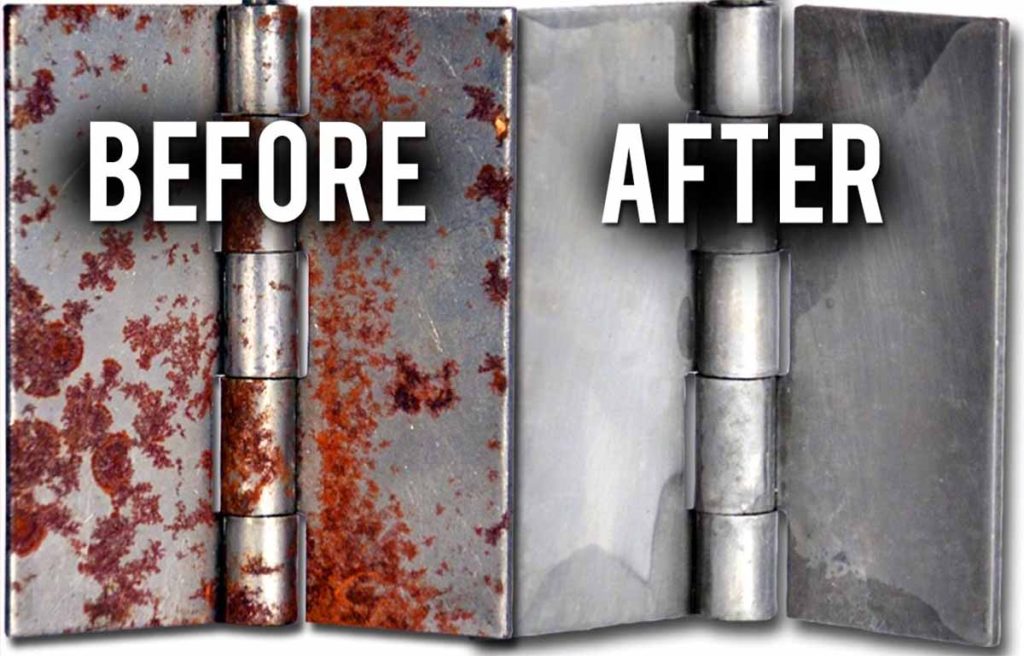
The global laser cleaning equipment market, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision surface treatment solutions, is witnessing robust growth. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 678.4 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1.36 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 11.8% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of laser technology for rust and paint removal in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing, where traditional methods like sandblasting and chemical stripping are being phased out due to environmental and safety concerns. Laser cleaning offers a non-abrasive, solvent-free alternative with minimal waste and high efficiency, making it a preferred choice for maintenance and restoration applications. As demand surges, a competitive landscape of manufacturers has emerged, specializing in industrial-grade laser systems capable of precise, large-scale decontamination. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers leading innovation and market penetration in laser-based rust and paint removal technology.
Top 10 Laser Removal Of Rust And Paint Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax is manufacturing efficient, innovative and safe laser solutions for the most demanding industrial applications. For over 10 years, we have produced ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: P-Laser specializes in the production of industrial laser cleaning systems….
#3 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#4 Laser Coating Removal Solutions for Industry
Website: surclean.com
Key Highlights: Our laser ablation solution reduces the time, money and risk associated with removing rust, dirt, paint and other coatings. Applications: Paint removal and de- ……
#5 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#6 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#7 Understanding Laser Rust Removal
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Laser rust removal is a non-contact cleaning process that uses a laser beam to remove rust, oxide layers, and other contaminants from surfaces….
#8 Laser cleaning
Website: p-laserusa.com
Key Highlights: Our laser machines are mainly used to remove the following contaminants: Rust – Paint – Coatings – Release Agents – Grease, Oils – Soot – Rubber- Organic ……
#9 Laser Rust Removal
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: We are a customer-centered company. Our innovation is purely driven by customer needs and requirements. Learn about our existing applications or work with ……
#10 Laser Rust Removal Guide
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: … website traffic, and to understand where our visitors are coming from. … PULSAR Laser – official logo of professional laser rust and paint removal cleaners….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Removal Of Rust And Paint
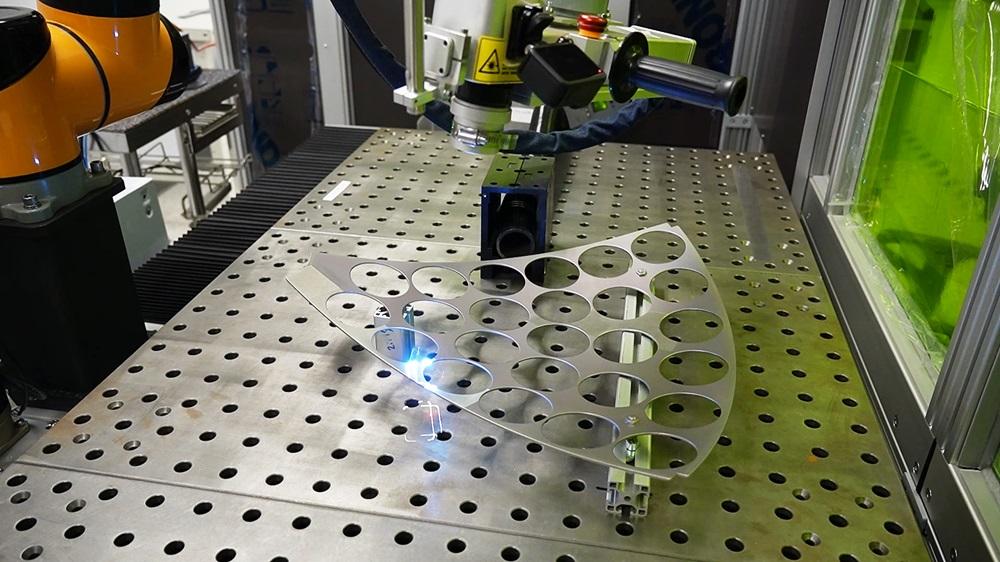

2026 Market Trends for Laser Removal of Rust and Paint
Market Growth and Expansion
The global market for laser-based rust and paint removal is projected to experience significant growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precise, and non-destructive surface treatment technologies. According to industry forecasts, the market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 12–15% between 2021 and 2026. This growth is fueled by rising awareness of the environmental and health hazards associated with traditional methods such as sandblasting and chemical stripping.
Industries such as automotive restoration, aerospace, shipbuilding, and heritage preservation are increasingly adopting laser ablation technology due to its ability to selectively remove coatings without damaging underlying substrates. By 2026, the market is expected to expand beyond niche applications into mainstream industrial operations, particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific.
Technological Advancements
By 2026, laser cleaning systems are anticipated to become more compact, energy-efficient, and user-friendly, thanks to ongoing innovations in fiber laser technology and automation integration. Advancements in pulse control, beam delivery systems, and real-time monitoring will enhance precision and operational speed. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are expected to be integrated into laser systems to enable adaptive cleaning protocols based on surface conditions.
Portable handheld laser devices are also gaining traction, making the technology accessible for field operations and smaller enterprises. These systems offer improved ergonomics and safety features, supporting broader deployment across diverse work environments.
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Environmental regulations are playing a pivotal role in shaping the adoption of laser cleaning. Stricter global standards on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, hazardous waste disposal, and worker safety are pushing industries to abandon conventional paint and rust removal methods. Laser ablation produces no secondary waste and eliminates the need for chemical solvents, aligning with sustainability goals and compliance requirements.
By 2026, governments and regulatory bodies are likely to offer incentives or mandate the use of clean technologies in industrial maintenance, further accelerating market penetration of laser-based solutions.
Industry Adoption and Applications
In the automotive and aerospace sectors, laser cleaning is expected to become a standard process for surface preparation before welding, coating, or repair. The ability to restore vintage vehicles and aircraft components without structural damage makes laser technology highly valuable for restoration projects.
In maritime and offshore industries, laser systems are being deployed for hull maintenance and corrosion control, reducing downtime and improving safety. Cultural heritage institutions are also adopting laser cleaning for the delicate restoration of statues, monuments, and historical buildings, where precision is critical.
Competitive Landscape and Market Players
The competitive landscape is evolving with both established industrial laser manufacturers and new entrants offering specialized cleaning systems. Companies such as CleanLas, Laser Photonics, and SPI Lasers are expanding their product lines to meet growing demand. Strategic partnerships with robotics firms and integration into automated production lines are expected to increase by 2026, enhancing scalability and efficiency.
Price competition is anticipated to intensify as manufacturing costs decrease and supply chains mature, making laser cleaning systems more affordable for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, the laser removal market faces challenges, including high initial investment costs and the need for skilled operators. Safety concerns related to laser radiation require proper training and protective equipment. Additionally, the technology may not be equally effective on all paint types or heavily corroded surfaces, limiting its universal applicability.
However, ongoing research into multi-wavelength systems and hybrid cleaning methods (combining laser with other techniques) aims to overcome these limitations by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, laser removal of rust and paint is poised to become a mainstream surface treatment solution across multiple industries. Driven by technological innovation, environmental regulations, and increasing cost-efficiency, the market will shift toward sustainable and automated cleaning processes. As systems become more accessible and versatile, laser ablation is expected to redefine industrial maintenance and restoration practices globally.
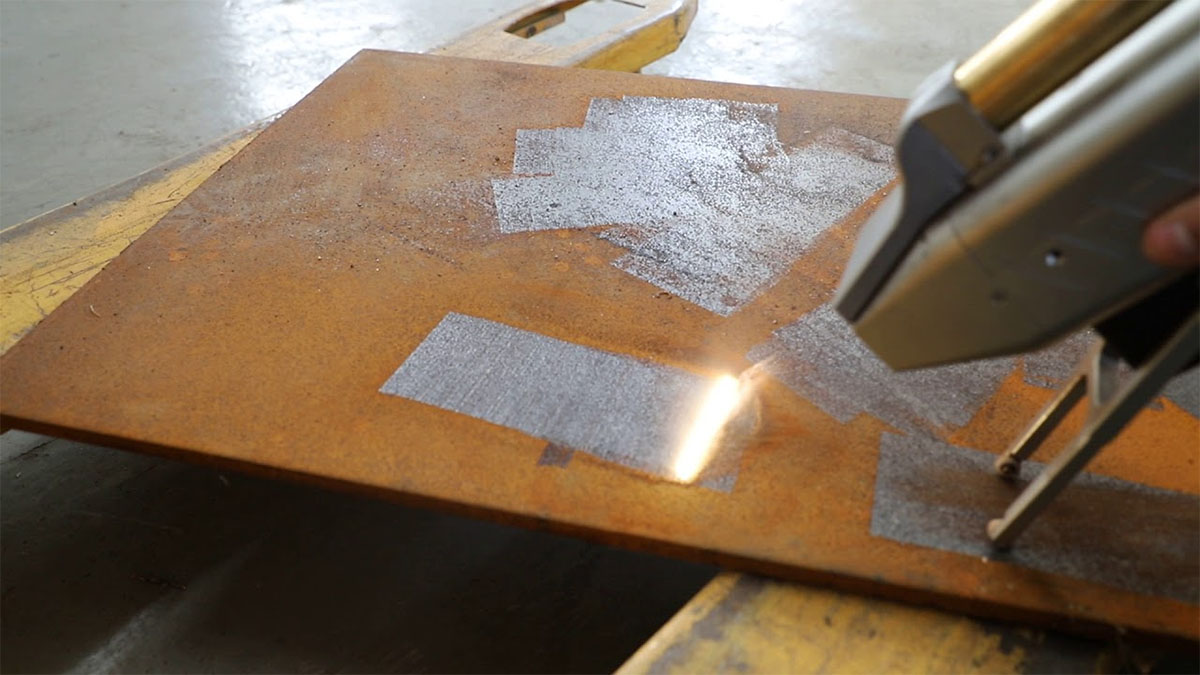

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Removal of Rust and Paint (Quality and IP)
When sourcing laser-based systems for rust and paint removal, organizations often encounter critical challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal risks, and compromised project outcomes.
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate System Validation
One of the most prevalent pitfalls is selecting a laser removal system without thorough validation of its performance and reliability. Many suppliers offer machines with exaggerated claims about speed, efficiency, or substrate compatibility. Buyers may fail to conduct on-site demonstrations or material-specific testing, resulting in systems that underperform in real-world conditions. Additionally, inconsistent beam quality, inadequate cooling mechanisms, or substandard safety features can compromise both effectiveness and operator safety. Without verified quality certifications (e.g., ISO standards) or third-party testing reports, sourcing decisions risk being based on marketing rather than technical merit.
Lack of Clear Intellectual Property Agreements
Another significant risk involves ambiguous or absent IP clauses in procurement contracts. Laser removal technology often incorporates proprietary software, scanning algorithms, or hardware designs protected by patents or trade secrets. When sourcing from overseas or emerging technology providers, buyers may unknowingly infringe on existing IP or fail to secure rights to modifications and improvements developed during integration. Furthermore, without clear contractual terms, the ownership of custom adaptations or process know-how may remain with the supplier, limiting the buyer’s ability to scale or maintain the system independently. This can lead to dependency, unexpected licensing fees, or legal disputes.
To mitigate these risks, due diligence should include technical audits, performance benchmarking, and legal review of IP rights prior to finalizing procurement. Engaging specialists in laser technology and intellectual property law is strongly recommended.
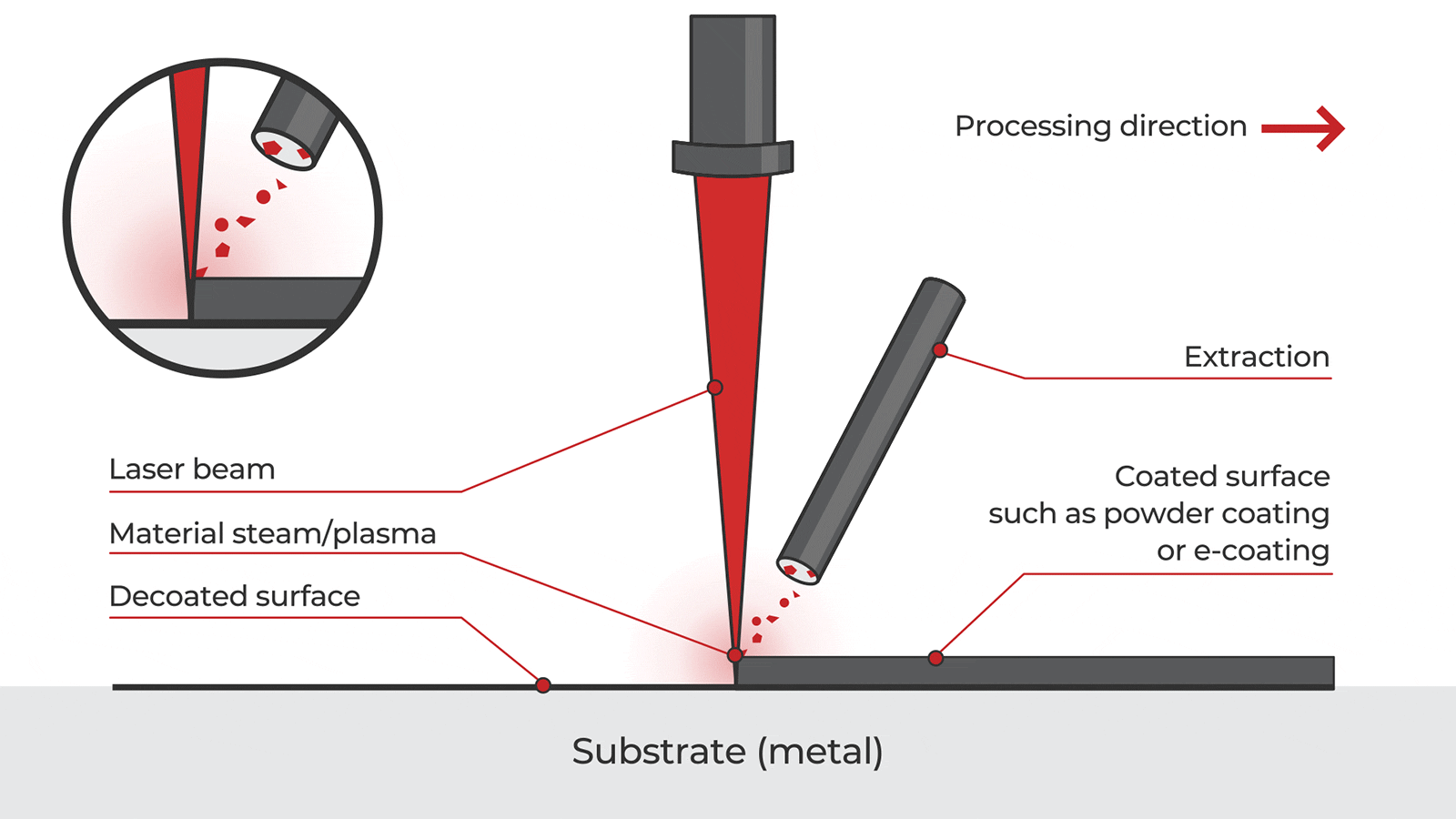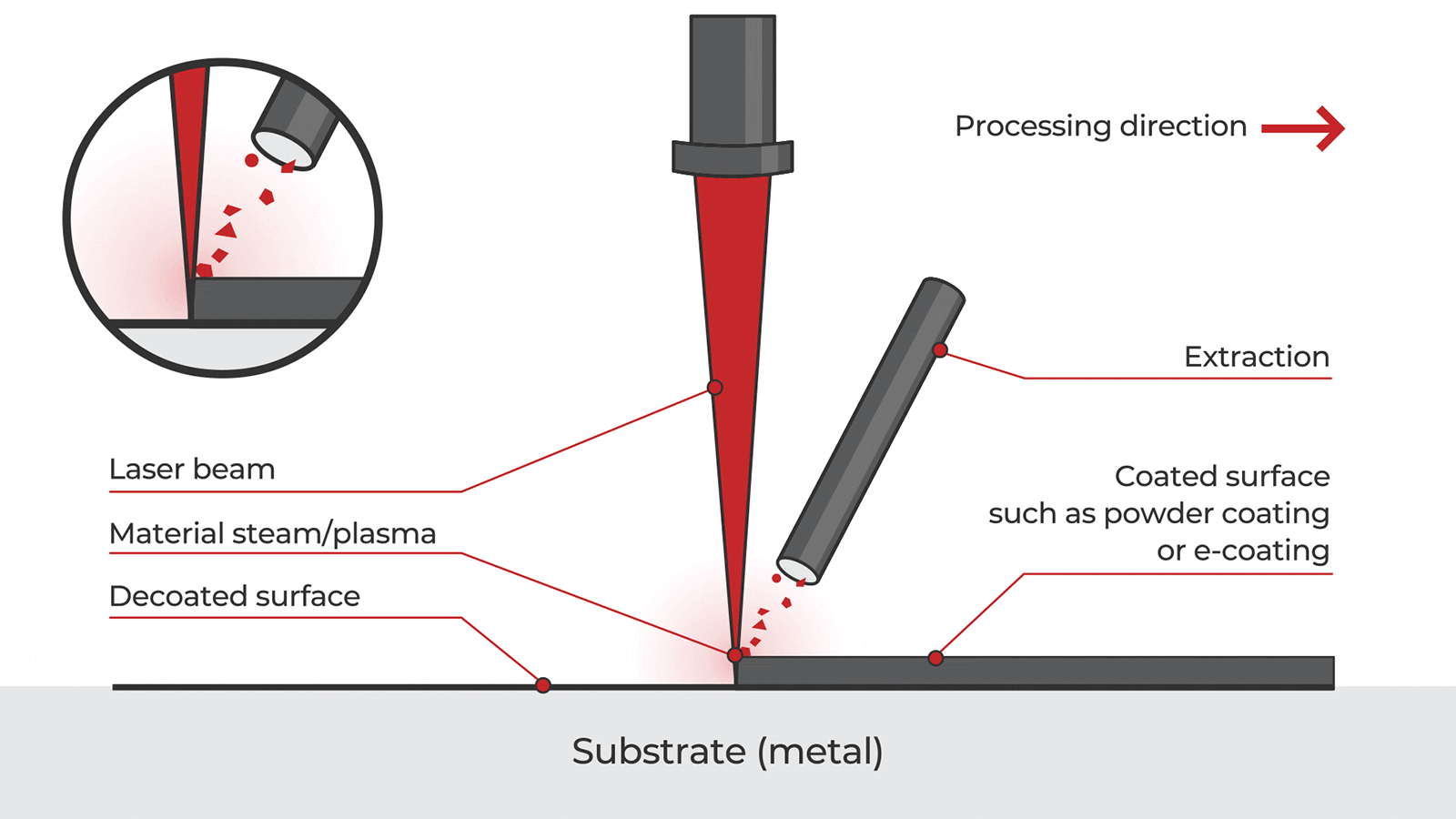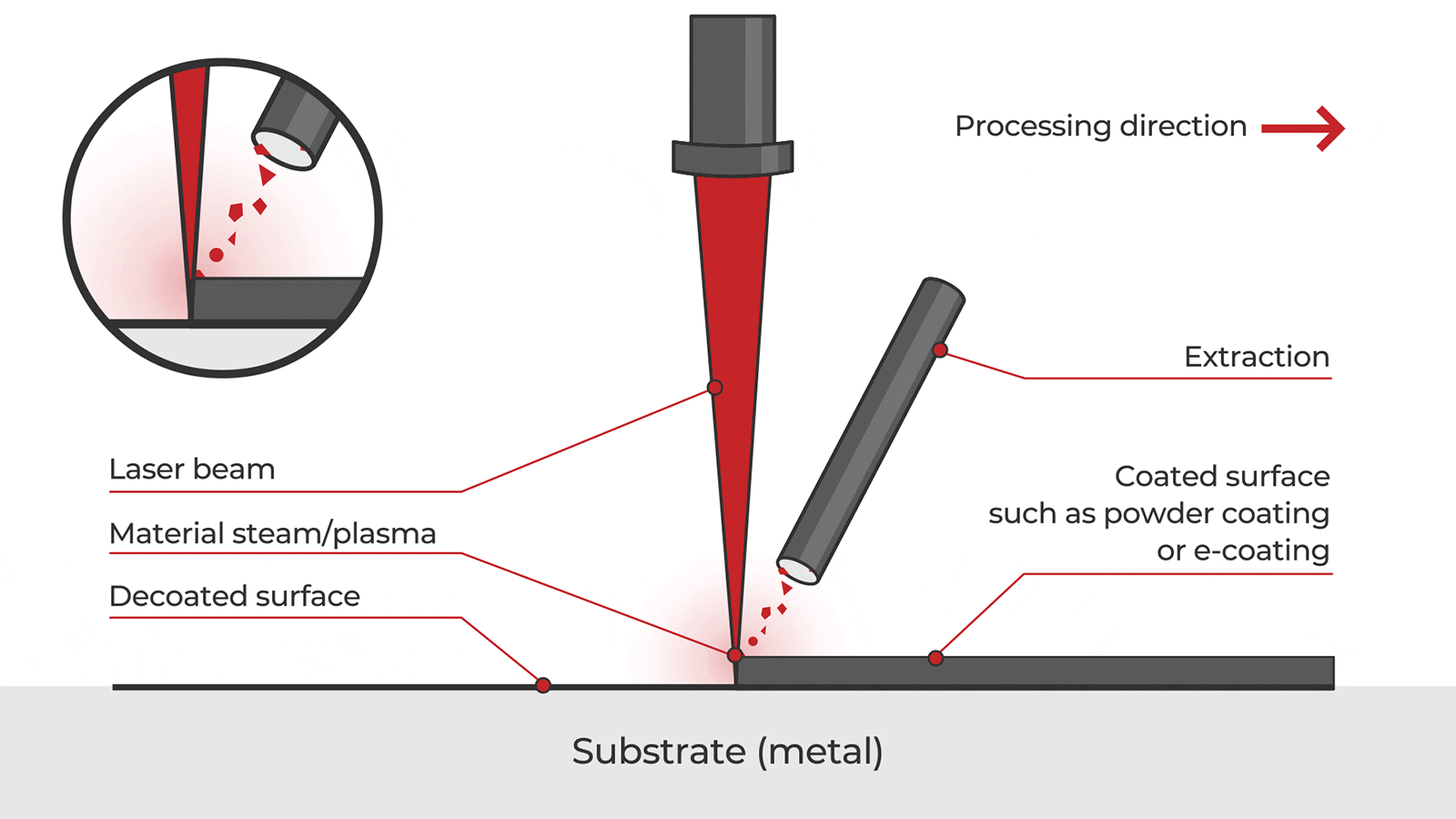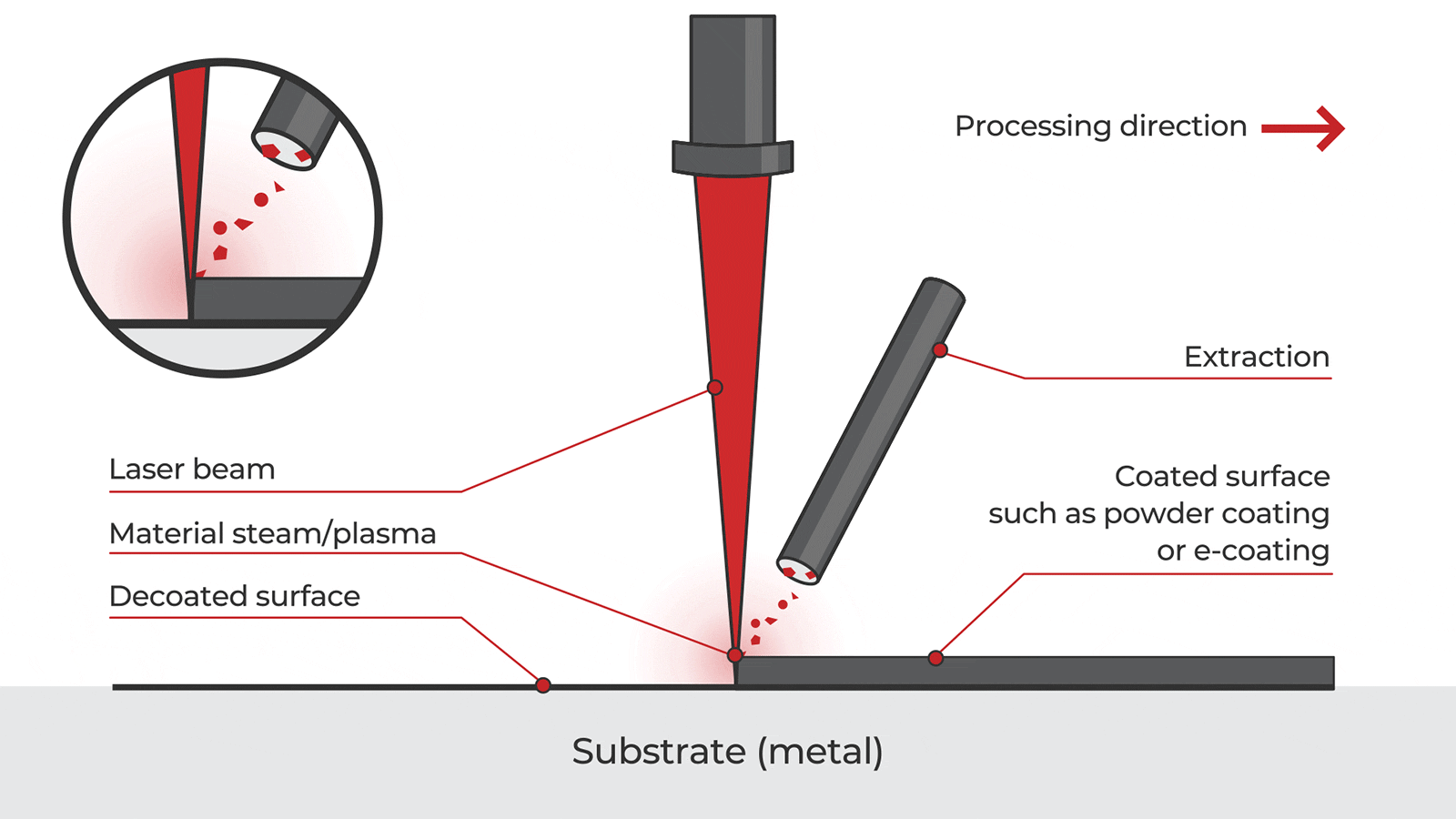
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Removal of Rust and Paint
Overview of Laser Removal Technology
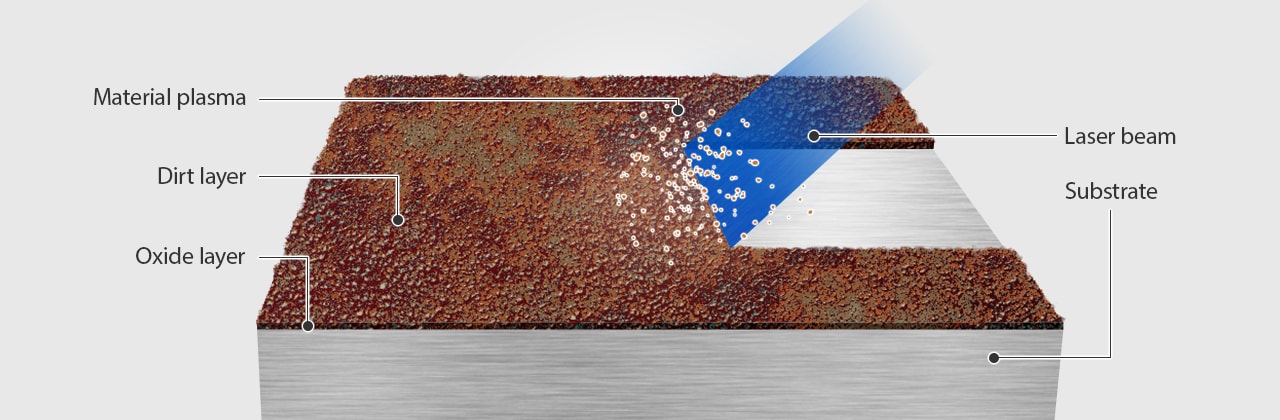
Laser removal of rust and paint is an advanced, non-abrasive cleaning method that utilizes high-intensity laser beams to vaporize contaminants from metal surfaces. This eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical stripping reduces waste, preserves substrate integrity, and improves workplace safety. However, deploying this technology requires careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance.
Equipment Logistics and Transportation
Equipment Specifications and Packaging
Laser cleaning systems vary in size and weight—from portable handheld units to large, stationary industrial machines. Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit. Use shock-absorbing materials and climate-controlled containers, especially for sensitive optical components.
Shipping and Handling Requirements
- Use freight carriers experienced in handling precision industrial equipment.
- Ensure all units are securely crated, labeled with fragility warnings, and equipped with tilt indicators.
- For international shipments, comply with IATA/IMDG regulations if transporting lithium batteries or laser modules classified as hazardous materials.
On-Site Setup and Installation
- Confirm site readiness: power supply (voltage, phase), ventilation, and space requirements.
- Employ certified technicians for equipment installation and calibration.
- Conduct a site safety assessment before activating the system.
Regulatory Compliance
Laser Safety Standards (IEC 60825 & ANSI Z136)
Laser cleaning devices typically fall under Class 4 laser products, which pose significant hazards. Compliance with international safety standards is mandatory:
- IEC 60825 (International Electrotechnical Commission): Defines laser classification, labeling, and user safety requirements.
- ANSI Z136.1 (American National Standards Institute): Provides U.S.-specific guidelines for safe use in occupational settings.
Key compliance actions:
– Install interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency stop mechanisms.
– Label equipment with appropriate warning signs.
– Conduct regular safety audits and maintenance checks.
Occupational Health and Safety (OSHA & EU Directives)
United States (OSHA)
- Follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subpart K (Medical and First Aid) and Subpart I (Personal Protective Equipment).
- Implement a Laser Safety Program, including a designated Laser Safety Officer (LSO).
- Provide training on laser hazards, fire risks, and safe operating procedures.
European Union
- Comply with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and the Artificial Optical Radiation Directive (2006/25/EC).
- Conduct risk assessments and maintain a Declaration of Conformity.
- Ensure CE marking on all equipment.
Fumes and Air Quality Management (EPA & REACH)
Laser ablation generates particulate matter and fumes (e.g., metal oxides, paint volatiles). Regulatory frameworks include:
- EPA (U.S.): Adhere to National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP). Use HEPA-filtered fume extraction systems and conduct air monitoring.
- REACH (EU): Identify and manage substances of very high concern (SVHCs) released during ablation. Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for processed materials.
Implement engineering controls:
– Local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems.
– Real-time particulate monitors.
– Regular filter replacement and maintenance logs.
Environmental Compliance
Waste Management and Disposal
Unlike chemical or abrasive methods, laser cleaning produces minimal waste—mostly condensed particulates captured in filters. However, waste classification is critical:
- Test collected residues for hazardous characteristics (e.g., heavy metals like lead or chromium).
- Dispose of hazardous waste through licensed facilities in compliance with RCRA (U.S.) or Waste Framework Directive (EU).
- Maintain waste manifests and disposal records for at least three years.
Noise and Energy Consumption
- Laser systems are generally low-noise, but auxiliary equipment (e.g., extractors, chillers) may exceed local noise ordinances.
- Optimize energy use and document efficiency metrics to meet sustainability goals (e.g., ISO 50001).
Personnel Training and Certification
Mandatory Training Programs
- Laser Safety Training: Cover beam hazards, reflection risks, and emergency procedures.
- PPE Use: Train on wearing laser safety goggles (wavelength-specific), respirators, and flame-resistant clothing.
- Equipment Operation: Certify operators through manufacturer-led programs.
Recordkeeping
- Maintain training logs, certifications, and incident reports.
- Ensure all personnel have access to up-to-date safety manuals and emergency protocols.
International Deployment Considerations
Import/Export Regulations
- Verify laser product classification under the U.S. FDA/CDRH (Center for Devices and Radiological Health) for exports.
- Comply with dual-use regulations if technology has military applications (e.g., Wassenaar Arrangement).
- Obtain necessary permits for cross-border shipment of controlled equipment.
Local Legal Requirements
- Research country-specific laser regulations (e.g., Health Canada, UK HSE, Australia’s ARPANSA).
- Adapt signage, training, and PPE to local language and standards.
Incident Reporting and Emergency Response
Reporting Obligations
- Report laser-related injuries, fires, or environmental releases immediately to relevant authorities (e.g., OSHA, local environmental agency).
- Investigate incidents and implement corrective actions.
Emergency Preparedness
- Equip work areas with fire extinguishers (Class D for metal fires if applicable).
- Establish evacuation routes and first-aid stations.
- Conduct regular drills for laser exposure and fire emergencies.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of laser rust and paint removal systems hinges on meticulous logistics planning and strict adherence to compliance standards. By integrating safety, environmental responsibility, and regulatory awareness into operations, organizations can leverage the benefits of laser technology while minimizing risk and ensuring legal conformity.
Conclusion: Sourcing Laser Removal for Rust and Paint
Laser ablation technology presents a highly effective, precise, and environmentally friendly solution for removing rust and paint from a variety of surfaces. When sourcing laser removal systems or services, organizations should consider several key factors to ensure optimal results and return on investment. These include the technical specifications of the laser system (such as power output, wavelength, and scanning speed), the nature of the materials involved, and the scale and frequency of the work required.
Sourcing decisions should also account for safety standards, required operator training, and compliance with industry regulations. While the initial investment in laser technology may be higher than traditional methods like sandblasting or chemical stripping, the long-term benefits—such as reduced waste, minimal substrate damage, lower environmental impact, and lower operational costs—make it a compelling choice for forward-thinking industries.
Ultimately, whether opting to purchase equipment or outsource to specialized service providers, partnering with experienced and reputable suppliers is crucial. As laser technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, it is poised to become a standard in surface preparation and restoration across aerospace, automotive, maritime, and heritage conservation sectors. Strategic sourcing of laser removal solutions not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports sustainability goals and ensures superior quality outcomes.