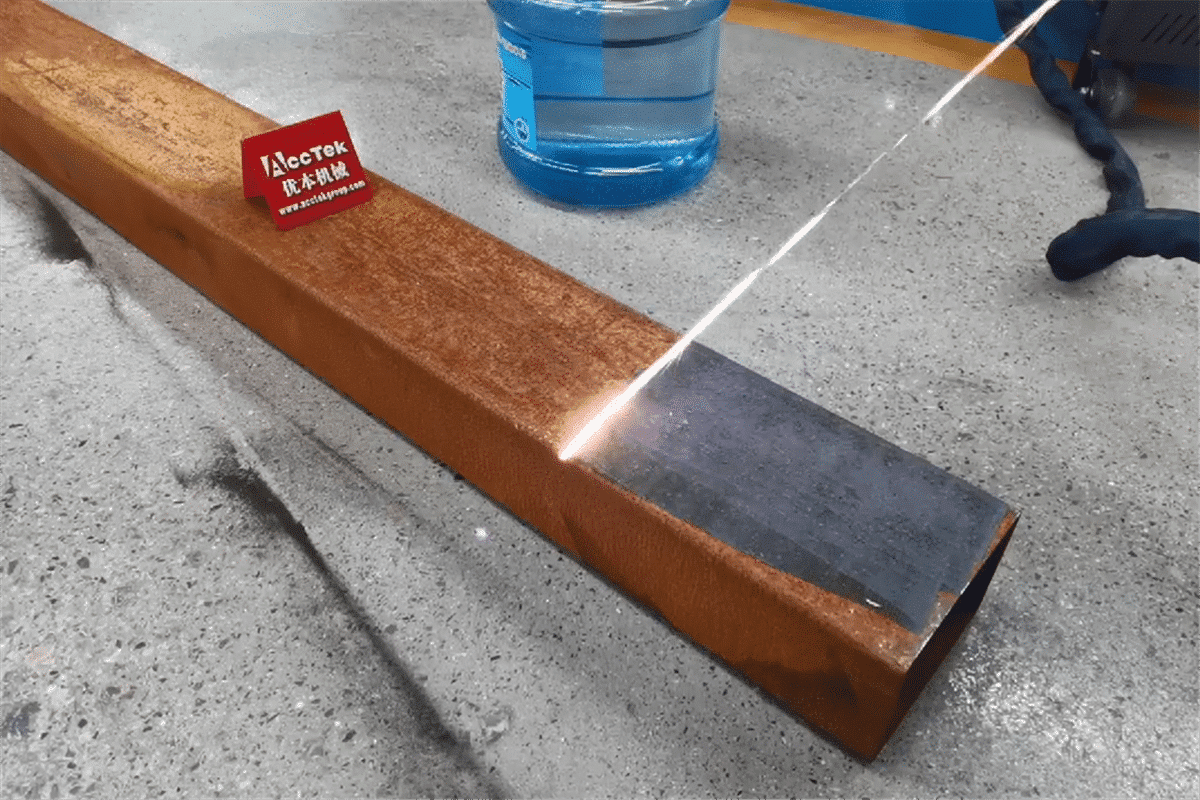
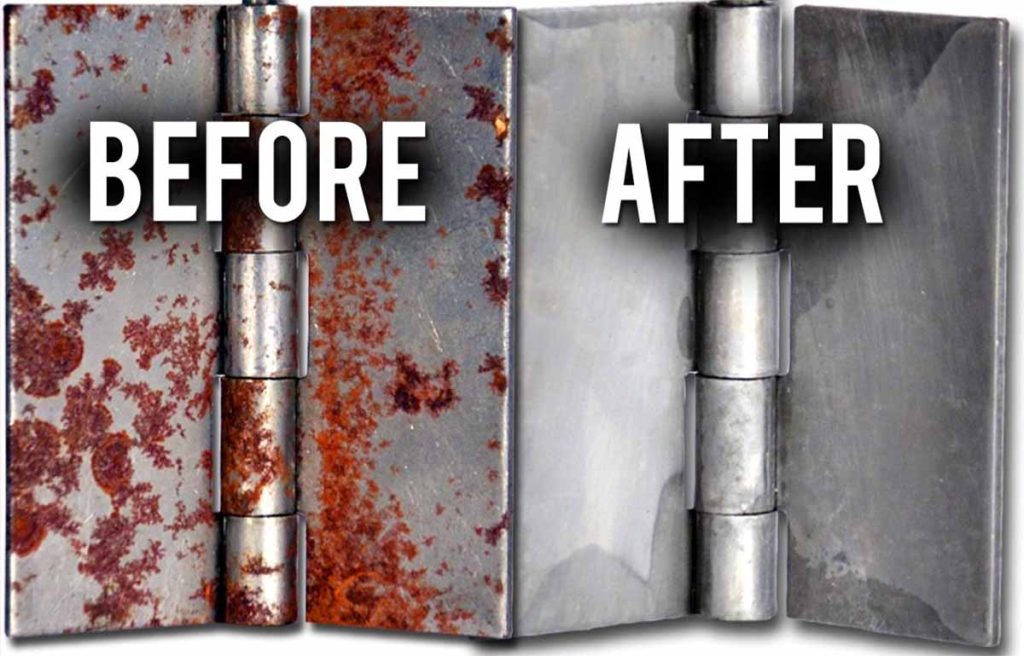
The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision-based surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 492.8 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research projects that the market will surpass USD 1.5 billion by 2030, fueled by the adoption of advanced laser technologies for rust and contaminant removal. As industries prioritize non-abrasive, chemical-free cleaning methods, laser-based solutions have emerged as a superior alternative to traditional techniques like sandblasting and chemical stripping. This surge in demand has catalyzed innovation among manufacturers specializing in laser rust removal systems. Below is a data-informed overview of the top nine manufacturers leading this transformation through cutting-edge technology, performance efficiency, and scalable industrial applications.
Top 9 Laser Removes Rust Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Top Laser Rust Cleaning Machines for Efficient Rust Removal
Website: woodrowscientific.com
Key Highlights: Let’s dig into the P-Laser QF Series—a line-up of industrial fibre laser rust cleaning machines from the Belgian manufacturer with over 35 years ……
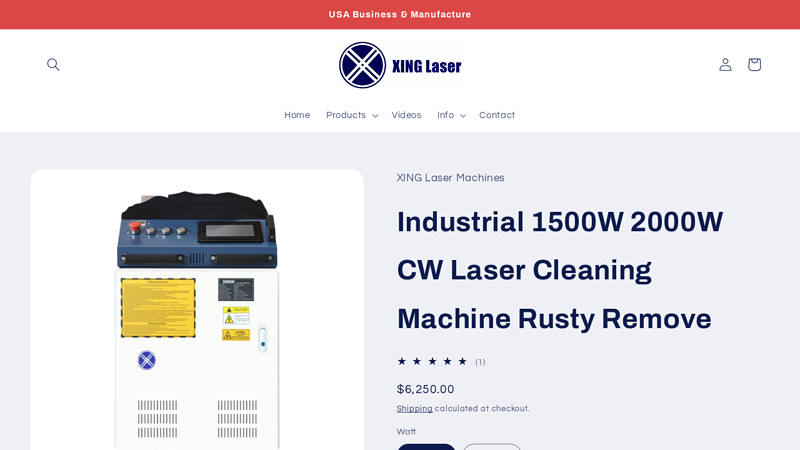
#2 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#3 Rust Removal with Laser Cleaning
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser rust removal is a non-contact method that continuously removes rust while drastically lowering maintenance costs….
#4 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#5 Laser Rust Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: KEYENCE offers two laser machines that can remove rust—the hybrid laser marker and the fiber laser marker. Both machines offer a non-abrasive way to remove rust ……
#6 Laser Rust Removal
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: Watch this super fast rust removal from carbon steel panel with the new ultra-lightweight Vulcan handheld from Powerlase. The nature of laser cleaning ……
#7 Understanding Laser Rust Removal
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Laser rust removal is a non-contact cleaning process that uses a laser beam to remove rust, oxide layers, and other contaminants from surfaces….
#8 Laser Cleaning Rust Removal
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Our equipment uses pulsating lasers to blast away any contaminants from metal surfaces. This process is eco-friendly, as you won’t need any ……
#9 Laser Rust Removal Guide
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A practical guide for professionals and entrepreneurs using PULSAR Laser systems to remove rust safely, efficiently and without abrasives….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Removes Rust

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Rust Removal
The global laser rust removal market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising environmental regulations, and growing demand across key industrial sectors. As industries prioritize precision, sustainability, and operational efficiency, laser-based surface cleaning technologies are emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional rust removal methods such as sandblasting and chemical treatments.
-
Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
By 2026, laser rust removal systems are expected to become more compact, efficient, and user-friendly. Innovations in fiber laser technology—offering higher power outputs, improved beam quality, and better energy efficiency—are enabling faster processing speeds and deeper rust penetration. Integration with robotics and AI-driven automation is enhancing precision in complex or large-scale applications, especially in aerospace, automotive, and maritime industries. -
Environmental and Regulatory Support
Stringent environmental regulations limiting the use of chemical solvents and abrasive blasting are pushing industries toward eco-friendly alternatives. Laser rust removal produces no secondary waste, requires no consumables, and emits no harmful chemicals, aligning with global sustainability goals. By 2026, compliance with environmental standards such as REACH and EPA regulations will further accelerate the adoption of laser cleaning solutions. -
Expansion in Key Industrial Applications
The automotive and aerospace sectors are leading adopters of laser rust removal due to their need for non-destructive, high-precision cleaning. The maritime industry, particularly in ship maintenance and offshore platforms, is also increasing investment in laser systems to combat corrosion in saltwater environments. Additionally, heritage conservation and infrastructure maintenance are emerging as niche but growing application areas. -
Cost Reduction and ROI Improvement
Although the initial investment in laser systems remains high, the total cost of ownership is decreasing due to longer laser source lifespans, lower maintenance, and reduced labor and waste disposal costs. By 2026, improved return on investment (ROI) is expected to make laser rust removal economically viable for mid-sized manufacturers and service providers. -
Geographic Market Growth
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region by 2026, fueled by industrial expansion in China, India, and South Korea. Europe continues to lead in innovation and adoption due to strict environmental policies, while North America sees steady growth in defense and infrastructure applications. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market is witnessing increased competition and strategic partnerships among key players such as CleanLASER, Laser Photonics, and ADL (Additive Dr. Laser). By 2026, further consolidation is expected, with larger industrial equipment manufacturers acquiring laser cleaning startups to broaden their product portfolios.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for laser rust removal will be defined by smarter, greener, and more accessible technology, positioning it as a cornerstone of modern industrial maintenance and manufacturing practices.
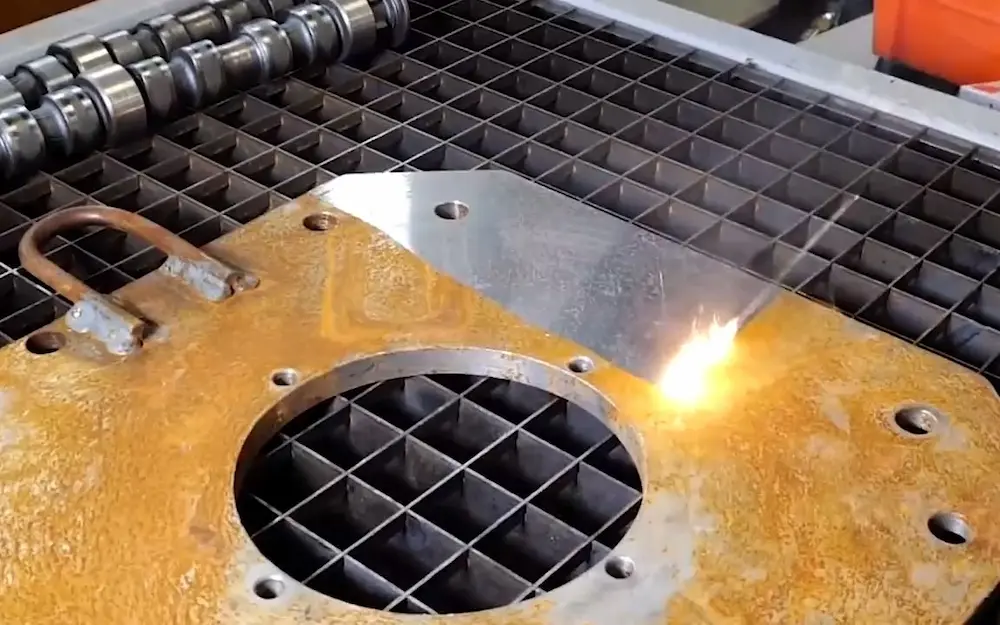

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Rust Removal Equipment (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing laser rust removal systems can be a complex process, especially for businesses new to industrial laser technology. While these systems offer precision, efficiency, and environmental benefits, buyers often face challenges related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Understanding the common pitfalls in these areas can help ensure a successful procurement process.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Power and Performance Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is misjudging the required laser power for effective rust removal. Many suppliers advertise high wattage lasers, but the actual cleaning efficiency depends on pulse energy, beam quality, scanning speed, and wavelength. Buyers may end up with underperforming systems if they rely solely on peak power ratings without proper testing or real-world performance validation.
2. Poor Build Quality and Component Sourcing
Lower-cost laser systems, especially from less reputable manufacturers, may use substandard components such as low-grade optics, unreliable cooling systems, or inadequate safety enclosures. These flaws can lead to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent performance, and increased maintenance costs over time.
3. Lack of Industry-Specific Testing
Not all laser rust removal systems are suitable for every application. For example, removing rust from delicate aerospace components requires different parameters than heavy industrial steel structures. Sourcing a system without verifying its performance on your specific materials and surfaces can result in ineffective cleaning or surface damage.
4. Insufficient Safety and Compliance Features
High-powered lasers require strict safety measures, including protective enclosures, interlocks, and proper labeling. Some imported systems may not meet international safety standards (e.g., CE, FDA, or IEC 60825), posing risks to operators and potential legal liabilities.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Technology
Some manufacturers, particularly in regions with lax IP enforcement, produce laser systems that replicate patented designs or software from established brands. Purchasing such equipment may expose your business to legal risks, especially if the technology infringes on existing patents or proprietary controls.
2. Lack of Transparent Software and Firmware Ownership
Many laser systems rely on proprietary control software. When sourcing from certain suppliers, buyers may not receive full access to the source code or may unknowingly use software that violates licensing agreements. This can limit customization, create dependency on the vendor, and lead to compliance issues.
3. Unclear Warranty and Support Due to IP Disputes
If a supplier is using infringing technology, they may be forced to cease operations or discontinue support due to legal action. This can leave buyers without technical support, spare parts, or software updates—effectively stranding critical equipment.
4. Difficulty in Technology Transfer and Innovation
Relying on IP-compromised systems hampers long-term innovation. Companies that invest in cloned or unlicensed technology may struggle to develop proprietary processes or gain a competitive edge, as their foundation is built on legally vulnerable or low-differentiation hardware.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and reference checks.
- Request on-site or third-party performance testing with materials relevant to your use case.
- Verify compliance with international safety and quality certifications.
- Consult legal or technical experts to assess IP risks, especially with low-cost or “white-label” systems.
- Prioritize suppliers who offer transparent documentation, full warranty support, and proof of original technology development.
By recognizing these quality and intellectual property pitfalls, businesses can make informed decisions and invest in reliable, legally sound laser rust removal solutions that deliver long-term value.
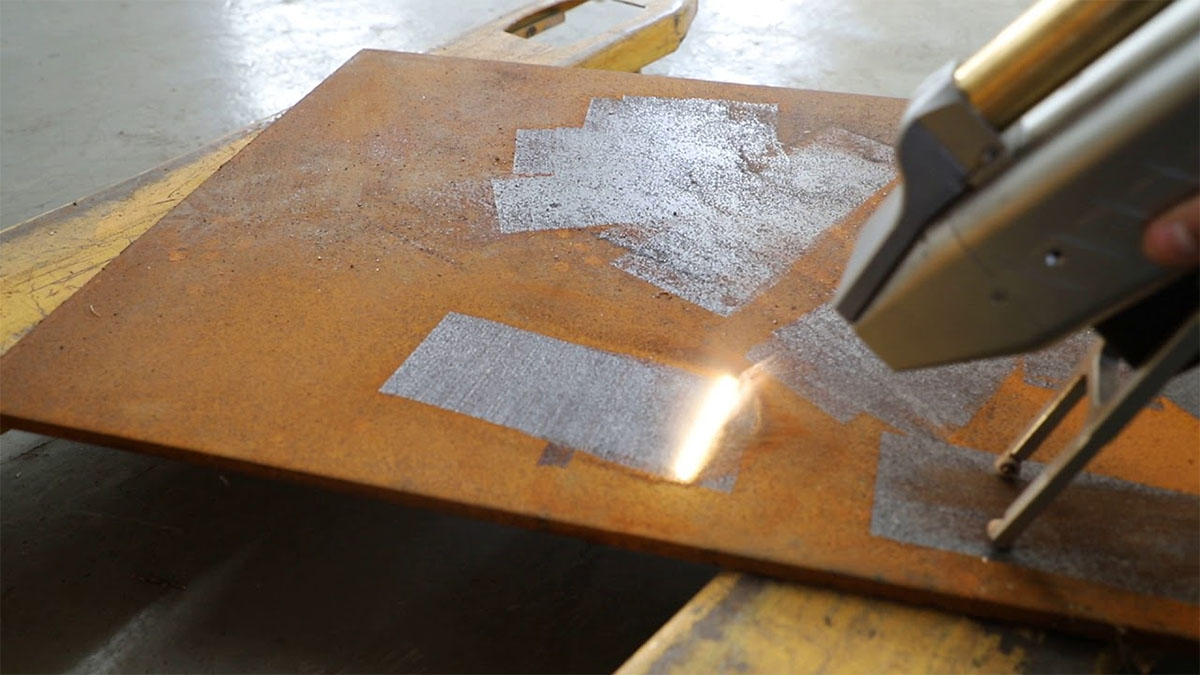

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Rust Removal Systems
Introduction to Laser Rust Removal Technology
Laser rust removal utilizes high-intensity laser beams to ablate rust, paint, and other contaminants from metal surfaces without damaging the underlying substrate. This non-contact, eco-friendly method is increasingly adopted in industries such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and heritage restoration. This guide outlines the logistics and compliance considerations essential for the safe, legal, and efficient deployment of laser rust removal systems.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser Safety Standards
Laser rust removal systems typically fall under Class 4 laser products, subject to stringent international and national safety regulations. Compliance with the following standards is mandatory:
– IEC 60825-1: International standard for the safety of laser products. Requires proper labeling, interlocks, and emission indicators.
– ANSI Z136.1 (USA): Provides safety guidelines for the use of lasers in workplaces. Requires a designated Laser Safety Officer (LSO) and implementation of a Laser Safety Program.
– OSHA Regulations: General Duty Clause and specific laser safety guidelines under 29 CFR 1910 apply. Employers must ensure a hazard-free workplace.
Electrical & Equipment Safety
- CE Marking (Europe): Ensures conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). Includes compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU).
- UL/CSA Certification (North America): Required for electrical safety in the U.S. and Canada. Equipment must be evaluated by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL).
- RoHS & REACH Compliance: Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations apply to electronic components and materials used in the system.
Environmental Regulations
- Waste Handling: Ablated rust particles (often containing iron oxide and heavy metals) are considered hazardous waste in many jurisdictions. Proper collection, containment, and disposal per EPA (USA) or EPA/Environment Agency (UK/EU) guidelines are required.
- Air Quality & Fumes: Laser ablation generates particulate matter and fumes. Use of HEPA filtration systems and local exhaust ventilation is necessary to meet OSHA PELs and EU Directive 2004/37/EC on carcinogens.
- Noise Emissions: Some systems generate significant noise. Compliance with EU Noise Directive 2000/14/EC or NIOSH recommended exposure limits may be required.
Logistics Planning & Deployment
Transportation & Storage
- Packaging: Systems must be shipped in shock-resistant, moisture-proof packaging, especially for optical components. Include desiccants and humidity indicators where necessary.
- Import/Export Controls: Laser systems may be subject to export regulations under ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations) if classified as dual-use technology. Obtain necessary licenses before international shipment.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 5°C–40°C). Avoid condensation and exposure to dust.
Installation & Site Requirements
- Power Supply: Ensure stable power input matching the system’s voltage and phase requirements (e.g., 208–240 VAC, single or three-phase). Use proper grounding and surge protection.
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction: Install dedicated fume extraction systems with HEPA or ULPA filters. Ductwork should be grounded to prevent static buildup.
- Laser Controlled Area: Define a controlled access zone with interlocked doors, warning signs, and emergency stop buttons. Use non-reflective surfaces and laser-absorbing backstops.
Operational Safety & Training
Personnel Training & Certification
- All operators must complete laser safety training compliant with ANSI Z136 or equivalent.
- Training should cover system operation, emergency shutdown procedures, PPE usage, and hazard recognition.
- Maintain training records and conduct annual refresher courses.
Required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Laser Safety Goggles: Wavelength-specific optical density (OD) rating to block the laser’s operating wavelength (typically 1064 nm for fiber lasers).
- Respiratory Protection: NIOSH-approved N95 or P100 respirators if engineering controls are insufficient.
- Protective Clothing: Flame-resistant lab coats, gloves, and face shields to guard against sparks and particulates.
Maintenance & Documentation
Preventive Maintenance
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules for optics, cooling systems, and electrical components.
- Regularly inspect and clean laser delivery optics and protective windows.
- Calibrate laser power output and beam alignment periodically.
Recordkeeping & Audits
- Maintain logs for:
- Laser usage and maintenance
- Operator training and certifications
- Incident reports and corrective actions
- Waste disposal manifests
- Conduct annual safety audits to ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory standards.
Waste Management & Disposal
Collection & Segregation
- Use integrated vacuum systems with HEPA filters to capture particulate waste.
- Segregate collected waste by composition (e.g., iron oxide, zinc, lead-based paint residues).
- Label containers clearly as “Hazardous Waste – Laser Ablation Byproducts.”
Disposal Methods
- Partner with licensed hazardous waste disposal companies.
- Obtain waste analysis and disposal certifications for audit purposes.
- Follow EPA 40 CFR Part 262 (USA) or Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directives where applicable.
Conclusion & Best Practices
Successful deployment of laser rust removal systems requires strict adherence to safety, environmental, and regulatory standards. Key best practices include:
– Appointing a qualified Laser Safety Officer (LSO)
– Conducting regular risk assessments
– Investing in proper engineering controls (ventilation, enclosures)
– Maintaining thorough documentation
– Staying updated on evolving regulations
By following this guide, organizations can ensure safe, compliant, and efficient use of laser rust removal technology across industrial applications.
In conclusion, laser rust removal is an effective, precise, and environmentally friendly solution for sourcing and implementing advanced surface cleaning technologies. Unlike traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical treatments, laser cleaning offers non-abrasive, residue-free rust removal without damaging the underlying substrate. Its automation capabilities, low maintenance, and minimal need for consumables make it a cost-efficient option in the long term, especially for industrial applications in aerospace, automotive, and heritage conservation. As sustainability and operational efficiency become increasingly important, sourcing laser-based rust removal systems represents a forward-thinking investment in clean technology and high-precision maintenance solutions.