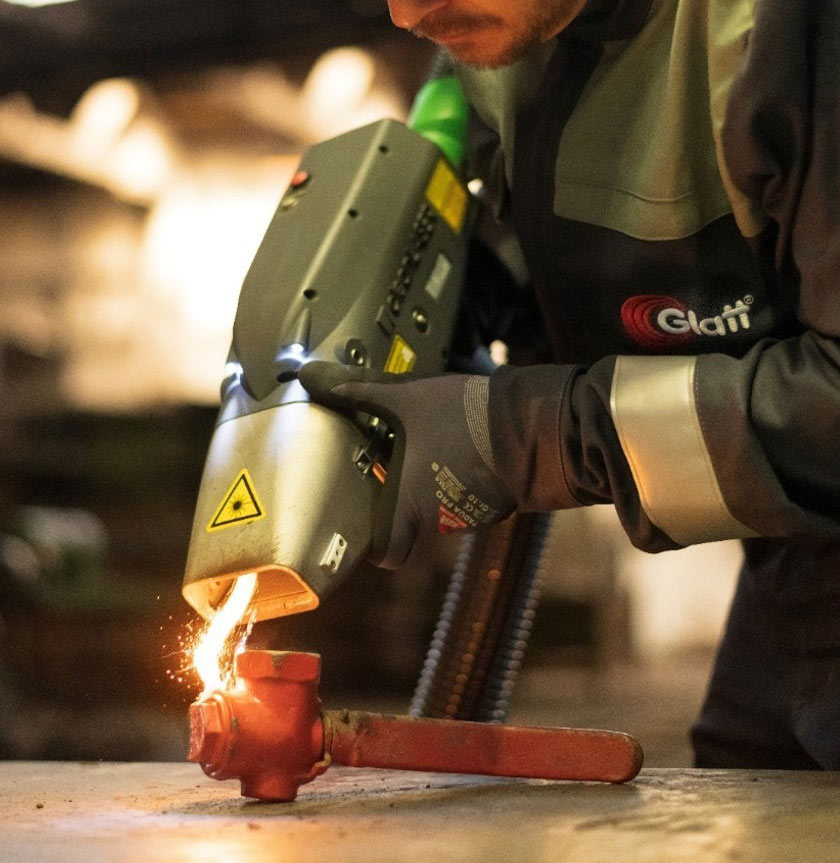
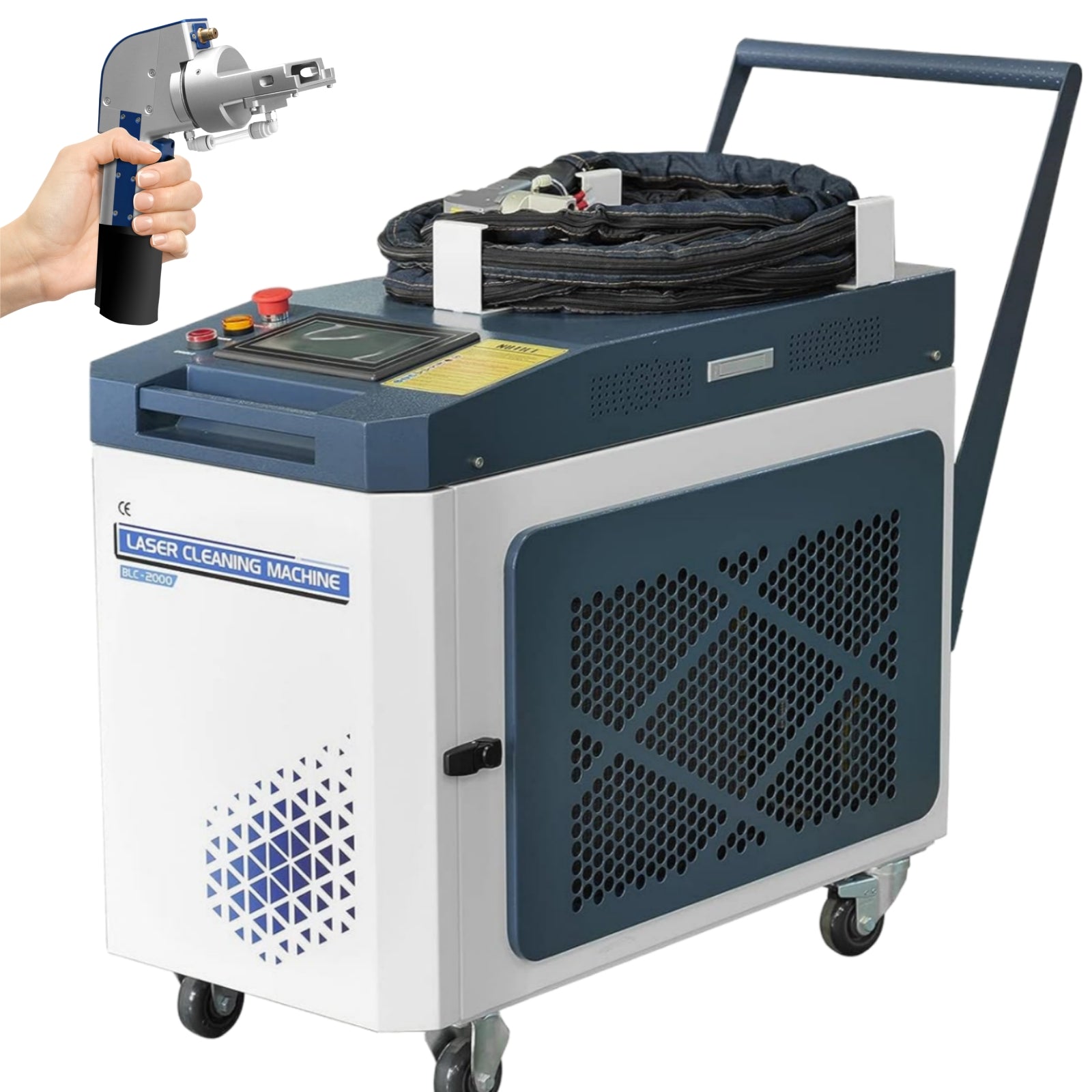
The global market for laser-based surface cleaning technologies has experienced robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-driven alternatives to traditional rust and paint removal methods. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cleaning equipment market was valued at USD 444.1 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by stringent environmental regulations, rising adoption in automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation industries, and the superior efficiency of laser ablation over sandblasting and chemical stripping. As manufacturers prioritize non-abrasive, residue-free surface preparation, a wave of innovation has emerged among industrial laser system developers. Based on technological advancements, market presence, and application performance, the following eight manufacturers stand out in delivering high-efficiency laser solutions for rust and paint removal.
Top 8 Laser Removes Rust And Paint Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FOX P CL – laser for removing rust
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: An innovative laser cleaner that revolutionizes the maintenance and restoration of large vehicles and industrial equipment….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: P-Laser: How does laser cleaning work? QF-2000 Laser removes almost any other kind of contamination, including grease, rust….
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: “Laser Photonics technology has really simplified our work, facilitating the cleaning of rust and the removal of old paint and contaminants. The technology ……
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: Our laser systems are primarily in operation with mold and tool cleaning, paint stripping and decoating as well as cleaning and modification of metallic ……
#5 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: In stockXING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#6 Laser Cleaning
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Elevate production quality with laser cleaning technology: remove dust, rust, and imperfections efficiently, reducing costs and improving precision….
#7 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#8 Laser Coating Removal Solutions for Industry
Website: surclean.com
Key Highlights: SurClean manufactures laser coating removal and surface preparation equipment that is precise, safe and clean. … removing rust, dirt, paint and other coatings….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Removes Rust And Paint

2026 Market Trends for Laser Rust and Paint Removal
The global market for laser-based rust and paint removal is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by technological advancements, environmental regulations, and increasing demand across key industries such as automotive, aerospace, maritime, and industrial maintenance. This analysis explores the key trends shaping the laser surface cleaning industry in the coming years.
Rising Demand for Eco-Friendly Surface Preparation
One of the most influential trends in the 2026 market landscape is the shift toward environmentally sustainable methods of surface cleaning. Traditional techniques like sandblasting, chemical stripping, and high-pressure water blasting generate hazardous waste, airborne particulates, and secondary contamination. In contrast, laser ablation is a non-contact, dry process that removes rust, paint, and coatings without chemicals or abrasive media. With tightening environmental regulations—especially in Europe and North America—industries are increasingly adopting laser cleaning as a compliant and eco-friendly alternative.
Advancements in Portable and High-Power Laser Systems
By 2026, laser cleaning technology is expected to become more accessible due to improvements in portability and power efficiency. Manufacturers are developing compact, handheld, and robotic-integrated laser systems that enable on-site maintenance in hard-to-reach areas. Innovations in fiber laser technology have led to higher power outputs (up to 3,000W and beyond), faster processing speeds, and improved beam control. These advancements reduce operational time and increase precision, making laser rust and paint removal more cost-competitive with conventional methods.
Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics Integration
The integration of laser cleaning systems with industrial robots and automated production lines is a key growth driver. In sectors like automotive manufacturing and aircraft maintenance, robotic laser systems offer repeatable, high-precision cleaning with minimal human intervention. By 2026, smart laser systems equipped with AI-driven vision and feedback control will be able to detect rust levels and adjust parameters in real time, optimizing cleaning efficiency and material preservation. This trend supports Industry 4.0 initiatives and boosts adoption in high-volume industrial settings.
Expansion in Maritime and Offshore Applications
The maritime industry is expected to be a major adopter of laser cleaning technology by 2026. Ship hulls, offshore platforms, and port infrastructure require frequent maintenance to remove rust and old paint. Laser systems offer a safer, cleaner alternative to sandblasting in confined and sensitive environments. Their ability to selectively remove coatings without damaging the underlying steel substrate makes them ideal for preserving structural integrity. With increasing focus on reducing downtime and improving worker safety, shipping companies and naval fleets are investing in laser cleaning solutions.
Increasing Adoption in Heritage and Infrastructure Restoration
Cultural heritage preservation and infrastructure maintenance are emerging as niche but growing markets for laser cleaning. Historical buildings, bridges, and monuments often require delicate restoration where traditional methods risk damage. Laser technology allows for precise control over cleaning depth, making it suitable for sensitive materials like stone, brick, and aged metal. By 2026, municipal governments and conservation agencies are expected to allocate more funding toward laser-based restoration projects, further expanding market reach.
Cost Reduction and Improved ROI
While the initial investment in laser cleaning systems remains higher than traditional methods, total cost of ownership is improving. By 2026, declining laser component costs, longer system lifespans, and reduced operational expenses (e.g., no need for consumables or waste disposal) are enhancing return on investment (ROI). As more case studies demonstrate long-term savings and productivity gains, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are expected to enter the market, broadening the customer base.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region for laser rust and paint removal, driven by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing and green technologies are accelerating adoption. Meanwhile, North America and Europe maintain strong market positions due to stringent environmental standards and early adoption of automation. Collaborations between laser manufacturers and industry stakeholders are expected to fuel regional growth through customized solutions and training programs.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser rust and paint removal market will be characterized by technological maturity, wider industrial adoption, and strong alignment with sustainability goals. As laser systems become more efficient, affordable, and intelligent, they are set to replace traditional cleaning methods across multiple sectors. Companies that invest in R&D, automation integration, and environmental compliance will be well-positioned to capitalize on this transformative trend.
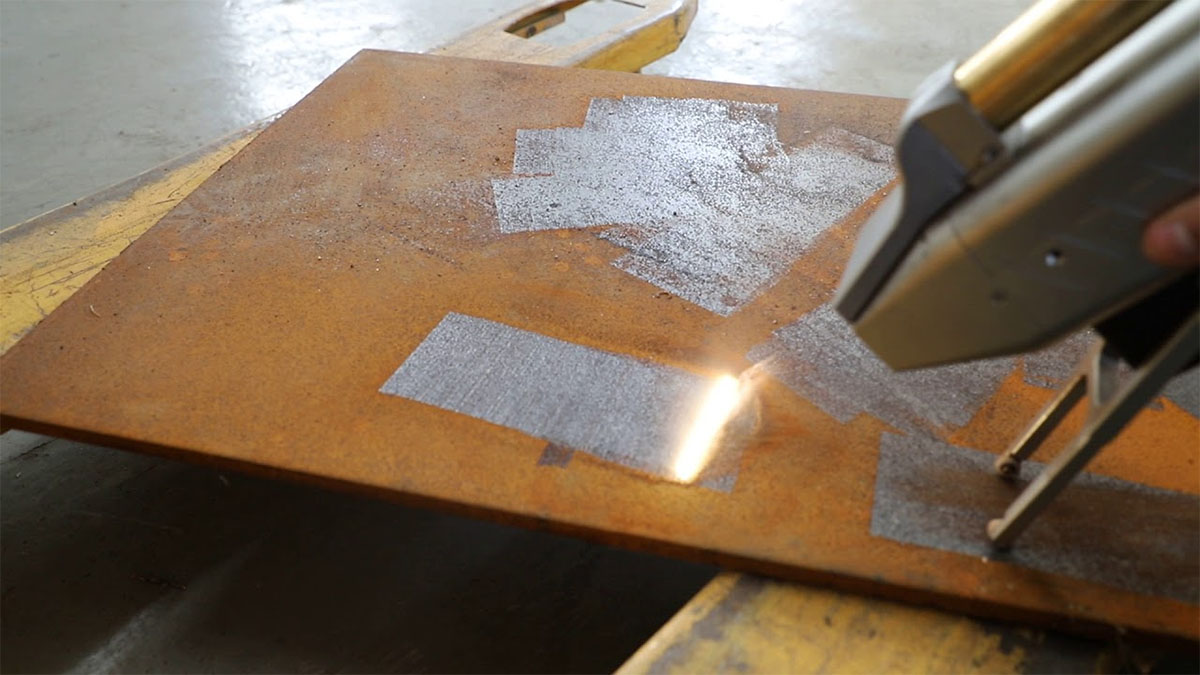

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Rust and Paint Removal Systems (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing laser-based rust and paint removal systems offers a modern, eco-friendly alternative to traditional blasting methods. However, without careful due diligence, buyers risk acquiring substandard equipment or inadvertently infringing on intellectual property (IP). Below are key pitfalls related to quality and IP that organizations should avoid.
Poor Build Quality and Unverified Performance Claims
Many suppliers, especially newer entrants or low-cost manufacturers, exaggerate cleaning speed, power, or reliability. Units may use under-spec components (e.g., low-duty-cycle lasers, weak cooling systems), leading to frequent downtime or failure in industrial environments. Always validate performance claims with third-party test reports or on-site demonstrations.
Lack of Safety Certifications and Standards Compliance
Reputable laser systems should comply with international safety standards such as IEC 60825 (laser safety) and CE or UL certifications. Sourcing from vendors without proper certification exposes users to safety risks and potential regulatory penalties, particularly in highly regulated industries like aerospace or automotive.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality systems require maintenance. Some suppliers, particularly those based overseas, offer limited technical support, training, or spare parts logistics. This can lead to prolonged downtimes. Ensure the supplier has a local service network or guarantees response times and part availability.
Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Using or distributing laser cleaning equipment that infringes on patented technologies (e.g., beam delivery systems, control algorithms, or safety interlocks) can result in legal action, import bans, or forced equipment seizure. Always request documentation confirming the supplier’s freedom to operate and verify patent landscapes in your region.
Copycat Systems with Hidden Design Flaws
Some manufacturers reverse-engineer successful models without understanding the underlying engineering. These clones may appear identical but suffer from thermal management issues, poor beam quality, or software instability. Conduct technical audits or request detailed component sourcing information to differentiate genuine innovation from imitation.
Insufficient IP Protection for Custom Integrations
If you’re modifying or integrating the laser system into your production line, ensure that any custom developments are protected and that supplier contracts clearly define ownership of improvements. Ambiguity can lead to disputes or loss of proprietary advantages.
Conclusion
Sourcing laser rust and paint removal systems requires balancing cost, performance, and legal compliance. Prioritize suppliers with proven track records, verifiable quality certifications, and transparent IP status. Conduct thorough due diligence—including site visits, reference checks, and IP audits—to avoid costly mistakes and ensure long-term operational success.
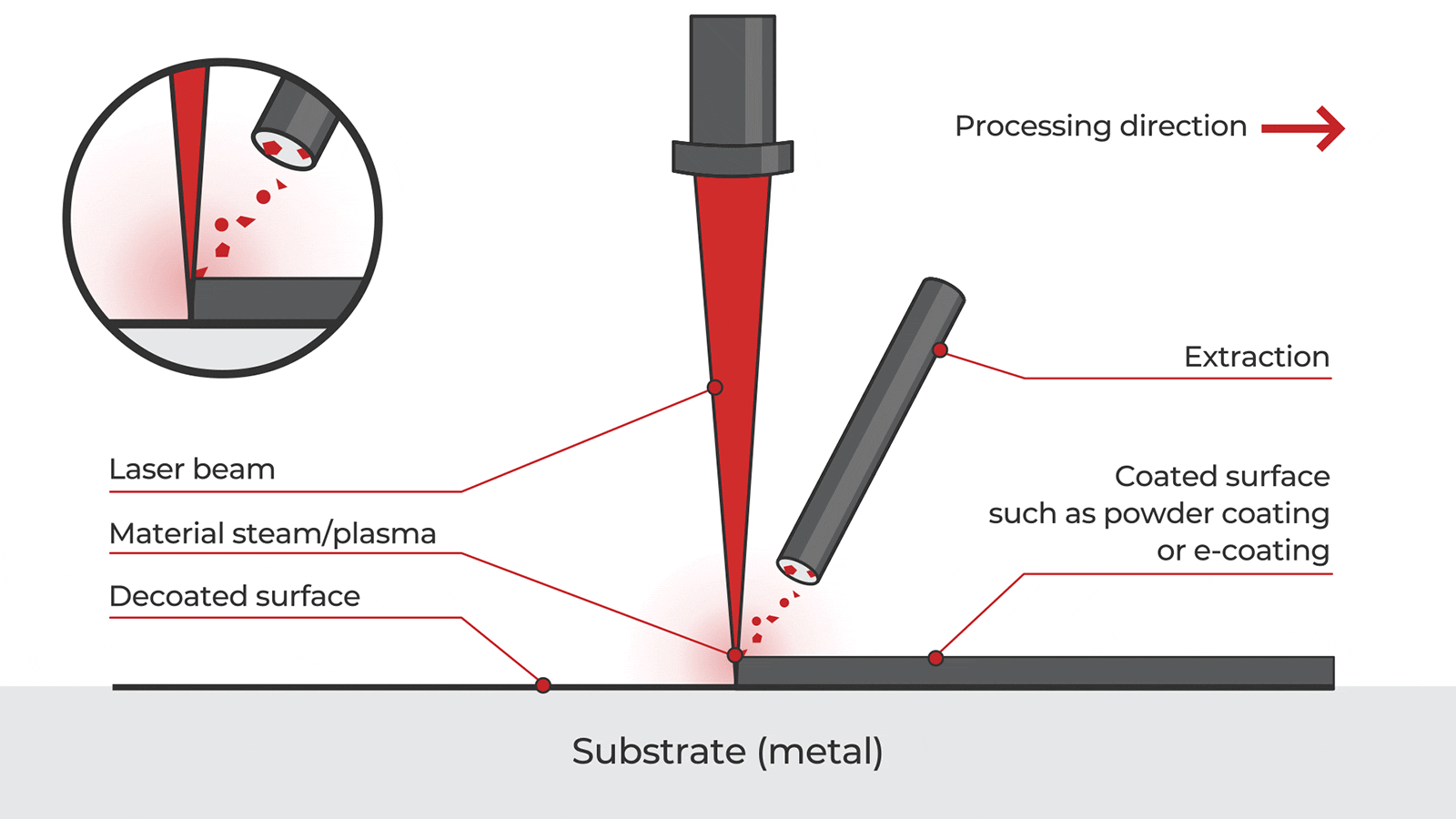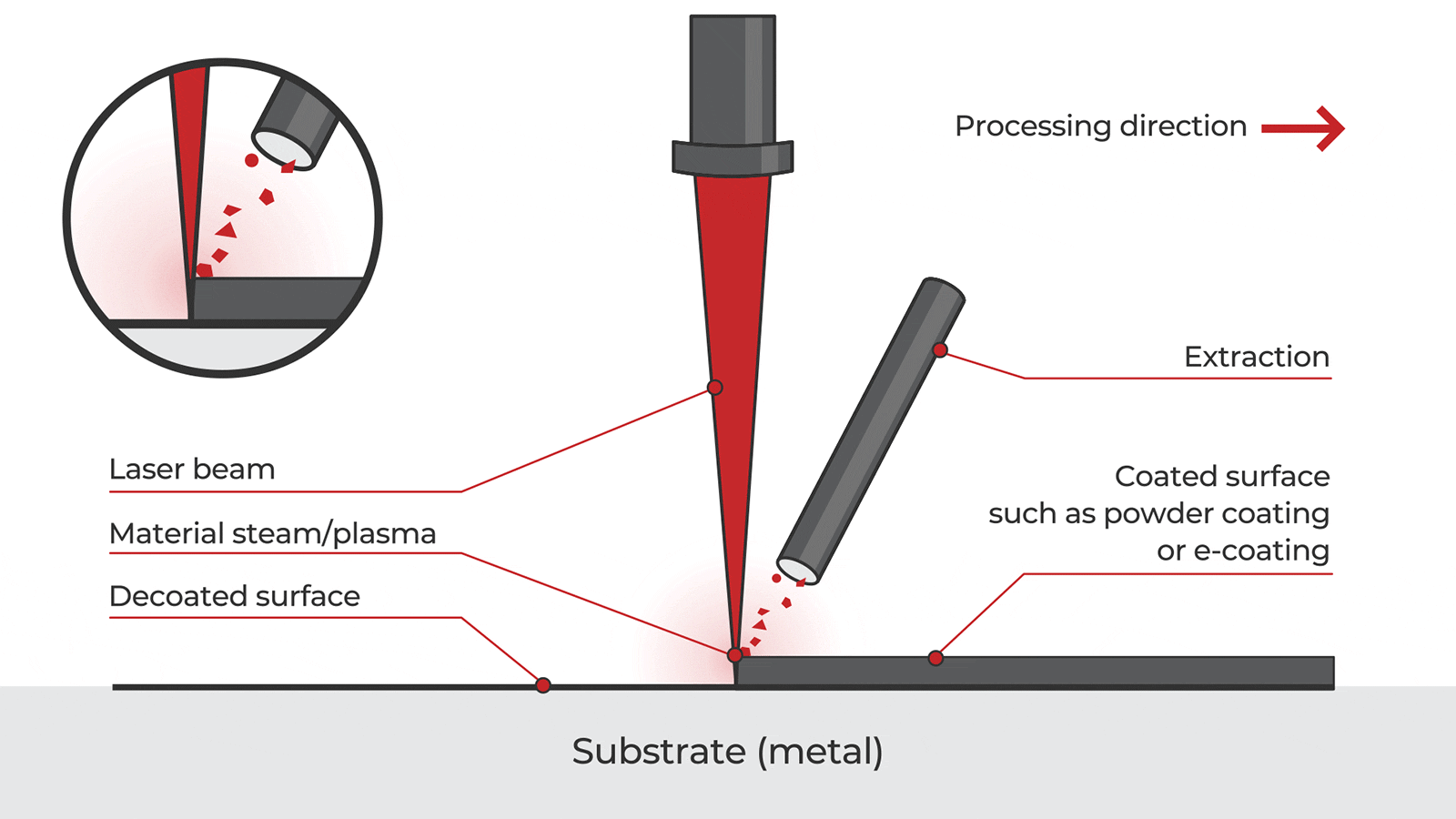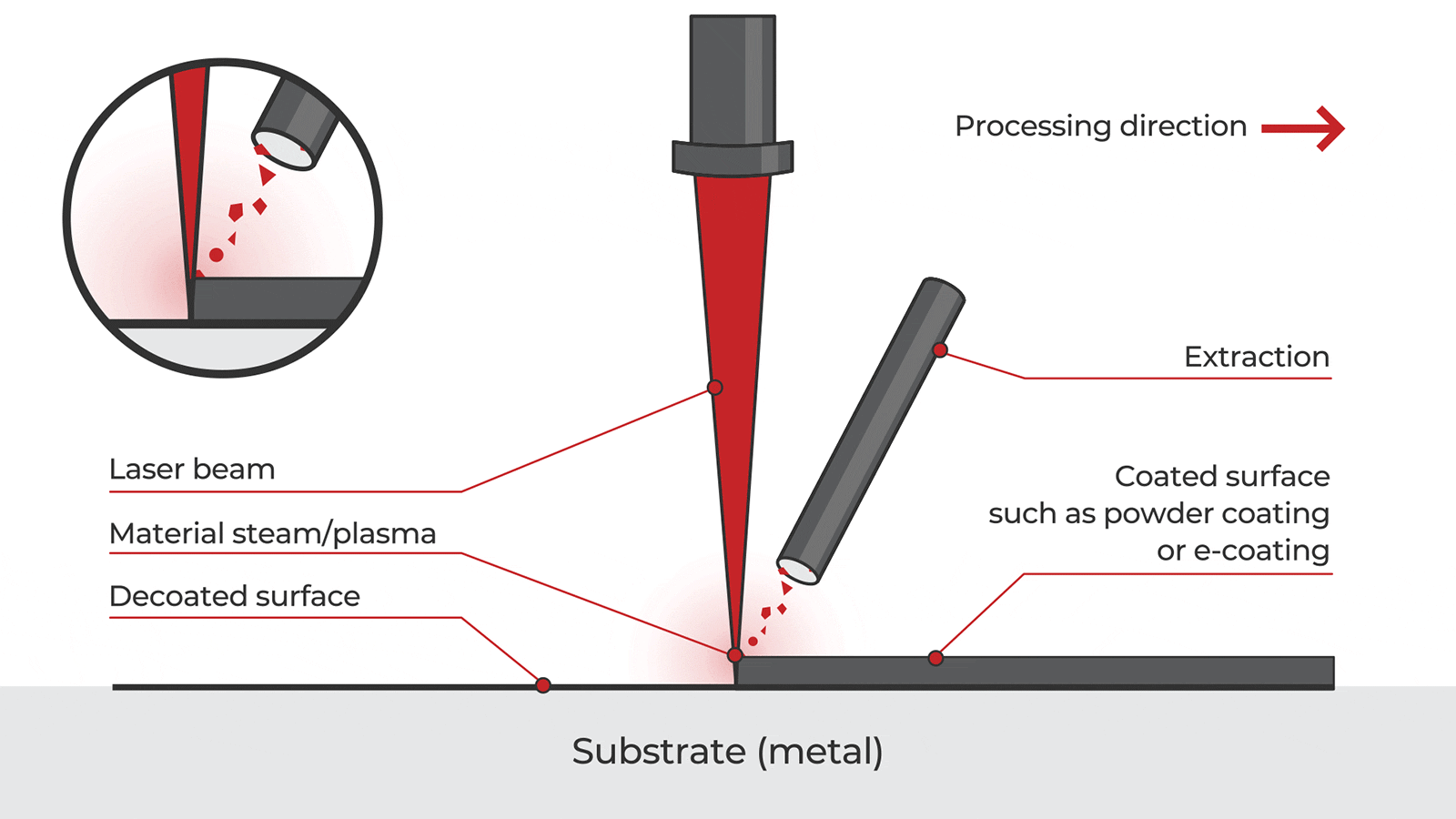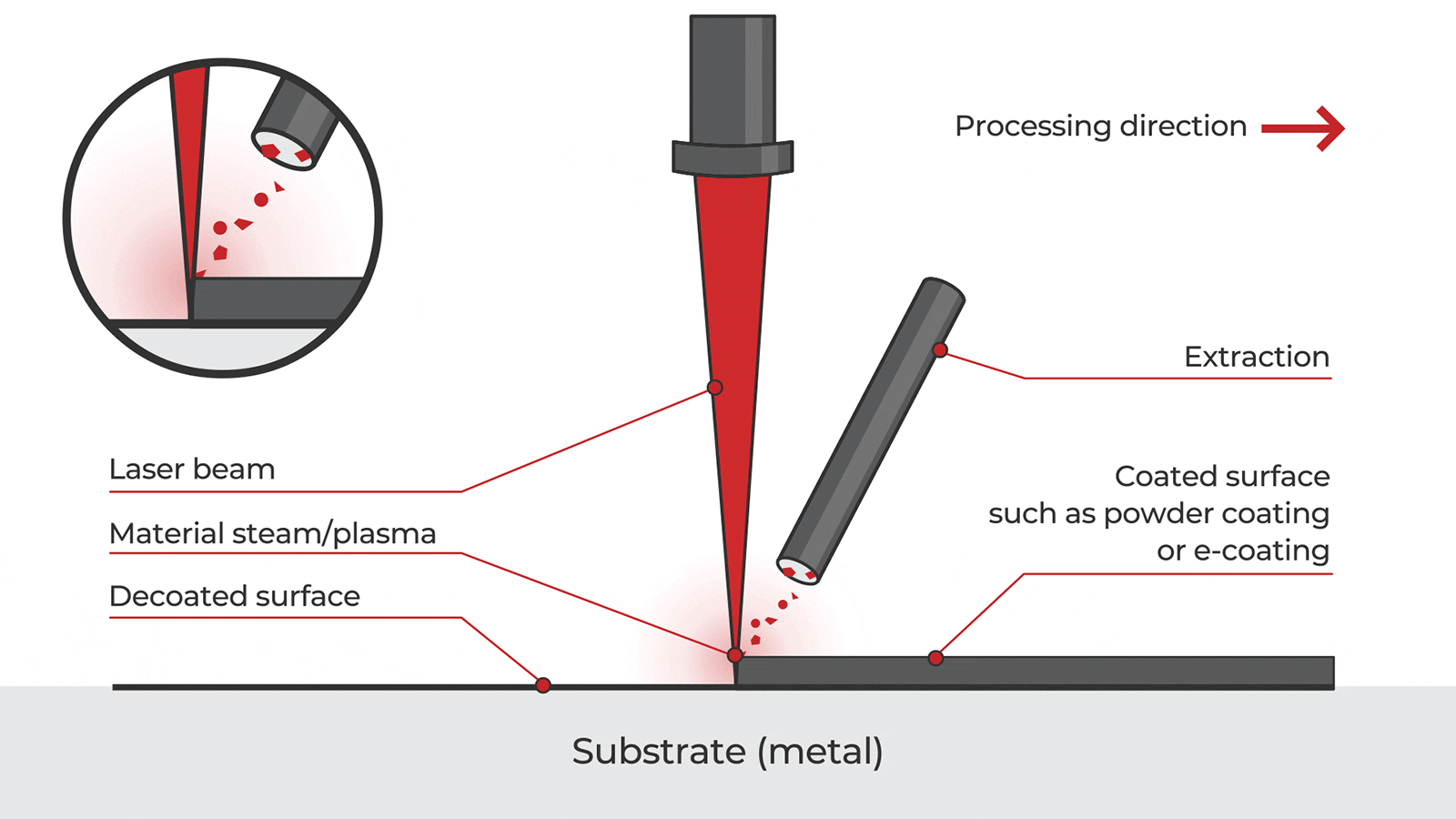
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Rust and Paint Removal Equipment
Overview of Laser Rust and Paint Removal Technology
Laser rust and paint removal systems use high-intensity pulsed lasers to ablate contaminants such as rust, paint, oxides, and coatings from metal surfaces without damaging the underlying substrate. This non-contact, chemical-free method is increasingly adopted in industries like automotive, aerospace, maritime, and manufacturing due to its environmental and safety advantages over traditional blasting or chemical stripping methods.
Regulatory Compliance Considerations
Laser cleaning devices are classified as Class 4 lasers under international safety standards (IEC 60825-1), requiring strict adherence to safety and operational regulations. Key compliance areas include:
- Laser Safety Standards (IEC 60825 / ANSI Z136.1): Equipment must be registered and labeled appropriately. Operators require laser safety training and personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles specific to the laser wavelength (typically fiber lasers at 1064 nm).
- Workplace Safety Regulations (OSHA, EU-OSHA): Employers must conduct risk assessments, implement engineering controls (e.g., enclosures, interlocks), and establish controlled access zones during laser operation.
- Environmental Regulations (EPA, REACH, RoHS): Unlike chemical or abrasive methods, laser cleaning produces minimal waste—primarily particulate matter. However, fumes and particulates generated must be captured via HEPA filtration systems to comply with air quality standards and prevent worker exposure to hazardous materials (e.g., lead, chromium, cadmium from removed coatings).
- Waste Disposal: Collected particulate matter may be classified as hazardous waste depending on substrate and coating composition. Conduct waste characterization testing and follow local disposal protocols (e.g., EPA 40 CFR, EU Waste Framework Directive).
Transportation and Shipping Logistics
Laser cleaning systems vary in size from portable handheld units to large automated workstations. Proper logistics planning is essential:
- Packaging: Use shock-absorbent, moisture-resistant packaging. Secure optical components and laser sources with anti-vibration mounts. Include desiccants in sealed containers to prevent condensation.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Equipment – Handle with Care.” Include compliance labels such as IEC 60825 warning symbols if applicable.
- Hazard Classification: While the laser itself is not hazardous when powered off, battery-powered units may contain lithium-ion batteries subject to IATA/IMDG regulations for air/sea freight. Comply with UN 3481 or UN 3091 requirements, including state-of-charge limits, packaging, and documentation.
- Customs and Import/Export: Declare equipment under correct HS codes (e.g., 8515.80 for laser machinery). Verify export control regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.) as high-power lasers may be subject to restrictions. Provide technical specifications and CE/FCC certification documents as needed.
Installation and On-Site Requirements
Ensure site readiness before deployment:
- Power Supply: Verify voltage (e.g., 208–480V, 3-phase), frequency, and grounding requirements. Laser systems often require stable power with surge protection.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Install certified fume extraction units with HEPA and/or activated carbon filters near the work area to meet indoor air quality standards (e.g., OSHA PELs, ACGIH TLVs).
- Space and Layout: Allocate space for the laser unit, operator access, fume extractor, and emergency shutdown controls. Maintain a minimum safety perimeter of 2–5 meters, marked with warning signs and interlocked barriers.
- Training and Certification: Only trained personnel should operate the system. Employers must maintain records of safety training and equipment maintenance.
Maintenance, Documentation, and Recordkeeping
- Preventive Maintenance: Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning optical components, checking cooling systems, and calibrating laser output. Maintain service logs.
- Compliance Documentation: Keep records of:
- Laser safety audits and risk assessments
- Operator training certifications
- Fume extraction filter change schedules and waste disposal manifests
- Equipment maintenance and calibration logs
- Incident Reporting: Report any laser exposure incidents or equipment malfunctions per OSHA or local authority requirements.
Conclusion
Laser rust and paint removal offers an efficient, eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods, but its deployment requires careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance. By adhering to laser safety standards, environmental regulations, and proper shipping and installation protocols, organizations can ensure safe, legal, and effective operation of laser cleaning systems. Always consult local authorities and equipment manufacturers for region-specific requirements.
In conclusion, laser technology presents a highly effective, environmentally friendly, and precise method for removing rust and paint from various surfaces. Unlike traditional techniques such as sandblasting or chemical stripping, laser cleaning offers non-abrasive, selective material removal that preserves the underlying substrate while eliminating contaminants. It reduces waste, eliminates the need for harmful chemicals, and improves workplace safety. Although the initial investment in laser cleaning systems may be higher, the long-term benefits—such as lower operational costs, minimal maintenance, and compliance with environmental regulations—make it a compelling choice for industrial applications. As the technology continues to advance and become more accessible, laser-based rust and paint removal is poised to become a standard solution in manufacturing, restoration, and maintenance operations across multiple industries.