establish standardized safety protocols and operational guidelines for laser rust removal. Clearer standards will boost user confidence, streamline training, and support global market expansion, especially in regions like Europe and North America where safety compliance is paramount.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser rust removal business will transition from a niche technology to a mainstream solution in surface preparation. Driven by sustainability mandates, technological progress, and economic advantages, the market will experience robust growth. Companies that invest in innovation, service diversification, and compliance will be best positioned to capitalize on this evolving landscape.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing a Laser Rust Removal Business: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a laser rust removal business—whether through acquisition, partnership, or technology licensing—presents significant opportunities in industrial cleaning and surface preparation. However, without due diligence, buyers or investors may fall into critical traps related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these pitfalls is essential to mitigate risk and ensure long-term success.
Inadequate Assessment of Laser System Quality and Performance
One of the most frequent pitfalls is failing to thoroughly evaluate the actual performance and reliability of the laser rust removal equipment. Many suppliers overstate capabilities such as cleaning speed, power efficiency, or compatibility with various metal substrates. Buyers may discover post-purchase that the systems do not perform consistently in real-world industrial environments, leading to customer dissatisfaction and reputational damage.
Key concerns include:
– Lack of standardized testing: Absence of third-party validation or industry benchmarking.
– Component quality: Use of low-grade optics, diodes, or cooling systems that degrade rapidly.
– Poor integration: Systems not properly designed for integration into existing production lines.
Without hands-on testing under operational conditions, the true quality of the technology remains uncertain.
Overlooking Technical Support and Serviceability
Even high-performing laser systems require maintenance, calibration, and technical support. A common mistake is neglecting to evaluate the seller’s after-sales infrastructure. If the sourcing target lacks a robust support network—especially in your region—downtime can become frequent and costly.
Red flags include:
– Limited availability of spare parts.
– Inadequate training programs for operators.
– No remote diagnostics or service agreements.
This pitfall directly impacts customer retention and operational continuity.
Failure to Verify Intellectual Property Ownership
Intellectual property forms the foundation of competitive advantage in laser technology. A major risk in sourcing is assuming that the business legitimately owns or has clear rights to the technology it uses.
Common IP-related pitfalls include:
– Unsecured patents: The technology may not be patented, or existing patents could be pending, expired, or limited in geographical scope.
– Third-party dependencies: Critical components (e.g., laser sources, control software) may be protected by third-party IP, restricting modification or resale.
– Infringement risks: The system might unknowingly infringe on existing patents, exposing the new owner to litigation.
Conducting a comprehensive IP audit—covering patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets—is essential before acquisition.
Ambiguous or Incomplete Technology Transfer Agreements
When sourcing a business involving proprietary technology, the transfer of know-how is often as important as the physical assets. Poorly structured agreements may omit critical details like source code access, design schematics, or manufacturing processes.
This can result in:
– Inability to modify or improve the product.
– Challenges in scaling production.
– Dependence on former employees or the seller for technical knowledge.
Ensure all IP and technical documentation is explicitly included in the transfer terms.
Ignoring Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Laser systems are subject to strict safety and regulatory standards (e.g., FDA, IEC, CE). A sourced business may claim compliance, but without verification, there’s a risk of inheriting non-compliant products. This can lead to product recalls, fines, or market access restrictions.
Due diligence should confirm:
– Valid certifications for target markets.
– Proper laser classification and safety interlocks.
– Compliance with environmental and export controls.
Neglecting this aspect can derail commercialization efforts.
Conclusion
Sourcing a laser rust removal business offers high growth potential, but it demands rigorous scrutiny of both technical quality and IP integrity. Skipping deep validation of system performance, support capabilities, and legal ownership can lead to costly setbacks. By proactively addressing these common pitfalls, buyers can secure a reliable, defensible, and scalable technology platform.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for a Laser Rust Removal Business
Operating a laser rust removal business involves more than just advanced technology—it requires meticulous logistics planning and strict adherence to regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations.
Equipment Logistics and Transportation
Transporting high-powered laser systems requires careful planning to maintain equipment integrity and ensure safety. Use shock-absorbing packaging and climate-controlled vehicles to protect sensitive components. Secure all lasers in transport using lock-down mechanisms to prevent movement. Maintain an equipment tracking system with serial numbers, service history, and calibration records. For mobile operations, equip service vehicles with proper ventilation, power inverters, and safety signage.
Facility and Workspace Requirements
If operating from a fixed facility, designate a controlled laser area with restricted access, appropriate signage (e.g., “Laser in Use”), and interlocks on entry points. Ensure adequate space for equipment setup, ventilation, and safe operator movement. Work areas must comply with ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers) standards, including controlled beam paths and non-reflective surfaces. Include a dedicated zone for personal protective equipment (PPE) storage and pre-operation checklists.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Adhere to federal, state, and local regulations governing laser use. In the U.S., comply with the FDA/CDRH (Center for Devices and Radiological Health) regulations for laser products (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11). Register Class 3B and Class 4 lasers with the appropriate regulatory body. Implement a Laser Safety Program with a designated Laser Safety Officer (LSO). Conduct regular safety audits and maintain documentation of safety training, incident reports, and equipment maintenance.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Protocols
All personnel must wear laser safety eyewear rated for the specific wavelength and power output of the laser in use. Additional PPE includes flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection when fumes or particulates are generated. Provide fit-testing for respirators and maintain an on-site PPE inventory with scheduled replacement timelines. Train staff on proper use, inspection, and storage of all safety gear.
Fume and Particulate Management
Laser rust removal generates metallic fumes and airborne particles, requiring effective air filtration. Use high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) fume extractors positioned close to the work area. Conduct air quality monitoring to ensure compliance with OSHA permissible exposure limits (PELs) for metals like iron oxide and chromium. Document filter change schedules and disposal procedures for contaminated filters in accordance with hazardous waste regulations.
Waste Disposal and Environmental Compliance
Collected rust residue and filter waste may be classified as hazardous depending on substrate materials (e.g., lead-based paint, cadmium-coated metals). Perform waste characterization testing as needed and follow EPA and local regulations for hazardous waste handling, labeling, storage, and disposal. Maintain manifests and disposal records for at least three years. For non-hazardous waste, recycle metal particulates where possible through certified scrap metal processors.
Client Site Assessments and Risk Mitigation
Prior to on-site work, conduct a thorough site survey to evaluate access, power supply, ventilation, and surrounding hazards. Assess materials being treated to identify potential toxic coatings. Develop a site-specific safety plan including emergency procedures, fire prevention measures, and communication protocols. Obtain necessary permits or notifications required by the client or local authorities.
Training and Certification Requirements
Ensure all laser operators complete certified laser safety training (e.g., LSO or ANSI-accredited programs). Maintain training records and require refresher courses annually. Train staff in emergency shutdown procedures, first aid for laser exposure, and fire response. Document competency assessments and assign authorized personnel only to operate equipment.
Insurance and Liability Coverage
Obtain comprehensive business insurance, including general liability, workers’ compensation, and equipment coverage. Add specific endorsements for laser operations and hazardous material handling. Verify that contracts with clients include indemnification clauses and require site safety coordination. Regularly review and update policies to reflect business growth and regulatory changes.
Recordkeeping and Documentation
Maintain a compliance binder or digital archive containing: equipment manuals, calibration certificates, laser registration documents, employee training records, safety inspection logs, waste disposal receipts, and incident reports. Implement a document retention policy aligned with legal requirements (typically 3–7 years). Use digital tracking tools to automate reminders for renewals, inspections, and training.
By integrating robust logistics planning with strict compliance protocols, your laser rust removal business can operate safely, efficiently, and within full legal standing—building trust with clients and regulators alike.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Rust Removal Business
Sourcing a laser rust removal business presents a compelling opportunity for entrepreneurs and industrial service providers seeking to adopt advanced, eco-friendly technologies. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, efficiency, and precision, traditional rust removal methods like sandblasting and chemical treatments are being phased out in favor of cleaner alternatives. Laser rust removal offers significant advantages, including non-abrasive surface cleaning, minimal waste generation, reduced environmental impact, and compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
By sourcing reliable suppliers of laser cleaning equipment and building expertise through training and technical partnerships, businesses can establish a competitive edge in sectors such as automotive restoration, marine maintenance, aerospace, and heritage conservation. Although the initial investment in laser technology is higher than conventional methods, the long-term cost savings, durability, and operational efficiency justify the outlay.
Moreover, the growing global demand for sustainable industrial solutions creates a favorable market environment. Success in this niche will depend on strategic sourcing of high-quality, scalable laser systems, continuous technician training, and effective marketing that highlights the environmental and economic benefits.
In conclusion, sourcing and launching a laser rust removal business is a forward-thinking venture aligned with the future of industrial maintenance. With proper planning, investment, and commitment to innovation, this business model can achieve both profitability and sustainability in an evolving market landscape.